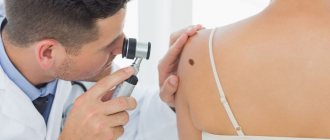
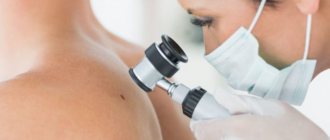
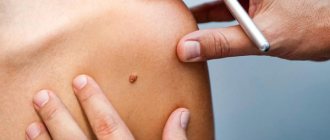
There are a large number of types of skin formations (both benign and malignant). They often do not pose a risk to your health, but they can cause physical or psychological discomfort, especially in areas of pressure, friction, areas of skin at risk of injury, and on visible parts of the body. You also need to know that some skin formations may be prone to discoloration, growth, and malignancy. Today we will talk about the types of skin formations and their possible changes, the appearance of which you need to be wary of. We will also look at the most delicate and gentle way to remove tumors.
What research is done before removing skin tumors?
The main optical device used by a dermatologist to examine moles and other skin growths before their removal is a dermatoscope. A dermatoscope consists of a magnifying lens and a light source to improve the visibility of subsurface structures of the skin.
The examination procedure using a dermatoscope is called dermatoscopy. This diagnostic method allows an experienced specialist to visually assess and diagnose the nature of a skin tumor under tens of times magnification.
Removal by radiosurgical method - indications and contraindications
Recommendations: Indications for radiosurgery:
- warts on the sole;
- papillomas;
- Nevi (moles);
- spider veins;
- keratoses;
- vulgar warts;
- Hemangiomas
- Skin basal cell carcinomas
- Ingrown nail
- removal of granulation tissue after surgery;
Attention: Contraindications:
- acute inflammatory processes;
- allergy;
- presence of viral infections;
- feverish condition;
- severe liver and kidney diseases;
- diabetes;
- period of bearing a child;
- herpes
What is the best method for removing skin tumors?
Our clinic's arsenal includes almost all methods for removing any benign skin tumors, except for surgical and chemical destruction: laser removal, radio wave removal - radiosurgery, diathermocoagulation - plasma coagulation and cryodestruction - removal with liquid nitrogen.
In each individual case, the question of choosing a removal method depends on the nature of the tumor, its size, location, and concomitant pathologies. Therefore, the concept of the best removal method simply does not exist.
Symptoms and causes, what to look for
Symptoms of a soft tissue tumor can vary widely. Most often, the clinical signs of benign neoplasms are the appearance of a painless but constantly growing lump. The sizes of formations can be very different, it all depends on the place of their appearance. Typically, tumors that form on the head, neck or upper extremities are small in size due to early detection. Whereas formations in the abdominal cavity and thighs can reach significant sizes.
It is worth noting that there are no 100% signs that could help distinguish a benign from a malignant formation. Therefore, during a clinical examination of benign soft tissue formations, there is always the possibility of finding a malignant tumor.
In most cases, the appearance of tumors on the skin has no reason. Most often, such tumors arise spontaneously. In some cases, the cause of benign tumors is a genetic predisposition.
How can a tumor be removed without leaving a trace on the skin?
All superficial neoplasms - papillomas, keratomas, etc., as well as small formations, are most often removed without scars or marks on the skin. After removal of large formations, traces of hypopigmentation or barely noticeable whitish scars may remain.
In any case, it is very important when removing! clearly assess the line separating the difference between the aesthetic result of the procedure and its effectiveness. This means that the wider and deeper the tumor is removed, the lower the likelihood of relapse. Conversely, minimal superficial removal is always an ideal cosmetic result, rapid epithelization, absence of a scar, but a high risk of developing recurrent neoplasm at this site. The experience of our doctors, mandatory diagnostics and the availability of a wide range of equipment allow our specialists to maintain a competent balance between removing the tumor in full and obtaining the best possible cosmetic result of the procedure.
What diseases are there?
Benign neoplasms on the skin include:
- fibroma;
- lipoma;
- hemangioma;
- papilloma;
- neuroma;
- myxoma;
- leiomyoma, etc.
Fibroma
Fibroma is a benign tumor of fibrous connective tissue. Such a neoplasm can occur in both men and women at any age. Upon palpation, benign formations are revealed as a mobile and dense tumor with clear contours.
Lipoma
Lipoma is considered one of the most common benign neoplasms, most often localized in the subcutaneous connective tissue. Quite often, such tumors are multiple. Their occurrence has nothing to do with the general condition of the human body.
Hemangioma
Hemangioma is a benign tumor of the skin that usually affects middle-aged people. The tumor is localized in the skin, mammary gland, liver, as well as on the lips and nasal mucosa. It tends to become malignant and develop into angiosarcoma. Among the types of hemangioma, there are capillary, grape-shaped, venous and cavernous angiomas, as well as benign hemangioendothelioma.
Papilloma
Papilloma is a benign neoplasm that is associated with excessive growth of the epidermis. Basically, papilloma manifests itself in the form of warty growths of various shapes and sizes that rise above the skin. Papillomas grow quite slowly.
Neuroma
Neuroma is a benign neoplasm of the Schwann nerve sheath. This tumor forms along the nerve trunks of the head, neck and upper extremities. People of all ages are susceptible to neuroma. Neuromas often form as a result of surgery or injury to the extremities. Neuroma can be determined by palpation or ultrasound examination.
Myxoma
Myxoma is a benign formation on the skin that is formed from connective tissue. There are two variants of such a tumor - primary (true) and secondary (false). Myxoma often appears in old age.
Leiomyoma
This benign tumor occurs in both men and women at any age. Most often it is multiple, and also tends to become malignant. Leiomyoma resembling Kaposi's sarcoma requires surgery.
What are the advantages of the radio wave method compared to other removal methods?
The radio wave method for removing skin tumors is the most non-traumatic procedure, which is based on the use of high-frequency waves (radio waves) on the Surgitron apparatus, USA. This method is used even if it is necessary to remove an element located in a hard-to-reach place (oral mucosa, eyelids).
The advantages of the radio wave method include:
- complete absence of pain during the procedure;
- no bleeding after removal;
- no trace remains at the site of removal;
- no risk of secondary infection;
- healthy areas remain untouched;
- fast healing process;
- The method is universal - you can remove warts, papillomas and moles.
One of the important differences between radiosurgery and laser and other destructive techniques is the possibility of performing a histological examination of removed tissue when using the radio wave method of removal.
Types of benign skin neoplasms
Benign skin tumors do not pose a serious threat to humans, but they cause psychological and even physical discomfort, especially when located in areas of the body that are not usually covered by clothing. The main benign neoplasms include:
- Warts and papillomas. Occur on the skin due to infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). They are painless and are small growths with a height and a diameter of several millimeters. These neoplasms are localized in the folds of the skin, have blood vessels and a loose structure, and can change color and grow.
- Nevi (moles). They are based on melanocytes - cells that contain the main coloring pigment of the body. Most moles are harmless, especially if they are small and do not cause discomfort, that is, they are not located on open areas of the body.
What happens after removal?
During the first day after the procedure, a dark brown scab (crust) will form at the site of the removed tumor. Healing takes from 2-3 days to 2-3 weeks, it all depends on the size of the tumor bed. After final epithelization, the crust will be torn off on its own. Within 1-3 months, the area of skin at the site of removal has a bright pink color, then it will acquire a normal skin color. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations and properly care for the skin at the site of removal, no marks or scars will form.
Types of benign formations:
- Dark spots
- Hemangiomas and lymphangiomas
- Warts
- Condylomas
- Molluscum contagiosum
- Lipomas
- Fibroids
- Keratomas
- Acrochordons
- Papillomas
Despite the fact that benign neoplasms do not pose a health hazard, they still require constant monitoring. If a growth suddenly appears or changes on your body, or a spot appears, immediately consult a doctor and get examined. Please note that neoplasms caused by papillomavirus can be contagious and can cause problems in your intimate life.
Are there any special recommendations for skin care after the removal procedure?
We issue the following recommendations in the form of a reminder to our patients:
- During the first 24 hours, do not wet the removal site.
- Treat the wound with Fukortsin solution 2 times a day for 3-5 days or Baneocin powder.
- Men: do not shave in the area of removal for 3-4 days.
- Women: do not apply cream or decorative cosmetics to the removal area for 3-4 days.
- You cannot pick or remove the crust yourself!!! in order to reduce the likelihood of atrophic/keloid scars, hypo- and hyperpigmentation.
- In cases of removal of large tumors, after the crust is rejected, apply Levomekol ointment locally 1-2 times a day for a month.
- Before going outside, be sure to use sunscreen on the face and open areas of the body with an SPF of at least 50, especially on sunny days (to prevent pigmentation of the treated areas).
How much does it cost?
Removal of 1 milia (grass, wen) in the eye area
950 rub.
Removal of 2 skin lesions on a wide base
(removal 8700, histology 2300)
11000 rub.
Removal of 3 skin lesions on a wide base
(removal 10400, histology 4600)
15000 rub.
If you doubt the price, find out the exact cost in advance. To do this, take a photo of the tumor against the background of a centimeter scale ruler and send it to my email address
Dmitry Beinusov: examination + consultation + surgery
- Dermato-oncologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences.
- Postgraduate studies at the Oncology Research Institute named after. N. N. Petrova.
- Specialization: skin neoplasms.
- Member of the European Association of Surgical Oncologists (ESSO).
- Author of 10 scientific articles and holder of 1 patent.
- Permanent consultant of the portal Health Mail.ru
- Teacher of advanced training cycle in dermato-oncology
Treatment of skin basalioma without relapse - photodynamic therapy for basalioma
Effective treatment of basal cell carcinoma in one procedure - without surgery, without relapse, without scars
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Afanasyev Maxim Stanislavovich, oncologist, surgeon, expert in photodynamic therapy of basal cell carcinoma.
Basalioma, or basal cell skin cancer, is a complex disease. Medicine offers many treatment methods, but all of them are traumatic, fraught with the formation of serious cosmetic defects, the development of long-term complications, and none of them eliminates relapses in the future.
Even Hollywood stars, who have access to the most high-tech and expensive treatments, have to undergo treatment for basal cell skin cancer for years. The most famous example is Hugh Jackman. The actor has been fighting the disease since 2013 to save his nose. And so far he has succeeded. But against the backdrop of his sixth relapse, Jackman has a serious risk of losing it.
Hugh Jackman began fighting basal cell carcinoma on his nose in 2013. He is a very disciplined patient. But despite active treatment, the actor has already suffered a sixth relapse of the disease.
Unfortunately, none of the existing treatment methods guarantees getting rid of basal cell carcinoma forever. And if even Hugh Jackman, who has access to the most modern medical care, cannot get rid of the problem, then a logical question arises: is this disease treatable? Is it possible to cure basal cell carcinoma?
Yes, I claim that basal cell carcinoma is completely curable . A new PDT method - photodynamic therapy of basal cell carcinoma - allows me to carry out aesthetic and relapse-free treatment of basal cell carcinoma in one procedure.
Is it necessary to remove basal cell carcinoma if it does not bother me?
Many people treat basal cell carcinoma treatment too leniently. Because this form of cancer grows slowly and almost never metastasizes, doctors rarely insist on treatment and usually do not warn about the consequences of failure. And if for elderly patients such tactics can be considered justified with a stretch, then for young people - and over the past 10 years basal cell carcinoma has become very “younger” - it does not stand up to criticism. With this approach, the patient does not take his seemingly insignificant disease seriously and decides not to do anything about it. Very often, treatment is limited to the use of so-called “green stuff”. But I believe that Hugh Jackman is right in his persistent desire to get rid of basal cell carcinoma. And not only because of an aesthetic defect. Treatment is necessary. Basalioma is a tumor that, although slowly, is constantly growing. It never goes away on its own . Sooner or later, it overcomes the skin, grows into muscles and nerves, penetrates cartilage and irreversibly disrupts the functioning of organs. If basal cell carcinoma is located on the face, it literally destroys it. Basalioma in the area of the eye or nose, growing, can lead to their loss. Over time, basalioma of the head can destroy the skull and grow to the brain. Need I say that these processes are also extremely painful?
Advanced basal cell carcinoma (pictured) cannot be treated. Therefore, it is necessary to begin treatment of the disease in its early stages.
At this stage, basal cell carcinoma is practically untreatable, because along with the basal cell carcinoma it will be necessary to remove part of the organ or the entire organ.
Therefore, if you notice a new growth on the skin, it is important to get diagnosed and remove the basalioma while it is small.
You need to know the enemy by sight
Before continuing our conversation, I must tell you about one type of basal cell carcinoma that cannot be recognized at the diagnostic stage. In approximately 6% of cases, treatment of basal cell carcinoma does not have any effect - removal of the basal cell carcinoma ends in relapse, and it reappears in the same place. And after the next removal, the whole process is repeated... This form of basal cell cancer is called persistently recurrent basal cell carcinoma . Unfortunately, modern medicine does not have a single effective means of combating persistently recurrent basal cell carcinoma. The mechanism why it returns has not yet been figured out. However, even for such a head start on basal cell carcinoma, the founder of PDT in Russia, Professor Evgeniy Fillipovich Stranadko, recommends using exclusively photodynamic therapy as the method of choice. Indeed, in the case of persistently recurrent basal cell carcinoma, repeated treatment will be required, the cosmetic effect of which will completely depend on the method of its removal chosen at an early stage. We must understand that any surgical treatment is always a “minus tissue” treatment, a mutilating treatment. Only PDT allows for effective treatment without removing healthy tissue and obtaining an aesthetic result even against the background of persistently recurrent basal cell carcinoma.
What treatment for skin basal cell carcinoma was used before the advent of PDT?
Below are the main treatment methods for basal cell carcinoma today:
- surgical methods
- radiation therapy
- chemotherapy.
To understand the difference, let's take a closer look at them.
Surgery for basal cell carcinoma: features of the method and its disadvantages
Surgical removal of basal cell carcinoma is usually performed with a laser, scalpel or radio wave scalpel with the obligatory capture of 5 mm of healthy tissue . Surgical techniques also include the cryodestruction method - removal of basal cell carcinoma with nitrogen, and the Mohs method. I strongly advise you not to agree to remove basal cell carcinoma with a scalpel - this method usually leaves behind a rough scar. In the early stages, surgical removal of basal cell carcinoma has a good effect. Therefore, it makes sense to remove very small and accessible formations up to 2-3 millimeters surgically. I myself prefer this method: the procedure is simple, quick and does not require special rehabilitation.
Only small basal cell carcinomas can be treated surgically. Excision of larger tumors always leaves behind an obvious cosmetic defect - a significant tissue deficiency and a scar .
Disadvantages of the surgical method:
- High percentage of basal cell carcinoma recurrence after excision. Advanced basal cell carcinomas, which have managed to grow beyond the skin, recur especially often.
You should not trust information that surgery to remove basal cell carcinoma has a low recurrence rate. This figure is relevant only for small entities. When basaliomas larger than 2-3 mm are removed, usually more than half of them recur.
- Difficulty and impossibility of re-treatment due to severe tissue loss.
Recurrence of basal cell carcinoma requires repeated surgery. But after the second or third relapse, surgery is usually impossible: imagine what happens to the area in which, with each removal of the basal cell carcinoma, an additional 6 mm of healthy tissue is removed.
- Relapse after surgery occurs in the scar area. This area is almost impossible to treat with PDT. Therefore, if basal cell carcinoma recurs after surgical treatment, you will have virtually no alternative method left - only repeat surgery or radiation.
- If the tumor is located on the wings of the nose, on the auricle or in the corners of the lips, if multiple basal cell carcinoma is to be treated, then the surgical method literally turns into a mutilating operation. In these areas, every millimeter of tissue is important, but often, along with the tumor, it may be necessary to remove up to half of the nose or ear, and the lack of tissue cannot be compensated for by plastic surgery methods.
- A contraindication to surgery is the location of the basal cell carcinoma in close proximity to the eye - there is a high risk of its loss.
Next, it makes sense to get acquainted with the limitations of each surgical method separately.
Laser removal of basal cell carcinoma: features of the method and its disadvantages
Laser treatment of basal cell carcinoma is a surgical operation. Laser removal of basal cell carcinoma has one significant drawback. The fact is that the laser beam does not cut the tissue, but evaporates it, layer by layer. After the laser, only a charred crust remains from the tumor. Thus, “cauterization” with a laser does not make it possible to send the removed tumor for histological examination. Only histology allows one to assess the completeness of basal cell carcinoma removal and exclude a more serious form of cancer, which in rare cases is hidden or adjacent to basal cell carcinoma. This method also has one more drawback. Laser treatment of basal cell carcinoma thermally damages tissue, and such a wound heals with the formation of a scar.
Removal of basal cell carcinoma using Surgitron: features of the method and its disadvantages
Radio wave removal of basal cell carcinoma, or electrocoagulation, or treatment with an electric knife, is another surgical method. In this case, a tip with a thin wire is used to remove the formation. When an electric current of a certain frequency is passed through a wire, it acquires the properties of a scalpel. Most often, treatment of basal cell carcinoma with radio waves is performed using American medical equipment, which gave the method its second name. This method is good because after its use, tissue remains for biopsy - the pathologist will be able to assess the completeness of basal cell carcinoma removal and rule out a more aggressive form of cancer. The disadvantage of electrocoagulation is the same as that of all surgical techniques - a high rate of relapse for all tumors exceeding 2 mm. You also need to be mentally prepared for the fact that excision of skin basal cell carcinoma using radio waves leaves behind a scar.
Cryodestruction of basal cell carcinoma: features of the method and its disadvantages
Cryodestruction, or cryotherapy, is the cauterization of basal cell carcinoma with liquid nitrogen. The method is cheap and quite widespread. However, you shouldn’t count on a miracle. Removing basal cell carcinoma by cryodestruction has a very serious drawback: the depth of exposure of liquid nitrogen to tissue cannot be controlled. That is, after treating basal cell carcinoma with nitrogen, there is a risk of both leaving lesions in the skin and, conversely, affecting too large areas of healthy tissue. In the latter case, after cauterization of basal cell carcinoma, there is a high probability of developing an extensive scar. Treatment of basal cell carcinoma with cryodestruction has another drawback. Since the method does not make it possible to assess whether the tumor has been completely removed or not, basal cell carcinoma after cryodestruction may well resume its growth and eventually require repeated removal.
Mohs method: features of the method and its disadvantages
This is a high-tech and expensive treatment method that requires special equipment, special training of the surgeon and the presence of the clinic’s own pathology laboratory. It is designed to achieve high aesthetic results in the treatment of tumors on the face, neck, legs and arms, and genitals. This is probably the method used to treat Hugh Jackman. The Mohs operation can be compared (very loosely, of course) to using a slicer: tissue is removed in thin layers, layer by layer, and immediately sent to the laboratory. The procedure is repeated until tumor cells are no longer detectable in the section. Since the entire operation is carried out under the supervision of a pathologist, there is no need to remove the basal cell carcinoma “involving” 6 mm of healthy tissue. The operation is highly aesthetic, and if there is a lack of skin in the operated area, it is replaced with implants.
Irradiation of basalioma: features of the method and consequences after irradiation of basalioma
Radiation, or radiation, treatment methods are used only if there are contraindications to alternative methods. This is the method of choice for complexly located (for example, on the face), deep or too large tumors up to 5 cm that cannot be treated surgically. They are also prescribed to elderly patients with contraindications to surgical treatment. Since the use of the method is always accompanied by complications, it is used mainly for elderly people over 65 years of age. Irradiation of skin basalioma is carried out:
- using close-focus X-ray therapy,
- using gamma rays,
- using beta rays (electrons).
The use of a particular method is not always determined by rationality. Close-focus X-ray therapy is presented in every oncology clinic, so most often patients are referred to it. Electronic installations are expensive and complex, so literally only a few clinics are equipped with them. Let's look at how radiation therapy works on basalioma. It is believed that treatment of basal cell carcinoma with radiation therapy negatively affects the DNA of tumor cells. Ionizing radiation makes their further division impossible; after radiation therapy, basal cell carcinoma stops growing and is destroyed over time. There is often information that radiation treatment of basal cell carcinoma does not have any serious consequences. Unfortunately, this is not true. Irradiation of skin basal cell carcinoma causes a lot of complications that cannot be avoided . Therefore, treating basal cell carcinoma with radiation is often comparable to shooting sparrows with a cannon, since the side effects of such treatment often exceed the severity of the disease itself.
Here is just an approximate list of complications of radiation treatment:
1. Radiation therapy for skin basal cell carcinoma causes the development of dermatitis and a non-healing radiation ulcer that does not scar for several weeks.
This is what a radiation ulcer looks like
If at the beginning of treatment the skin in the training area only turns red and itches, then by the third week of therapy a non-healing bright red ulcer develops. It becomes very easily infected, has an extremely unpleasant odor, and heals with great difficulty only 1.5 months after the end of treatment.
2. A radiation ulcer always heals with the formation of a scar. This creates not only a defect in facial expressions, but also greatly complicates the treatment of basal cell carcinoma in case of recurrence.
3. It is impossible to predict in advance how radioactive particles will act. On the one hand, therapeutic radiation is aimed at rapidly dividing cells, and this is the main property of malignant neoplasms: radiation damages basal cell carcinoma cells and makes them non-viable.
But on the other hand, radiation exposure itself has high mutagenic properties. Healthy tissue is also exposed to radiation, and the DNA of healthy cells is damaged.
Thus, an initially safe basal cell carcinoma is highly likely to “degenerate” into metastatic forms of cancer – for example, squamous cell skin cancer.
The risk of developing this complication persists for the rest of your life after basal cell carcinoma irradiation. It is for this reason that radiation treatment is not given to patients under 50 years of age. Due to the high risks of complications, radiation treatment is not used for recurrent basal cell carcinoma.
4. If basal cell carcinoma occurs on the head, irradiation leads to hair loss in the affected area, which grows brittle and dull after treatment.
5. The risk of complications increases in proportion to the depth of penetration of basal cell carcinoma and the intensity of irradiation.
6. When treating tumors located near the eyes, cataracts may occur.
7. Treatment of basal cell carcinoma with radiation leads to changes in the functioning of the sebaceous and sweat glands in the area of radiation exposure.
8. Anatomically difficult areas are not treated with any of the methods of radiation therapy.
9. With radiation treatment of basal cell carcinomas on the face, the risk of relapse is higher than on other areas of the skin.
Close-focus X-ray therapy: features of the method and its disadvantages
Most often, the radiation treatment method refers to close-focus X-ray therapy - all specialized oncology dispensaries are equipped with installations for its implementation. In this case, irradiation is performed with short-wave X-rays.
This is what a device for close-focus X-ray therapy looks like.
Since the depth of exposure to this radiation ranges from a few millimeters to 7–8 cm, the dosage and number of sessions are calculated individually. Close-focus X-ray therapy is effective only in the initial stages of basal cell carcinoma and is used only on accessible areas of the skin. For example, the corner of the nose is considered difficult to treat. This method also has its drawback. X-ray radiation is well absorbed by dense tissues, such as bones. Therefore, when basal cell carcinoma is located close to the bone - in the area of the ears and on the head - electron radiation therapy is recommended.
Electronic therapy for basal cell carcinoma: features of the method and its disadvantages
Beta rays are called electrons. Accordingly, beta ray treatment is called electron therapy. Compared to X-rays, electron radiation is considered more gentle, selective and highly targeted. Electrons are absorbed by tissues equally and regardless of their density. Unlike X-rays, which lose energy as depth increases, the energy of an electron beam rises to a peak at a certain depth and then drops off sharply. All this means that with the correct dose calculation, radiation minimally injures healthy tissue around the tumor. Electronic therapy also allows irradiation of large areas of skin for multiple basal cell carcinomas. But electronic therapy treatment also has limitations. On the one hand, this is the high cost of equipment. On the other hand, the technique is indicated in advanced stages - the size of the basal cell carcinoma should be no less than 4 cm2, since the device is quite labor-intensive to set up and does not allow focusing the flow onto a smaller area. Electron irradiation is also not used to treat basal cell carcinoma in the eye area: modern radiology does not effectively protect the organ of vision.
Drug treatment of basal cell carcinoma
Large and advanced inoperable tumors are treated with chemotherapy. But the effectiveness of such treatment is not very high.
The main disadvantage of all existing treatment methods is the high risk of relapse. As a result, you have to cut or irradiate again and again. Moreover, each stage of treatment is accompanied by significant loss of healthy tissue and scarring. The need for deep tissue excision is a critical moment in the treatment of basal cell carcinomas on the face - especially on the nose, ears and corners of the lips, when each recurrence of basal cell carcinoma is accompanied by irreversible loss of a significant part of the organ.
Recurrence of basal cell in the scar is perhaps the worst consequence of treating basal cell carcinoma with classical methods. You need to understand that almost all existing treatment methods lead to the formation of a scar, which is a dense connective tissue, weakly penetrated by blood vessels and poorly supplied with blood. In this case, relapse of basal cell carcinoma occurs in the area of its original localization - that is, always in the scar area. Unfortunately, in this case, PDT loses its effectiveness - the microcirculation of the rumen does not allow the photosensitizer to accumulate in sufficient concentration. Accordingly, recurrence of basal cell carcinoma in the scar is poorly amenable to any alternative treatment methods other than surgery. So, having performed an operation to remove basal cell carcinoma just once, you become a hostage to the surgical method.
What to do? The most effective method of preventing basal cell carcinoma after surgery is not to have surgery at all: its treatment after surgical removal closes the possibility of using almost all other methods except surgery.
How to treat basal cell carcinoma to cure it. Treatment of basal cell carcinoma using PDT
PDT is an effective method of relapse-free treatment of basal cell carcinoma in one procedure. Extensive personal experience in treating basal cell carcinoma using PDT allows me to confidently say that:
- In 96% of cases, PDT permanently eliminates basal cell carcinoma in one procedure,
- Photodynamic treatment of basal cell carcinoma shows the highest efficiency among all existing techniques. The method targets cancer cells and completely eliminates them. The risk of recurrence of even large basal cell carcinoma after correct and fully performed PDT is several times lower than from other treatment methods and is only a few percent.
- Only the photodynamic method of treating basal cell carcinoma provides the highest aesthetic result: either no scar remains or it is almost invisible.
- The method is suitable for the most complex basal cell carcinomas in the nose and eyelids.
- PDT shows very good results in the treatment of large basal cell carcinomas.
- It has almost no side effects, since healthy cells are not harmed during PDT.
For PDT, the location of the basal cell carcinoma, its stage, type or size does not matter. There are practically no contraindications for this treatment method due to age or health status.
What is the essence of the technique
Photodynamic removal of skin basalioma begins with a dropper - a photosensitizer drug is injected into the patient’s blood, which increases the photosensitivity of tissues. The photosensitizer has the special property of being retained only in old, atypical, damaged and cancer cells. 2-3 hours after injection, the tissues are irradiated with a laser according to a special scheme. The photosensitizer is activated by light and enters into a complex photochemical reaction, which results in the release of toxic compounds and reactive oxygen species that destroy cancer cells. The duration of the procedure depends on the size and number of tumors and takes from 20 minutes to 2.5 hours.
I would like to especially emphasize once again that each changed cell accumulates a photosensitizer. Therefore, after correctly performed photodynamic therapy, we can say that there are no cancer cells left in the treatment area . This means that there is simply nowhere for relapse to occur.
It is this targeted effect on cancer cells that ensures complete tumor removal and an excellent aesthetic result after the procedure.
Is it that simple?
Of course, the PDT procedure is not at all as simple as it might seem at first glance. To obtain a guaranteed result, it requires very high-quality equipment, the highest craftsmanship, jewelry precision and a strictly individual treatment plan . For each patient, I develop my own treatment protocol , which depends on age, medical history, size and location of the tumor, and concomitant diseases. I make sure to diagnose and differentiate the tumor:
- visual examination with dermatoscopy;
- collection of material for cytological evaluation;
- taking a fingerprint-smear in the case of an ulcerated form;
- taking a biopsy for tumors larger than 5 cm2.
This procedure allows you to accurately diagnose basal cell skin cancer and exclude the more aggressive squamous cell cancer. Before the procedure, I carefully calculate the dosage of the photosensitizer, as well as the intensity and time of laser exposure. I carefully control the power of laser radiation during the procedure. Compliance with the PDT protocol and an individual approach allows me to achieve good treatment results of 96% the first time. By the way, not all specialists trained in PDT are able to trigger the necessary photochemical reaction and achieve a cure. I would like to share with you what an incorrect tissue reaction looks like during the so-called PDT.
The photograph shows hyperthermia - a tissue burn that should not occur after a correctly performed PDT procedure. From the reaction of the tissues, I understand that no photochemical reaction occurred in this case, even if before the procedure the patient was injected with a photosensitizer and a laser was used. The treatment result shown in the photograph does not give the right to call it PDT. Therefore, after completion of treatment, the patient will not receive the benefits of the technique that I spoke about above.
I cannot say whether this procedure helped or not: the photo was provided by colleagues, and I do not know the patient’s further fate. Below are photographs that will show what the treatment area looks like after PDT.
The photochemical reaction may be accompanied by whitening of the tissue in the affected area, as shown in the photograph.
5 days after PDT, the irradiation zone darkens, which indicates the effectiveness of the treatment, which will lead to the death of basal cell carcinoma.
On days 14-20, a crust forms, under which epithelization occurs.
After recovery, a small and barely noticeable scar remains.
Rehabilitation
After the procedure, cyanosis appears at the site of treatment, which becomes covered with a black crust on days 14-20. If the patient carefully follows the doctor’s requirements in the postoperative period for 4–6 weeks, after the PDT procedure a small and almost invisible scar remains on the skin. If a small basal cell carcinoma is removed, the tumor often disappears without a trace after PDT.
Why is the PDT method poorly represented in Europe and the USA?
Many patients ask me a reasonable question: why, if the PDT method is so effective, is it little known in the USA and Europe? The main reason for this state of affairs is the inflated cost of the photosensitizer in these countries - the cost of the drug there is about 3,000 US dollars. This is a high price; therefore, PDT of basal cell carcinoma is not covered by insurance companies. And if the method is not used, then it does not develop or develops very weakly. I have been practicing photodynamic therapy for more than 10 years, and the accumulated experience allows me to achieve complete cure of the most complex tumors.
To get advice on whether photodynamic therapy for basal cell carcinoma is indicated for you, and to calculate the cost of the procedure, send your medical history and tests by e-mail or call + 8 (800) 555-77-26 in Moscow. The reception is conducted by Afanasyev Maxim Stanislavovich, oncologist, doctor of medical sciences, professor and member of the academic council of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenov Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, surgeon, expert in the treatment of basal cell carcinoma. Reception is carried out in 5 clinics in Moscow, as well as in centers in Makhachkala, Kursk, Stavropol, Barnaul, Samara and other regions of Russia. You can check the date, location of the appointment in your city and sign up for a consultation with the administrator by phone. For assistance in preparing the material, I thank Tatyana Georgievna Grishacheva, research fellow at the Center for Laser Medicine of PSPbSMU named after Acad. I.P. Pavlova.