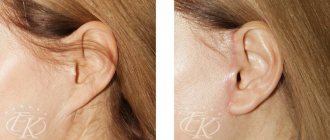
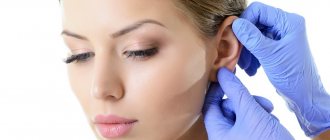
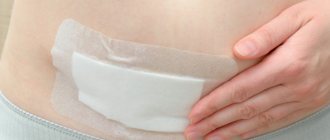
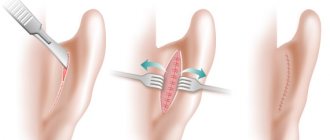
Rehabilitation after otoplasty
As with many other plastic surgeries, the outcome of otoplasty depends only partly on the work and skill of the plastic surgeon. 50% of the responsibility rests with the patient: much will depend on how exactly the rehabilitation period goes and whether the doctor’s recommendations will be strictly followed, or the patient will treat their implementation “carelessly.” The rehabilitation period can be divided into early and late.
Early rehabilitation period after otoplasty
The early postoperative period lasts 7-10 days, during which the risk of postoperative complications is highest. That is why it is very important that all doctor’s prescriptions during this period are followed very precisely!
During the first time after otoplasty, swelling, pain and bruising are normal. This is not surprising, since the operation affects not only the skin, but also cartilage and soft tissue. Alas, it is not yet possible to completely neutralize the unpleasant consequences of the operation, however, the doctor must prescribe painkillers, and in some cases, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics and decongestants, both locally and for oral administration. Remember that your doctor will not prescribe you any drug if it is not necessary , so please do not cancel your doctor's prescription yourself - this can lead to serious consequences. Moreover, not only for your appearance, but also for your health!
In most cases, most of the bruising and swelling will subside by the end of the second week after surgery. The postoperative suture is made on the outside of the auricle, behind the ear, making it virtually invisible to others.
Bandage after otoplasty
For the first time after surgery, it is necessary to wear a compression bandage, which will help fix the ears in the desired position. It is thanks to the bandage that the new shape of the ears is fixed, so you should wear a fixing bandage until complete healing. In addition, it will protect the ears after plastic surgery from the touch of hair or foreign objects, which can be painful in the first time after surgery. A compression bandage is not necessarily a special device: it can be a regular bandage made of a sterile or elastic bandage. But special compression bandages also exist: you can purchase such a bandage after consulting with your plastic surgeon. Depending on the recovery period, which varies from person to person, the bandage will need to be worn for about 30 days and should only be removed once your surgeon has given permission to do so.
Dressings
Ears after otoplasty need at least 2 dressings: the first is done during the first day after surgery, the second - on the 7th day. Also, on the 7th day, the sutures are usually removed, unless self-absorbable threads were used during the operation.
the washing up
This is one of the most unpleasant consequences of the operation, but, alas, this is a necessary condition: after otoplasty, you should not wash your hair for 7-10 days so as not to wet the bandage. You can wash your hair only after a certain time has passed and only in consultation with your doctor. During this period, you can use dry shampoos and other products to maintain the proper appearance of your hair.
Late rehabilitation period after otoplasty
It is calculated after the compression bandage is removed, and includes mainly abstaining from heavy physical activity and creating the most favorable conditions for a speedy recovery after surgery. In particular, during the postoperative period it is better to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Refrain from visiting baths, saunas, solariums and other places where the air temperature is too high
- Do not abuse alcohol and tobacco
- Refrain from strenuous exercise and sports, as excessive physical activity can cause sutures to separate and tissue to shift.
- You can do a light warm-up, from which bending, squatting, jumping and running should be excluded. Moderate cardio exercise is allowed
- Contact sports should be postponed until a later period and returned to them no earlier than 2 months after surgery.
The final result of otoplasty can be assessed 4-6 months after surgery.
Otoplasty, price:
- Otoplasty (ear plastic surgery) - 120,000 rub.
- Consultation - 1,000 rub.
- The cost of anesthesia is determined on the day of consultation and depends on the volume of the operation.
If you still have questions, you can ask them in the “question-answer” section.
You can make an appointment for a consultation with plastic surgeon A.P. Panayetov in Moscow by phone (viber, whatsapp) or through the feedback form on the website:
When is it filmed?
The exact period after which the stitches are removed is 10-14 days. At the same time as the threads, the fixing bandage is also removed and the dressing is done again. From now on, the patient can wear the bandage during nighttime sleep, rather than wearing it on an ongoing basis.
But the withdrawal period may vary, since the recovery rate is different for all patients. If threads that can dissolve on their own were used, there is no need to worry about removal. In this case, a visit to the surgeon will only be necessary for a second examination.
After otoplasty, the seams, or more precisely, the scars at the incision sites, are almost invisible. At first, traces of the intervention will be visible, but in the process of tissue restoration, the visibility will gradually disappear.
General Tips
How the suture heals after otoplasty and what kind of scar remains after it is also influenced by the patient’s general attitude towards the recommendations for recovery. Firstly, this concerns sports and physical activity. These things need to be excluded from life during the recovery period. After rehabilitation is completed, you will be able to return to your normal lifestyle.
Cigarettes, salty and spicy foods, and any thermal procedures such as a hot bath, sauna, steam room or steam room also negatively affect the healing rate. At first, it is not advisable to sleep in a position other than on your back. It is advisable to limit exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the operated areas.
It is worth noting that all restrictions are temporary and not lifelong. Therefore, there is no need to worry that the operation will somehow affect your usual everyday comfort. The main thing is to carefully follow all recommendations and observe prohibitions.
Types of tympanoplasty
Myringoplasty
– restoration of the integrity of the eardrum. This type of tympanoplasty is indicated for patients who have preserved and mobile all the auditory ossicles in the tympanic cavity; they only need to close the perforation of the eardrum. The material for myringoplasty is an autograft - a flap of skin with underlying layers is taken from behind the patient’s ear. Own tissues take root well and are not rejected by the body, which is their huge advantage as opposed to foreign materials.
Tympanoplasty with ossiculoplasty
– reconstruction of not only the eardrum, but also the destroyed auditory ossicles.
In chronic purulent otitis media, the auditory ossicles (there are three of them - the malleus, the incus and the stapes, their connections to each other resemble a microscopic joint) can be damaged due to a constant inflammatory process. Without them, it is impossible to conduct sound to the perceptive nerve endings of the inner ear. Therefore, the missing elements of these ossicles are replaced by artificial prosthetic hearing ossicles made from Tiflon, bioceramics and other synthetic materials. Our clinic uses modern titanium prostheses. If the chain of auditory ossicles has minimal destruction, then it is possible to do without artificial materials - the preserved elements are somewhat rebuilt, while maintaining their mobility. The final stage of surgery is myringoplasty
.
In the case of fusion of the two surfaces of the middle ear after complications with otitis, it is possible to restore the tympanic cavity using the remnants of the eardrum and grafts connecting the tissues to each other.
All types of tympanoplasty are performed using a modern microscope for otosurgery.
Possible complications
After otoplasty, as after any other plastic surgery, complications cannot be ruled out. Most complications are the result of the patient's negligence in caring for the operated areas during the rehabilitation period. Complications include:
- asymmetry,
- severe pain,
- high body temperature,
- suppuration and more.
In these situations, you cannot treat yourself. You should definitely consult your surgeon first.
If unusual symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor.
It is important to understand that bruising, swelling and minor pain are not considered complications. These are natural companions to almost any surgical intervention. You can worry if the severity of these effects either does not decrease over a long period of time or increases.
Preparing for surgery
During the period of preparation for surgery, conservative treatment is carried out. Vasoconstrictor, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents are injected into the middle ear cavity. These procedures are necessary for sanitation (cleaning) of infection - the postoperative wound will heal faster and the risk of inflammation after surgery is significantly reduced. At the same time, the patency of the auditory tube improves, which is also very important for a good postoperative result.
As before any other operation, the patient must be fully examined. The examination includes: general and biochemical blood test, urine test, coaguloramma, blood test for infections (hepatitis B and C, syphilis, HIV), ECG.
A week before surgery, the patient is contraindicated to take blood thinners such as Warfarin, as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin or paracetamol.
In case of chronic diseases, during preparation the patient will need to consult with a specialized specialist. 6 hours before surgery, the patient is strictly forbidden to eat, drink water, or chew chewing gum.
Indications and contraindications
Surgical intervention is necessary in the following cases:
- central or marginal perforation of the eardrum, that is, there is damage to it, which leads to displacement of the auditory ossicles;
- perforation of the eardrum without significant inflammation of the middle ear;
- fibrosis of the middle ear;
- tympanosclerosis;
- middle ear polyps;
- chronic inflammation of the middle ear with severe suppuration.
An absolute contraindication to surgery is:
- severe general condition;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- purulent complications and sepsis;
- complete deafness;
- adhesive otitis media;
- persistent disturbances in the patency of the auditory tube - these can be either congenital anomalies or the formation of adhesions and scars as a result of inflammation.
Relative contraindications:
- epidermization of the tympanic cavity - absolute replacement of the mucous membrane of the tympanic cavity by the epithelium of the external auditory canal;
- functional (temporary) obstruction of the auditory tube;
- upper respiratory tract diseases;
- allergic diseases in the acute stage;
- acute inflammatory process in the middle ear.
The doctor assesses the required volume of surgical interventions and always informs the patient about possible risks.