Today, treatment of burns is a pressing problem. According to state statistics for 2022, at least 30,000 people suffered thermal or chemical injuries. This is one of the most common household injuries. However, you can often get a burn at work, where safety conditions are not met.
If burns occur, you must be able to provide proper first aid in a timely manner. How quickly you help yourself or the injured person will determine his further condition and the speed of treatment.
The human body is able to regenerate itself and remove minor burns without serious consequences for health. More serious burns require immediate medical attention to prevent complications. Such wounds need to be monitored to prevent infection and regularly treated with anti-inflammatory medications or anti-burn wipes.
If you find yourself close to a burnt person, you really need to know how to treat a burn, otherwise you will do more harm than good with your actions.
Causes of burns
A burn can occur due to exposure to:
- fire;
- hot liquid or steam;
- hot metal, glass or other objects;
- electric current;
- radiation (x-rays or radiation therapy);
- ultraviolet radiation (sun or solarium);
- active chemicals.
It is worth noting that the causes of burns may be different, but all types of such injuries are classified depending on the degree of damage caused and symptoms:
- First degree. This burn affects only the outer layer of the skin. The injury is characterized by redness, swelling and pain. The victim is given first aid and a short course of treatment is prescribed.
- Second degree. This burn leads to damage not only to the epidermis, but also to the underlying layer - the dermis. The lesion is characterized by redness, whitening or mottled skin, pain and swelling. It is possible to develop blisters from burns and severe pain.
- Third degree. With this type of damage, the fat layer under the skin is affected. Burnt areas of the body become charred, blackened or white. Third degree burns often disrupt the functioning of the nervous and respiratory systems.
First steps to neutralize thermal burns
- remove the victim as far as possible from the heat source;
- If clothing or equipment is smoldering, you should get rid of it immediately. If clothing is stuck to the skin, you must carefully cut it off or remove it;
- apply dry ice or use cold water to the damaged area;
- treat damaged areas of the body with burn ointment;
- In case of serious injuries, call an ambulance.
Neutralization of chemical burns
- Rinse the affected area with a strong stream of water. Under no circumstances should you treat a wound with oil.
- If a burn is caused by quicklime or sulfuric acid, it should be
- treat with a dry cloth, the use of water is unacceptable;
- apply a sterile antiseptic bandage.
There are situations when people get severe burns. Treating them outside the hospital requires special knowledge and skills. If a person does not have them, it is better to immediately consult a doctor.
Complications and consequences
The victim often experiences neuropsychiatric disorders, disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys and liver, the formation of scars and contractures, loss of limbs or parts thereof.
The prognosis of how long it takes for a burn site to heal depends on the area and depth of the lesion, as well as the age of the patient. High mortality rates are observed among older people over 60 years of age and children.
Life-threatening burns represent 10% of the surface of the face or perineum and 15% of the surface of other parts of the body.
Degree of burns
There are three main degrees of burns: first, second and third. The rating of each grade is based on the severity of the skin damage, with grade one being the most minor and grade three being the most severe.
Signs of damage look like this:
- first degree burns: the epidermal layer is damaged, the skin is red, slightly swollen;
- Second degree burns: blisters appear and skin peels off;
- third degree burns: tissue necrosis is observed, the skin becomes white, a crust forms;
There are also fourth degree burns. This degree includes all the symptoms of a third degree burn. The damage penetrates beyond the skin and spreads to the tendons and bones. It is in this case that scars remain after a burn.
Chemical and electrical burns require immediate medical attention because they can affect internal organs, even if external damage is barely visible.
The type of burn does not depend on the cause of its occurrence. A scald, for example, can cause all three types of burns—thermal, chemical, and physical—depending on how hot the liquid is and how long it remains in contact with the skin.
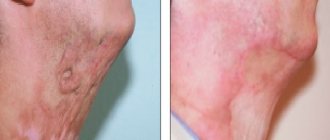
Operating principle of fractional CO2 laser
This is a latest generation device that acts on the skin with micropulses - the laser evaporates scars not as a continuous sheet, but pointwise, leaving microscopic untreated areas. As a result of this gentle action, the skin recovers faster, and accordingly, the rehabilitation period is reduced to a minimum.
Also to combat post-burn scars in our clinic we use: ClearSkin 1540Nm and ClearSkin 1540Nm in-motion (Fractional non-ablative erbium laser Er:Glass 1540nm)
The effect of the procedure is achieved due to the possibility of creating scar tissue at a depth of up to 2 mm. many microthermal treatment zones. The depth of impact affects the entire thickness of the scar without damaging its surface layer.
Therefore, rehabilitation is very short and comfortable!
When the laser beam impacts the deep layers of scar tissue, old collagen and excess pigment are destroyed. After the procedure, intensive cell regeneration processes are launched. The advantage over other lasers is that the skin does not need to spend time on long-term healing of the top layer; the activation of the natural internal resources of the skin begins immediately, which allows you to get excellent results in several sessions.
ClearLift 4D (fractional non-ablative Q-Switched laser with a wavelength of 1064 nm)
Upon reaching the dermal layer, the Q-Switched 1064 nm laser creates a photoacoustic effect similar to a microexplosion; at the site of this effect, a rarefaction area is formed, breaking up the structure of scar tissue, and then filling with new full-fledged molecules. In one flash, 25 point areas are formed, between which remains untouched dermal tissue, which is the source of remodeling of scar structures.
Moreover, this entire process is absolutely painless; moreover, the light, barely noticeable warmth has a relaxing effect. The Q-Switched 1064 nm laser penetrates the skin to a depth of 3 to 5 mm, making the procedure safe for use even on areas with thin skin. Since the top layer of skin - the epidermis - remains intact, the skin looks presentable immediately after the procedure and in the following days, the effect increases over 1.5 months, this is the period necessary for the production of new collagen.
Treatment after burns
If you receive minor injuries, you can try to neutralize them on your own. If you have knowledge of how to treat superficial wounds, you can handle this yourself.
Ointment or gel for burns from boiling water helps well with kitchen problems. If second or third degree burns have been sustained, hospital treatment is required. It should be done in a clinic under the supervision of doctors. The therapist will recommend how to treat the burn or how to treat a burn with blisters.
What else can you do at home?
To speed up the healing of superficial burns, preparations with dexpanthenol are recommended - preferably in the form of sprays, so as not to create a film over the affected area. It is applied to the wound 2-4 hours after the burn and only in the first degree. Sometimes it is allowed to treat a child at home and for burns with small blisters. In this case, it is necessary to promptly change clean bandages and, if the doctor prescribes, treat the wound with chlorhexidine.
In 2008, WHO issued a report on the prevention of childhood injuries. Pediatricians have developed a brochure for children, “Live an interesting and safe life”: it is written in simple language that children can understand and is presented in the form of stories and entertaining quizzes, and the advice from it is still relevant today.
Skin restoration after a burn
What helps with burns is careful hygiene and regular wound care.
After injury, a blister immediately forms on the skin, filled with clear plasma, which can seep through the burned tissue. With proper treatment, inflammation and suppuration can be avoided, and regeneration will occur faster.
Within a few days, the blisters from the burns will begin to subside and peel off, and new skin will begin to form under the blister. At this time, the wounds may itch, but you should not touch the affected area - by the end of the first week the itching will go away on its own.
If the wound is neglected, a process of suppuration may develop. It may be accompanied by fever, sudden weakness and chills. With such a history, regeneration of the skin may take weeks. In this case, compacted growths and ridges are likely to appear.
Why does it hurt so much
The skin is the largest organ: 4−6% of the total body weight. It contains up to 82% water and a third of the total blood volume. There are 2 million nerve endings in the skin, 1.5 million of them are pain receptors.
Temperatures above 44 °C destroy skin proteins - the integrity of the cell membranes is disrupted and water from the cells goes into the space between them. This can be illustrated using an egg as an example. It contains approximately 73% water, 13% protein, 12% fat and minerals. When cooked, the proteins in the cell membrane are destroyed and folded - water comes out. The same thing happens to the skin, only the water goes into other tissues. Therefore, swelling occurs.
Then platelets stick together in the vessels of the dermis and clog the lumen. The blood supply to the burned area is reduced, which can lead to complete tissue death if help is not provided in time. A burn also leads to the release of substances into the blood that provoke inflammation.
Treatment of scars after burns
If you are interested in how to get rid of the external consequences of a burn, you need to know that in case of serious damage to the skin, the scar will remain in any case. Here you will need the help of a cosmetologist who will help restore the normal appearance of the skin.
Typically, for such an operation, a scar excision technique is used, after which several cosmetic sutures are applied to the tissue. When the sutures are removed, the damaged area is treated with ointments that prevent the formation of new scars on the skin.
For particularly difficult cases, for example, burns from boiling water, the laser resurfacing technique is used. Modern equipment allows you to completely remove scars and achieve perfect skin. If the severity of the burn is insignificant, chemical peeling with fruit acids is recommended.
Burns are treated using medical methods, folk remedies, pharmaceutical and cosmetic products. There is no clear answer as to which method is more effective. It depends on the severity, localization of the defect, and skin characteristics. Let's look at each method in more detail.
Medical methods
Medicine and cosmetology offer two methods of getting rid of scars: radical, that is, surgical intervention, and cosmetic procedures.
Surgery is indicated for burns of the third or fourth stage, for hypertrophic, keloid scars.
To remove scars, the patient does:
- Skin grafting. The tissue is taken from a healthy area and moved to the post-burn area.
- Excision – removal of scar tissue, application of a cosmetic suture.
- Laser resurfacing – smoothing the skin by removing part of the epidermis and dermis.
- Microdermabrasion – gentle polishing with microcrystals.
Before carrying out procedures, consult your doctor. He will select the best way to remove a cosmetic defect.
Folk recipes
To treat burns, some prefer to resort to folk remedies. Among them there are quite a lot of effective ones, for example:
- Masks based on badyagi. Accelerate metabolic processes, regeneration, and blood supply to tissues.
- Compresses with camphor oil. Prevents inflammation, nourishes the skin, and quickly heals wounds.
- Composition of chicken egg shells and melon seeds. To prepare, grind the ingredients, then add vegetable oil to the mixture. The course is about two months.
If the scar has appeared recently, it is easier to get rid of it. Therefore, there is no need to delay treatment. Otherwise, surgery may be required.
Creams and ointments for scars and burns
If the post-burn defect was not eliminated, a scar remains, the situation can be corrected even at home. For this purpose, effective ointments, creams for scars and burns are used. If the case is complex, plastic surgery cannot be avoided.
Doctors prescribe absorbable drugs with a regenerative effect, usually immediately after the wound has healed. For keloid scars, products with a silicone base are used, which inhibits pathological tissue growth. Drugs are selected taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s body to avoid side effects.
The following drugs are most often used at home to remove post-burn cosmetic defects:
Cream for scars and burns, hyperpigmentation Lakshma Maxi. A popular product for lightening, including in delicate areas. Eliminates scars without risk to health, reliably and quickly. The result becomes visible after 18 days. The effectiveness of the product is 95%. The cream is easy to use. The product is applied every day before bed to the area that needs lightening. The composition does not contain alcohol, parabens, hydroquinone, the drug does not cause an allergic reaction, and is suitable for different skin types. Active components - kojic acid, vitamins, natural bioactive ingredients. The product is made from natural raw materials. Used for both fresh and old scars.
Contractubex. It contains onion extract and allantoin, which soften healed tissue well and accelerate regeneration processes. Used for different scars, applied twice a day. The effect will be noticeable after a month of use.
Strataderm. Used to get rid of hypertrophic scars and keloids. Contains silicone. The film that appears after applying the cream prevents the scar from growing. Moisturizes and softens rough tissues, dissolving keloids. Apply twice a day for 2-3 months. The maximum therapeutic course is 6 months.
In addition to the listed drugs, cosmetic defects are eliminated with essential oils with a brightening effect - sea buckthorn or jojoba oil, parsley, cucumber extracts, liquid vitamins in ampoules E and A. The products are often used in combination.
Remedies for burns
How to treat a burn, and what kind of surgical assistance can be provided independently in the field or at home?
The use of creams such as Levomikol or Rescuer is guaranteed to help with minor injuries, such as briefly touching a hot pan. Dexpanthenol works very well for first degree burns. If the degree of damage is more serious, creams can only be used as a preventive measure and there is no point in relying on them.
Anti-burn products such as sprays or gels - for example, Burnshield Anti-burn Hydrogel - are more effective because they are dispersed and are better absorbed by the skin. These drugs combine two functions - anti-inflammatory and analgesic.
Buy
Buy
Buy
There is another type of treatment - special anti-burn dressings. They are recommended when the patient needs to be outdoors. Such dressings prevent dirt and dust from entering the wound.
The area is determined by several fairly simple and quick methods.
The "palm" rule - the surface of the victim's palm is approximately 1% of the surface of his body.
The rule of “nines” - the entire surface of the skin is conditionally divided into areas that are multiples of nine in area. Thus, the head and neck approximately make up 9% of the body area, the anterior surface of the torso - 18%, the posterior surface of the torso - 18%, the arm - 9%, the leg - 18%, the perineum - 1%.
There are also more accurate methods for determining area by measuring on graph paper with subsequent conversion to percentages, but they are not widely used and are used more for scientific purposes.
With burns of more than 15% of the body surface, burn disease develops - a severe violation of the general condition, accompanied by dehydration, shock, intoxication, the development of a septic condition, and failure of vital organs and systems. At the same time, burns of more than 40% of the body surface are considered very severe, and more than 80-90% of the body surface are often incompatible with life.
To reduce the risk of general burns
At home, you can quite simply reduce the risk of burns; you just need to follow a few recommendations:
- Do not leave cooking or already cooked food on the stove unattended;
- frying pans are placed on the stove with handles towards its back;
- any hot liquid must be placed out of the reach of children and animals - boiling water is a common cause of thermal burns;
- Do not store electrical appliances near water;
- Do not cook in flammable clothing;
- You should block your child’s access to electrical and gas appliances;
- Protective caps must be put on sockets that are not in use;
- you should not smoke at home;
- smoke detectors require regular maintenance and battery replacement;
- the house or apartment must be equipped with a fire extinguisher;
- Chemical burns are caused by chemicals - they must be stored in a place inaccessible to children and animals.
How to prevent
GMS Clinic pediatrician Maria Fadeeva recommends:
- Keep matches and lighters out of the reach of children
- keep hot foods and drinks away from the edge of the table
- Place irons and curling irons that are turned on so that the child cannot reach them
- cook on the back burners, turn the handles of pots and pans towards the wall or to the side so that the child cannot accidentally grab them
- use protective devices that block the switching on of stoves
- do not carry the child in your arms while preparing food
The kitchen is no place for a small child, especially when preparing food.
- Do not leave your child unattended in a room with heaters on.
- Check the temperature in the bathroom before bathing children
- Keep children away from bonfires and do not set off fireworks nearby
- Avoid inhalation over hot decoctions and boiled potatoes for ARVI - this is ineffective and creates a high risk of burns to the respiratory tract and face.