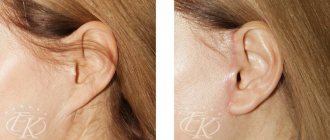
Otoplasty is an operation on the ears for the purpose of their aesthetic correction. Defects in the ears, unlike parts of the body covered by clothing, are quite difficult to hide, so such defects in appearance become the cause of serious psychological problems. How to remove protruding ears? – the most common question from patients requiring ear otoplasty. However, this type of plastic surgery can also solve a number of other problems - today it is possible to correct the shape and size of the ears - both the auricles and the lobes, and eliminate asymmetry. Modern plastic surgery makes it possible to restore the auricle that has been lost for any reason.
Depending on the indications, plastic surgery of one earlobe (or auricle) or two earlobes (or auricles) can be performed. This corrective operation is quite easily tolerated, so ear otoplasty is often performed in childhood, but not earlier than 6 years, due to the need to wait for the final formation of the ear cartilage. Cosmetic surgery on the ears allows one to cope with both congenital and post-traumatic defects of this area.
Where is ear otoplasty performed? If there are defects in this area, it is important to seek advice and subsequent assistance from specialized clinics where experienced surgeons work. The success of ear plastic surgery, as well as other types of correction, is largely determined by the professionalism of the doctor. Our project offers promotions for free ear correction in well-known clinics in Moscow and St. Petersburg, with surgeons who have extensive practical experience in this area. It is possible to have otoplasty at almost any age - it is never too late to change your appearance for the better, getting rid of life-limiting complexes.
Indications and contraindications for otoplasty
Plastic surgery to correct the ears may be indicated if necessary:
- correct protruding ears (protruding ear);
- eliminate congenital or acquired deformities of the auricles as a result of trauma;
- change the shape and size of the earlobes (correct fused or excessively large earlobes, sew up a lobe if it is torn);
- form lobes in their absence;
- correct ear asymmetry (for example, if one ear is larger than the other).
If, in your opinion, you have any defects: protruding or unsightly shape of the shells, a pronounced seal on the earlobe, a fused or hypertrophied large lobe, or other defects that cause concern, just come for an initial consultation with the surgeon. After a thorough examination and conversation, the doctor will determine whether you really have indications for correction of the earlobes and conchae, and will tell you what results can be achieved by performing surgery.
Surgery to reduce ears, eliminate protruding ears, correct lobes, correct asymmetry and eliminate other defects in this area also has contraindications, such as:
- severe forms of chronic diseases of internal organs;
- diabetes;
- impaired blood circulation in the area of the auricle;
- chronic ear infections;
- oncology;
- inflammatory processes of the ear;
- acute respiratory diseases;
- blood clotting disorder.
Thanks to otoplasty, the question that worries many people, how to get rid of protruding ears, has ceased to cause great concern. Correction of protruding ears (and it does not matter whether we are talking about protruding ears in a child or an adult) can be easily solved with the help of an operation that is tolerated quite simply, as is the subsequent rehabilitation period. No less masterfully, modern plastic surgeons cope with such defects as seals in the earlobes, asymmetry, unaesthetic shape and size of the ears. Currently, there is practically no external ear defect that could not be successfully corrected.
Sources
- Zanin EM., Maximiliano J., Oliveira ACP., Arpini NE., Duarte DW., Portinho CP., Collares MVM. Otoplasty: Rasps or Puncture Needles? A Clinical Trial. // Aesthetic Plast Surg - 2022 - Vol45 - N2 - p.521-527; PMID:33123781
- Li Z., Filobbos G. What is the UK Public Searching for? A Correlation Analysis of Google Trends Search Terms and Cosmetic Surgery in the UK. // Aesthetic Plast Surg - 2022 - Vol44 - N6 - p.2312-2318; PMID:32986171
- Kalmar CL., Patel VA., Humphries LS., Zimmerman CE., Vu GH., Swanson JW., Taylor JA. Pediatric Otoplasty: Does Surgical Specialty Training Affect Safety and Rates of Adverse Perioperative Events? // J Craniofac Surg - 2022 - Vol31 - N6 - p.1739-1742; PMID:32433130
- Ors S. Prominent Ear Correction With Anterior Rasping. // J Craniofac Surg - 2022 - Vol31 - N5 - p.1408-1411; PMID:32310890
- Siegert R., Magritz R. Otoplasty and Auricular Reconstruction. // Facial Plast Surg - 2022 - Vol35 - N4 - p.377-386; PMID:31470466
- Ordon A., Wolfswinkel E., Shauly O., Gould DJ. Aesthetic Otoplasty: Principles, Techniques and an Integrated Approach to Patient-Centric Outcomes. // Aesthetic Plast Surg - 2022 - Vol43 - N5 - p.1214-1225; PMID:31289880
- Kang N.V., Sabbagh W., O'Toole G., Silberberg M. Earfold: A New Technique for Correction of the Shape of the Antihelix. // Laryngoscope - 2022 - Vol128 - N10 - p.2282-2290; PMID:29658102
- Gantous A., Tasman AJ., Neves JC. Management of the Prominent Ear. // Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am - 2022 - Vol26 - N2 - p.181-192; PMID:29636149
- Smittenberg MN., Marsman M., Veeger NJGM., Moues CM. Comparison of Cartilage-Scoring and Cartilage-Sparing Otoplasty: A Retrospective Analysis of Complications and Aesthetic Outcome of 1060 Ears. // Plast Reconstr Surg - 2022 - Vol141 - N4 - p.500e-506e; PMID:29595722
- Brian T., Cheng PT., Loo SS. Audit of 117 otoplasties for prominent ear by one surgeon using a cartilage-cutting procedure. // ANZ J Surg - 2022 - Vol89 - N3 - p.E66-E70; PMID:29415346
Otoplasty technique
Correction of the ears takes place under general or local anesthesia, depending on the characteristics and scale of the intervention.
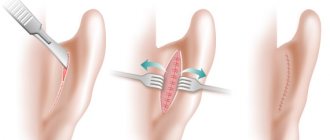
During the operation to eliminate protruding ears using the Mustarde method, an incision is made by the surgeon along the back wall of the auricle, after which the cartilage is remodeled, the cartilage tissue is moved and secured in a new position with sutures. In some cases, excess skin and cartilage are also excised. After such an operation, minimal stitches remain on the ear, which over time become almost invisible.
If the angle between the auricle and the head is very large, otoplasty is performed using the Furnas method, in which the surgeon excises a wide flap of skin behind the ear. After this, the cartilage tissue is sutured to the temporal region - this operation allows you to press the ears to the head.
Ear plastic surgery using the Etenstrom-Stenstrom method is performed through a small incision that the doctor makes on the back surface of the auricle. Then the cartilage tissue is thinned along the anterior surface of the shell and, with access through minimal (2-3 mm) posterior incisions, sutures are applied to the cartilage, with the help of which the desired shape is modeled and fixed.
In some cases, correction of protruding ears is performed using the so-called sutureless method, which is based on the ability of cartilage tissue to bend in the opposite direction relative to the notches made. During this operation, a large surface of the cartilage tissue is freed from the skin, after which the position of the cartilage is modeled by the surgeon using loosening incisions made on the anterior surface. Then the cartilage is rolled up and moved closer to the head at the required distance.
How is ear surgery performed for earlobe defects? When correcting such defects, the doctor chooses the surgical technique based on the complexity of the case. In case of a minor tear, the lobe is simply stitched together; if there are more serious damages, then the atrophied and deformed area is excised. The size of an excessively large lobe is corrected by removing excess tissue through incisions that the surgeon makes on the inside of the lobe.
Plastic surgery after radical ear surgery, when it is necessary to form the external auditory canal, is more complex and refers to a separate type of ear plastic surgery, associated not with aesthetic, but with medical indications, with the restoration of the normal functioning of the hearing organs.
What types exist
The anesthesia used for otoplasty usually includes the same types as for other surgical interventions. The main types are local and general anesthesia, as well as sedation. The first option is anesthesia of the local areas where the intervention is performed. This is convenient if the patient does not need a large amount of work or complex surgery.
In some cases, local anesthesia is used.
The second option is to completely turn off the patient’s consciousness. In this case, drugs can enter the body through a mask or venous catheter. In otoplasty, this type is used quite rarely, only with interventions of great complexity and volume.
Sedation is a milder option that does not imply complete unconsciousness of the patient. Under sedatives, the patient remains conscious, but at the same time is calm and does not experience anxiety or worry. The patient is able to respond to the doctor’s commands, which is convenient for both the surgeon and the patient.
Otoplasty results - before and after photos
Aesthetic ear correction is a fairly popular type of plastic surgery, so on the Internet you can see many photos of examples of ear correction. Such photographs make it possible to verify that today there are practically no aesthetic problems in the ear area that could not be successfully solved.
Our project materials also contain reviews and photos of real people after ear surgery for ear deformation, protruding ears, asymmetry, and lobe defects. Such information is valuable because it allows you to see the possibilities of modern plastic surgery and get acquainted with the work of specific doctors. Visual results of ear correction with reviews can help decide for those who are thinking about surgery, but have not yet made a final decision.
Ears after otoplasty, while acquiring a beautiful appearance, also change the aesthetics of the entire face, making the appearance more harmonious. Feedback from patients about otoplasty will also allow you to learn about such issues as preparation for surgery, medical procedures, the complexity and duration of the rehabilitation period, and impressions of the results of plastic surgery.
In what cases is repeated otoplasty performed?
- Failed otoplasty.
- Complications after surgery.
- Returning ears to their original state.
- Asymmetry (the difference is visible to the naked eye).
- Second stage of otoplasty.
Unsuccessful otoplasty - the patient is not satisfied with the result of the procedure, and there is a desire to turn to a plastic surgeon again. The main reason for revision otoplasty. Problems can arise due to: non-compliance with recommendations, violations of the postoperative regimen, specialist errors, poor-quality material, body reaction, etc.
Rarely, the following complications are possible after otoplasty:
- inflammation of soft tissues and cartilage;
- suppuration;
- keloid scar;
- rough scars.
These negative consequences are an indication for a second surgical intervention. To prevent complications after otoplasty and avoid an unsatisfactory outcome, it is necessary to follow the postoperative regimen.
Rehabilitation period after otoplasty surgery
Rehabilitation after this type of plastic surgery goes quite well and is not long. Immediately after the operation, a special sterile elastic bandage impregnated with antibacterial ointment is applied to the ears, which will need to be worn for several days. The doctor will remove the sutures after otoplasty in about 7 days. Since during surgery, incisions are made on the back surface of the ears, postoperative scars will not be noticeable.
In the postoperative period, when otoplasty is performed, swelling and hematomas in the corrected area disappear after 2-3 weeks. According to reviews from patients who have undergone surgical treatment of protruding ears, correction of the ears or earlobes, the main inconvenience for almost everyone is the need to sleep only on their back. Restrictions after changing the shape, size, position of the ears and/or lobes apply to physical activity, sports, and visiting the bathhouse and solarium is also not recommended.
On the forum, in discussions and reports on otoplasty, you will find first-hand information - directly from the patients themselves - about the features and difficulties of the recovery period after ear correction.
How to avoid complications
The main recommendation is to carefully select a surgeon who specializes in just such operations. This will remove many risks on its own.
The second important point is the patient’s discipline after surgery. You will need to wear a special fixing bandage for two weeks, in which you will eat and even sleep. It is also not recommended to engage in strength sports and generally intense physical training, lift weights, or catch a cold during the recovery period. A weakened immune system can be detrimental to a postoperative wound. And training can even lead to divergence of the seams.
Remember : the doctor can do the most to make you happy with your ears. But it’s worth making some effort for you too!
Plastic surgery on the ears for free in the Omorphia project
If you have appropriate indications and you want to have ear surgery, take part in our project. By becoming a winner, you will receive a unique opportunity - otoplasty will be performed absolutely free of charge.
Any plastic surgery must be performed in specialized clinics by experienced surgeons, and ear correction is no exception. If you have already decided on otoplasty, but are wondering where to have the operation in Moscow or St. Petersburg, then you can safely join our project.
Leading clinics in the capital and St. Petersburg, which employ top-class otoplasty specialists, participate in the Omorphia campaigns.
Preoperative preparation of the patient
In the preoperative period, the patient undergoes blood tests (general, for the presence of syphilis, hepatitis viruses and HIV). If the operation is performed under anesthesia, then an additional biochemical test of blood and urine is taken, an ECG and fluorography are performed. 2 weeks before surgery, it is not advisable to take drugs that affect blood clotting (for example, aspirin, cough suppressants). When performing general anesthesia, it is necessary to spend a day before the operation on a “fasting” day (light food in small quantities), and in the morning before the operation, do not eat or drink anything. The day before surgery, wash your hair.