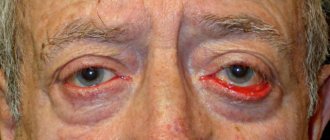
The human pupil is a special structure of the eye, which is formed by the cornea and the muscles of the eyeball. Essentially, it is just a hole in the cornea, the diameter of which is regulated by muscle structures. Its main task is to regulate the light flux that hits the retina. This is achieved by dilating or constricting the pupil.
The pupillary reflex, depending on the degree of light hitting the retina of the eyeball, regulates the diameter of the pupil, and also synchronizes both pupils over time. This reflex is controlled by the brain stem. Most often, brain stem pathology causes eye pupils of different sizes.
The sympathetic nervous system causes large pupils. This occurs during periods when a person experiences fear, anger or excitement. The parasympathetic nervous system, on the contrary, causes constriction - the pupils of the eyes are narrow. Normally, these two systems are antagonists of each other.
In medicine, different pupils of the eyes that are identified in a patient are referred to as anisocoria.
Why is one eye larger or smaller than the other: common reasons
Keep in mind! If there is a clear difference and one eye is larger than the other and this is not a congenital feature, then in this case we can talk about a number of diseases.
Let's consider the most common pathologies that this symptom may indicate.
Infectious eye diseases
These include stye and conjunctivitis.
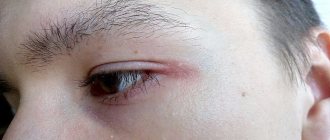
In this case, the disease can affect the mucous membrane of the eye, the tissue of the eyelid or the hair follicles of the eyelashes. The tissues surrounding the diseased eye swell and prevent it from opening completely . If a person develops internal inflammation, a clear difference between the eyes will indicate a problem.
Neuritis
This disease can occur as a result of banal hypothermia or tooth root infection .
The pathology affects the facial nerves , resulting in obvious asymmetry of the eyes.
It is worth noting! In more complex cases, asymmetry affects half of the face completely. From the outside it seems that the face is “sliding” to one side.
Poor blood circulation in the brain
A change in the shape of the eyes is a characteristic symptom of cerebrovascular accident.
Additional symptoms of brain problems include difficulty swallowing food and memory problems .
Various injuries
The eye can shrink as a result of various injuries and hematomas .
Violation of the rules for wearing contact lenses, contact with a foreign object on the mucous membrane, or rubbing of the eyelids can affect the size of the eye.
How to distinguish between physiological and pathological anisocoria
This is an important problem, since pupils of different sizes are a symptom of serious diseases. You should definitely consult a doctor if anisocoria is accompanied by:
- pain in the eyes;
- red eyes or swollen eyelids;
- protrusion of the eyeball forward;
- excessive tearing;
- headache and dizziness;
- distortion of images, decreased visual acuity, impaired spatial perception, the appearance of circles or spots before the eyes;
- nausea, vomiting;
- confusion;
- problems with body control, hand tremors.
Eye asymmetry in a child: causes
The causes of ocular asymmetry in children are practically no different from the causes of pathology in adults . The most common of them include:
- kidney disease - in this case, the outflow of fluids from tissues is disrupted, swelling is formed, which often leads to similar problems;
- injuries, for example, as a result of playing sports;
- eye infections;
- disorders of the brain.
You should definitely contact your pediatrician in the following cases::
- if the defect occurred unexpectedly against the background of the child’s complete health;
- if, in addition to the difference between the eyes, the child experiences additional symptoms in the form of pain, itching or burning;
- if the difference between the eyes is large enough, or if the eye practically does not open.
Why did the pupils become different sizes?
To answer this question, it is necessary to understand the physiology of the visual organs. Thus, the pupil is a special hole in the center of the iris, through which light rays penetrate the retina (inside the eyeball).
Everyone knows that in too bright light the pupils constrict, and in complete darkness they dilate noticeably. When one eye is exposed to bright light, you may notice a synchronous constriction of both pupils, which is normal. Expansion can also be observed during a pronounced feeling of fear, severe pain or fright.
The processes of dilation (miosis) and constriction (mydriasis) of the pupils are regulated by the human autonomic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for mydriasis, and the parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for miosis. Therefore, the reasons why the pupils have different diameters may be due to a malfunction of these systems. However, there are other factors that influence this process.
In normal conditions, the pupils are the same size: 2-4 mm in daylight, and 4-8 mm in poor lighting. If the difference in their size exceeds 0.4 mm, anisocoria, or loss of pupil symmetry, is diagnosed.
It can be both physiological and pathological in nature. In the first case, this is an individual characteristic feature of the human body, which, as a rule, is inherited.
Often the phenomenon can occur in children whose parents had similar characteristics. Doctors attribute this to a genetic factor.
Eye asymmetry in newborns
Know! This problem occurs quite often in infants and raises many questions among parents.
Only a pediatrician can determine the exact cause and make the correct diagnosis. However, we can give the most common reasons for different eye sizes, according to Dr. Komarovsky .
Congenital edema
Swelling after childbirth can last a long time in a child.
The main symptom of this condition is a decrease in eye size.
After some time, the problem goes away on its own and does not require any outside intervention.
Human pupils have different sizes: reasons
Pupils can be different sizes from birth. In this case, we are talking about physiological (congenital) anisocoria, in which the difference in the diameter of the left and right pupil does not exceed 1 mm. The physiological form of the pathology does not require treatment, since it does not affect visibility in any way and does not pose any threat to the health of the human visual organs. The correct standard reaction of the pupils to light is maintained, they work synchronously.
Pupils that are different from birth are often an individual trait that is most often inherited. In addition, congenital pathology can be caused by an abnormal development of the nervous system of the eye (and it is often accompanied by strabismus). Also, physiological anisocoria in some cases occurs with intrauterine abnormal development of the eye and its structures. In this case, the infant may have pupils of different sizes, as well as a decrease in visual acuity in the right or left eye.
If different pupils appear suddenly, this indicates the pathological nature of anisocoria. This pathology is mainly caused by some third-party malfunction in the body.
Pathological anisocoria can occur due to:
- Horner's syndrome (disorder of the sympathetic nervous system). As the brightness of the light decreases, the difference between the pupils increases, while in daylight it is about 1 mm.
- Disorders of the oculomotor nerve. Pathology can occur due to ischemic or diabetic neuropathy, or as a result of mechanical trauma.
- Damage to the muscles of the iris (due to various types of trauma, surgery or inflammatory processes). There is no reaction to light.
- Acute angle-closure glaucoma, which is characterized by impaired functioning of the iris and decreased pupillary reactions.
- Trauma, swelling or concussion, intracranial hemorrhage.
- Retinal burn leading to blepharospasm.
- Use of drugs and certain medications.
- In addition, the cause of pupils of different sizes can sometimes be migraine, poor circulation of the brain, malfunction of ciliary ganglion neurons caused by viral and bacterial infections, as well as damage to the nervous system by syphilis.
- Different pupils in infants: an individual trait or a pathology?
Pupils of different sizes in a newborn may indicate a congenital abnormality in the development of the visual organs or brain. This condition is usually detected immediately after childbirth, so the doctor immediately prescribes a number of additional examinations.
If the results of an ultrasound do not reveal characteristic defects, for example, a decrease in brain size, hydrocephalus (hydrocephalus), etc., it is stated that the pupils of different sizes in the infant most likely appeared due to a hereditary factor. Sometimes the cause of the pathology is poisoning with toxic substances, including plants containing anticholinergics. In general, different pupils in newborns can appear for the same reasons as in adults.
Treatment of ocular asymmetry
Treatment of this problem depends entirely on the root cause that caused the pathology.
Thus, eye infections require consultation with an ophthalmologist , and a problem arising from a stroke requires treatment by a neurologist.
Stay up to date! In general, the following treatment plan for different eye sizes can be distinguished:
- undergoing a comprehensive examination by a therapist or pediatrician . In this case, the doctor conducts an external examination and asks the patient about the presence of accompanying symptoms;
- taking tests and undergoing an ultrasound examination.
Once the examination provides general information about the underlying cause, the patient's physician should make a referral to a specific specialist, such as a surgeon, nephrologist, or ophthalmologist.
Diagnosis of anisocoria
Since different pupils can be a symptom of a large number of diseases, a careful history is required to look for concomitant pathologies. To do this, ophthalmologists use the following examinations:
- slit lamp examination.
- retinoscopy;
- diaphanoscopy;
- biomicroscopic examination;
- iris sensitivity test for M-cholinomimetics.
Additionally, for anisocoria, MRI, CT, contrast angiography, ultrasound, and general blood test are prescribed.
Franceschetti syndrome
A genetic disease that develops in the fetus 6-7 weeks after conception. This anomaly is diagnosed immediately after the baby is born. At the same time, his appearance has characteristic features: the corners of the eyes are drooping, sometimes the upper or lower eyelid is missing, and the jaw is underdeveloped. Paresis of the extraocular muscles and microphthalmos, leading to hypermetropia, are also observed. Unfortunately, even advanced modern medicine cannot control genetic mutations. A sick child can be born to completely healthy parents. This is why it is so important for a pregnant woman to monitor her health during pregnancy.
Anatomical size of the eyeball
The normal size of the eye in an adult is approximately 23-25 mm. However, in infants its diameter is 17-18 mm, so all children at birth have physiological farsightedness. Its value is approximately 2-3 diopters. As the child grows, the diameter of his eyeball increases. By the age of one year, the value of hypermetropia should be no more than 2-2.5 diopters, and with normal development, by approximately 10-12 years, the optical focus moves to the retina, and physiological farsightedness disappears.
Albinism
A hereditary disease in which the body’s production of melanin, a special pigment responsible for the color of the skin and hair, is limited. The iris of albinos is very transparent, completely transmitting light, so their eyes may appear reddish due to translucent blood vessels. This pathology is often accompanied by various visual impairments. This may be hyperopia of 3-6 diopters, mild to moderate myopia, or astigmatism. Farsightedness with albinism usually does not progress and can be successfully corrected with glasses or contact lenses.
Treatment of congenital hypermetropia
To maintain the quality of vision in good condition, as well as to prevent further progression, various therapeutic methods are used. In childhood, these include glasses, contact lenses (from 10 years old), special exercises for the extraocular muscles, and hardware therapy. Before the age of 18, laser vision correction is generally prohibited, since the eyeball still continues to grow, and the amount of hypermetropia may change or the pathology will disappear altogether. Before purchasing correction products, you must visit an ophthalmologist. He will measure your eye parameters and write a prescription. It is best to purchase custom-made glasses rather than ready-made models. As a rule, the optical power in the left and right eyes is not the same, and the difference can reach several diopters. In addition, the interpupillary distance is of great importance - it is different for all people. Ready-made models do not take these nuances into account. Incorrectly selected optics can lead to vision impairment. Treatment of congenital farsightedness should be carried out from an early age in order to prevent the development of irreparable consequences.
Is it necessary to treat anisocoria?
Anisocoria is only a symptom: first you need to find out why the pupils are different, and then begin to treat this disease. For example, if miosis is caused by iritis, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents are prescribed. If the patient has Horner's syndrome, neurostimulation with low-amplitude electrical impulses is prescribed and, if the disease occurs due to a hormonal imbalance, hormone replacement therapy. In case of mechanical damage to the eyes, the foreign body is removed, atropine or pilocarpine is instilled, autohemotherapy and antibiotics are prescribed. For Adi syndrome, pilocarpine is prescribed.
Differences Between Bodybuilding and CrossFit Workouts
To someone outside the gym, it may seem like bodybuilding isn't much different from Crossfit. People exercise strength, lift weights, and often do similar exercises. However, bodybuilding and crossfit are two different worlds. CrossFit training differs from bodybuilding primarily in the intensity of the exercises performed. For example, a two-kilometer run. A bodybuilder will run the route in 12 minutes, and a person practicing CrossFit will do it in 8. The training is the same, but the effects are completely different. A person who exercises in CrossFit has four times more endurance than a bodybuilder. The same thing, but the intensity of the training is much higher. Those are the basics, but what about the other differences?