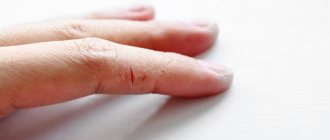
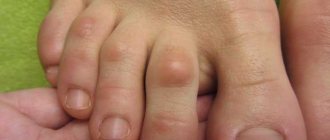
Many of our patients seek advice regarding cracked and chafed skin between their toes. Especially in summer, the problem seems to grow. Patients notice small whitish blisters or ragged skin on their own or their children's legs and think it is ringworm.
However, in most cases we can reassure: dermatophytosis is a relatively rare disease in our latitudes, provided hygiene standards are observed. Most often we deal with maceration.
What is maceration?
On hot summer days, almost all the feet sweat. One of the purposes of sweat is to cool the body, and therefore it is completely natural in the summer. Then the whole body, and therefore the feet, cool down. After all, there are over 500 sweat glands on the soles of our feet.
However, too much sweat on the feet can cause maceration, that is, softening of the epidermis. The macerated epidermis loses the features of vital tissue and becomes dead tissue.
Maceration in the interdigital spaces appears as cracked, uneven whitish epidermis. If this occurs on skin with hyperhidrosis, the skin around the maceration becomes intensely red and noticeably moist.
What ointments are used to heal cracks?
There are different ways to heal cracks - the use of creams, gels, lotions, special patches and compresses, various baths. The best option is to alternate between two or three products of different types. If the skin is cracked and hurts, and the cause is external factors or systemic diseases, with the exception of a fungal infection, then you need to buy a pharmaceutical foot cream designed to heal cracks.
There are many such creams - for example, Gehwol, Ambulance, 5D and others.
It is necessary to read the composition of the drug. The best effect is achieved by ointments containing urea. Despite the presence of this ingredient, they smell neutral, and the epidermis heals quite quickly. Creams are applied to all problem areas, including under the little finger.
If the problem is only dry skin, then you can even use regular Vaseline or Shostakovsky ointment (vinyline).
Some people who are not afraid to use unconventional methods treat cracks with creams from a veterinary pharmacy, for example, Zorka. Such products were originally intended to heal cracks in the cow's udder. The concentration of the active substance in them is quite high, hence the quick result - the epidermis heals in a few days. But this remedy is not suitable for everyone. Firstly, allergic reactions cannot be ruled out. Secondly, the smell of this ointment is not the most pleasant, and the texture is too thick and greasy, which can cause discomfort.
For diabetes mellitus, you can use not only the universal ointments listed above for the treatment of cracks, but also series specially designed for this. For example, there is the SixtuMed line. It includes bath oil and balm with natural herbal ingredients.
Such products heal cracks well and prevent the penetration of secondary fungal or bacterial infections. Use them as follows: 1 tsp. oil per 1 liter of warm water. After the bath, your feet should dry, but do not dry them with a towel so as not to injure the skin. Then a balm from the same series is applied to areas with cracks.
Why does the skin between my toes crack?
In summer, maceration often occurs on normal skin, which usually does not sweat much. The reasons for this are increased air temperature, and, consequently, skin temperature, lack of air circulation between the fingers and accumulation of moisture. The friction of the toes against each other and the pressure of the surface of the skin on the soles of the shoes cause cracking of the thin and delicate epidermis between the toes.
Sometimes the cracks in the transitions from the interdigital surfaces to the sole are deep. We then see whitish, uneven areas of the epidermis surrounding the crack in the skin, which is often painful. Then we are faced with a wound that requires fast and effective treatment, because not only fungi, but also bacteria can penetrate through an open wound.
Maceration can occur on all areas of the foot. Calluses, plantar indentations and the area on the lateral surfaces of the toes can become macerated, that is, softened by sweat and other fluids.
Remedies for fungal diseases
The fungus can be treated at home. For this, antifungal ointments are usually used, the most popular of which is nystatin. It has proven itself well in the treatment of mycoses in adults along with systemic drugs (for example, Fluconazole).
There are other external remedies for the treatment of fungus based on ketoconazole, miconazole, clotrimazole, terbinafine. They can have a variety of trade names: Thermikon, Lamisil, Exoderil, Mikoderil, Nizoral, Mikospor, Batrafen and others.
It is advisable that such remedies be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the type of fungus and all related factors.
But treatment also requires more thorough than usual daily care. You need to wash your feet with warm, but not hot water (it makes the skin itch even more). But it shouldn’t be cold either, because this makes the skin rougher, which aggravates the situation. After washing, it is recommended to powder your feet with talcum powder or a medicinal antifungal composition. Classic remedies also help well - iodine or brilliant green, which are applied directly to areas where the skin is cracking.
Often the infection spreads to the nails. This is clearly visible on the thumb, where the nail plate turns yellow and cracks. In this case, it is advisable to immediately consult a doctor who will select an antifungal agent based on bifonazole and clotrimazole.
Fungal diseases are much less common in children than in adults.
Folk remedies for treating fungus are not suitable as basic ones. They can only be auxiliary, that is, used together with drug therapy. For example, a soap and soda bath. It is prepared like this: 1 tbsp. l. soda and 50 g of grated laundry soap are dissolved in 2 liters of warm water. Place your feet in the water for 10-15 minutes. After this, the skin is blotted and treated with the prescribed ointment. If the fungus appears on the nails, then the layers softened after the bath are removed using nail clippers or disposable nail files.
Hypergranulation and maceration
Maceration is often accompanied by ingrown nails and hypergranulation. The area is always wet, and therefore an infection easily attaches to the wound, which quickly moves from the side to the back, that is, the base of the nail plate. A purulent paronychia forms with pronounced redness and pain.
If timely treatment is not carried out, paronychia can spread to the finger tissue and cause panaritium, inflammation of the lymph nodes.
If maceration can be treated in a podologist’s office, then associated complications require contacting a surgeon.
The mechanism of occurrence of pathology
External or internal factors lead to poor circulation and degenerative processes in the epidermis. The cells of the outer layer of skin die, resulting in peeling. Oxygen starvation leads to damage to the deep layers of the cover and the appearance of cracks.
Infectious infection with a fungal infection develops when the pathogen gets on the skin surface; the risk of the disease increases with a decrease in the body's immune response.
Increased sweating is a provoking factor for the growth of fungus. Maceration of the upper layers is one of the reasons for the violation of the integrity of the integument on the toes and on top of the foot. Damage to the epidermis can also be observed in the heel area and on the crook of all toes.
What is the difference between maceration and mycosis?
In contrast to maceration, mycosis is sometimes caused by Trichophyton rubrum or Trichophyton interdigitale. Mycosis on the feet differs from maceration in both appearance and smell. The smell of mycosis is very characteristic and is easily recognized by an orthopedist.
The appearance of mycosis is distinguished by its yellowish-brown color and the presence of additional, not yet cracked, microscopic bubbles that appear next to the already cracked and jagged ones. The vesicles are filled with liquid containing fungal spores. Often they are so small that only the experienced eye of a podiatrist can see them with a magnifying glass. Deposits of necrotic, fungal epidermis can stick together, becoming a threat to the formation of interdigital ulcers, which are very painful and difficult to remove and heal.
Traditional methods
For fungal infections and diabetes mellitus, special medications are used, but their effect can be supplemented with folk remedies.
Baths
Foot baths have a good effect. A recipe based on baking soda and laundry soap has already been given above. You can also prepare herbal baths from string or oak bark. The decoction is prepared in the same way:
- Take 2 tbsp. l. raw materials for 2 cups of boiling water.
- Bring to a boil again and leave on low heat for 5 minutes.
- Dilute this volume in 2 liters of water for a bath. The duration of the procedure is half an hour.
Other herbs have similar properties - chamomile, calendula, sage, coltsfoot. The proportions for preparing the decoction will be the same.
A bath with boric acid, which can be purchased at a pharmacy, is also effective. To do this you need to take 2 tsp. substances per 2 liters of warm water.
You can replace this remedy with lemon juice mixed in equal proportions with vinegar. This mixture is added to the bath water. You can add a few drops of tea tree essential oil.
Regular black tea has wound-healing and anti-inflammatory properties. For a bath it is convenient to take a packaged one. It is prepared like this: 6 tea leaves per liter of hot water. This bath is also suitable for diabetics, but the water should not be too hot. Procedures can be done every day, preferably at night, until the main symptoms disappear.
Lotions and compresses
Traditional methods involve the use of lotions and compresses. They are even considered more effective due to the high concentration of the active substance. They are recommended for use for deep cracks between the toes, especially if they take too long to heal. For the lotion you need:
- Take 10 aspirin tablets.
- Crush them and mix with 1/2 cup of ethyl alcohol.
- Add a few drops of iodine there and stir.
This product can be stored for several days, but first you need to pour it into a dark glass bottle. Lotions from this infusion can be made every day for two weeks, during which time the cracks should heal.
Liquid honey has anti-inflammatory properties. It can be applied to problem areas at night in a small amount. To enhance the effect, you need to wrap your feet in a bandage and put cotton socks on your feet. This compress will last all night. In the morning, unabsorbed residues are washed off with warm water and a nourishing cream is applied to the skin.
Why is it important to diagnose and treat maceration?
Eliminating maceration is the basis of foot health: eliminating unpleasant odors and the risk of infections.
Recommendations:
- Medical pedicure. Removal of keratinization and affected epithelium using a hardware method.
- Treatment of an ingrown toenail. (If pathology is present). The method is selected individually and depends on the position of the nail and the condition of neighboring tissues.
- Foot hygiene. Regular independent and proper care reduces the risk of infection and maintains the results of a hardware pedicure. Recommendations for care will be given individually by a podiatrist.
- Comfortable shoes. According to season and size, made of natural materials and orthopedic insoles.
If, due to maceration, the interdigital spaces are affected by mycosis, along with a medical pedicure, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist to receive pharmacological treatment.
Prevention
In order to avoid cracks in your legs, it is important to follow the rules of hygiene. Under no circumstances should you wear someone else’s shoes or take care items that are not your own, such as a pumice stone or a nail file. After visiting the gym or swimming pool, it is recommended to treat the skin with a solution of salicylic alcohol.
Foot massage using essential oils of coniferous trees (spruce, fir, cedar) is also a good preventive measure. You need to monitor your diet, include vegetable oils, pumpkin seeds, egg yolk, carrots and other foods containing vitamins A and E.
Causes of itching
The most obvious cause of itching is athlete's foot, scabies, dry or wet eczema. Infection can occur through contact with contaminated surfaces in public places, household items, and also by wearing someone else's shoes. In the presence of predisposing factors, the pathogen penetrates the skin, causing irritation, burning, and bruising. The fungus most often affects the tissues around the little finger and thumb.
Main symptoms
In the initial stages, the disease resembles common prickly heat in appearance: small pimples and redness appear on the epidermis. Over time, they begin to itch very much; when scratching, the upper layers are damaged and begin to peel off. Other unpleasant signs include:
- the formation of ulcers on the surface of the skin, which bleed heavily when damaged;
- the skin peels off and smells like cheese (in case of a fungal infection);
- After scratching, an infection gets into the wounds and the inflammatory process begins.
Peeling often occurs without itching or other unpleasant symptoms. This indicates excessive dryness of the epidermis, however, in the absence of timely treatment, the problem will only worsen.
Cracked heels
Fungus
Iron deficiency
Diabetes
19470 November 18
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Cracked heels: causes of occurrence, what diseases cause them, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Description
Cracks in the heels are linear tears in the skin that occur as a result of loss of elasticity and thickening of individual areas. Most often, cracks form in places where the skin is naturally folded and stretched and can be of varying depths. A person often complains of itching, burning, pain, and discomfort while walking.
For most people, cracked heels are a problem related to the appearance of the feet. However, in some cases they can cause considerable discomfort - they can be painful, lead to bleeding, and as a result there is a risk of infection.
In addition, cracked heels are one of the symptoms of certain diseases.
Types of cracked heels
The following types of heel cracks can be distinguished:
- superficial and deep;
- dry (arising from excessively dry skin) and wet (arising from excessively wet skin - this phenomenon is called maceration);
- uninfected and infected;
- resulting from:
- endogenous causes (dermatological diseases, hormonal disorders, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract; associated with a lack of vitamins, microelements);
- external factors.
Possible causes of cracked heels
The most common causes of cracked heels include conditions associated with local physical effects on the skin of the foot: exposure to the sun, wind and cold, temperature changes, chlorinated water, dry air, poor hygiene, excessive care (frequent peeling - removal of the upper stratum corneum of the skin), use of alkaline soap, improperly selected shoes.
However, in some cases we may be talking about general conditions that affect the skin of the heels: smoking and alcohol abuse, fasting, unbalanced diets, small amounts of fluid to drink, congenital skin characteristics (dryness, sensitivity), pregnancy, menopause, aging of the body.
Pathologies that provoke the appearance of cracked heels include fungal infections, dermatological diseases (psoriasis, ichthyosis), diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, helminthiases, conditions of deficiency of vitamins and microelements (iron deficiency anemia, hypovitaminosis), hormonal disorders (thyroid diseases, diabetes mellitus). diabetes), as well as diseases leading to impaired trophism (nutrition) of the lower extremities (impaired innervation and blood supply).
As a result of negative environmental influences (sun, wind, etc.), the skin loses its elasticity, becomes thinner, and the function of the sebaceous and sweat glands decreases. As a result, growths of thick, rough, dry skin appear on the heels. Against the background of increased pressure on the foot (prolonged standing, wearing tight shoes, obesity), cracks may appear. Failure to comply with the drinking regime and lack of vitamins aggravates the problem.
Cracked skin is not only an aesthetic problem, over time it can cause pain when walking, cracks can bleed and become infected. Poor hygiene and the presence of concomitant diseases complicate the problem.
Insufficient levels of thyroid hormones (hypothyroidism) leads to a decrease in metabolism in the body, blood supply to tissues, and the function of sweat and sebaceous glands. Dry and rough skin on the feet becomes prone to excessive keratinization and cracking.
Psoriasis is a chronic systemic disease affecting the skin, nails, and joints. It is characterized by the appearance of small red spots with scales (psioriatic plaques) rising above the skin, which tend to enlarge, merge, and thicken. Thick and hard skin on the feet itches and cracks. Since psoriasis of the feet is associated with a high risk of trauma to the elements of the rash, they often become infected.
Psoriatic plaques on the skin of the feet Diabetes mellitus is a chronic endocrine disease, which is based on metabolic disorders due to insulin deficiency and the resulting high level of glucose in the blood. The long course of the disease leads to damage to nerves and blood vessels with impaired innervation and blood supply to tissues. If the feet are not properly cared for, ulcers and cracks form on their surface, and patients with diabetes need more time to heal.
Foot fungus can be another cause of cracked heels. The disease is characterized by redness, itching, peeling and thickening of the skin, and the appearance of cracks of varying depths and sizes. An unpleasant odor may be present. Based on the picture of the disease and the patient’s complaints, the doctor suggests a fungal infection of the feet, but to confirm the diagnosis, a laboratory test is necessary to determine the presence of the pathogen in the affected area of the skin.
Foot fungus
Keratoderma is a group of skin diseases characterized by disruption of the keratinization process. With this disease, keratosis of the palms and soles is observed. Keratoderma can be diffuse (continuous lesion of the skin of the palms and soles) and focal (the lesion is located in the form of islands, linearly, pointwise).
Keratoderma of the skin of the feet
In children with Unna-Tost keratoderma (congenital ichthyosis of the palms and soles), excessive keratinization of the skin is observed at 1-2 years of age. The disease begins with mild thickening of the skin of the palms and soles. The horny layers are smooth, yellowish in color. Deep cracks may form.
Acquired ichthyosis develops at a later age and is manifested by dry and rough skin with a large number of scales. The skin is affected not only on the torso and limbs, but also on the palms and soles. Acquired ichthyosis is a sign of other diseases (hypovitaminosis A, malignant neoplasms of internal organs, mycosis fungoides, etc.).
Which doctors should I consult for cracked heels?
If changing tight shoes and performing hygiene procedures do not help get rid of cracked feet, you should consult a podiatrist (a doctor who diagnoses and treats foot diseases).
To exclude diseases that provoke the occurrence of cracked feet, you may need to consult a dermatologist or rheumatologist.
Diagnostics and examinations for cracked heels
To determine the causes of cracked heels, the doctor may prescribe a set of laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods.
- Tests for fungal infections of the skin of the feet.
Symptoms of fungus
The course and development of the disease is influenced by the physiological characteristics of the skin of the feet, increased sweat production, disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system, and leg injuries. Fungal pathogens can remain dormant for a long time without showing symptoms. If there are disturbances in the body, they can become active. Athlete's foot is characterized by the presence of several forms of the disease, which can be supplemented by damage to the nail plates.
Fungal infection can be determined if several symptoms are present:
- the nail plate changes its natural color: usually yellow or dark color is fixed, but the nails can even become white or completely black;
- tissue keratosis under the plate: outwardly it looks as if a hard growth has appeared under the nail;
- thickening and delamination of the plate;
- deformation of the nail: protrusion, growth to the side, ingrowth into the skin;
- fragility of the nail plate: parts of it may break off.
When should you contact your healthcare provider?
Call your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following:
- temperature rises to 100.4°F (38°C) or higher;
- chills;
- symptoms do not go away or get worse;
- any of the following symptoms appear on the skin of your palms or soles: skin that is hard, warm, or hot to the touch;
- bright yellow or green discharge;
- bleeding;
- unpleasant odor from the palms and feet;
- increasing redness or swelling;
- increasing pain or discomfort;
to come back to the beginning
Diagnostics
Itching, after which the skin cracks, and subsequently becomes wet and peeling, usually indicates a fungal infection.
To determine the cause of the pathological condition, consultation with specialists will be required:
- dermatologist;
- endocrinologist;
- vascular surgeon and phlebologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- nutritionist.
The following diagnostic examination methods will help confirm the diagnosis:
- microscopic examination of the epidermis;
- sowing the collected material to confirm mycosis;
- biochemical blood test for sugar content and determination of thyroid hormone activity;
- phlebography and ultrasound scanning of veins;
- Clinical urine analysis and according to Zimnitsky to determine the excretory function of the kidneys.
A comprehensive examination is necessary when the patient also has other symptoms of the disease.
Seeing a doctor is mandatory: only a specialist will be able to determine why the skin on your toes is cracking and prescribe the correct regimen of health measures.
Therapy
Treatment of fungal infections on the legs is carried out on an outpatient basis. Complex therapy includes pharmaceutical and folk remedies.
When a bacterial infection occurs, anti-inflammatory, antibiotic and bactericidal agents are added to the treatment regimen.
Medicines
Fungus between the fingers is difficult to treat. Therapy for the disease lasts from 1 month to a year. Mild forms of pathology are eliminated faster and easier. The disease cannot be ignored in the early stages, when the first mild symptoms appear. If you experience discomfort in your toes, you should immediately visit a doctor.
Anti-inflammatory therapy
Inflammation is relieved using 20-minute foot baths with the addition of manganese permanganate. After the procedure, the skin is dried and cleaned of dead and flaking tissue. Then treated with an antiseptic:
- make an application with boric acid or resorcinol,
- Fukortsin.
When the weeping disappears, the epithelium dries out, the lesions are lubricated:
- brilliant green,
- Fluorocort,
- Ultralan with corticosteroids.
Antimycotic drugs begin to be used after suppression of inflammation.
Treatment for bacterial infection
If the fungus is complicated by a bacterial infection, combined medications are used. Apply to damaged epithelial tissues:
- Betamethasone,
- Akriderm,
- Pimafucort is an ointment based on hydrocortisone,
- Natamycin,
- Neomycin.
Systemic treatment with drugs in tablets
Various complications develop against the background of fungal infections. Patients develop allergies, erysipelas, eczema, and concomitant pathologies become aggravated.
Allergic reactions and itching are relieved with antihistamines:
- Suprastin,
- Diazolin,
- Zyrtec.
Simultaneously with antiallergenic tablets, injections of 10% calcium gluconate are given. To cure the disease, antimycotic drugs in tablets or capsules are used.
Patients are prescribed tablets based on terbinafine:
- Lamisil,
- Terbinafine-Teva.
- Orungal,
- Irunin.
To relieve a fungal infection, medications containing fluconazole are used. Tablets with this active substance are called:
- Diflucan,
- Flucosan,
- Mycomax.
Basic therapy is supplemented with medications that improve certain functions of internal organs:
- Festal normalizes intestinal function and restores the process of absorption of nutrients.
- Trental improves blood flow in the feet.
- Arbidol and Taktivin increase immunity.
At home
Baths are made according to the following recipe:
- Soda-salt solutions are an effective home remedy for fighting fungus. The water is heated to 38-40 ℃. Add 1 teaspoon of salt and soda to the liquid. Soar your feet for 20-30 minutes. Cleanses the skin of dead tissue. Treat feet with local antimycotics. The procedure is carried out daily before bedtime.
- Herbal. Prepare the collection: mix chamomile, plantain, and celandine in equal quantities. Boil 1 liter of water, add 3 tablespoons of raw materials. Cool the infusion to 38-40 ℃. Immerse your feet in the liquid for 20 minutes. Remove dead tissue from the surface of the skin. Treat your feet with antifungal drugs.
Lotions help fight fungus:
- soak a cotton pad with a 9% vinegar solution,
- apply the application to the lesion,
- wrap in plastic wrap, leave for 5 minutes,
- wash the foot with warm water,
- lubricate the affected areas with a local antimycotic.
This recipe is used to treat adult patients. On the delicate skin of children, the application may leave a burn.
All folk remedies are used in combination with medications. Use home methods on the recommendation of a dermatologist.
Treatment
Particular attention should be paid to careful treatment of lesions.
The patient should take daily warm foot baths with potassium permanganate. In this case, it is necessary to remove the crusts, open the blisters, cut off the fringe along the edges of the erosions, as well as the covers of the festering blisters. After the bath, wet-dry bandages or lotions are applied with an aqueous solution of copper (0.1%) and zinc sulfates (0.4%) or with a 1% aqueous solution of resorcinol. After the weeping stops, dermozolon, mycozolon are used, and then alcohol fungicidal solutions, Castellani paint, and finally, if necessary, fungicidal pastes and ointments.
The effectiveness of treatment depends not so much on the choice of pharmacological drug, but on their correct, consistent use in accordance with the nature of the inflammatory reaction.
Fungicidal treatment is carried out until the fungal test results are negative.
Anti-relapse treatment carried out within a month after the elimination of lesions is extremely important - wiping the skin of the feet with 2% salicylic or 1% thymol alcohol and dusting with 10% boron powder. For the same purpose, it is necessary to thoroughly wipe the inner surface of the shoes with a solution of formaldehyde, wrap them in an airtight fabric for 2 days, then ventilate and dry them, and socks and stockings for 10 minutes. boil.
When athlete's foot is complicated by pyococcal infection, antibiotics are prescribed - methicillin, cephaloridine, oleandomycin, metacycline, erythromycin. The patient must remain in bed.