Scalp diseases: names and causes
Common skin diseases are considered to be:
- diseases of a dermatological nature (including seborrhea, eczema and hyperkeratosis);
- autoimmune diseases of the scalp (including psoriasis and scleroderma);
- infectious (formation of pustules, appearance of lice, etc.);
- fungal rashes.
Whatever the cause of the disease, it must be eliminated in time. It is important to start treatment as early as possible, because wasted time can have serious consequences.
Oily seborrhea
If too much sebum is produced, this can also lead to dandruff. The fact is that the secretion does not contain enough antibacterial substances. Favorable conditions are created for an increase in fungal colonies. The active activity of Malassezia leads to detachment of the epidermis and the appearance of oily dandruff.
Symptoms of oily seborrhea:
- greasy hair;
- itching;
- The scales stick together and peel off very poorly.
Oily seborrhea is often accompanied by acne and furunculosis. The skin of the scalp becomes crusty; scratching during itching leads to bloody wounds. If adequate treatment is not carried out, hair will begin to fall out.
Seborrhea, associated with increased sebum production, occurs not only on the scalp. It also appears on the face, especially in the area of the nasolabial triangle, behind the ears and on the chin. On the face, the disease is characterized by enlarged pores and graying of the skin.
The most common cause of oily seborrhea is hormonal imbalances. The disease often plagues adolescents during puberty. Most often, young men suffer, because it is male hormones that provoke the activity of the sebaceous glands.
Normally, seborrhea is temporary; by the age of 25, it goes away in most people. In 10% of cases the disease becomes chronic.
Another common cause of oily seborrhea is genetics.
Also, the impetus for the disease can be:
- frequent stress;
- deviations in the functioning of the nervous system;
- taking hormones;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the genitourinary system.
Causes and signs of dermatological diseases
The appearance of dermatological diseases of the scalp in a patient occurs when the sebaceous glands work abnormally. For example, the well-known disease seborrhea occurs in people who constantly live in a stressful state, which leads to a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, and constant snacking on fast food and sweets only worsens the clinical picture.
Seborrhea can occur as a result of hormonal imbalance. Moreover, it is observed equally in both the male and female populations in equal numbers. Rare causes of the disease include hereditary predisposition. It's rare, but it happens. At the moment, doctors cannot answer with certainty which link in the genetic code is responsible for the transmission of seborrhea in the family.
Self-medication is not recommended - it can only cause harm. To establish an accurate diagnosis, you need to contact a specialist in skin diseases, who will refer you to an andrologist/gynecologist to identify pathological processes in the reproductive system. Based on the results obtained, adjustments are made to the diet, physiotherapy is prescribed, and, if necessary, a diet and a course of medications.
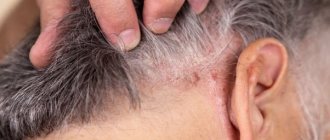
What does dandruff look like?
White flakes, clearly visible on dark clothes, are nothing more than dandruff. It consists of scaly particles of keratinized skin, appears at the roots of the hair, and then easily falls off. Most often, the disease is provoked by the activity of the Malassezia fungus. It is present on the skin of every person, but only under certain conditions does it begin to multiply and cause dandruff.
When the fungus on the scalp becomes active, a person feels itchy. Depending on the reasons that caused the spontaneous reproduction of microorganisms and the characteristics of the sebaceous glands, seborrhea (this is what the disease accompanied by peeling is called) is divided into dry, oily, and mixed. It can also manifest itself in other forms.
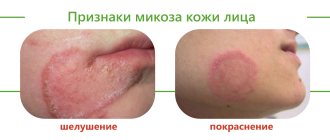
Fungal diseases: causes and symptomatic picture
Fungal diseases of the scalp partially or completely affect the scalp. They are transmitted through tactile contact and the use of shared personal hygiene products (towel, comb), clothing and hats.
A common fungal disease is ringworm. The superficial form most often affects children of preschool and school age due to curiosity and frequent contacts with animals - cattle and rodents. According to statistics, lichen more often affects residents of villages and villages.
In most cases, it is characterized by the appearance of small spots, pinkish with a pale edge. Despite its frequent distribution among children, trichophytosis can appear in men and women of different age categories.
Treatment of fungal diseases of the scalp can take an indefinite period of time. If the disease is chronic, treatment of the scalp disease in this case does not guarantee complete relief.
Mixed seborrhea
Mixed seborrhea has characteristics of dry and oily varieties. In particular, patients note that the skin on the face in the middle part is oily, and on the cheeks it is dry. Especially a lot of fat is released in the areas of the crown, chin, forehead, and nose. In other places the fat content is moderate or insufficient.
Doctors also note that a person may be bothered by dry dandruff and oily skin on the face.
Symptoms of mixed seborrhea:
- inflammatory process on the cheeks, scalp, chin, forehead, chest, nose;
- in the area of inflammation, the skin becomes rough;
- redness, itching;
- increased secretion of sebum on the forehead, but decreased secretion in other areas of the face;
- peeling in the area of increased activity of fat-secreting glands, yellowish or gray scales;
- peeling of dry areas of skin.
All the factors listed above as causes of other types of the disease can provoke mixed seborrhea. Most often the problem is associated with hormonal changes or disruptions. Heredity plays an important role. Stress and anxiety can also contribute to the growth of fungi.
Message sent!
Autoimmune diseases: causes and methods of treatment
For healthy people, patients with psoriasis or scleroderma do not pose any threat; these diseases are associated with a deficiency of essential vitamins and minerals in the body. The patient must be protected from situations that cause depression, anxiety and stress, after which the doctor prescribes oral drug treatment, namely:
- take a course of medications with a high content of vitamins, amino acids and minerals necessary for the recovery of the body;
- sedatives (if the patient is unable to get rid of stress on his own).
Dry seborrhea
If there is a lack of activity in the sebaceous glands, dry seborrhea can occur. The reason is not only low sebum production, but also:
- stress, anxiety, psychological shocks;
- hereditary factors;
- hormonal disruptions (puberty or abnormalities in the functioning of the glands);
- use of incorrectly selected cosmetics, as well as cosmetic paints with ammonia;
- poor hygiene, excessively frequent hair washing and blow-drying;
- lack of vitamins (this affects the general health and functioning of the glands).
A deficiency of sebum contributes to the appearance of inflammatory processes on the scalp, which provoke the proliferation of Malassezia fungi. Symptoms of dry seborrhea:
- discoloration, dryness and brittleness of hair;
- formation of cracks in the epidermis;
- the appearance of large scales that quickly peel off.
If measures are not taken, dry seborrhea moves into the next stage. In addition to dandruff, a person is bothered by redness of the skin and seborrheic spots. Sometimes dry seborrhea is an advanced form of oily seborrhea, in other cases the problem arises on its own.
Seborrheic dermatitis
When listing the types of dandruff, one cannot fail to mention seborrheic dermatitis. This is a general term for diseases that are associated with the active proliferation of fungi, the formation of crusts, redness, itching and peeling.
Seborrheic dermatitis can occur with infectious diseases such as lichen, or non-infectious diseases - psoriasis, neurodermatitis. Symptoms appear on the skin in areas with impaired sebum secretion.
The fungus produces lipotic enzymes that break down fatty acids. When there are too many enzymes, an inflammatory reaction occurs on the skin. Outwardly, at first it looks like peeling. Scratching leads to the formation of bleeding wounds.
The symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis are similar to dandruff. However, we are talking about it only if more than 83% of the microflora of the scalp consists of pathogenic fungi. For dandruff, this figure is 74%. Thus, dandruff is the first stage of seborrheic dermatitis. If left untreated, it will lead to serious consequences.
Prevention of psoriasis on the head
Prevention of psoriasis on the scalp is especially necessary for people with a hereditary predisposition who have sick relatives. It includes eliminating the impact of the following factors:
- any prolonged exposure to the skin;
- poor nutrition and sedentary lifestyle;
- prolonged stress and heavy loads;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- hormonal disorders - if you suspect such disorders, you should immediately contact an endocrinologist;
- intoxications - promptly treat all chronic diseases that contribute to metabolic and immune disorders.
A dermatologist after an examination can tell you how to cure psoriasis on the scalp. Therefore, you should not delay consulting a specialist, because the initial stages of the disease are much easier to treat. Can this process be cured? It is impossible to cure the disease completely, but if a person is treated regularly, there is a great chance of getting rid of relapses for a long time.
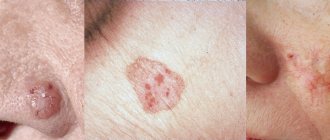
Psoriasis and dandruff
Dandruff on the head appears not only due to the activity of the sebaceous glands and fungi. Sometimes scales on the hair occur with psoriasis. This is a common disease associated with heredity and the body's immune system. The disease is chronic, its therapy is designed to reduce symptoms.
Signs of psoriasis:
- the appearance of pink or red spots (occur not only on the head, but also on the arms, legs, and other parts of the body);
- gray scales on plaques;
- itching, sometimes pain.
An outbreak of this autoimmune disease can easily be confused with seborrhea. It is important to see a doctor on time, because the treatment of these ailments is very different.
Psoriasis appears between the ages of 15 and 35 years. Outbreaks of the disease can be caused by:
- poor nutrition;
- cold or dry air;
- stress.
The causative agent is not fungi, but the person’s own immunity, which attacks healthy cells, which causes active growth of the epidermis.
Therapy requires close supervision by a dermatologist. Both local and oral medications can be prescribed. Phototherapy, IV courses, and injections help relieve symptoms.
Drug therapy for scalp psoriasis?
Medicines are selected according to the patient’s condition and the presence of certain symptoms of the disease. In the initial stage of psoriasis on the scalp, the following external remedies are used:
- when weeping, solutions and creams are prescribed that eliminate these symptoms and prevent bacterial and fungal infections; Picladol, Psorilom, Zinocap creams are suitable; Belosalik is prescribed from solutions; apply the medicine to the affected skin areas every day;
- if the skin is dry, then it is treated with ointments; ointment with salicylic acid - has a softening effect; ointments with tar have the same effect; Ointments with zinc and Daivonex ointment (an analogue of vitamin D3 + glucocorticoid betamethasone - help quickly eliminate the symptoms of psoriasis);
- ointments and creams with corticosteroid hormones are prescribed for the treatment of common forms of psoriasis on the scalp;
- Shampoos are widely used; Thus, tar shampoos (Psorilom, Friederm Tar, etc.) relieve inflammation and soften crusts; shampoo with zinc has an antiseptic and softening effect, relieves inflammation; shampoos are used for a long time.
Features of diagnosing hair fungus
A specialist can determine the presence and type of fungus relatively easily and reliably with the help of laboratory tests using microscopic and cultural methods. The first involves taking hair and skin flakes from the patient to examine for the presence of mycelial spores, gas bubbles, and fragments of large mushrooms. The cultural method is used if the presence of a fungus is nevertheless detected and allows one to determine the specific type of mycelium that has colonized the patient’s scalp. To do this, the detected fungus is grown in a nutrient medium, after which the grown colony is examined, in particular, the growth pattern is assessed (the process takes several days).
One of the modern tools used to determine mycosis is a Wood's lamp. The device emits a wave of a certain length and allows you to illuminate the colonies, giving an idea of the size and location, but not providing an answer regarding the type of microorganism, and therefore the treatment tactics.
How to properly treat hair fungus
As already noted, a person discovers the fungus when it has already “settled” in the hair. Like any disease, mycosis at a later stage is much more difficult to treat and relying on traditional methods in this matter means risking precious time.
Treatment tactics are determined by a specialist, based on data such as the depth and area of the lesions, the type of fungus, the general condition of the body, and the patient’s medical history. Treatment is usually complex and includes systemic medications and external agents (for example, taking tablets and using ointments). Immunotherapy or vitamin therapy may also be prescribed, since the fungus develops “with the permission” of the immune system.
Mycoses can be successfully treated - today there are effective antifungal drugs. However, a fungal infection is much more difficult to treat than a bacterial one - fungal cells are very similar in structure to human cells. If in the case of antibacterial therapy the results can be judged already on the second day, then in the case of mycosis - only on the seventh. After the clinical manifestations subside, it is important to take antifungal drugs for another 2 weeks. Thus, treatment requires time and patience - it may take up to 3 weeks. But in no case should you stop as soon as the results appear - this will definitely lead to a relapse, and new colonies may turn out to be more resistant to the drug used.
Dermatomycosis is not always an independent disease. They are often triggered by other diseases. A competent trichologist will not only be able to prescribe an effective course of treatment that will get rid of hair fungus as soon as possible, but will also be able to suspect the root cause of mycosis, thereby ensuring that the disease is detected at an earlier stage.
The conclusion is simple: to get rid of hair fungus, it is best to go to an appointment with a trichologist, who will accurately determine the type of mycosis and prescribe treatment. You should not self-medicate, leaving colonies of pathogenic microorganisms even the slightest chance of survival. In addition, you should take into account the fact that antifungal drugs have a serious effect on the liver, so treatment with such medications can only be prescribed and under the supervision of a specialist who will help you choose the most gentle and effective treatment tactics.