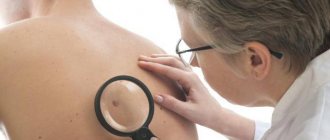
Cheilitis is an isolated inflammatory process in the area of the mucous membrane, skin and red border of the lips. Outwardly it looks like swelling with redness and peeling of tissue. It can be an independent disease or a symptomatic manifestation of other pathologies. Sooner or later, almost every person encounters it, but at a young age the disease is noticeably milder, recurs less often and has no complications. In older people, due to a weakened immune system, periodic relapses of cheilitis can cause malignant tissue degeneration.
Reasons for the development of cheilitis
The main causes of the disease include:
- Dermatoses seem to be the most common cause of cheilitis. Skin diseases such as psoriasis, lupus erythematosus, syphilis, tuberculosis, lichen, also often provoke inflammation of the red border of the lips.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Allergies to various kinds of external factors, professional activities.
- Adverse weather conditions.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Decreased immunity, gastrointestinal diseases.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of rashes around the mouth, proper prevention is important. You should strengthen the body's defenses, spend more time in the fresh air, do exercises, and harden yourself.
Nutrition is of great importance. It is necessary to exclude fast food, smoked foods, carbonated drinks, sweets, citrus fruits, and baked goods. The diet should be enriched with fresh herbs, vegetables and fruits collected in the region of residence, fermented milk products, and cereals. To improve the health of all organs and systems, it is useful to drink at least 2 liters of clean water per day.
To prevent fungal, bactericidal and viral infections, you should regularly wash your hands, use individual towels and adhere to other personal hygiene rules.
You can prevent the development of allergies by limiting contact with allergens. To do this, you need to adjust your diet, protect your hands with gloves when working with household chemicals, and use natural care products and mineral cosmetics.
Types of cheilitis
All types of cheilitis are divided into two groups:
- symptomatic (cheilitis, as a manifestation of the underlying disease);
- true (as an independent disease).
Types of symptomatic cheilitis and their clinical manifestations
The symptomatic group includes the following types of cheilitis:
- Eczematous - develops against the background of eczema, characterized by redness, swelling, burning and pathological changes in the skin of the lips. If left untreated, it becomes chronic.
- Macrocheilitis - this form of cheilitis is considered a component of Melkersson-Rossolimo-Rosenthal syndrome. There is severe itching and swelling of not only the lip, but also other parts of the face.
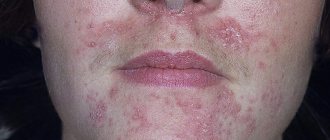
- Atopic - a predisposition to allergies to medications and food is a prerequisite for the development of inflammation. It manifests itself as peeling, redness, itching of the skin of the lips, and the formation of cracks in the corners of the mouth.
What are the causes of the disease?
It is necessary to distinguish between the cause and triggers of atopic dermatitis.
The reason is not fully known to modern science; the main version is a set of genetic, immune and skin changes, in particular, a deficiency of the skin protein filaggrin, which is responsible for retaining moisture in the skin.
The triggers of atopic dermatitis are very diverse, atopic skin is overly sensitive to irritation, so exacerbation can be caused by increased sweating, heat, rough clothing, detergents, dry air, etc. Children with atopic dermatitis may simultaneously have allergies to food, household or other animals, dust mites, tree and grass pollen - these allergens can also be triggers for exacerbations.
In general, atopic dermatitis has a wave-like course, periods of exacerbations (most often occurring for unobvious reasons or for no reason) are replaced by periods of remission - hence there is a great temptation to associate exacerbations with factors that are not directly related to the disease, and vice versa - to attribute healing properties to completely extraneous factors (for example, a diet that parents started by mistake or out of desperation).
It is impossible not to mention the established harmful domestic tradition of calling atopic dermatitis allergic (usually associating it with an allergy to cow’s milk protein) and treating it with diets (a strict “hypoallergenic” diet for a nursing mother, and/or a hydrolysis/amino acid mixture for a child). Indeed, if a child has an intolerance to cow's milk proteins, it may aggravate or cause atopic dermatitis, but not vice versa. Not every child with atopic dermatitis has an intolerance to cow's milk proteins or any other allergens. This means that by prescribing a diet, or an expensive and unpleasant-tasting mixture, the doctor adds problems to the family without helping them. In most cases of atopic dermatitis, identifying allergies and excluding allergens does not provide any benefit.
Types of true cheilitis
True cheilitis includes:
- Contact - manifests itself as a result of the body’s reaction to contact with an irritant: cosmetics (determined mainly in women), the bad habit of holding a pen or pencil in the mouth, professional activity (musicians due to prolonged use of the mouthpiece of a wind instrument) Characterized by redness, itching, feeling burning, swelling of the lips.
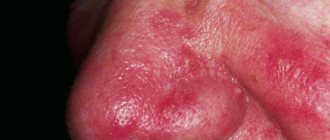
- Actinic - involves the development of an inflammatory process as a result of special sensitivity to natural phenomena: sunlight, wind, frost, radiation. It manifests itself as small blisters or erosion, swelling of the red border. This type of cheilitis is also called meteorological.
- Exfoliative - occurs mainly in women. The development of pathology occurs against the background of depression, anxiety, and various disorders of the nervous system. The main symptoms are dryness, severe, prolonged peeling of the lip border. Exfoliative cheilitis has two forms: dry and exudative. With exudative inflammation, crusts form, causing pain in the patient.
- Glandular - occurs against the background of hypertrophy of the minor salivary glands. This phenomenon can be congenital (appears after puberty) or acquired as a result of chronic inflammation. There is a risk of suffering from glandular cheilitis in people with periodontal disease, numerous carious cavities, after lupus erythematosus, and leukoplakia. It is initially characterized by increased dryness, which does not disappear with the use of hygiene products. Later - the presence of cracks due to the constant exposure of saliva to the red border of the lips. 20-30% of patients with glandular cheilitis develop squamous cell carcinoma. It is necessary to take a responsible approach to the treatment of this disease and seek qualified help from doctors in a timely manner - surgical intervention may be required.
Causes of peeling skin around the mouth
Most often, the skin around the lips peels due to:
- traumatic care. The abundant presence of alcohols, harsh surfactants, preservatives, and other unpleasant substances in cosmetic products provokes the appearance of peeling and skin problems in general. You should avoid components such as: Denatured Alcohol, Ethanol, Ethyl alcohol, and also do not do chemical or mechanical cleaning more often than required. By the way, scrubs can be the reason why the skin peels, since they traumatize it quite strongly even with visible cleansing.
- improper diet. The foods we eat affect our appearance. In order to keep it in order and minimize the risk of peeling, acne, and other defects, you need to remove sweet, fatty, spicy, smoked foods from your menu, reduce the consumption of light carbohydrates, add fiber and lactic acid drinks, such as kefir, fermented baked milk, yogurt .
Interesting! Eating fermented milk products can really help get rid of flaking, as they contain a lot of lactic bacteria. They produce lactic acid, which is widely used in cosmetic production - it acidifies the body’s environment, destroys subcutaneous fat, regulates the functioning of the sebaceous glands, and also exfoliates keratinized particles, which, in fact, are peelings.
- Sudden temperature changes. This is especially true on cold winter days and autumn evenings. The dermis could simply be frozen or chapped, like the lips, for example, which is much easier to deal with.
- Deficiency of certain vitamins. These may include vitamins A, E, B or C. These vitamins have the greatest impact on our dermis. They accelerate regeneration, due to which the skin recovers faster after peeling, moisturize it, preventing their appearance, and do not allow dead skin cells to remain on the face for a long time.
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract or hormones. The gastrointestinal tract and the hormonal system of our body are one of the most vulnerable human systems. Problems with them can be hereditary or congenital, but very often acquire over time. They are accompanied by a deterioration in facial tone and relief, and can cause the skin around the mouth and nose to peel.
- Dermatitis may be oral (scaly), contact (bleeding), or seborrheic (similar to dandruff). Peeling is an eternal companion of dermatitis, and ordinary cosmetics can no longer cope with it.
Attention! You should never forget that in some cases the skin is prone to flaking, especially dry skin.
Treatment of cheilitis
This disease requires special treatment, depending on the cause, type and degree of the inflammatory process. The main methods of treating cheilitis:
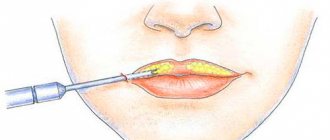
- local treatment of the surface of the skin of the lips with disinfectant solutions, ointments, vitamin oil solutions;
- physiotherapeutic methods: Bucca radiation, ultrasound, laser therapy;
- a course of vitamin therapy;
- rinsing the mouth with decoctions of medicinal herbs.
If necessary, to eliminate the causes of the disease, specialized specialists may be involved: a dermatologist, an allergist, an infectious disease specialist.
What to do if the skin around your mouth is peeling
The flaky skin around the lips needs treatment to prevent it from flaking. However, different reasons require different remedies. For cosmetic defects, proper care will be enough, but at the first suspicion of dermatitis, you should visit a dermatologist who will prescribe not only cosmetic products, but also internal ones.
The skin on the face around the mouth is often an indicator of whether a girl is taking care of her face as a whole, so it is very important to keep it in good condition. And even after treatment, it is worth paying great attention to prevention and advice from a cosmetologist.
Experts advise that if the skin around your mouth is already peeling, ask yourself a few questions:
- Am I drinking enough water? Water is involved in many processes in the body, including playing an important role in keeping the face in order.
- Am I allergic to any foods/organisms? Red spots near the mouth of an adult, which also peel, may be a manifestation of an allergic reaction.
- Should I reduce the level of alcohol/nicotine/fat/sweets and add more fruits, milk and fiber? After all, this not only causes redness and irritation around the mouth, but also generally has a bad effect on the body.
- Do I wash off my makeup every time I come home? You need to wash your face with micellar water and foam after a hard day at work, despite your fatigue. In all that dust, secretions of the sebaceous glands, particles of cosmetics, a huge amount of bacteria accumulates overnight, due to which the skin around the mouth begins to peel off, and oral dermatitis or herpes may even appear.
The best anti-flaking remedies
If, as a result of an examination by a dermatologist, it was revealed that the skin near the lips is peeling not due to any gastrointestinal diseases or hormonal imbalances, then to get rid of the defects it will be enough to use cosmetics.
- Alpha hydroxy acids, or, in other words, AHA acids. Despite the aggressive name for an anti-peeling agent, these acids are completely safe when used correctly. They are used for many problems with the dermis, as they perform the function of exfoliating peeling. It is recommended to use creams, peelings and tonics with alpha acids if the skin around the mouth is peeling - they will relieve you of traces of peeling. If used no more than 2-3 times a week in the dark, they will not cause harm, but they cannot be used in the sun. Acids only affect the top layer of the skin and do not penetrate deeper, so it is impossible to worsen the condition of the face with them.
Attention! You should start with small doses of acids - for example, first purchase a product from “White Flax”, then from “Bark”, and when the skin gets used to it, you can look at the 30% AHA peeling from The Ordinary.
- The AEvit series from the Russian brand Libriderm. The line includes: gel for washing, face mask, face cream and separately for the area around the eyes, hygienic lipsticks that will not allow peeling to affect the lips. The care is aimed at softening, eliminating peeling, nourishing, and is especially relevant in winter and autumn. It also smoothes out fine wrinkles. In the composition of AEvit products you can find a complex of vitamins A, E, herbal components - extracts of raspberry, edelweiss, rosemary. Also take a closer look at the series with hyaluronic acid.
- Sulfur soap. It perfectly helps with irritation of the skin around the mouth, if it is flaky, red, tight. Using a soft sponge or konjac, the foam is fine, fluffy, and does not harm the lips if it accidentally gets on them. But sulfur has a specific smell, which should be taken into account.
Special mention should be made for the treatment of peeling and spots resulting from allergies or urticaria. In this case, it is recommended to use drugs containing loratodine, but the dosage and frequency of use must be indicated by a doctor.
Before choosing any of these products, pay attention to the contraindications under which their use is prohibited.
Some useful home recipes against peeling lips:
Contraindications
To ensure that the process of treating skin from peeling is absolutely safe, before using the product, pay attention to its composition. You must be absolutely sure that there are no alcohols or substances to which you are allergic, even if these are herbal supplements that are effective against the problem.
You should not use creams and other products with vitamins A and E if there is an excess of these substances in the body, and acids should be put aside during active sun exposure or if your skin is very thin and sensitive.
Attention! If a child has peeling, none of these methods (except going to the doctor) will work.
Allergic cheilitis
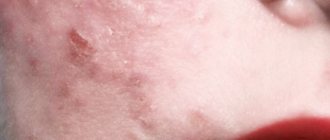
A disease that develops in allergy sufferers upon contact with an allergen and affects the surface of the lips. Typical manifestations of this type of cheilitis are a feeling of itching and burning on the lips, dryness and significant discomfort. The lips begin to dry and peel, and the scales of dead epithelium begin to flake off.
The main cause of this disease is the patient’s increased sensitivity to external irritants, in particular to allergens. Allergic, or, as it is also called, contact cheilitis can develop gradually.
It all depends on the patient’s personal sensitivity to allergens, and it can develop over several weeks, months and even years. The duration of this process is determined by the peculiarities of the endocrine system, as well as the degree of manifestation of allergic reactions.
This disease practically does not appear in children. According to statistics, most patients with allergic cheilitis are women over twenty years of age.
Causes of the disease
In most cases, allergic cheilitis is caused by contact allergic irritants. Among the most common allergens that cause cheilitis is lipstick. It is not the lipstick itself that is dangerous, but the substances it contains - rhodamine, eosin and others. Provoking factors also include low-quality dental implants and plastic dentures.
Allergic manifestations may appear after contact with citrus fruits, as well as in patients who have the habit of chewing pencils or pens. The disease is also common for those whose work involves playing wind instruments or hazardous chemical production.
Symptoms of the disease
The disease manifests itself as hyperemia and swelling of the lips, as well as a sensation of itching and burning, accompanied by the formation of erythema. Small painful blisters appear and burst on the affected areas of the lips. If the pathogenic process is prolonged, over time, small scars and scars will form in their place on the lips. Dry lips only increase over time.
Inflammation almost never extends beyond the red border around the lips. In rare cases, it may spread to adjacent skin. Sometimes the inflammatory process moves to the oral mucosa. This form of allergic cheilitis is characterized by hyperemia (significant redness of the tissues), the appearance of noticeable swelling of the tissues, and when trying to palpate, pain occurs.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by a dentist together with an allergist. To determine the allergen, it is necessary to conduct allergy tests.
When making a diagnosis, it is important to distinguish allergic and atopic cheilitis, as well as exclude exfoliative and actinic cheilitis. Treatment of this disease includes the mandatory elimination of the irritant or allergen that caused it.
Systemic (general) and topical (local) drug therapy is used. General therapy refers to the use of medications taken orally. To relieve allergy symptoms, a course of antihistamines is used. If the case is sufficiently complex, the use of corticosteroids may be indicated. In addition, calcium supplements may be prescribed.
Local treatment of allergic cheilitis includes the use of a variety of emollient oils, ointments and balms based on sea buckthorn, vitamin E and others. To avoid the recurrence of the pathology, it is necessary to take an allergy test in order to eliminate any contact with the allergen in the future. It is also advisable to reconsider your diet and carefully consider the choice of cosmetics.
Diagnostics
There is no specific test or examination to confirm the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis; the diagnosis is made clinically. The doctor will examine the rash and ask about the child's symptoms and family history of atopy and allergies. A history of eczema in family members (either as a child or still today) will be an important clue.
Your doctor will rule out other conditions that may cause your skin to become inflamed or itchy. In case of difficulties with diagnosis or severe course of the disease, the pediatrician will refer the child to a pediatric dermatologist or pediatric allergist.
The doctor may ask you to eliminate certain foods (such as eggs, milk, soy, or nuts) from your child's diet for 2 to 3 weeks before reintroducing them and monitoring symptoms. If the diet leads to relief of the rash, and provocation leads to its obvious exacerbation, this will confirm the diagnosis and the need for a diet.
Since there are no accurate laboratory methods for confirming the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis, there are criteria for standardizing the clinical diagnosis (the best known are the Hanifin and Raika criteria).
The criteria are divided into “large” and “small”. To make a diagnosis of atopic dermatitis, it is necessary and sufficient to detect three major and three minor criteria in the patient.
The big ones include:
- itching;
- dermatitis affecting the flexor surfaces in adults, or the face and extensor surfaces in infants;
- chronic or recurrent dermatitis;
- a personal or family history of skin or respiratory allergies.
Small ones include:
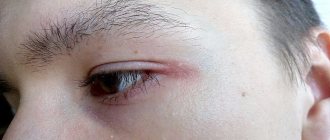
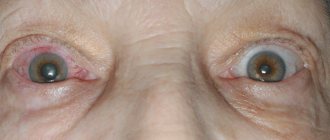
- specific facial features: facial pallor, erythema, hypopigmented spots, dark circles under the eyes, cheilitis, infraorbital folds, recurrent conjunctivitis, anterior neck folds;
- typical triggers: emotional factors, environmental factors, food, skin irritants;
- typical complications: susceptibility to skin infections, impaired cellular immunity, predisposition to keratoconus and anterior subcapsular cataracts, immediate skin reactivity;
- other signs: early age of onset, dry skin, ichthyosis, hyperlinearity of the palms, piliary keratosis, dermatitis of the hands and feet, nipple eczema, white dermographism, white pityriasis, perifollicular accentuation.
An explanation of each of these symptoms is beyond the scope of this article; The criteria are given here to help you understand what the doctor is guided by when making a diagnosis of atopic dermatitis.
There are also various scales for assessing the severity of atopic dermatitis used by doctors and scientists, the most famous of which is the SCORAD scale. In this scale, the doctor must note the number, prevalence and severity of symptoms of atopic dermatitis, express them in points, sum up the points and, based on this sum, set the severity of the disease.
Diathesis and its causes
Atopic dermatitis (diathesis) is the most common allergic skin disease in children and adults, which is characterized by inflammation, itching, and a chronic relapsing course. Atopic dermatitis typically has different skin manifestations depending on the person's age. Let's look at it in more detail below.
Atopic dermatitis (diathesis) is the most common allergic skin disease.
Causes of diathesis
A special role in the development of the disease is played by the hereditary ability to develop allergic diseases.
The disease is also based on other causes, which can be divided into internal and external. Internal characteristics include the characteristics of the organism itself. External causes include those with which a person comes into contact from the outside.
Internal reasons
- Hereditary – determined ability of the body to increase the production of IgE (immunoglobulin, responsible in most cases for allergies).
- Increased, excessive reaction of the skin to irritants (allergens).
- Increased skin dryness.
- Violation of the epidermal barrier.
External reasons
- In children of the first years of life - food allergies, as well as intestinal dysbiosis, vaccination (DPT). It is important to emphasize that vaccination will not lead to the development of atopic dermatitis in every child. There is only a higher likelihood of developing this disease in children with a history of allergies.
- Preschool children have household and fungal allergens. Often the cause can be helminthiasis.
- In adolescence – stress, emotional experiences.
- The causes of diathesis in adults are a combination of the factors described above. This could be a food allergy, an allergy to flowering plants, a contact allergy (when allergens come into contact with the skin), stress, or emotional distress.
Symptoms of diathesis in children and adults
Diathesis can appear at any age. The main manifestation is constant severe itching in combination with local skin manifestations . The disease is characterized by a relapsing course.
Diathesis can appear at any age.
The first signs of the disease appear at an early age. They are preceded by the appearance of scales on the scalp and eyebrows (gneiss). One of the main and main manifestations of dermatitis in young children is redness and dryness of the skin of the cheeks. A characteristic feature is that the nasolabial triangle and nose remain untouched by allergic rashes. If parents do not take any measures, the process progresses. Lesions also appear on other parts of the body: scalp, ears, torso, extensor surfaces of the limbs. Often the rash can be located on the buttocks, around the anus. Without treatment, the process progresses, and small blisters appear against the background of redness and swelling of the skin, which quickly collapse. As a result, wounds appear that become covered with crust and scales. After peeling off the crusts, smooth, bright pink skin remains at the affected areas. Sometimes, against the background of the described rash, small nodules may also appear on the skin, which rise above the skin level. on the skin are usually located symmetrically .
With age, many patients experience clinical transformation of skin rashes. In adults they look different and are located in different places. The lesions look like thickened and dry skin. They are located on the neck, elbow and popliteal folds, on the back of the hands, in the axillary and inguinal folds, sometimes around the mouth, eyes and in the genital area. Characterized by intense itching of the skin, which intensifies at night. Because of this, sleep is disturbed, the person becomes irritable and moody. Constant itching leads to the fact that a child or adult scratches dry areas of the skin and a wound surface appears that becomes covered with crusts.