Causes of acne around the mouth
Not all experts agree that this is a disease on its own. Some associate it with allergic and seborrheic dermatitis. Those who are inclined to believe that the disease is independent also call it perioral and steroid dermatitis. This disease affects women and girls aged 18 years and older. Cases of the disease in children and men are rare. The exact provocateurs have not yet been discovered, but there are a number of reasons contributing to the development of the disease. Basically, this is a weakening of the body’s protective functions, which occurs due to the influence of external factors and internal problems in the body.
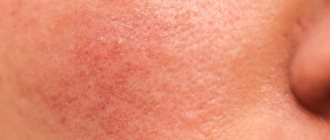
Rosacea (rosacea) - symptoms and treatment
The mechanisms of development of the disease are still being studied and clarified[1][9][10], but a key role in the pathogenesis of rosacea is now played by a violation of vascular tone - angioneurosis. In particular, the mediator bradykinin is involved in the development of transient and persistent facial redness, the level of which also increases during menopause, causing characteristic hot flashes. The same effect can be observed during the reaction to psycho-emotional stimuli[15], especially in people with an unstable psyche and a particular tendency to pronounced vegetative manifestations.
With rosacea, there is a release of other vasoactive inflammatory mediators - histamine, serotonin and prostaglandins.[8]
Some studies confirm that changes in the microvascular bed also activate special proteins - cathelicidins [2], which affect the cells of the inner lining of blood vessels (endotheliocytes), and can also affect local immunity and cause inflammation. It is noted that in people with rosacea, the level of cathelicidins, as well as protease enzymes in the facial skin, is sharply increased.
Excessive ultraviolet irradiation[6] can also change vascular tone due to its damaging effect on the vascular wall, which leads to its atony and increased fragility. In addition, UV irradiation causes degradation of dermal fibers, which also makes the skin more vulnerable to external factors.
Rosacea, provoked by taking topical corticosteroid drugs (especially fluoride-containing ones), has a special development mechanism. The fact is that with the superficial occurrence of intradermal small blood vessels, the network of which is especially well developed on the face of people predisposed to rosacea, corticosteroid drugs are absorbed more intensively. In addition, their peculiar “depot” on the surface of the skin is formed in the dilated follicular ostia, through which they penetrate into the sebaceous glands. Long-term use of steroid drugs worsens the bactericidal properties of the skin, thins the epidermis, which increases the likelihood of pathogenic microorganisms penetrating into the deeper layers of the skin with the subsequent development of inflammation.
Inflammatory processes during the appearance of papules and pustules are also stimulated by the bacterium Bacillus oleronius, which is secreted by Demodex mites.[16] In addition, Staphylococcus epidermidis is often involved in the formation of pustular elements of the rash and visual disturbances.
Chronic inflammation is accompanied by functional insufficiency of small blood and lymphatic vessels of the face, which leads to the development of edema (lymphedema), fibrotic changes and thickening of the skin.
The main pathogenetic links of rosacea
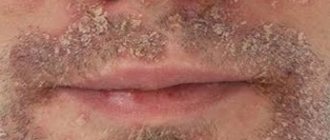
Appearance of perioral acne
Typically, the affected area of skin has a light pink or red tint.
Inflammations can be called small nodules that contain fluid. They can be grouped or located separately from each other. Together, groups of pimples become inflamed and resemble acne. How to distinguish acne that appears due to dermatitis around the mouth? They are rough, a little itchy, and there is a constant feeling of tightness on the skin. However, there are no skin rashes directly around the lips, approximately 3-5 mm. These signs distinguish pimples with perioral dermatitis from rosacea and rosacea. If the disease is started and treatment is not started in time, it will affect new areas of the skin. To prevent this, you need to immediately contact a dermatologist, otherwise his help alone will not be enough.
Perioral dermatitis
dermatitis
Perioral dermatitis is a chronic skin disease characterized by limited erythema, accompanied by
in which papules and papulopustules appear, localized mainly around the mouth (perioral dermatitis), or less often around the eyelids (periorbital dermatitis) or eyes (periocular dermatitis). Until recently, the disease was considered characteristic mainly of women aged 15-25 years; in recent years, it has often occurred in children. A type of the disease is granulomatous perioral dermatitis , which is histologically characterized by the presence of granulomas in the lesions. Synonyms for perioral granulomatous dermatitis are facial rash of African-Caribbean children, granulomatous periorificial dermatitis. Clinical picture. Perioral dermatitis begins with the appearance of small discrete or grouped reddish papules or papulopustules, localized mainly around the mouth, in the naso-buccal folds, on the cheeks, bridge of the nose, around the eyes (sometimes in isolation). The rashes are usually located symmetrically, sometimes unilaterally, and appear gradually over several weeks or months. A characteristic feature is a narrow, about 5 mm in diameter, rim of healthy skin, directly adjacent to the red border of the lips. There is a special “granulomatous” variant of perioral dermatitis, which is observed mainly in children, characterized by the appearance of papules of pink, yellowish-brown color or the color of normal skin, localized in areas of the face typical for perioral dermatitis. Sometimes papules tend to merge. There are also reports of localization of lesions on the ears, scalp, trunk, labia majora and extremities. Subjective sensations in patients with perioral dermatitis are usually absent; they are concerned about a cosmetic defect, a feeling of slight itching, burning and tightness of the skin, intolerance to moisturizers and some cosmetics. Occasionally, granulomatous perioral dermatitis may cause blepharitis or conjunctivitis. Epidemiology. Perioral dermatitis was first described in the late 1950s and 1960s. Over the past decade in European countries, the number of such patients has decreased, which is explained by a decrease in the use of strong corticosteroid hormones on the face in medical practice. Mostly young and middle-aged women (20-45 years old) are affected; it is rarely observed in men and children. Pediatric perioral dermatitis occurs equally frequently in boys and girls of all races. Granulomatous perioral dermatitis is most often observed in prepubertal children. Perioral dermatitis is sometimes considered a variant of rosacea, but it differs from the typical rash localization of rosacea; its relative monomorphism; absence of the phenomenon of episodic erythema and telangiectasia; Perioral dermatitis usually develops at an earlier age than rosacea. The etiology and pathogenesis of the disease have not been precisely established. The main role in the development of perioral dermatitis is played by corticosteroid hormones (both fluorinated and non-fluorinated), used in the form of ointments and creams, sometimes inhaled (for the treatment of bronchial asthma) and taken orally. Perioral dermatitis can be caused by weak corticosteroids (hydrocortisone) and even short-term use can cause the disease. Corticosteroids prescribed for the treatment of banal cosmetic or inflammatory changes in facial skin become a necessary factor for it and cause perioral dermatitis. Corticosteroid ophthalmic ointments may cause periorbicular dermatitis. In some cases, perioral dermatitis is associated with the use of fluoridated toothpastes or dentures. In these cases, after curing perioral dermatitis, repeated use of these pastes does not always lead to relapse of the disease. Since the disease occurs predominantly in young women, the pathogenetic role of sex hormones cannot be ruled out. The etiological role of oral contraceptives has not been established. Perioral dermatitis is currently believed to be unrelated to rosacea, although it may have some clinical and histological similarities, especially when rosacea is treated with corticosteroid ointments (“rosacea-like dermatitis”). Provoking factors are insolation (“photosensitive seborrheide”); irrational use of cosmetics (“flight attendant disease”); lipsticks, synthetic fabrics, etc. Treatment of perioral dermatitis. It is mandatory to discontinue all cosmetics and previously used ointments, especially corticosteroid drugs. Remains of ointments must be removed with care. After washing, your face should be blotted (do not rub) with a towel. In the initial period of the disease, it is recommended to prescribe indifferent powders or cooling creams. Medicines are prescribed by a doctor. Forecast. Perioral dermatitis usually resolves within a few weeks or months and responds well to antibiotic therapy; relapses are not typical. With long-term use of corticosteroid hormones, the process, however, can have a long course. Before treatment, it is necessary to consult a specialist - a dermatologist.
Rodionov A.N., Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor.
| Make an appointment | Make an appointment by calling +7 (812) 600-67-67 or filling out the online form - the administrator will contact you to confirm your appointment |
UNION CLINIC guarantees complete confidentiality of your request.
Treatment methods for demodicosis
Treatment of demodicosis is a long process. On average it takes 4-6 weeks, but in some cases it may take several months.
The difficulty of treating demodicosis, in particular, is that the most effective anti-mite remedies are quite toxic. Therefore, means for the treatment of demodicosis are selected individually, depending on the degree of damage and the patient’s condition.
Treatment must be comprehensive. The course of treatment includes both local and systemic therapy.
Local therapy
Local therapy for demodicosis is aimed at suppressing the activity of the mite. Without the use of local therapy, treatment success cannot be expected.
Systemic therapy
Systemic therapy for demodicosis involves measures to strengthen the immune system and normalize metabolism.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating