Every woman experiences temporary changes in breast size. The bust can shrink with sudden weight loss or swell during menstruation. This may indicate both natural physiological processes and serious malfunctions in the body. It is very important to separate familiar symptoms (mild discomfort, sensitivity) from unnatural pain, suspicious lumps and disruption of the mammary glands. What is the mechanism of breast swelling, for what reasons does this happen and in what cases is a doctor’s help necessary?
Anatomical structure of the organ
The mammary gland is a secondary sexual characteristic that develops in all female mammals. In mature women, the glands form two symmetrical elevations that are adjacent to the anterior chest wall (between the 3rd and 7th ribs). On the surface of the breast is a nipple surrounded by an areola. The mammary gland itself is a dense body in the shape of a convex disk. It is surrounded by a layer of fatty tissue and is literally “attached” to the body with the help of muscles. The organ is supplied with blood through the internal and lateral mammary arteries.
Content:
- Anatomical structure of the organ
- Mechanism of breast swelling
- Possible causes of breast enlargement
- In what cases is it necessary to consult a doctor?
- Do I need to examine my breasts myself?
Throughout life, a woman's breasts undergo cyclical changes. They are closely related to the menstrual cycle and the body’s preparation for fertilization. Before menstruation begins, the mammary glands swell and become more sensitive, and the nipple and areola may change color slightly. If fertilization does not occur, the balance of hormones is restored, sensitivity disappears, and the breasts return to their usual size.
Causes
The causes of mammary gland mastopathy are not fully understood; it is often believed that it is caused by excessive or insufficient amounts of hormones produced by the body. The most common hormonal disorder in mastopathy is an excess of estrogen with a deficiency of progesterone. It's not just a matter of changing the hormonal balance, but also an excessive growth of hormonal receptors in the breast tissue. However, the reasons for these processes are currently unknown. Sometimes the cause of mastopathy cannot be detected, but quite often the cause of the disease is inflammatory diseases of the endocrine and neuroendocrine sphere.
The risk of the disease increases with age. Factors that increase the likelihood of disease also include:
- heredity;
- overweight;
- hormone replacement therapy;
- late labor or absence of labor;
- late menopause;
- early onset of menstruation.
A connection between breastfeeding and mastopathy has not been identified.
Mechanism of breast swelling
An increase in breast size and sensitivity is an absolutely normal symptom that develops in most mature women. This is due to the complex structure of the mammary gland. The breast consists of three types of tissue - connective, adipose and glandular. Connective tissue forms the framework of the breast and rarely undergoes significant physiological changes. The fat and glandular layer are more pliable and hormone-dependent. They can grow or, conversely, decrease in size under the influence of certain hormones, weight fluctuations, and general health.
In addition to fat, blood vessels can cause breast swelling. The size and structure of the mammary glands largely depends on blood supply. How it works? Blood rushes into the chest area, dilates blood vessels, which affects the volume of the chest. A similar effect can be observed during sports or other active pastime. As soon as the blood supply is normalized, the volume of the vessels and breasts will decrease.
If breast swelling in women is a symptom of both normal and pathological internal changes, then enlarged male breasts indicate a specific disease. It is called gynecomastia. This is an enlargement of the mammary gland with hypertrophy of adipose tissue. The disease indicates an imbalance of female and male hormones.
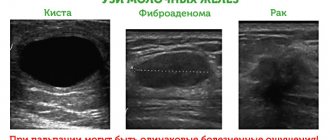
Cystic mastopathy
The main stages of treatment for cystic mastopathy:
- Dietary changes
It is recommended to exclude from the diet foods that provoke the growth of fibrous tissue and the formation of liquid contents in the cyst. These include coffee, strong brewed tea, chocolate products, and carbonated sweet drinks. Experts say that diseases of the mammary glands are often associated with poor intestinal functioning: constipation, disruption of the bacterial flora. Therefore, with mastopathy, a woman should eat food that contains a large amount of fiber: fruit, vegetable dishes, seasoned with herbs. You need to drink at least 1.5 liters of clean water per day (tea and coffee do not count). The consumption of alcohol and fatty foods should be minimized or completely eliminated, because they negatively affect the production of hormones.
- Correct selection of underwear
If you suffer from frequent mastopathy, a woman should pay close attention to what kind of underwear she wears. When choosing, you need to take into account all breast parameters. Irregular shape and size of cups can compress the breasts and deform them. This is especially true for those who have large mammary glands.
- Taking vitamins
Vitamins are necessary to strengthen the immune system, normalize hormone levels and function of the endocrine system. First of all, for cystic mastopathy, doctors prescribe vitamins B, A, E and ascorbic acid.
- Diuretics
Often, mastopathy is combined with edema of both the breast itself and the extremities, which requires the prescription of mild diuretics. In this situation, it is better to use diuretic teas based on herbs, and also eliminate or sharply limit the amount of salt in the diet.
- Prescription of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, nise)
These remedies are needed to eliminate chest pain, a common symptom of cystic mastopathy. The pain is worst before the critical days. Taking these drugs in long courses is not recommended.
- Prescribing sedatives
These medications are needed to combat stress, which is one of the factors contributing to the development of mastopathy. Preparations of valerian or motherwort, soothing teas and infusions, which are the most natural and harmless remedies, are common.
- Hormonal treatment
The development and functions of the mammary gland are impossible without the action of a number of hormones. First of all, these are estrogens and progesterone. But sometimes the body produces too much of these hormones, which is why some gland tissues grow excessively. In order to reduce their effects, so-called antihormones are prescribed - drugs that reduce the bioactivity of estrogens. These drugs include toremifene and tamoxifen. For the same purpose, doctors prescribe oral contraceptives - primarily Janine, Marvelon. They suppress the production of steroids, androgens, and estrogens, stabilizing significant changes in hormonal levels in the body. However, not in all cases of cystic mastopathy, contraceptives are effective, so sometimes the doctor has to reconsider this prescription. The doctor may prescribe gestagens - progesterone preparations (Utrozhestan, Duphaston, etc.), which prevent the growth of the cystic formation with subsequent gradual regression. In addition, antiprolactins (parlodel), androgens (methyltestosterone), and gonadotropin antagonists (zoladex, buserelin) are often prescribed.
- Non-hormonal treatment
A non-hormonal product based on indole-3-carbinol - Mammolen - will help restore the hormonal balance of estrogen and progesterone and also reduce excessive tissue growth in the mammary glands.
Mammolenn is a herbal remedy indicated for use by women with mastopathy and mastodynia to increase the effectiveness of hormonal treatment or as an alternative to hormone therapy (if there are contraindications to the use of hormones).
- Homeopathic treatment
Special homeopathic preparations for the treatment of cystic mastopathy effectively reduce the amount of prolactin, with virtually no side effects observed. Another big plus is that they have very few contraindications for use. Among such agents, cyclodinone, remens, and mastodinone are the most effective.
- Iodine preparations for thyroid dysfunction
These drugs are effective for hypothyroidism. But they are not prescribed for autoimmune thyroiditis or thyrotoxicosis. Iodine preparations for the treatment of cystic mastopathy: iodomarin, mamoclam.
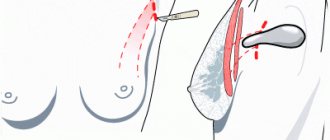
- Surgery
If medications do not give the desired effect, they resort to surgical methods of treating cystic mastopathy. Surgery is also used if there is a suspicion of the development of oncological pathology.
Don't self-medicate! The choice of drugs and their combination is determined by the doctor. The treatment regimen is influenced by the characteristics of the patient and the development of cystic mastopathy of the glands.
Prognosis for cystic mastopathy of the breast
In most cases, with cystic mastopathy of the mammary gland, the prognosis is favorable. But in the absence of treatment, the disease gradually progresses, clearly manifesting itself when the patient reaches 30 years of age. The earlier treatment is started, the greater the chance of complete recovery without consequences.
Cystic mastopathy of the mammary gland threatens breast cancer. This is the reason why it is important to identify the disease in time and begin therapy. The prescribed treatment must be carried out correctly, adhering to the scheme from beginning to end. This is the only way to prevent the terrible consequences of breast cancer.
Possible causes of breast enlargement
Swelling of the mammary glands can be long-term or short-term. For example, during pregnancy, the maximum breast volume remains until the end of feeding, and during sexual arousal it disappears after a few minutes or hours. How is this possible?
Menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle has a tremendous impact on the health, mood and well-being of sexually mature women. Each day of the cycle is associated with the production of a certain amount of hormones. These hormones affect both the internal state and external beauty. For example, progesterone and prostaglandins, which accumulate in the body during the second phase of the menstrual cycle, increase the pain threshold, provoke swelling and increased sensitivity of the breast.
If your breasts become swollen, become too sensitive or hurt during the first phase of your menstrual cycle, consult your doctor. Perhaps the balance of hormones is disturbed or other pathological processes are occurring in the body.
Pregnancy and lactation period
Active breast growth during pregnancy is associated with the important hormone prolactin. Most of prolactin is produced in the pituitary gland, after which it enters the blood and intensively prepares the female body for the future role of mother. Already in the second month of pregnancy, the breasts increase significantly in size, and the nipple and areola become darker. Changes affect not only the external, but also the internal characteristics of the organ. The mammary gland is rebuilt to provide the unborn child with milk.
During the feeding period, breast weight can reach from 300 to 900 grams (normally this figure varies from 150 to 200 grams).
Breast swelling during pregnancy and lactation is temporary. Upon completion of feeding, the hormonal balance is gradually restored, and the female body again prepares to become pregnant. Soon the mammary gland loses volume and shape, but usually does not return to its original pre-pregnancy size.
Stimulation and arousal
Most women identify the breasts as one of the erogenous zones. She is extremely sensitive to touch, sudden movements and any other stimulation. In response to stimulation, the mammary glands may increase slightly in size, become firm and slightly firm. The body's reaction to a particular influence can be specific and depends on each individual woman. Some do not experience any emotions during active breast stimulation, others even react to the friction of clothes or underwear. Feeding the baby can also be considered as stimulation. As soon as the baby latch onto the breast, a signal is sent to the brain to produce milk. As a result, the fluid fills the milk ducts and visually enlarges the gland.
Temperature changes
Exposure to high or extremely cold temperatures can also affect bust size. It's all about impaired blood circulation. When overheated, the liquid rapidly fills the blood vessels, significantly expanding them, which leads to swelling of the mammary glands.
When hypothermia occurs, the body launches a natural defense process and speeds up blood flow to survive. This can be seen in the reaction of the skin to cold water - it turns red, slight swelling appears, and uncomfortable tingling is possible. Similar changes occur in all soft tissues, including the breast.
Lifestyle specifics
Not only the quality of life, but also a person’s appearance depends on the daily diet. If you consume many more calories than you can burn, excess weight gradually accumulates in your body. Excess fat is distributed to each part of the body, according to the specifics of its structure, affecting the breasts.
Lack of drinking fluid can lead to swelling. Most often they are accompanied by discomfort, dry skin, and sometimes pain.
Pathological causes of swelling
Swelling and hardening of the breast does not always indicate natural physiological processes within the body.
Sometimes this is a symptom of such diseases:
- Lactostasis. This is stagnation of milk in the ducts of the mammary glands. The condition is typical only for nursing mothers. Stagnation can form in one gland or affect both at once. To neutralize lactostasis, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids and frequently put the baby to the breast. If this does not help, you should consult a doctor.
- Mastopathy. Overgrowth of breast tissue, which is accompanied by pain and pathological secretion. For ten years, mastopathy has remained one of the most common breast diseases.
- Fibroadenoma. A benign neoplasm caused by a lack of progesterone and estrogen. The tumor grows or provokes new cancerous lesions, which literally put pressure on the tissue and provoke its swelling.
- Mastitis. Inflammation of the mammary gland. It can develop in any woman, regardless of pregnancy, childbirth and number of children.
What is mastopathy of the mammary glands and why is it dangerous?
Breast mastopathy is a pathological proliferation of breast tissue. There are different types of disease depending on the type of expanding breast tissue.
- Fibrous mastopathy is an excessive proliferation of connective tissue.
- Cystic mastopathy is excessive growth and obstruction (blockage) of the ducts, the formation of cysts.
- Adenomatosis is an excessive proliferation of glandular ducts.
There are also mixed types of mastopathy, for example, fibrocystic.
It is also important how exactly the tissue begins to grow. There are diffuse and nodular mastopathy. When it is not possible to determine clear boundaries of tissue changes, such mastopathy is called diffuse. And when the heterogeneity is clearly localized, they speak of nodular mastopathy.
It is important to understand that mastopathy can be benign (when the compaction does not threaten the body) or malignant. To determine the type of tumor, a biopsy or puncture is usually done. The sooner the type of compaction is established, the easier it will be to cope with the problem, especially in the case of a malignant neoplasm. Therefore, it is so important to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of mastopathy.
In what cases is it necessary to consult a doctor?
First of all, determine the nature and cause of the pain. If you have never experienced such sensations, contact your gynecologist. Describe your condition, tell us about the conditions in which it arose. If the doctor finds suspicious symptoms, then you can immediately undergo diagnosis and neutralize the disease in a timely manner. Often, natural swelling of the mammary glands does not cause significant discomfort. The main thing is to be reasonable and learn to listen to your own body.
Where to go if your breasts are swollen?
If swollen breasts cause physical or psychological discomfort, consultation with a mammologist and an ultrasound of the mammary glands will help determine the cause and find a solution to the problem.
When looking for a suitable clinic, you will find the “Your Doctor” service useful, which provides its visitors with information about private medical clinics. Here you can not only get the necessary information, but also make an appointment with the selected specialist.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.