Small marks in the form of moles and birthmarks sometimes add charm, and sometimes cause a lot of inconvenience to their owners. Unfortunately, not every mole can be removed. And the main difficulty is not the postoperative scar, but safety for human health. The potential danger of a mole is that it can become malignant - evolve into a malignant tumor. And to eliminate the cosmetic effect, the patient is required to undergo several tests to exclude malignant degeneration of the tumor.
Before applying for mole removal, we recommend that you observe it. There are “calm” and “suspicious” moles. Only a specialist can make a final verdict regarding this or that formation, who will direct you to a series of tests and make the correct conclusion. But you can first determine how “calm” an unattractive mole is on your face or body. Our leading specialist Kirill Viktorovich Listratenkov has extensive practical experience in laser surgery, so we will be happy to help you remove your mole painlessly, atraumatically, and of course, safely.
What do we know about moles?
What we have always heard about moles: “Does it bother you? Live in peace, don’t touch your mole!” This advice, which was very common in the past, convinced us that moles that were originally given by nature or that appear over the years should remain inviolable. If you touch it, you won’t be able to avoid trouble. This is partly true - indeed, removing moles can lead to the most dire consequences. But in fairness, it should also be noted that not every mole needs to be removed. The most harmless - flat moles
(pink to dark brown).
Usually they behave “quietly”, do not get injured and do not create inconvenience. The only thing you need to remember is to protect such moles (on open areas of the body) from sunlight. Convex moles
, especially if they are often touched by clothing, need to be treated more carefully. If they are on the back and in other places inaccessible to your view, you should entrust someone close to you with monitoring them. And, of course, if any changes occur—the mole becomes larger, turns from flat to convex, or changes its shape—you should immediately contact a specialist.
Acquired melanocytic nevus (mole) - symptoms and treatment
Depending on the location of melanocytes, three groups of acquired nevi are distinguished:
- Transitional nevi are formed by nests of melanocytes located at the border of the dermis and epidermis. They may be in the form of a spot or slightly raised above the skin. The color varies from light brown to black, and the center of the mole is darker than its edges.
- Complex nevi consist of nests of melanocytes located both at the border of the dermis and epidermis, and in the dermis itself. They are pigmented nodules that rise above the skin at different heights. Their surface can be smooth or spherical, color - from light to dark brown.
- Intradermal nevi occur when nests of melanocytes are located in the dermis. Nevus cells often stop producing melanin, so moles practically do not differ in color from the surrounding skin, but rise above it. They have the shape of a papule, dome or papilloma, their texture is soft and elastic [42].
Acquired nevi can be classified into typical and atypical. Some atypical variants are divided into separate forms: blue nevus, halo nevus, Spitz nevus, eclipse nevus and nevus of the sebaceous glands.
Atypical, or dysplastic nevi are benign acquired melanocytic nevi that have the characteristics of melanoma: asymmetry, irregular borders, heterogeneity of color and a diameter greater than 6 mm.
Atypical nevi are more common when there are a lot of nevi on the body as a whole. Among white-skinned people, atypical nevi occur in 2–10% of the population [22]. As a rule, they appear after puberty [23]. Typically, there are more nevi in areas exposed to sunlight, such as on the torso and legs, and fewer on the chest and buttocks.
Based on their origin, atypical nevi can be divided into two groups:
- Sporadic nevi appear spontaneously under the influence of various external factors leading to mutations in cells. Relatives of patients usually do not have atypical nevi or melanoma.
- Genetically determined nevi (dysplastic nevus syndrome) - occur due to hereditary predisposition. Relatives also have atypical nevi, and there may be cases of melanoma in the family.
Main characteristics of atypical nevi:
- diameter from 0.6 cm;
- irregular outlines with lighter edges;
- the shape is flat, the mole is flush with the surrounding skin;
- the borders are uneven, smoothly blending into the skin;
- the color is heterogeneous, the color intensity can vary from pale brown to black.
An eclipse nevus is a type of complex nevus that is brown in color with a light center and a darker, star-shaped edge. In children, it often develops on the scalp. Despite the heterogeneous color and uneven borders, such nevi are benign. If there are no other warning signs, such as induration and ulceration, then biopsy or removal of such nevi is not necessary [24].
Halo nevus (Sutton's nevus) is a melanocytic nevus surrounded by a symmetrical round or oval halo of depigmentation, i.e., a lighter area of skin. Haloing usually occurs in acquired melanocytic nevi, but can also occur in congenital nevi, blue nevi, Spitz nevus, and melanoma.
Halo nevi occur in almost 5% of white-skinned children aged 6–15 years, most often located on the back [26]. Common in people with vitiligo or relatives with vitiligo. In approximately half of the cases there are multiple nevi (more than 30) [27].
There are four stages of halo nevus development:
I. Pigmented nevus surrounded by a halo of depigmentation.
II. Pink nevus with a halo of depigmentation.
III. Round area of depigmentation without nevus.
IV. Skin of normal color after repigmentation of the halo.
Any of the four clinical stages can last from several months to several years [28]. Up to 10 years can pass between stages I–II and IV.
If the halo nevus has a typical appearance, then a biopsy is not required [29]. Since children with halo nevi usually have many nevi on their entire body, the entire body is examined. This will help identify atypical nevi and determine whether they need to be monitored or biopsied and removed. If there are atypical or concerning signs, a biopsy of the central portion of the nevus is performed. There is no need to remove the halo.
Multiple halo nevi are common among adolescents and young adults. They are rare in middle-aged and older people and may be a manifestation of an immune reaction to cutaneous or ocular melanoma. In this case, a biopsy may be required.
Blue (blue) nevus is a benign growth of dendritic skin melanocytes that actively produce melanin. The blue color is produced when short wavelengths of light are scattered by melanin in the skin, a phenomenon known as the Tyndall effect. Most often, blue nevi appear on the scalp, neck, back of the hands and feet, and in the sacral region.
There are several variants of blue nevi:
- A common blue nevus is a single, dome-shaped, blue or black-blue papule less than 1 cm in diameter. Such nevi often appear during adolescence and are found on the dorsum of the hands and feet.
- A honeycombed blue nevus is a more raised and larger nodule or plaque, measuring more than 1 cm with a smooth or slightly uneven surface. Such nevi can be congenital or acquired; they are most often found on the scalp, face, sacrum and buttocks.
If the blue nevus is stable, then it does not need to be removed. But if it appears suddenly and grows quickly, or a pre-existing nevus increases sharply, then a biopsy is necessary.
Spitz nevi are benign, usually acquired nevi, which are a collection of melanocytes. They most often appear in childhood and are located on the face and legs. Such nevi grow quickly, which often worries patients and parents.
A Spitz nevus is a papule or nodule that is uniformly pink, brown, red, or red-brown in color. Usually symmetrical with a clear outline, less than 1 cm in diameter. The surface may be smooth or warty. Sometimes the nevus includes dark pigment in the form of a star or peripheral stripes.
Pigmented spindle cell nevus of Reed is a variant of Spitz nevus that is common among adolescents and young adults. It often appears on the thighs and has the appearance of a thin papule ranging from dark brown to black in color [30].
A small, stable Spitz nevus with typical features can be observed [31]. Such nevi may shrink or disappear over time [32]. But if the Spitz nevus has atypical signs (size more than 1 cm, asymmetry or ulceration), then it is removed after a biopsy.
A sebaceous nevus is a localized lesion, predominantly consisting of the sebaceous glands. It occurs with equal frequency in men and women, regardless of skin color. It is observed in 0.3% of newborns [15]. Often at birth or in early childhood it appears as a single linear or rounded area with a smooth or velvety surface. It comes in pink, yellow, orange or light brown. Typically found on the scalp or face, extensive lesions are rare.
During adolescence, it becomes warty or nodular and may darken and enlarge. In approximately 1% of cases, such a nevus degenerates into cancer. This almost always occurs after puberty [15].
No independence.
Some people believe that you can remove moles yourself by tying them, for example, with silk thread. This is a deep misconception. Attempts to bandage warts and papillomas with a thin silk thread often only provoke the growth of these formations. Today, there are celandine-based preparations on sale that are intended to eliminate warts. But it is better not to remove moles, papillomas, or warts yourself by any means. Celandine juice is similar in composition to iodine, so prolonged exposure to the drug causes skin burns. Cauterization with iodine is even more dangerous - it is more aggressive than celandine. Trying hard to get rid of papillomas with iodine, you can get scars on the skin. Only a dermatologist can properly remove a mole.
Why can't you remove moles?
It is not recommended to comb, cut or rip off nevi, since damage to a benign mole can lead to infection and the development of a tumor. If this does happen, it is necessary to treat the injury site with an antiseptic and stop the bleeding.
The torn mole should be taken to a histology laboratory for examination. If the mole is only partially damaged, you need to pay attention to whether it has changed its color, shape or size after the injury.
Doctors advise removing nevi if, due to their location, they are susceptible to accidental injury and rubbing, as well as in case of suspected degeneration. It is also possible to remove moles for aesthetic reasons.
Removal methods.
Removal of moles and warts
- Cost: 2,000 rub.
More details
Mole removal can be carried out using a laser, radio wave coagulation or electrical coagulation. These manipulations are performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. The choice of treatment method is determined by the doctor in each specific case. In my opinion, the most effective and painless method is radio wave coagulation. We use this technique in most cases, although in some cases we use excision with conventional surgical instruments followed by suturing. When using radio wave coagulation, tissue damage during material collection will be minimal, blood loss is reduced, and the rehabilitation period is shortened, while, for example, with the laser method, the healing process is extended over a fairly long period. Repeated formations do not appear after removal, but if precautions are not followed by the patient himself, infection may occur.
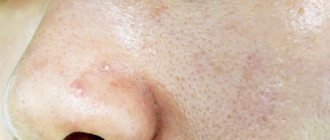
Prices for removing nevi on the nose
Removal of nevi (moles), fibroids in adults and children over 12 years of age
| Delete area | Size | Price, rub |
| Initial appointment with a cosmetologist, consultation free of charge - subject to completion of procedures on the day of application Make an appointment | 1000 0 | |
| Removal on the nose Make an appointment | up to 1 cm. | 2 500 |
| Removal on the nose Make an appointment | more than 1 cm. | 3 000 |
Unattended moles.
Some types of moles can degenerate into one of the most malignant tumors - melanoma (skin cancer). The initial site of formation of most melanomas is congenital pigment spots and warty moles. How does this dangerous development begin?
For example, after damage, a person only notices how the color of the mole begins to change, it enlarges, cracks, turns into an ulcer, and sometimes into a tumor. Therefore, without panicking, pay attention to the above symptoms, especially the progressive enlargement of the mole and change in its color. If all these symptoms occur, immediately rush to the dermatologist. The unfavorable prognosis of melanoma dictates the need for regular monitoring by a doctor. In addition to irritant factors (ultraviolet radiation, trauma), the development of melanoma can also be caused by genetic and endocrine factors. However, in the first place is, of course, excessive exposure to the sun. Ultraviolet radiation in large doses causes irreversible changes in skin cells, greatly increasing the risk of their degeneration. Light-skinned and fair-haired, red-haired people with blue and gray eyes are most susceptible to the mutagenic effects of sunlight. Those at risk also include those who have a lot of freckles, age spots and moles.
How to identify a malignant mole?
A simple reminder called “ACORD of melanoma” will help to identify signs of degeneration of a benign mole:
- A – asymmetry ;
- K – contour (fuzzy, blurry, uneven);
- O – color (any changes);
- P – size (changes in size in adulthood);
- D – dynamics (appearance of crusts, cracks, peeling, bleeding, sudden disappearance of a mole).
The detection of even one of the five signs listed above is a reason for a visit to a dermatologist, who, through a survey and examination, will help make the correct diagnosis.
Melanoma, located at the level of the superficial layers of the skin, is not dangerous and is completely curable, but if it is allowed to grow deeper, tumor cells will spread through the blood and lymph throughout the body, forming metastases in the internal organs. Mortality in such cases reaches 50%.
Dangerous sun.
For each person, the critical duration of exposure to sunlight is highly individual. It’s not easy to determine this line, so it’s better to just remember that prolonged exposure to the sun is harmful to the body. The skin is forced to protect itself from ultraviolet radiation. Excessive tanning means inevitable burns. If you love beach holidays so much that you simply cannot deny yourself this pleasure, at least listen to the following tips. By following these simple recommendations, you will not only improve your health, but also reduce the risk of a dangerous disease.
- Staying in the sun is safe from morning until 10 o'clock, in the evening after 17 o'clock.
- For people with a large number of moles, it is better to reduce their exposure to the sun.
- Try to avoid redness and sunburn on your skin. If this happens, spend 2-3 days in the shade.
- After swimming in the sea, be sure to rinse your skin with fresh water.
- Even young and healthy people can spend no more than one and a half to two hours a day in the sun.
- Taking certain medications increases the skin's sensitivity to light. Please consult your GP before going on holiday.
- Use sunscreen cosmetics: at the beginning of the holiday, the indicator should be maximum, about 40 units.
- Do not use decorative cosmetics, deodorants and perfumes on the beach - they can cause the appearance of age spots on the skin.
Why are hanging moles dangerous?
The main risk of any mole, including hanging ones, is the possibility of its transformation into skin cancer. If a hanging nevus does not cause discomfort and does not change its visual characteristics, most likely it is a benign structure, the degeneration of which into melanoma is unlikely. At the same time, the following manifestations are considered the first signs of malignant transformation:
- Itching, pain, burning in the mole area;
- A noticeable increase in size and change in the shape of the nevus;
- Change in density and surface of the formation to the touch;
- Color transformations of a hanging mole;
- Bleeding and the appearance of ulcerations on its surface.
Having noticed any signs of transformation, it is necessary to contact a dermatologist or oncologist as soon as possible, who, based on a visual examination and diagnostic measures, will determine the level of danger and method of therapy.
Cryodestructive method for raised moles
This technique is based on exposing mole tissue to extremely low temperatures. The procedure is quite simple; it involves touching the mole with a medical instrument or a regular cotton swab dipped in liquefied nitrogen. When this touch occurs, the cells freeze. This leads to their rupture as a result of the expansion of water freezing in them. After these manipulations, their life activity becomes impossible, and they die. After the procedure, a patch of healthy skin remains at the site of the mole without noticeable traces of intervention.
The cryodestruction session is short - just a few minutes, after which the patient is sent home. When removing large nevi, the procedure can be painful and require the use of an anesthetic.
What if a mole appears under the nose?
No one would dare to call the owner of a mole located under the nose (regardless of whether it is on the right or left side) frivolous. This person is very wise and experienced, consistent and fearless.
People with a mark under their nose give the impression of being smart and reliable - those around them trust them, turn to them for advice and help, because they are sure that their secrets will remain secret.
Those with a mole under the nose make excellent lawyers. They are suitable for professions that require resourcefulness, calmness, and erudition.
Such people make excellent family men and caring parents. However, they don't let one area of their life overshadow everything else. For example, women with a mole perfectly combine both family life and career development.
Contacting specialists
Doctor of Medical Sciences, famous surgeon Elena Vladimirovna Salyamkina offers laser removal of moles in a high-tech medical office. Laser removal is the optimal procedure; it is completely painless and therefore does not require anesthesia. For some, the mole will go away after the first procedure; people with bright pigmentation will have to resort to several sessions. Within 1-2 weeks, the skin at the site of the removed mole will return to its normal color. During this period, you will need to take care of this area, avoid direct sunlight, and also avoid injuring the skin. Laser removal has no age-related contraindications, with the exception of children under 5 years of age. Almost all moles are most successfully removed by a laser procedure.
The magical power of a mole
Moles can appear on a variety of areas of the skin, even on the heels and inside of the cheek. It is believed that each mark performs its own unique function, which affects a person’s life. For example, a mole on the nose promises its owner incredible luck and endless success. A mole on the tip of the nose is considered a doubly lucky sign; most of these people are very open to communication and always have a positive attitude. A mole on the right nose is a sign of exposure to excitement, and a mole on the left nose, on the contrary, indicates that a person is in complete control of his emotions and desires. However, such a label also has a downside. For women, it characterizes frivolity, and men with a mole on the nose rarely sit still, as a result of which they do not always achieve high positions and are good family men.
Surgical excision
Surgical excision of a mole is used quite rarely, since there is a high risk of complications such as infection of the postoperative wound in the postoperative period, as well as hemorrhage. In addition, when moles are localized on the face, surgical removal is accompanied by the formation of scars and cicatricial changes, which is extremely undesirable for this area (especially in women). In the surgical treatment of nevi, infiltration anesthesia is used, which is administered to the patient after a preliminary test for anesthetic. After the operation there is a long period of rehabilitation. The use of this method is indicated in the presence of large nevi.
Radio wave removal of convex moles
This technique is based on the use of high-frequency waves, which, by causing the cells of moles to warm up, actually cut them off from the skin. As with laser removal, during this procedure the blood vessels are sealed, which ensures the absence of bleeding both during the removal of the mole and during the process of tissue regeneration. At the same time, the wound is disinfected and gently cauterized, which significantly accelerates the healing of the postoperative wound. As for the disadvantages, the main one is considered to be the high probability of burns to the skin surrounding the mole if it is accidentally affected. It is not uncommon for patients to experience scarring from thermal injury. It is worth saying that this rarely happens in high-level clinics, where experienced doctors work, therefore, when it becomes necessary to extract convex tumors using this method, it is better to choose a trusted medical center.
Contraindications
Hanging moles are not recommended to be removed in the following cases:
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Acute infectious and inflammatory processes in the body.
- Pregnancy and lactation period.
- A decrease in the body’s protective properties as a result of surgical interventions undergone in recent months.
- Skin damage in the area of intervention.
Mole removal is not recommended during menstruation and at high body temperature. If there are relative contraindications, the doctor will suggest postponing the procedure for a while until the body recovers and is ready for outside intervention.
Laser therapy to remove moles
Today, this procedure is most in demand due to the large number of advantages: the absence of marks on the skin, bleeding, and the risk of infection in the postoperative period. One cannot fail to note the rapid recovery, which is not available for most procedures for removing the skin defects in question.
During the procedure, the laser beam acts exclusively on the tissue of the mole, which guarantees maximum accuracy. Healthy skin tissue is not affected, even if the CO2 laser light reaches it. Under the influence of the laser, the cells in the mole warm up to a temperature of 70-80 °C, which leads to their peculiar evaporation on the upper layers of the nevus. Evaporation is carried out layer by layer until the laser beam reaches the lower layers of the mole and eliminates it completely.
The only disadvantage of this method is the fact that the removal of large convex nevi sometimes requires several sessions, which means that the patient will have to visit the operating room more than once, and he will see the result only months after the start of therapy.
Reasons for the formation of moles on the face
So, first, let's figure out what classical medicine and folk remedies are, and whether it is possible to cure moles yourself.
Moles - or nevi, as they are also called, have a large number of types, but the mechanism of their formation involves one of the factors provided below.
Hormonal surges in the human body
A large number of various types of neoplasms on the skin are formed in adolescents during puberty, during pregnancy or menopause in women, as well as after taking medications that contain hormones.
To prevent this formation, it is recommended to visit a doctor in advance, namely an endocrinologist, so that he can prescribe you a special course of medication. This course can somewhat smooth out the upcoming imbalance of hormones in the human body.
Diseases of internal organs
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (especially the pancreas) and cardiovascular system can cause the appearance of red moles ( nevi ) on the skin.
Such moles pose absolutely no threat to a person and his body, because they do not know how to degenerate into malignant tumors.
Heredity factor
If parents have a huge number of moles all over their body, then their child will receive the same increased tendency to display moles at certain moments or throughout their life, and they can also be caused by hormonal imbalances.
Special large moles-marks can also be inherited, but in general they are not dangerous.
Viral infection
When the papillomavirus enters the human body, completely different nevi can form on the human body. If this is your situation, then it requires immediate treatment, but first the disease must be confirmed using a laboratory test.
Radiation from the sun
Almost any person who really likes to sunbathe in the sun can find a huge number of moles on their body, this also applies to lovers of solariums.
Often, such nevi form in areas that are constantly exposed to ultraviolet radiation, namely on the face, back, arms and chest.
Other factors: bites of various insects, severe stress, injury to a mole.