Many people believe that mastopathy only applies to female diseases. But the strong half also suffer from this type of disease due to pathologies in the chest.
Sometimes this diagnosis takes men by surprise, as they do not attach importance to some symptoms, attributing it to anything but a disease of the mammary glands. In most cases, teenagers and older men suffer from this disease. This is due to the fact that the impetus for the disease is hormonal changes in the body during adolescence or adulthood.
In this article we will talk about breast mastopathy in men, what it is and how to treat it.
Causes of breast swelling in boys
Swelling of the mammary glands in a teenage boy
In an adult man, the mammary glands remain in a rudimentary, underdeveloped state. Their increase or tissue hypertrophy is a pathology and is called gynecomastia.
The baby is also susceptible to physiological mastopathy. Its development in a newborn baby is associated with a transient increase in the level of estrogen in the blood, which came from the placenta and the mother’s body.
Swelling of the mammary glands in teenage boys is a polyetiological condition that develops due to exposure to a large number of provoking factors. For ease of diagnosis and selection of subsequent treatment and diagnostic tactics, they are divided into physiological and pathological. Physiological reasons include hormonal imbalance caused by the onset of maturation of the reproductive system, which begins at the age of 12-13 years. As the mammary glands mature and the normal balance of hormones becomes established, the mammary glands return to their previous size. During life they remain in an underdeveloped, rudimentary state. Pathological factors include various disorders or diseases that result in an increase in the mammary glands in size, these include:
Excess weight contributes to the accumulation of fat in the mammary glands
- Excess weight in a teenager, which contributes to the accumulation of fatty tissue in the mammary glands, causing them to enlarge. This is false gynecomastia, since the volume of glandular tissue remains at the same level.
- Suffered injuries to the mammary glands, as a result of which the processes of cell division and differentiation are disrupted, and the breast begins to swell.
- A pathological change in the hormonal background of the body, the consequence of which is a decrease in the amount of the male sex hormone testosterone and an increase in the female sex hormone estrogen.
- A child's delay in physical or mental development, which is often caused by genetic changes.
- Irregular feeding of the child - changes can be caused by overeating after previous fasting. Typically, such situations occur during improper rehabilitation of a child after suffering severe infections or somatic diseases.
- Use of narcotic compounds.
Testicular tumor is a pathological factor affecting various disorders and diseases - Irrational use of testosterone-based drugs, which leads to feedback suppression of the synthesis of one’s own sex hormones.
- Testicular tumors, diseases of the adrenal glands, kidneys, liver, leading to disruption of the synthesis or utilization of steroid hormones.
- An irrational diet, in which fats and simple carbohydrates predominate - a feature of the diet of modern children is an excess of fast food and high-calorie semi-finished products.
- A metabolic disorder that affects carbohydrates, fats and often results from the development of diabetes.
- Wearing low-quality, tight, uncomfortable underwear, mainly made of synthetic fabric, is a factor that leads to a local increase in temperature in the tissues of the testicles, resulting in a violation of their functional state.
If a teenage boy has a swollen mammary gland, an examination is required. With the development of pathology, including hormonal imbalances, the risk of complications increases. Some diseases require prompt diagnosis and treatment, as they can lead to negative consequences in the future.
Pediatric mammology
Hello, dear parents!
Allow me to introduce myself: Sergey Vladimirovich Kaplunov – I am a pediatric surgeon and pediatric oncologist. And today I would like to talk with the parents of my potential patients aged 0 to 18 years on such a very rare topic as pediatric and adolescent mammology. The relevance of this topic is due to the fact that parents do not know who to contact with this or that problem that has arisen in such a sensitive and intimate area, and doctors - pediatricians, gynecologists and ordinary pediatric surgeons are not fully aware of all the variants of pathology that can occur in the area of the mammary glands in children of different ages, and therefore cannot prescribe qualified treatment.
Let me look at breast problems in children according to the age at which these situations may arise.
But first, just a little bit of anatomy: both girls and boys have rudiments of glandular tissue located immediately under the nipple area - so from these tissue rudiments in adolescence, girls will develop glandular tissue of the mammary gland, and in boys these rudiments of glandular tissue will develop. the tissues will normally remain in their rudimentary form.
I. Newborn period. During this period, the so-called “sexual crisis” often occurs, one of the manifestations of which is engorgement (swelling, thickening, increase in volume) of those same rudiments of mammary gland tissue due to the passage of female sex hormones (estrogens) from the mother to the newborn child (sometimes it can even be released scanty secretion from the nipples) – usually this condition can be observed on the 3rd – 10th days of the child’s life, followed by a slow decrease in the severity of tissue engorgement in the nipple area.
But when infections penetrate through the thin and therefore easily vulnerable skin of a baby, against the background of this transient and physiological state, purulent-inflammatory diseases such as mastitis of newborns and necrotizing phlegmon of newborns (which is often localized in the area of the anterior chest wall) can occur.
Already in the neonatal period, parents may notice various developmental anomalies associated with the mammary glands in the child, such as:
atelia - absence of a nipple (absence of a nipple can be a symptom of syndromic pathology - an anomaly in the development of all tissues of the chest wall on the side of the missing nipple);
polythelia - an increase in the number of nipples: most often there is one additional nipple (on one side), which is located along the so-called “milky line” (from the armpit to the groin area), as a rule, the additional nipple is smaller in size (the nipple itself is also reduced and the surrounding areolar area of the skin) – a vestigial appearance
II. Girls in the period from 9 months to 1.5 years. During this period of life, female children sometimes experience a “second wave” of tissue engorgement in the area of the future mammary glands and, as a rule, this condition occurs precisely in those girls whose mothers continue to feed them breast milk. This condition is explained by the fact that hormonal changes occur in the mother’s body associated with the resumption of the cyclic production of sex hormones (as before pregnancy).
III. Pre-adolescence in girls. Often, mothers are concerned about the fact that the first signs of the beginning of the formation of mammary glands in girls begin at 8–9 years of age. This very often looks like a one-sided thickening (engorgement) of tissue in the retro-nipple area, measuring no more than 1 cm (“pea-sized”) on one side. On the opposite side, such engorgement is either absent or less pronounced. So this unilateral engorgement of the tissue under the nipple (girls complain of some tactile pain in this area) can be perceived by parents as a tumor (neoplasm) or as premature development of the mammary gland. However, we must remember that tumor diseases at this age in the area of the future mammary glands in girls are extremely rare, and the asymmetry of the beginning of the growth of the mammary glands in the first few months is not a sign of pathology starting from 8-9 years of age. Moreover, it has been noticed that more often it is the tissue of the future mammary gland on the left that begins to swell. The development of glandular tissue of the mammary glands often occurs not smoothly, slowly and gradually, but spasmodically. And, as a rule, a noticeable increase in mammary gland tissue begins only from 10 to 12 years of age - at this age, tissue development occurs more or less symmetrically.
But an increase in the size of the mammary glands in girls under 8 years of age - “thelarche” - requires the attention of both parents and a doctor! Thelarche can be isolated (i.e., only an increase in the size of the mammary glands without the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics) or as one of the symptoms of premature sexual development. Premature sexual development of a girl requires, first of all, the exclusion of hormone-producing tumor processes (most often in the ovaries) and a careful detailed examination by an endocrinologist! False thelarche can be mistakenly mistaken for true thelarche (proliferation of glandular tissue of the mammary gland) - this is an increase in subcutaneous tissue in the area of future mammary glands due to adipose (and not glandular) tissue. This condition usually occurs in overweight girls, and in diagnosing this condition, the key diagnostic role is assigned to an ultrasound specialist.
IV. Teenage years. This period accounts for the maximum amount of various pathologies, because during this period the greatest activation of the development of glandular tissue of the mammary glands occurs. Let's look at just a few of the problems.
The growing mammary gland requires the most gentle approach to itself in order to avoid problems with breastfeeding in the future associated with the presence of scars on the skin and inside the breast tissue, which will interfere with the formation and release of milk and the very process of feeding the baby. In such cases, there is an equally effective alternative to surgical treatment - a puncture type of treatment, which does not leave any scars behind!, is less painful, there is no need for general anesthesia and long-term painful dressings. The choice of treatment method for a purulent process in the mammary gland (surgical or puncture or even conservative) is, of course, a matter for an experienced specialist and depends on each specific clinical situation. The main rule for parents is to contact a specialist early with inflammatory changes in the mammary gland area in a teenage girl.
The most common tumor in the mammary glands in teenage girls is fibroadenoma - a benign tumor! Cancerous tumors of the mammary glands in children under 18 years of age (carcinoma, lymphoma, sarcoma) are a rare situation.
It is believed that fibroadenoma is a hormonally dependent tumor, the development of which depends on the reaction of breast tissue to the increasing concentration of estrogen in the growing female body. Often, fibroadenomas can be multiple, ranging in size from 5 mm to 5 cm (sometimes they occupy most of the breast tissue - leaf-shaped or phylloid fibroadenoma).
The only method of treating breast fibroadenoma is a surgical approach - operations in this case (especially in adolescents) should be organ-preserving and aesthetic in nature. Incisions and sutures are made using cosmetic techniques, and only the tumor is removed without involving surrounding healthy tissue.
In this informational article, I focused only on some of the most common problems that can arise in the mammary glands, mainly in girls. A separate topic is the occurrence of tissue proliferation (increase) in the area of the mammary (mammary) glands in boys - this is especially relevant (emotional, cosmetic, social aspects) in adolescence: the so-called gynecomastia. There are also a number of nuances and differences here. This topic will be discussed in the next information article.
Kaplunov S.V.
pediatric surgeon, pediatric oncologist of the highest category
Make an appointment
Make an appointment
Symptoms of gynecomastia
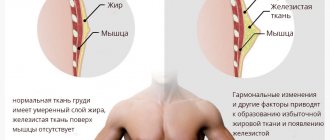
In a large number of cases, changes do not have subjective manifestations. The only symptom is an increase in size of one or both mammary glands. Depending on the nature of the changes and the mechanism of their development, there are 2 types of breast enlargement:
- True gynecomastia - maturation occurs according to the female type with an increase in the volume of glandular tissue. In adolescence, the process is in most cases one-sided. There is a simultaneous increase in the size of the nipple; the areola can reach 5 cm in diameter. The boy is worried about itching, pain in the area of the changed gland, the nipple is painful, it begins to thicken. Redness of the skin around the nipple, which is called hyperemia, is often detected.
- False gynecomastia - changes develop due to an increase in the amount of adipose tissue. At the same time, hormonal levels and testosterone remain at the same level. Both mammary glands enlarge, they remain underdeveloped, the nipples and the volume of glandular tissue do not increase, hyperemia does not develop.
Depending on the severity of tissue hypertrophy, there are 4 degrees of true gynecomastia:
- A minimal increase in tissue volume, which is almost invisible at first glance.
- The swelling does not exceed the diameter of the nipple areola.
- Swelling and engorgement corresponds to the diameter of the areola.
- The lump exceeds the size of the nipple areola.
It is important to pay attention to symptoms in order to facilitate subsequent diagnosis of the causes of changes.
Diet
Gynecomastia can be caused by poor nutrition, so when treating this disease, diet is essential:
- It is necessary to exclude easily digestible fats and carbohydrates from the diet, namely: fast food, flour products, sweets. They should be replaced with cereals, fresh fruits and vegetables.
- It is also necessary to include foods rich in zinc in the menu: meat, offal, seafood, dried fruits, nuts.
- Avoid alcohol.
- Drink enough fluids, about 1.5 liters of water per day between meals.
Why does only one mammary gland swell?
If a 13-year-old boy has one mammary gland that is swollen, this usually indicates physiological pubertal gynecomastia. The development of changes is associated with the beginning of maturation of the reproductive system, when a more rapid increase in estrogen begins to enlarge the breasts, and the concentration of testosterone increases later. Then, as the functional activity of the glandular cells of the testicles increases, testosterone activity increases, leading to involution of the mammary gland tissue. Swelling, itching of one nipple, in which it is larger than the other, is associated with an uneven number of estrogen receptors.
False gynecomastia in adolescents, associated with excessive deposition of adipose tissue, is always accompanied by an enlargement of both mammary glands. Uneven and asymmetrical accumulation of fat cells is a very rare occurrence.
How often does it occur?
In adulthood, a situation may arise when a young man’s breasts become visually larger, but this may be due to excess weight or a jump in the level of estrogen (female hormone).
Swollen breasts occur in 60% of the male population during puberty. In some cases, boys are diagnosed with swollen nipples, while the gland remains normal.
The pathology can persist for a long time. Usually, swollen breasts in a newborn baby “go away” after a few weeks or months, sometimes after a year. In a teenager or young adult, the glands return to normal after two years of growth.
Do I need to see a doctor and get treatment?
Stages of gynecomastia
Physiological gynecomastia in adolescence does not require special treatment. As the level of male sex hormones levels out against the background of maturation of the reproductive system, the mammary glands return to their original state. It is recommended to consult a doctor in the following cases:
- Hypertrophy corresponds to grade 3-4, while the breast continues to grow.
- There is a suspicion of the development of false gynecomastia caused by obesity. At the same time, both breasts begin to swell, which is associated with the accumulation of adipose tissue.
- The development of severe discomfort, which includes itching, burning, can also hurt in the area of enlarged mammary glands.
- The appearance of pathological discharge from the nipples, which may include clear liquid or mucus streaked with pus and blood. When the nipple is squeezed, pain increases.
- The development of other symptoms indicating hormonal imbalance or maturation of the reproductive system.
Pathological gynecomastia has an ICD-10 code - N62. The condition requires therapeutic measures aimed at eliminating the impact of the cause. Treatment of the disease begins only after a reliable diagnosis.
With physiological pubertal gynecomastia, breast size decreases over several years, usually up to 14. Sometimes normalization can last up to 15-16 years. It is not always necessary to wait for symptoms indicating a pathological origin of gynecomastia to appear. To reliably exclude a pathological origin of the condition, experts, including Dr. Komarovsky, recommend undergoing a preventive consultation with a pediatrician.
Surgical treatment of female breasts in men
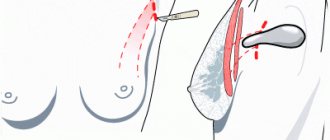
Surgery for gynecomastia in most cases is cosmetic in nature, preventing the formation of various psychological problems and complexes about one’s own body. Surgery for female breasts in men itself includes removal of breast tissue and liposuction.
The laser technique has proven itself very well, allowing the operation to be performed almost bloodlessly, radically and quickly, and also to achieve a good aesthetic result. Hospitalization in a hospital is not required, and the rehabilitation period is quite short and quite comfortable.
Diagnosis of causes
First of all, a laboratory test should be done to determine the level of certain hormones that are synthesized by the pituitary gland, testicles, and adrenal glands. To assess the morphology and exclude the possible presence of pathological formations, ultrasound is prescribed. In complex diagnostic cases, as well as in cases of suspected oncological pathology with the formation of a malignant or benign neoplasm, mammography is additionally prescribed. X-ray examination may be performed using contrast compounds for better visualization.
How much treatment should be given, what medications to use, and the need for surgical intervention is determined individually by the attending physician based on the results of all diagnostic studies.
In 70% of cases, gynecomastia in teenage boys is of physiological origin. This is confirmed by the large number of reviews that can be found on various forums. Most of them include recommendations for undergoing a preventive examination by a pediatrician, who will help exclude a pathological origin of the condition.
Diagnostics
First of all, to make a correct diagnosis, the doctor palpates the mammary glands. If palpation reveals lumps or the patient’s complaints confirm the possibility of mastopathy, the following diagnostic procedures are prescribed:
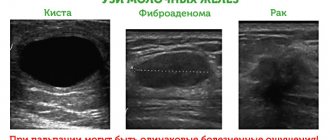
- Mammography , which will allow you to see darkening and pathological manifestations in the mammary glands on x-rays. Establishing a diagnosis using this method is the most accurate. With the help of such an examination, you can determine whether there are cancerous formations in the breast.
- An ultrasound will allow you to diagnose the presence of seals, their shape, size, and location.
- A biopsy is performed if a man is suspected of having cancer. To do this, a small amount of diseased tissue is collected and sent for cytological studies to the laboratory. Tissue studies are carried out at the cellular level, which makes it possible to accurately determine whether the formations are cancerous or not.
- Analysis for the presence of hormones such as androgens, estrogens, prolactin.
Additionally, they may prescribe an ultrasound of the thyroid gland and an ultrasound of the pelvis.