Causes of complications after mammoplasty
We will discuss the possible unpleasant consequences of surgical breast augmentation and methods for correcting them in the second part of the material, since from a practical point of view it is more important for the patient to know the reasons for which they arise.
There are many reasons; a mistake can be made at the planning stage. When breast augmentation occurs, one of the key issues is the choice of prosthesis. Many women initially decide to install a large implant because they want to increase their bust by two or even three sizes at once. Installing an implant that is too large and does not correspond to the anatomical features of the breast is one of the reasons for unpleasant consequences in the medium and long term.
Not least among the reasons for the development of complications after mammoplasty is the choice of an insufficiently qualified, inexperienced surgeon. Doctor's mistakes at the stage of planning the strategy and tactics of surgical correction, as well as during the implementation of plans during the operation, can lead to the development of not only aesthetic and functional, but also medical problems - suppuration, hematoma, breast edema, seroma formation.
The third group of reasons is neglect of basic recovery rules. Many complications after breast augmentation occur due to the fact that a woman does not wear compression garments, or wears them from time to time, inconsistently. Early expansion of physical activity (strength training, dancing, cardio, yoga) is another source of unpleasant consequences. Thermal treatments, visiting a solarium or relaxing on the beach, swimming in natural or artificial reservoirs in the first one and a half to two months after surgery - all this can also lead to the development of medical or aesthetic problems.
So, in order to prevent complications after mammoplasty or at least significantly minimize the risk of their development, an integrated approach to planning surgical correction is necessary. Prevention measures should include:
1. Rational approach to choosing an implant . Women with thin subcutaneous tissue, small breasts and some other structural features of the chest do not need to strive for the installation of a massive prosthesis. It is very important to listen to the surgeon’s recommendations in this matter.
2. Extremely careful selection of a specialist. Breast modeling can only be entrusted to a doctor with extensive experience, high qualifications and an impeccable reputation. Mammoplasty is a complex operation that requires a certain degree of skill from the surgeon.
3. Attention to all rules of the recovery phase. It is necessary to wear compression garments without removing them for 4 weeks. Intense physical activity is contraindicated, not only strength training, but also yoga, cardio, running, and jumping rope. You can’t even swim in the pool, you can’t sunbathe, you can’t take hot baths or resort to other thermal procedures.
Another recommendation concerns an adequate assessment of the current condition of the mammary glands. For patients with signs of age-related or post-lactation ptosis, installation of a large implant without a bust lift is not recommended. Due to a decrease in skin elasticity and stretching of the ligamentous apparatus, the risk of implant displacement increases with increased manifestations of mastoptosis. It is advisable to carry out a complex correction - installation of a prosthesis simultaneously with mastopexy.
What are “chest deformities”, their types
Deformations of the chest consist of changes in its shape, received at birth or acquired during life. They can have a negative impact on the development and functioning of the chest organs, but this does not always happen. It happens that skeletal deformities do not cause physical discomfort, but affect the symmetry of the mammary glands. It is customary to distinguish the following types of chest deformities:
- Funnel-shaped - characterized by hollowness of the chest;
- Keeled - characterized by protrusion forward;
- Flat - characterized by flattening.
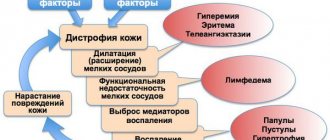
Medical complications after breast augmentation
The category of medical complications after breast augmentation includes seroma, persistent swelling of the mammary gland, bleeding with the formation of a hematoma, suppuration and tissue necrosis.
Seroma . The reason for the development of this complication of mammoplasty is the accumulation of a significant volume of tissue (serous) fluid in the anatomical cavity into which the implant was installed. As seroma develops, the breast enlarges and becomes asymmetrical.
This unpleasant consequence can be treated without surgery. The doctor performs a puncture of the serous cavity and removes the fluid accumulated in it. The exudate is aseptic (without inflammation or infection), antibiotics are not prescribed. Seroma occurs as a result of violation of rehabilitation rules. The main preventive measure is constant compression using medical knitwear.
Edema . The only complication is persistent pronounced swelling that lasts longer than two weeks. Congestion in the early postoperative period is a normal reaction to injury. If swelling does not go away or worsens two weeks after surgery, you should contact a plastic surgeon.
To combat congestion, conservative measures are used - medications with vascular action, physiotherapeutic procedures. The list of reasons for the development of edema includes refusal of compression hosiery, thermal procedures, and early expansion of physical activity.
Hematoma . The cause of hematoma formation can be either accidental mechanical damage to the wound in the early postoperative period or a surgeon’s error. Externally, this is manifested by a characteristic change in skin color and increased pain.
For treatment, it is necessary to inspect the surgical wound: remove blood clots from it, take measures aimed at preventing re-bleeding. An effective measure to prevent hematomas is wearing compression garments and choosing an experienced plastic surgeon.
Suppuration . An infectious-inflammatory process is the result of infection of a surgical wound. Most often, the infection is introduced during surgery, that is, this complication develops due to the fault of the doctor.
Treatment begins with removing the pus and washing the wound with powerful antiseptics. After this, the wound is drained, and the woman is prescribed a course of antibiotics. In the future, it is necessary to visit the clinic for dressing changes and routine examinations by the surgeon until the wound is completely healed.
Introduction
Augmentation mastopexy is often recommended to simultaneously correct ptosis and restore fullness of the upper slope of the breast. It is important for the surgeon to understand how early postoperative results may change over time in order to communicate this to the patient. Without such information, the patient will have unrealistic expectations and may perceive the result as a poorly performed operation.
P. Mallucci and O. Branford [1] studied ideas about ideal breast proportions and found that the optimal ratio of the upper and lower slopes of the breast is 45:55. These are the parameters that the surgeon and the patient want to achieve when performing breast augmentation with mastopexy. Patients with aesthetic hypoplasia and ptosis of the breast want to return the good filling of the upper slope of the breast, as it was before involutional changes. For these purposes, an implant and resection of excess skin are used.
However, it is difficult to maintain early postoperative results for a long time, since breasts with reduced skin turgor are burdened by the implant.
The purpose of the study is to identify the time and magnitude of reptosation of the mammary glands,
Functional complications of mammoplasty
What complications after breast augmentation are classified as functional? This group includes two complications after breast enlargement: impaired sensitivity of the nipples, impaired lactation function.
The reason for the decrease in sensitivity of the nipples and areolas is the dissection of the nerves responsible for tactile innervation. These nerves pass in the inframammary fold, so most often the problem occurs after mammoplasty, in which the implant was installed through an incision under the breast. There is no threat to health, no treatment is required. Sensitivity is restored after 4-6 months.
Lactation dysfunction occurs when the milk ducts are crossed. The risk of injury to the ducts is especially high if the prosthesis was installed through access around the areola. This complication after mammoplasty cannot be treated; damage to the ducts is irreversible.
Women who want to give birth to a child in the future and feed him breast milk are not recommended to have implants through the areola. It is preferable to undergo endoprosthetics through the armpit or inframammary fold.
What implants should I use?
Mammoplasty for chest defects is often performed using German POLYTECH® implants.
They are available in four shapes and projections, which allows you to select their ratio as accurately as possible to eliminate breast asymmetry. POLYTECH® implants have proven themselves with repeated use in the practice of plastic surgeons around the world. They are filled with cohesive silicone gel, which allows them to achieve a natural and soft feel. Thanks to him, they retain their original shape well and quickly restore it after compression. The use of POLYTECH® implants will allow you to achieve a natural appearance of the breast and effectively disguise existing chest defects. You can get more information about them on our website or from a Bute Matrix consultant by phone: +7 (499) 918-77-70! Read more
results
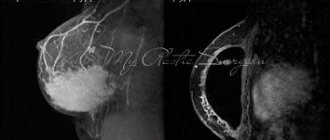
Breasts with ptosis of the 2-4th degree SAH and ptosis of the parenchyma 1-4th degree according to the G. Botti classification were subjected to correction. Basically, a circumvertical approach with excision of excess skin was used.
The result of surgical correction was a natural breast shape with a normal-sized areola. Postoperative patient satisfaction decreased over time. In all cases, breast prolapse was observed.
After surgery, the shape of the breast and its position on the chest undergo transformation. The best aesthetic results were observed within 1-3 months after surgery; in some patients, after just six months, significant breast prolapse occurred (the distance from the nipple to the IMB increased to 1-1.5 cm). After 18 months, none of the women maintained their early postoperative results. Some patients had better and more durable results than others, although the same technique was used, which was associated with the condition and tone of the glandular tissue and the quality of the skin.
Observations showed that not all sizes changed equally. On average, the distance from the jugular notch to the nipple increased, and accordingly the position of the nipple dropped by 1.2 cm, from the midclavicular line to the nipple - by 1.7 cm, from the midline to the nipple - by 1.7 cm. Most of all (up to 2 .2 cm) the distance from the nipple to the IMB increased (size 4). This was due to the fact that, in addition to stretching the skin, the implant stretches the fibers of the IMB, which is the attachment zone and prevents breast prolapse caused by gravity. The lower border of the breast (IMB) is lowered, even if it was not displaced during surgery. The position of the SAC and the proportions of the breast change accordingly.
Even when the surgeon is careful not to destroy the IMB fibers when placing a breast implant, the sulcus tends to droop. This can be observed in most patients if her position is measured [3].
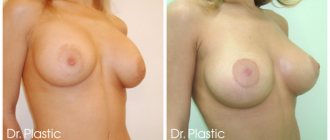
Examples of postoperative results are presented in Fig. 2-4.
Rice. 3. Patient, 28 years old, after mastopexy with installation of a round implant weighing 295 g in a biplane pocket to correct breast hypoplasia and ptosis. a — before surgery, b — after 2 months, c — after 6 months, d — after 12 months, e — 18 months after surgery.
Rice. 4. Patient, 22 years old, after mastopexy with installation of a round implant weighing 295 g in a biplane pocket to correct breast hypoplasia and ptosis. a - before surgery; b — after 2 months, c — after 6 months, d — after 12 months, e — 18 months after surgery.
Rice. 2. Patient, 32 years old, after mastopexy with installation of a round implant weighing 255 g in a biplane pocket to correct breast hypoplasia and ptosis. a — before surgery, b — 2 months later, c — 6 months later, d — 12 months after surgery.
How is the operation performed?
Breast correction after unsuccessful operations is carried out strictly on an empty stomach, under general anesthesia. It takes from 1 to 3 hours, depending on the complexity of the procedure. For anesthesia, safe drugs are used that do not cause complications, are easily tolerated by the body and allow you to quickly recover.
The correction method and surgical technique are selected individually. Unsuccessful operations for breast augmentation or for mastitis and tumor removal are often accompanied not only by changes in the shape, density and size of the mammary glands, but also by unaesthetic, rough scars. To eliminate such defects, both plastic and reconstructive surgeries are required.
If necessary, the doctor will perform a breast augmentation by installing implants and a lift by removing excess skin and eliminating sagging breasts. As a rule, one operation is sufficient to achieve the desired aesthetic result. But if necessary, the doctor will perform additional corrective plastic surgery.