From this article you will learn:
- What is alopecia areata
- What are the causes of alopecia areata?
- What are the symptoms of alopecia areata
- How is alopecia areata diagnosed?
- What is the treatment method for alopecia areata
The occurrence of a disease such as alopecia areata depends on many reasons, but its external signs are the same for men and women. In any case, we are dealing with an autoimmune process, when there is a “war” between the body’s own cells, and specifically, in the hair follicles. The disease is also accompanied by neurotrophic and microcirculatory changes that affect hair growth. Many experts are of the opinion that the risk of developing this pathology is only 1.7%, and it is not contagious. What do you need to know about the signs and forms of alopecia areata?
Causes of alopecia
The occurrence of alopecia areata in women is associated with the appearance of disorders in the immune system. Hair follicles have a special structure, therefore, during pathological changes, they are perceived by the cells of the body as strangers, and they are forced out of the skin.
Factors influencing the occurrence of the disease:
- Heredity. Close relatives are at risk.
- Hormonal disorders. The cause of alopecia areata in both men and women can be a malfunction of the adrenal glands, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, or thyroid gland.
- Inflammatory processes such as tonsillitis, rhinosinusitis, caries.
- Prolonged stress.
- Local baldness may be a consequence of disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, leading to spasm of blood vessels and small capillaries, which increases blood viscosity.
If alopecia areata is suspected, it is necessary to perform a diagnosis in order to identify the true cause that provokes the development of the disease, and not to deal with symptoms that may be signs of various diseases.
Recommendations for patients
- Avoid mechanical trauma to hair when washing and combing.
- Avoid tight hairstyles.
- Eat fully and balanced.
- If necessary, do not be afraid to correct with a wig or hair replacement system.
- Some men (and women) prefer shaving to treatment.
- Do not forget about photoprotection; a hairless scalp is not protected from exposure to sunlight.
- Be careful with coloring, young growing hair may turn a different color.
- Be careful with extensions, artificial eyelashes and eyebrows, tattooing, and the use of masking fibers.
- Psychological and informational support can be obtained from special resources on the Internet and in communities for patients with alopecia areata. If you need specialized help, see a psychotherapist.
Author:
Voronina Vera Removna dermatologist
Clinical forms of alopecia
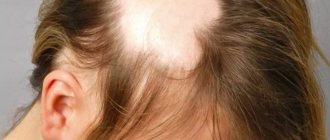
Most often, alopecia areata occurs on the head, affecting the scalp.
Experts identify the following forms of the disease:
- Local. This type is characterized by round or oval shaped areas of baldness.
- Ribbon-shaped. The hair loss area looks like a ribbon stretching from the temporal part to the back of the head.
- Subtotal. Several lesions form one large one.
- Total baldness. In this case, the hair falls out almost completely, not even eyebrows and eyelashes remain.
- Universal look. This form of alopecia areata affects no more than 7% of patients. The pathology becomes chronic, baldness occurs in new areas with regular exacerbation. There is no hair on the body completely.
- Nest form. The most severe is when not only hair falls out, but the disease also affects nails.
The first signs and symptoms of the disease
The most important manifestation of pathology is causeless baldness in a certain area of the body (usually the face or head). At the site of the loss, oval or round foci of “bare” skin remain without the slightest trace of trauma to its structure or loss of integrity, but with characteristic redness, itching or slight pain. However, there are several clinical signs that may indicate the presence of a pathological process. These include:
● Fragility of curls and their easy pulling out; ● The appearance of “loose hairs”, which are short in length and surround the area of loss; ● Transformation of the nail plates (at later stages of development) in the form of compression, transverse striations or waviness, as well as dullness.
Based on the symptomatic complex, alopecia in women (as with all types of alopecia) typically occurs in three main stages:
1. Progression - characterized by the appearance of edema and hyperemia of the skin (manifestation of the inflammatory process) at the site of complete hair loss. Patients complain of annoying itching, a slight tingling or burning sensation. Around the bald spot, areas with pathologically short hairs are found, which in a short period of time will also turn into “empty” skin lesions. As a rule, women notice the disease while scratching or after touching their head. At the initial stage, you can easily pull a strand and understand that it is not fixed to the surface of the body. The bulbous end of the rod undergoes dystrophic changes and acquires the characteristic appearance of a “dangling rope.” 2. Subacute - may be accompanied by minor manifestations of inflammation or occur completely without them. The second stage is characterized by the skin becoming pale in color. 3. Regression - is the final stage and is characterized by the smooth germination of pigmented terminal and vellus light hairs. They begin to slowly increase in size and acquire their original color.
Manifestation of alopecia
Alopecia areata is observed more often in men than in women, but for the latter this disease brings more discomfort. As long as there is one area of hair loss, it can still be hidden under the hairstyle, but if the disease develops and new areas of baldness appear, this complicates the matter. You can reassure yourself that the disease is being fought with modern methods. In some cases, after some time, the hair begins to grow again. There are many causes of alopecia. The growth and structure of curls can be affected by perm, styling with a hairdryer, curling iron, and flat iron.
Bald spots can form due to an overdose of medications or long-term use of drugs prescribed for depression. Alopecia areata may be a consequence of hormonal changes during pregnancy or the postpartum period.
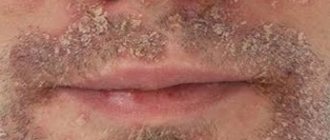
Most often, baldness begins from the crown area. If the disease progresses, the size of the lesion gradually increases. Symptoms of the disease can be seen on the chin and cheeks, when the stubble grows unevenly, in patches.
Signs of alopecia areata can appear in people of any age. Quite often the disease affects teenagers. In young people, a symptom of pathology is considered to be areas with excessively porous skin, along the edges of which weak and thin hairs grow.
Causes of scalp hair loss
It is known that the tendency to hair loss can be genetically determined (programmed), however, there are a number of other reasons that can contribute to the development of alopecia. Among them are:
- Regular stress;
- Hormone imbalance;
- Childbirth and the postpartum period;
- Unbalanced nutrition and uncontrolled diets;
- Unfavorable environmental situation;
- Mechanical or chemical damage to the scalp;
- Infectious processes.
In addition, hair loss may develop during specific treatment. Alopecia is often observed in patients who have undergone chemotherapy, as well as after long-term use of certain groups of antibiotics, antidepressants, systemic retinoids or other drugs.
Establishing the cause of hair loss is one of the most important tasks for a trichologist, since further treatment and its effectiveness will depend on this.
Stages of alopecia
- Spicy.
During this period, the hair roots become thinner, and additional unpleasant phenomena occur: itching and burning in the area of hair loss, redness and inflammation of the skin.
- Subacute.
Baldness is not accompanied by inflammation, or it is slight. There are also no associated unpleasant sensations.
- Regression stage.
Hair stops falling out. Bald spots begin to become covered with “fluff,” which is gradually replaced by normal strands.
Symptoms of alopecia areata
| Disease stage | Characteristic |
| Acute | · Inflammation and swelling appear in places on the skin; · the process is accompanied by burning, itching, tingling in the baldness area; hair breaks easily; · the bald spot expands, in the border areas the hair can be pulled out painlessly; · the diameter of the lesion is from 0.3 to 1 cm |
| Subacute | · Areas of baldness are formed; · no longer bothered by redness and swelling; · itching disappears; · normal skin tone returns; Hair loss stops |
| Regression stage | · Thin vellus hair appears on the bald spot; · hair follicles are strengthened; Pigmentation is restored |
Description of the pathology
Alopecia Areata (pattern baldness) is an acquired abnormal hair loss in a certain area of the skin with clear contours, which looks like rounded areas of various diameters. According to demographic studies, 0.05–0.1% of humanity suffers from this pathology in the world. It is not characterized by gender or age predisposition, so the disease equally affects people of any gender and even children.
Area baldness is characterized by a chronic course, which is often accompanied by inflammation without the formation of a skin scar. The target of the lesion is the hair follicle, much less often the nail plate. As a result of disruption of the cells of the root system, the bulb dies and, as a consequence, the formation of bald patches. Based on their shape, bald spots can be round, oval, or have a dotted outline.
Despite the benign course of the disease and the absence of an immediate threat of harm to human health, alopecia areata can cause significant damage to the psychological component. Often people suffering from localized hair loss plunge into prolonged depression and close themselves off from the outside world. Such disorders are especially typical for girls and adolescents, who are most susceptible to criticism of their appearance.
Diagnosis of alopecia areata
First of all, the disease can be diagnosed by an external examination of a person’s hair, and it can be confirmed using a dermatoscope - a powerful magnifying glass combined with a light source.
To clarify the causes of alopecia areata, tests and studies are prescribed:
- A scraping from the scalp, which reveals the presence of fungal infections.
- Determination of the presence of inflammatory processes using general and biochemical blood tests.
- Checking blood for possible infection with HIV infection and syphilis.
- Detection of hormonal disorders based on the results of hormone analysis.
- Carrying out trichoscopy, which helps to evaluate the structure of the hair and dermal cells.
- Spectral research allows you to clarify which vitamins and minerals are missing for proper nutrition of the body.
Treatment of alopecia areata
In most cases, doctors find it difficult to decide on a treatment method for alopecia areata due to the fact that the true causes of the disease are unknown.
Therefore, complex therapy is usually chosen, consisting of the following measures:
- A psychotherapeutic consultation, when the doctor uses questions to find out the psychological factors of the disease, helps to cope with stress and calm down.
- Taking medications in the form of tablets, sprays or ointments.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures: cryomassage, phonophoresis, microcurrent therapy, laser therapy.
Noticeable results from the set of measures appear three months after the start of treatment. In some cases, the hairline is restored on its own without much external intervention. However, sometimes the effect of therapy does not occur, and more complex procedures are required, for example, hair transplantation.
Medical statistics confirm that about 80% of patients with alopecia areata are cured. The hairline is restored in about one year. It is worth keeping in mind that the disease can return: up to 90% of patients note a recurrence of baldness situations.
1. Drug treatment.
In complex therapy, various local and systemic drugs are used. There is no single scheme. How to treat alopecia areata in a particular patient, the doctor decides in each case individually, based on the suspected causes of the pathology.
Here is a list of drugs used:
| Group of drugs | Titles | Mode of application |
| Anti-inflammatory | · "Ibuprofen". · "Indomethacin". · "Diclofenac". · "Piroxicam" | The ointment is applied to the affected area once or twice a day |
| Vitamin complexes | · "Alerana". · "Perfectil". · "MerzBeauty". · "Pantovigar". | Tablets should be taken according to the doses prescribed in the instructions for each drug |
| Sedatives | · "Novopassit". · "Persen". · Motherwort | Taking the medication orally, one or two tablets per day |
| Nootropic | · "Piracetam". · "Nootropil". · "Phenibut" | Administration orally, intramuscularly or intravenously |
| Solutions and sprays | · "Regaine". · "Generolon". · "Minoxidil". · "Dualgen" | Apply to the skin in the area of hair loss once or twice a day |
| Shampoos | · “Fitoval”. · "Alerana". · "Selencin" | Wash your hair with medicinal products as usual, you just need to hold them on damp hair for three to five minutes for effect, and then rinse |
| Metabolic stimulants | · "Solcoseryl". · "Actovegin". "Cerebrolysin" | Use intravenously or orally |
| Corticosteroids | · "Dexamethasone". · "Betamethasone". · "Prednisolone" | The drugs are available in the form of tablets or injections and are used as prescribed by the doctor. Ointments should be applied to the affected area once or twice a day |
2. Treatment of alopecia areata with alternative methods.
To treat alopecia areata, you should consult a trichologist as soon as you notice severe hair loss. It is necessary to undergo tests to more accurately diagnose the disease and identify its causes, so that a specialist can select appropriate medications and refer you for additional procedures. You can get rid of alopecia areata using different techniques. Let's look at them below.
There are a variety of ways to treat alopecia areata, most of which are physical therapy. More radical methods of hair restoration have also been developed, for example, a surgical operation to transplant healthy hair follicles to the area of baldness. This option can be used for androgenic type of alopecia. Viable hair follicles are transferred to the affected area of the head to “wake up” skin cells and start the recovery process. To achieve the goal, you will have to be patient and undergo a long course of treatment. You also need to take into account the risk that after hair transplant surgery, scars may remain on the scalp.
Laser therapy is another well-known treatment for alopecia areata. The beam stimulates skin cells. Under the influence of light, they are activated and begin to function as before the onset of the disease. After several sessions of laser therapy, skin nutrition is restored, hair begins to grow back on areas of baldness.
Recommended articles on the topic:
- Diffuse alopecia in women
- Plasma therapy for the scalp
- Useful vitamins for hair: against hair loss and for growth
Medication methods also help in the fight against thinning hair. Medicines should be purchased only after consultation with a doctor. Taking medications will be effective together with other procedures. Separately, tablets and ointments will have a short-term effect.
You can also say about shampoos and special restorative masks, which are presented in pharmacy chains. These medicinal cosmetics consist of certain components that stimulate the hair follicles. The use of shampoos and masks will only have an effect if alopecia areata is caused by improper hair care, a deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the human diet, or some other reasons.
Mesotherapy is also considered a popular treatment procedure. Its effectiveness is based on the fact that special medicinal substances penetrate into the inner layers of the dermis. This allows you to stimulate capillaries and increase blood flow in the affected area. Blood begins to better supply the cells of the hair follicles, filling them with nutrients.
With the help of mesotherapy you can cope with:
- seborrhea;
- dandruff;
- severe itching;
- androgenic type alopecia areata.
During mesotherapy sessions, the cells of the hair follicles are saturated with essential nutrients faster than when applying ointments and creams used externally. The composition of the injections is selected according to an individual program, that is, the combination of vitamins and minerals will match your condition and help fill deficiencies. Mesotherapy is often used in the treatment of alopecia areata in pregnant women, as it is considered a safe method, but at the same time allows for rapid hair restoration in the affected areas.
After completing the course you can get the following results:
- hair loss will stop;
- natural renewal of hair will be restored;
- by cleaning the vessels and capillaries, blood flow in the skin will increase, which will allow oxygen and nutrients to be delivered to the follicles;
- the skin will look healthy;
- you will get rid of severe itching and dandruff.
3. Treatment of alopecia areata with ampoules.
Effective treatments for alopecia areata include sets of special ampoules. To purchase high-quality drugs, you need to contact only specialized stores and pharmacies, otherwise you may run into a fake. The composition of the ampoules has a high concentration of useful components, which allows you to quickly cope with the problem of hair loss, strengthen it and restore a healthy appearance. Hair follicles receive the necessary microelements, and the deficiency of vitamins and minerals is eliminated. Baldness stops, increased nutrition stimulates hair follicles, and new strands grow.
Each ampoule contains a concentrated therapeutic cocktail of many components. They must be used in accordance with the recommendations of specialists. Alopecia areata resolves by stimulating the hair follicles. However, long-term therapy will be required to completely get rid of baldness. Treatment and hair restoration can take two or three months. This will depend on the severity of the disease. In addition, you will have to use ampoules with the medicine daily.
Necessary prevention
Unfortunately, not all types of alopecia can be prevented. But in some cases, prevention can be a salvation from baldness.
Necessary preventive measures:
normalization of hormonal levels
· stress reduction
· normalization of sleep and rest patterns, proper nutrition
· performing physical exercises that improve blood circulation and lymph flow
· use of high-quality cosmetics
· preventive examinations and exclusion of diseases that indirectly affect the condition of the hair
The Nanoesthetic Center for Medicine and Aesthetic Cosmetology offers a number of procedures that improve the condition and growth of hair.