Gynecomastia is a disease associated with breast growth in men. It affects 30-50% of males.
The enlargement process occurs due to the accumulation of adipose tissue or the presence of gland hypertrophy. The size of enlarged male breasts can range from one to ten cm, the average is 4 cm.
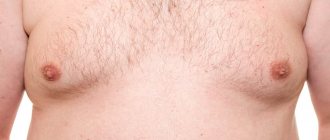
This aesthetic defect can be noticed both externally, when small, effeminate breasts are visually visible, and can be determined by touch. When palpated, a dense elastic formation is detected, which is mobile and has a clear contour.
Gynecomastia is not dangerous to a man’s health, but it causes complexes and psychological discomfort.
What types of male breasts are there?
Treatment and removal of gynecomastia in men depends on many factors. First, you need to determine what type of education.
- True gynecomastia. Breast growth is ensured by development directly due to the increase in glandular tissue. In this case, a seal forms under the nipple, which does not cause pain when palpated. To confirm, it will be necessary to do an ultrasound. If the diagnosis is confirmed, gynecomastia in men will be removed by removing the gland.
- Lipomastia. Breast enlargement is caused by the growth of adipose tissue. Most often, this type is typical for people who are overweight. Removal of gynecomastia in men in this case can be performed using liposuction.
- Mixed. A combination of the first two types: a combination of an enlarged gland and the presence of fatty deposits. Removal of gynecomastia in men occurs by combining liposuction and excision of the gland.
Both bilateral enlargement is observed, when both glands grow evenly, and unilateral, when only one breast can be enlarged.
How does the disease progress (degree of development)?
To determine which removal of gynecomastia in men will be optimal, it is necessary to understand the stage of development of the disease.
- Developing stage. The gland is just beginning to form. This period usually lasts for 4 months. Gynecomastia at this stage responds well to conservative treatment.
- Intermediate stage. The approximate period is from 4 months to 1 year from the beginning of development. The chances of returning to its previous size are quite small. Most often, at this stage, removal of gynecomastia in men is performed surgically.
- Fibrous stage. At this stage, there is fully formed connective tissue, which, most often, begins to become overgrown with fatty compounds. Removal of gynecomastia is performed exclusively through surgery.
What is a men's bra
The men's bra was created by the developers of the Kahei Oyasumi Bra company from Japan. Specialists from the Land of the Rising Sun regularly present their new inventions, but not all of them are popular. The first bra for men could be bought in 2014 in the Wishroom online store, and the first batch of goods immediately sold out. Such demand was a surprise even for the creators of men's underwear themselves.
It is likely that in the future the bra will become an exclusively male item of clothing. Numerous studies have shown that women who wear a bra are more likely to develop breast cancer.
The men's bra is designed to reduce the effect of gravity on the male chest
Why do men grow breasts?
The causes of this disease may be hormonal problems.
- Physiological. A boy is either already born with this disease, or it appears during puberty, when hormonal disruptions occur. Gynecomastia can appear in old age, when hormonal changes occur.
- Pathological. The reason for breast enlargement is associated with disturbances in the functioning of the body. This may be a consequence of a number of diseases, for example, mumps, castration, testicular injury, kidney disease, liver disease, lung tumor, stomach tumor, etc.
- Idiopathic. This type includes cases where it is difficult to identify the exact cause of the disease.
Anomalies and pathologies
Unilateral gynecomastia
There are several cases when enlarged mammary glands in a man are considered normal:
- during the first two weeks after birth;
- during puberty (the duration of the phenomenon should not exceed two years, otherwise there is a reason to consult a doctor);
- in old age, when the level of androgens in the blood naturally decreases in the human body.
In all other cases, an increase in size and pain in the mammary glands is a deviation from the norm, which indicates a hormonal imbalance. To identify pathology, the first thing you need to do is visit an endocrinologist.
In most cases, after laboratory and instrumental examination, a diagnosis of gynecomastia (enlargement of the mammary glands in men) is made. The main provoking factors for the development of the pathological condition:
- metabolic disorder;
- developmental pathologies or liver diseases, such as cirrhosis;
- long-term use of a certain number of medications, for example, vincristine, Relanium, antidepressants, methyldopa, estrogens;
- developmental pathologies or kidney disease;
- recovery period after exhaustion.
Metabolic disorders most often provoke the development of the disease. The impetus for the manifestation of discomfort can be inflammation of the testicles, the development of benign or malignant neoplasms in them, against the background of which the production of androgens decreases.
Manifestation of gynecomastia
With diffuse disorders, the mammary glands of the stronger sex are uniformly affected, while the ducts are blocked, which causes the formation of cysts. Seals are predominantly localized behind the nipple or in the areola area on both sides.
During self-examination, palpation reveals a compaction with unclear contours and a granular structure. As a rule, the tumor moves easily. The skin, nipples and areolas do not undergo any visible changes. However, aggressive behavior of the disease is extremely rarely observed, characterized by retraction, deformation of the nipple, and discharge with bloody patches.
A characteristic feature of the development of the nodular form of gynecomastia is the formation of a dense node, which is predominantly located on one side and does not cause discomfort or pain. In this case, the nipple is deformed extremely rarely, and discharge from them is also observed infrequently. The neoplasm requires a thorough examination to exclude the possibility of degeneration into a malignant tumor. Before drawing up a therapeutic course, a puncture of the node is performed and its contents are collected.
In most cases, the problem can be solved conservatively; removal of the mammary gland in men is most often required to get rid of a cosmetic defect.
In newborns, the disease goes away on its own without outside intervention. When pathology develops during puberty, drug therapy, as a rule, is also not prescribed. The teenager should be seen by a doctor. In the absence of positive dynamics within 6-8 months, hormonal correction is indicated.
Medications are prescribed, for example, Tamoxifen, Dihydrotestosterone, Testolactone, Clomiphene and Danazol.
In parallel with drug therapy, it is recommended to regularly visit a psychologist, since due to cosmetic defects, adolescents often develop neuroses and other psychological abnormalities.
Breast cancer
Gynecomastia, with a number of negative influences, can become a background for the development of oncology. According to statistics, men with gynecomastia are 5 times more likely to develop breast cancer. The reasons for the degeneration of tissues into malignant ones can be exposure to carcinogenic substances, as well as prolonged and regular stay in an environment with high temperatures, and irradiation of the chest.
Most often, the disease is diagnosed in men after 60 years of age, but in recent years the disease has become younger and is increasingly developing in younger men.
Clinical picture:
- formation of one or multiple nodules;
- as the disease progresses, ulcers may form on the skin;
- the neoplasm is predominantly localized under the nipple or near the areola;
- enlargement and pain of the lymph nodes located in the armpits;
- nipple discharge.
Mastectomy
If cancer was diagnosed during the examination, depending on the form of the disease, stage of development and well-being of the patient, the following treatment methods may be offered:
- hormone therapy;
- irradiation;
- chemotherapy courses;
- breast removal in men.
To increase the chances of a full recovery with minimal chance of complications, you need to start cancer treatment as early as possible.
Male breast enlargement due to medication
Gynecomastia can be a side effect of taking a number of medications. Among them:
- Anabolic steroids are drugs that imitate the action of the male sex hormone, testosterone. They are used by bodybuilders to build muscle mass;
- hormonal drugs;
- medications for high stomach acidity
- some diuretics;
- drugs for heart treatment;
- lavender oil and tea tree oil.
Pathological gynecomastia can be caused by alcohol and drug abuse.
The female face of the male problem
Murzaeva Irina Yurievna
Endocrinologist, Preventive Medicine Doctor
April 6, 2014
The unusual title of this entry hides a fairly well-known problem - changes in the mammary gland in men, making it similar in shape to a woman's breast. Sometimes this is accompanied by pain, unilateral changes in the mammary gland, discharge from the gland, and focal compaction.
If the change in shape is associated with the appearance of adipose tissue (and an ultrasound examination can show this), this is called “lipomastia” , and is mainly associated with excess weight gain.
And if this is the appearance of glandular tissue (which is absolutely not typical for men, only for women!) - this is already a hormonal problem that requires careful diagnosis, the name of this condition is “gynecomastia” .
Lipomastia and gynecomastia can occur at any age.
There are many reasons for hormonal gynecomastia:
- various forms of hypogonadism (lack of male sex hormones), acquired and congenital (Klinefelter syndrome);
- prolactinoma (benign tumor of the pituitary gland that produces the hormone prolactin);
- testicular tumors (leydigoma, sertolioma, tumors producing estrogen and hCG);
- partial androgen insensitivity syndrome;
- 5-alpha reductase deficiency syndrome (partial);
- syndrome of excessive aromatase activity (an enzyme that converts testosterone into estrogens (female hormones);
- diseases of the liver, kidneys, MEN-1, taking drugs, and these are more than 20 types of drugs (anabolic steroids - first of all).
During the course of gynecomastia, several phases are distinguished, which will determine further treatment tactics.
Developing (proliferating) gynecomastia.
This is the initial stage of the disease, which lasts about 4 months. This stage is reversible, that is, with appropriate therapy, the enlarged mammary gland can return to its previous size.
Intermediate stage of gynecomastia.
Lasts from 4 months to a year. During this period, maturation of breast tissue occurs. This stage is rarely reversible.
Fibrous stage of gynecomastia.
It is characterized by the appearance of mature connective tissue in the mammary gland and the deposition of adipose tissue around the glandular tissue. At this stage, the mammary gland never undergoes reverse development.
It is quite rare, but it happens that the cause of changes in the mammary gland in a man is cancer! mammary gland (usually ductal carcinoma). It is very aggressive (growth over 19 months), so it is so important to diagnose it on time.
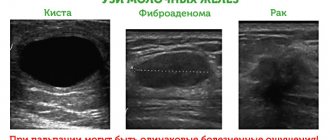
Diagnosis of gynecomastia is complex:
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands
- mammography
- biopsy of abnormal tissue
- Ultrasound of the scrotum
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs
- blood test for hormones - TSH, T4 free, prolactin, hCG, estradiol, total testosterone, GSPS, LH, FSH, 17-OH-progesterone, dihydrotestosterone, total PSA, alpha-fetoprotein
- blood tests for liver biochemistry - ALT, AST, bilirubin, creatinine and some other parameters, depending on the suspected cause of gynecomastia.
Treatment depends on the diagnosis. For lipomastia, a set of measures aimed at losing weight, and if they are ineffective, surgical removal of “excess” tissue.
For gynecomastia:
Firstly, treatment of the underlying pathology that caused the development of gynecomastia. If this is gynecomastia that has developed within a year, at stage 1-2 of the process treatment is medicinal (there is a small choice - according to the drug regimen Tamoxifen / or Danazol).
After 1 year of the process, at stage 3 of gynecomastia, if drug therapy is ineffective, surgery is indicated. Our clinic provides surgical treatment for gynecomastia at the Outpatient Surgery Center.
For cancer, further surgical treatment depends on the stage of the disease.
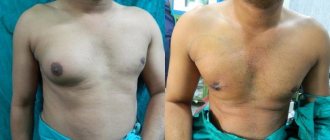
How to remove male breasts (treatment process)?
In cases where breast enlargement occurs by 4 cm or more, incomplete regression is possible. Then surgical removal is performed. The technique is selected based on the type of gynecomastia.
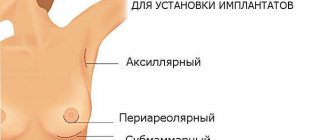
Surgery for pseudogynecomastia
If the reason for the growth of male breasts is adipose tissue, then, in most cases, liposuction is performed. The clinic performs modern vacuum liposuction through micro-punctures. There are no cuts or seams on the chest.
Surgery for true gynecomastia
If the glandular tissue is too rough and dense, then the hypertrophied mammary gland is removed. The plastic surgeon makes an incision along the lower edge of the areola, removes excess glandular tissue and, if necessary, fatty tissue, and then applies a cosmetic suture to the wound. The surgery is similar to breast reduction surgery, which is often performed on girls.
Surgery for mixed forms
For mixed forms of gynecomastia, the operation is performed by combining 2 techniques.
The choice of technique for performing an operation is always individual and is determined by a plastic surgeon during a consultation.
The structure of the male breast
The structure of the male breast
The mammary gland in men is formed during the period of intrauterine development. There are practically no differences in the anatomical structure of the mammary glands in boys and girls before the onset of puberty (puberty). Puberty in girls is characterized by active growth of glandular tissue under the influence of the genital organs - prolactin, gestagen and estrogen. The organ changes its structure, shape and size. In young men, the breasts undergo virtually no changes during this period.
An adult male has a relatively small areola and a nipple with a height of 2 to 4 mm. The mammary glands are located in the interval between the fourth and fifth ribs on both sides relative to the midline. The soft tissues of the rudimentary organ are white. The passages and lobules are poorly developed and short. Normally, the thickness of the gland does not exceed 5 cm, and the width is 15 cm.
The histological structure includes two sections:
- interstitial section, which consists of connective tissue;
- secretory section, includes epithelial ducts.
The condition and quantity of glandular tissue is influenced by a whole list of hormones - somatotropin, gonadotropin, estrogen, prolactin and androgens.
Is it possible to do without surgery (conservative method)?
Physiological gynecomastia, which often manifests itself in newborns, and gynecomastia during puberty do not require special treatment.
A conservative method of treating gynecomastia, to some extent, can alleviate symptoms and adjust hormonal levels. In this case, an integrated approach of specialists is required: an endocrinologist, a therapist, a cardiologist. They develop an individual treatment plan. If a conservative treatment method does not produce results within 6 months, then it is better to contact a plastic surgeon for plastic surgery.
What should you consider after surgery?
Liposuction for gynecomastia is performed under local anesthesia. The sensations can be compared to anesthesia in the dentist's chair - the patient is conscious, but does not feel pain. This operation is performed on an outpatient basis - the patient spends several hours in the clinic under observation, and then goes home. Intravenous anesthesia may also be used.
Rehabilitation after surgery takes 2 weeks. An important step is wearing a compression bandage. This is important to reduce the risk of swelling and stabilize the result.
The patient will be able to evaluate the final result 1 month after the operation.