Description and reasons
Women are used to being upset if they have small breasts, but there are cases when large breasts can weigh several kilograms, which causes considerable difficulties.
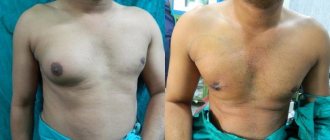
Hypermastia in women occurs mainly in adolescence and after 30 years. Gynecomastia occurs in a rare form in men. It manifests itself as an increase in glands and adipose tissue, which is why the breasts become similar to those of a woman. The pathology is caused by a violation of the ratio of the hormone testosterone or disease of the adrenal glands. Requires immediate medical attention and treatment.
Macromastia is associated with a sharp increase in fat and connective tissue over a period of 6-8 months. Reasons for the development of pathology:
- hormonal imbalances during puberty, during pregnancy and lactation;
- endocrine diseases leading to metabolic failures;
- overweight;
- injuries and previous surgeries.
Hypermastia causes not only physical, but also psychological inconvenience. Heaviness and pressure on the chest are felt, posture is disturbed, and scoliosis forms. Characteristic symptoms: shortness of breath, stretch marks and irritation in the skin folds.
To understand how to reduce large breasts and relieve discomfort, you need to consult a doctor. He will conduct a diagnosis and prescribe a correction. For the puberty period, therapy with a course of hormones is possible. For other situations, surgical correction of large breasts is effective.
How to solve a problem
Gigantomastia is a congenital genetic pathology in which the mammary glands lose their shape and grow to incredible sizes. The process can start at any age, due to any imbalance in the body.
Types of gigantomastia
| Puberty | Glandular tissue grows during puberty |
| Postpartum | Adipose tissue increases due to a malfunction in lipid metabolism. Additional complications may arise due to uncontrolled weight gain. |
| Double sided | Bilateral gigantomastia is expressed on both mammary glands |
| One-sided | The manifestation is noticeable only on one side |
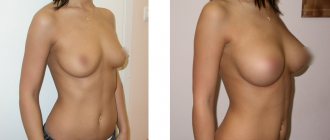
The only way to eliminate the problem is reduction mammoplasty (breast reduction). With the help of plastic surgery, women can experience physical relief and psychological balance for the first time.
Additional problems with gigantomastia in women
Chest pain gradually intensifies, causing pain in the neck, back and shoulders- If medical recommendations are not followed, mastitis and mastopathy develop
- Feeling of chest tightness
- The appearance of skin stretch marks
- Disorders of the menstrual cycle
- Constant tension of the glands themselves
- Pathological discharge from the nipples
Contraindications for surgery
- Acute and chronic infectious diseases in the stage of decompensation
- Minor age
- Heart defects
- HIV AIDS
Important. Gigantomastia in girls can develop at a rapid pace, but even with the written consent of the parents, the operation is prohibited; it is necessary to wait until adulthood.
Indications for surgical intervention
Breast macromastia causes a lot of inconvenience: it is impossible to play sports, sleep on the stomach, it is difficult to cover long distances, choose clothes, and regular pain is a concern due to the load on the spine. The main indication for reduction mammoplasty is physiological and psycho-emotional discomfort. A huge bust not only disrupts your comfortable lifestyle, it also affects how you perceive and accept yourself. May lead to depression and poor health.
There are a number of reasons why plastic surgery cannot be performed:
- oncological and other pathological diseases;
- period of pregnancy and lactation;
- skin diseases and other abnormalities in the breast area;
- poor blood clotting.
An experienced doctor will diagnose, determine the risks and tell you what to do if your breasts are too large.
Symptoms and diagnosis of macromastia
All nations consider female breasts to be a symbol of sexuality and attractiveness, but ideas about ideal breasts vary significantly. Europeans consider “normal” breasts of size “C”, although a larger volume of mammary glands does not give grounds to talk about macromastia; rather, it indicates the peculiarities of the constitution of a particular woman. Macromastia is a serious pathology that involves not just enlargement, but intensive growth of the mammary glands (usually both), which within a few months (usually up to a year) reach gigantic sizes . The glands enlarge so quickly that the skin does not have time to stretch and stretch marks form on them, and in some cases the skin even bursts: bleeding occurs, and sometimes trophic necrosis develops, especially if the wound gets infected.
Symptoms of macromastia:
- sharp enlargement of the mammary glands;
- pain in the chest and back;
- nipple discharge;
- weeping ulcers on the skin;
- menstrual irregularities;
- miscarriages;
- posture disorders;
- fast fatiguability.
Attention! In macromastia, the mammary glands are saccular or pear-shaped, hang below the navel, and are usually hot to the touch. The nipples and areolas look unusual - they are stretched and smoothed out so much that they are difficult to distinguish. The skin of the mammary glands is dense and stretched, veins are often visible through it; In the areola area, the skin resembles a lemon peel.
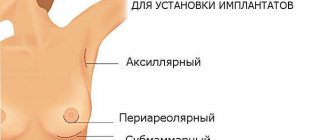
Reduction mammoplasty
Macromastia is treated surgically. During the operation, excess glandular and fatty layers are removed, reducing the volume to an acceptable size. They also slightly correct the shape of the breast and tighten stretched skin. Reduction mammoplasty is performed under general anesthesia and takes from 1.5 to 4 hours. The rehabilitation period lasts up to six months, during which time you should strictly adhere to the doctor’s recommendations:
- reduce physical activity;
- Healthy food;
- wear compression garments;
- do not overcool and do not overheat.
Surgical treatment of macromastia
Macromastia is a pathology that is difficult to treat, since the process must be monitored by several specialists, including a gynecologist, mammologist, endocrinologist and oncologist. In most cases, the surgeon has the final say.
Unfortunately, the most effective method of treatment, especially in cases of aggressive macromastia, remains mastectomy (removal) of the mammary glands - an operation that patients agreed to with great reluctance just a few years ago . Today the situation has changed - the possibility of breast prosthetics has become possible during resection or after some time . Modern techniques make it possible to restore breast volume, and the woman retains her external attractiveness and positive attitude.
According to indications, reduction mammoplasty is used - an operation aimed not at complete removal, but at reducing the volume of the mammary gland . Such an operation involves taking antiestrogens, and in most cases, without drug support, surgical intervention does not make sense. Experience shows that reduction mammoplasty does not eliminate macromastia forever; the pathology can develop again when hormonal levels change.
Drug treatment of macromastia
It is impossible to completely recover from the proliferation of mammary gland tissue with the help of medications; it is possible to only slightly restrain the process. For such purposes, the drugs Norethindrone and Parlodel are used , however, after stopping the use, the breasts begin to grow again - only surgical intervention will stop the process.
According to experts, for macromastia, taking the synthetic anti-estrogen Tamoxifen is indicated, which suppresses estrogens in the mammary glands. In most cases, experts recommend taking this drug for three months after surgery to prevent relapse of the disease. Tamoxifen can be used in the early stages of macromastia to restore the reproductive system, as well as eliminate the woman’s gynecological diseases and problems with the thyroid gland.
All questions and answers for the tag #gigantomastia in breast reduction surgery
General provisions
1.1 The site administrator (hereinafter referred to as the Operator) makes respect for the rights and freedoms of citizens one of the most important conditions for carrying out its activities.
1.2 The Operator’s policy regarding the processing of personal data (hereinafter referred to as the Policy) applies to all information that the Operator can obtain about visitors to the dr-vedrov.ru website. Personal data is processed in accordance with the Federal Law “On Personal Data” No. 152-FZ.
Basic concepts used in the Policy:
2.1 Website - a collection of graphic and information materials, as well as computer programs and databases that ensure their availability on the Internet at the network address dr-vedrov.ru;
2.2 User – any visitor to the dr-vedrov.ru website;
2.3 Personal data – any information relating to the User of the dr-vedrov.ru website;
2.4 Processing of personal data - any action with personal data performed using a computer, as well as without their use;
2.5 Depersonalization of personal data – actions that result in the impossibility of determining the ownership of personal data to a specific User or person without the use of additional information;
2.6 Distribution of personal data – any actions that result in the disclosure of personal data to an indefinite number of persons;
2.7 Providing personal data – any actions that result in the disclosure of personal data to a certain circle of persons;
2.8 Destruction of personal data – any actions that result in the irreversible destruction of personal data on a computer or any other media.
The operator may process the following personal data:
3.1 User's email address
3.2 User's phone number
3.3. Last name, first name, patronymic of the User
3.4. The site also collects and processes anonymized data about visitors (including cookies) using Internet statistics services (Yandex Metrica and Google Analytics and others).
Purposes of processing personal data
4.1 The purpose of processing the User’s email address, phone number, last name, first name, patronymic is to clarify the details of the service. The Operator also has the right to send notifications to the User about new products and services, special offers and various events. The User can always refuse to receive information messages by sending a letter to the Operator to the address [email protected]
4.2 Anonymized data of Users, collected using Internet statistics services, is used to collect information about the actions of Users on the site, improve the quality of the site and its content.
Legal grounds for processing personal data
5.1 The Operator processes the User’s personal data only if it is sent by the User through the forms located on the dr-vedrov.ru website. By sending his personal data to the Operator, the User expresses his consent to this Policy.
5.2 The Operator processes anonymized data about the User if this is allowed in the User’s browser settings (saving cookies and using JavaScript technology are enabled).
The procedure for collecting, storing, transferring and other types of processing of personal data
6.1 The Operator ensures the safety of personal data and takes all possible measures to prevent access to personal data by unauthorized persons.
6.2 The User’s personal data will never, under any circumstances, be transferred to third parties, except in cases related to the implementation of current legislation.
6.3. If inaccuracies in personal data are identified, the User can update them by sending a notification to the Operator via email to the Operator's email address, marked “Updating personal data”
6.3 The period for processing personal data is unlimited. The User may at any time withdraw his consent to the processing of personal data by sending a notification to the Operator via email to the Operator's email address [email protected] , marked “Withdrawal of consent to the processing of personal data.”
Final provisions
7.1. The user can receive any clarification on issues of interest regarding the processing of his personal data by contacting the Operator via email [email protected]
7.2. This document will reflect any changes to the Operator’s personal data processing policy. In case of significant changes, the User may be sent information to the email address specified by him.
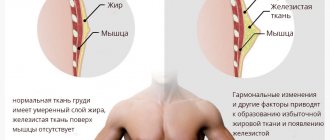
Factors affecting breast development
Active breast growth occurs at 13-15 years of age, and it acquires adult shape only at 16-17 years of age. The final size of the mammary glands in women is determined only after the lactation period. Breast development depends on many factors. First of all, the size and shape of the breast depend on genetic factors. The second thing that influences breast formation is hormones.
Estrogen is the main hormone that influences breast growth, although this does not mean that increasing its levels in the body will result in larger breasts. It plays an important role in the formation of ducts and connective fibers. When there is an excess amount of estrogen in the body, a protective function is activated, which consists of closing the receptor sites responsible for the appearance of new cells. As a result, breast growth stops.
Xenoestrogens, organohalogens that are structurally similar to estrogens, have a negative effect on the breast. They are in the external environment due to industrial activities. When they enter the body, they destroy the connections necessary for the normal functioning of the endocrine system.
Side hormones found in meat and entering the body through the gastrointestinal tract also have a similar effect. The body of all animals contains estrogen and testosterone, which, when consumed in excess, inhibit the formation of mammary glands.
Prolactin, a hormone produced by the pituitary gland, has a positive effect on breast formation. This hormone increases the number of estrogen-sensitive receptors in the mammary gland and accelerates breast growth. Its level increases greatly during puberty and pregnancy.
Testosterone greatly inhibits breast growth. When you eat a lot of foods high in sugar, the body begins to produce insulin to lower glucose levels, which leads to an increase in testosterone levels in the blood. With a large amount of insulin, DHT is formed - this is testosterone in a more active form, which has a much greater effect on the receptors. With excess DHT, growth arrest and even breast atrophy can occur.
Beautiful breasts grow only with normal hormonal levels.
Breast growth is also influenced by the monthly cycle. The formation of the mammary glands ends 1-2 years after the menstrual cycle has stabilized.
In addition, the amount of fatty tissue in the body affects breast size. When gaining 1 kg of fat, the mammary glands increase by 20 g.
Description of a clinical case
Patient F., 43 years old, was admitted to the Federal State Budgetary Institution “National Medical Research Center of Endocrinology” in January 2022 with complaints of actively progressive enlargement of the mammary glands, pain in the thoracic and lumbar spine, limitation of physical activity (shortness of breath when walking).
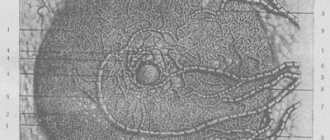
It is known from the medical history that 2 years ago, as part of preimplantation preparation for in vitro fertilization (IVF), the patient received therapy with estradiol (Divigel). In the first two months of taking the drug, there was a pronounced increase and thickening of the breasts, after which the drug was discontinued. To avoid further progression of mammary hyperplasia, total mastectomy was strongly recommended. In the winter of 2022, reduction mammoplasty was performed leaving a minimal amount of glandular tissue, mastopexy with transfer of the nipple-areolar complex, and implantation of silicone prostheses (500 ml). Postoperative mammography data of the breast are shown in Fig. 1. In September 2022, during the IVF protocol, an embryo was transferred into the uterine cavity. Starting from the 5th week of pregnancy, rapid enlargement of the mammary glands and redness of the skin in the para-areolar zone were recorded. In November, when I visited a surgeon, my breast size increased from 3 to 20. Data from hormonal blood tests dated December 2, 2022, at the time of gestation 12 weeks, are shown in the table.
Rice. 1. Mammography in 2022 after subtotal reduction plastic surgery with prosthetics.
Table. Hormonal blood test, 12th week of gestation
| Parameter | Result | Norm at 12 weeks |
| Prolactin | 361 mIU/l | 189–4011 mIU/l |
| Estradiol | 9880 pmol/l | 2280–3120 pmol/l |
| Progesterone | 75.39 nmol/l | 92.1–110 nmol/l |
Since mid-December, the patient noted a sharp deterioration in her condition: there were complaints of pain, increased body temperature, and ulceration of the lower parts of the chest. Drug treatment with tamoxifen, danazol, medroxyprogesterone was not considered due to the unsafety of these drugs during pregnancy, and given the normal prolactin levels, therapy with cabergoline or bromocriptine in this patient seemed irrational. In turn, surgical treatment in the first trimester is associated with a high risk of premature termination of pregnancy. Due to the desired pregnancy, a decision was made on expectant management until the placenta is fully formed. At the gestational age of 18 weeks, after a control ultrasound to determine the formation of the placental and fetal barrier, the patient was hospitalized for planned surgical treatment.
Physical examination findings
The patient's condition is moderate. Independent movement is difficult due to the large mass of the breast (about 16 kg). There is shortness of breath at rest. Forced position - lying down. Body temperature – 37.2 °C. Body mass index – 26.6 kg/m2. Upon examination, the breast was of gigantic size (Fig. 2, 3). The right one is slightly larger than the left one. The skin is hyperemic, tense, hot to the touch. On the anterior surface of the chest there is an expansion of the superficial veins with signs of thrombosis (Fig. 4). On palpation, the breast has a glandular structure with nodular formations 3–5 cm in diameter, painful, with symptoms of lymphostasis and trophic disorders in the lower sections. In the distal part of the right and left breast (areola area) there is an area of necrotic tissue, with dense edges and serous discharge.
Rice. 2. Gigantomastia at the 18th week of pregnancy. Frontal view.
Rice. 3. Gigantomastia at the 18th week of pregnancy. Profile view.
Rice. 4. Dilatation of superficial veins with signs of thrombosis.
Laboratory data upon admission
- Hemoglobin (Hb) – 116 g/l (117–155 g/l)
- ESR – 33 mm/h (0–20 mm/h)
- D-dimer – 2534.0 ng/ml (216.0–1211 ng/ml)
Treatment
In January 2022, at 19 weeks, a bilateral total mastectomy was performed with removal of prostheses and nipple-areolar complexes.
Among the features of the operation: in the subcutaneous fat tissue, closer to the necrotic areolas, there was pronounced vitreous edema, non-collapsing dilated veins, and therefore intraoperative blood loss was 1.5 liters. Immediately after surgery, against the background of adequate blood transfusion, Hb was 88 g/l.
Subcutaneous removal of the mammary glands with simultaneous removal of implants was performed with significant technical difficulties. The weight of the removed left gland is 6400 g, the right one is 6900 g. According to intraoperative transabdominal ultrasound, the fetal heart rate is 110 beats/min.
Due to significant blood loss and the development of toxic anemia (decrease in Hb level to 65 g/l), transfusion of blood and plasma components, blood substitutes, as well as prophylaxis of stress ulcers with proton pump inhibitors were carried out in the early postoperative period. It should be noted that there was a certain resistance of red blood parameters in response to blood transfusion, in the absence of other signs of blood loss, which indicates the toxic nature of anemia caused by the use of electrocoagulation equipment during the operation and, as a consequence, an extensive burn wound. On the second day after surgery, normalization of D-dimer was noted (384 ng/ml). The drains were removed on the fifth day. She was discharged from the hospital in satisfactory condition on the seventh day, the Hb value at discharge was 90 g/l. The entire postoperative period, the patient and the fetus were under daily monitoring by an obstetrician-gynecologist; no deviations in fetal parameters or placental barrier were noted. The second (cosmetic) stage of the operation is planned after delivery.
According to histological examination: mammary gland tissue with the presence of areas of sharply enlarged glandular lobules, adenosis, ductal hyperplasia, as well as hyperplasia of loose myxomatous connective tissue. There are foci of edema and full-blooded vessels in the stroma.
What else you need to know about macromastia
- Macromastia in girls develops in adolescence, although isolated cases of the disease have been recorded in girls under ten years of age .
- Tissue proliferation can be caused by infectious diseases, most often tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils).
- Macromastia is often accompanied by fibrocystic mastopathy, thyroid disease and secondary hypothyroidism.
- The disease is benign ; to date there have been no cases of malignant tissue degeneration.
- The mass of breast tissue with macromastia can reach 20 kilograms.