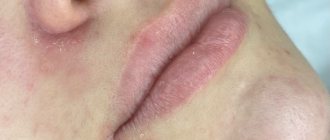
Actinic keratosis is a manifestation of sun damage to the skin. It is manifested by the formation of rough plaques covered with multiple scales. Such plaques usually appear on areas of the skin that are constantly exposed to direct sunlight.
Rice. 1a. Actinic keratosis
Rice. 1b. Dermoscopy of actinic keratosis
Most often, lesions are found on the face, lips, eyelids, hands, forearms, head and neck. Keratosis progresses slowly over the years without causing significant discomfort. The first foci of keratosis can be noticed after 40 years. The danger of actinic keratosis is that it is a precancerous disease. The likelihood of developing a skin cancer against this background is very high. Actinic keratosis can be treated by reducing your skin's exposure to direct sunlight, avoiding it, or using sunscreen.
Symptoms of actinic keratosis:
- Rough, rough scaly plaques up to 2.5 cm in diameter;
- Plaques are usually flat or slightly raised above the skin;
- Sometimes the plaques can resemble a wart;
- The color of the plaque can range from red, brown to pink;
- There is itching and burning at the site of the keratotic lesion.
Actinic keratosis lesions are usually located on exposed areas of the skin. Since only a specialist can distinguish actinic keratosis from skin cancer, it is better to immediately consult a doctor if such changes appear.
Rice. 2. Actinic keratosis occurs as a result of many years of sun exposure.
Causes of foot hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis of the feet is a corns that occurs due to the growth of the stratum corneum to 1 cm or more. This disease can also have complications, which manifest themselves in the form of calluses (soft or hard), ulcers due to excessive pressure on the foot, as well as hemorrhages. All this does not pose any threat to human health, but is an unpleasant cosmetic defect that interferes with normal movement. In order to get rid of it, various measures are taken. Most often, the pathology appears in those who suffer from diabetes, so in this case, in addition to procedures aimed at eliminating external symptoms, treatment of the disease itself is required.
Often, with hyperkeratosis of the feet, cracks appear, which bring the patient quite severe discomfort. However, this phenomenon is not necessarily associated with hardening of the stratum corneum of the skin, since the cause may simply be poor foot care.
Hyperkeratosis can be divided into the following groups according to the clinical picture:
- Follicular hyperkeratosis.
In this case, the disease appears due to a lack of vitamin A in the body and poor hygiene. Due to the stratum corneum, the hair follicles become clogged, which ultimately leads to the formation of small pimples.
The most common places for this form of pathology to appear are the hips, elbows, buttocks and knees.
If treatment is not started in a timely manner or is not given, the disease may spread further and there will be more acne. This form of the disease can often be found in children, and it most often affects the arms, legs, and face.
Recommended articles on the topic:
- How to massage the abdomen for weight loss: different techniques for health and beauty
- Stone massage: description, benefits, methods
- MRI of three parts of the spine: when is it necessary and what are the features of the procedure
- Warty hyperkeratosis.
In this case, the disease manifests itself in the form of yellow formations resembling warts. The main location is the feet and palms.
Warty hyperkeratosis is most often observed due to insufficient keratin production or excessive stress on the feet.
- Diffuse hyperkeratosis.
The main symptom of this type of hyperkeratosis is the presence of large flaky areas of the skin. It can be observed on the elbows, head, arms, face, legs, etc. There are cases when the disease affects all the skin on the human body.
- Lenticular hyperkeratosis.
This type of disease most often affects adult men. It practically never occurs in women.
An examination is sufficient to diagnose the disease. Large brown or yellow papules (0.1–0.5 cm) can be observed on the skin. The main sites of injury are the legs and thighs. If left untreated, hyperkeratosis can spread to the oral mucosa and ears.
Regardless of the form of the disease, they most often appear due to problems with keratin synthesis.
The reasons for the development of hyperkeratosis of the feet (photo above) may be different, but they are all divided into external and internal.
The development of pathology, which is the growth of the stratum corneum, is influenced by:
- Exogenous factors (external).
Prolonged stress on certain areas of the foot can lead to illness. The fact is that with constant pressure, accelerated reproduction of germ cells begins. When a person is in good health, the renewal of the upper layer of the epidermis occurs methodically, that is, the old one peels off and a new one is formed. But when cell division begins too quickly, this process is disrupted, since the surface layer does not have time to peel off, and the stratum corneum continues to grow, which ultimately leads to hyperkeratosis.
Wearing shoes that don't fit is also a common external factor, which becomes the cause of this pathology. Moreover, pressure on the sole is exerted not only by very tight or narrow shoes, but also by shoes that are too loose and worn out. The fact is that in such shoes there is no necessary fixation of the foot, which leads to friction and increased load on the foot, and then to a pathological change.
An equally common external factor is large body weight or high stature, which also contributes to excess pressure on the lower limbs. The cause of hyperkeratosis can also be a congenital foot deformity (in the form of clubfoot or flat feet) or acquired (surgeries, injuries). Load in excess of the physiological norm placed on some areas leads to increased pressure on them.
- Endogenous factors (internal).
Hyperkeratosis occurs quite often due to diseases associated with the skin or endocrine system. When a person has diabetes, the body begins to have problems with carbohydrate metabolism. As a result, the sensitivity of the legs (pain and tactile) changes, tissue trophism and blood circulation are disrupted, the dermis dries, ulcers appear and other factors that can lead to the development of hyperkeratosis.
Problems associated with the skin, for example, ichthyosis, psoriasis, palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK), complications with keratin synthesis (congenital) also often cause this defect.
The likelihood of the onset of the disease and its subsequent progression increases several times if a combination of external and internal factors occurs. If a person suffering from diabetes wears too tight shoes, then the prognosis for the hard stratum corneum (HSC) will be completely unfavorable for him.
How does hyperkeratosis of the skin of the feet manifest?
Symptoms of the disease may vary depending on its form and severity.
Most often a person experiences:
- roughening of the skin;
- peeling;
- corns;
- dry skin;
- decreased elasticity;
- change in color of the dermis in the affected areas.
It must be remembered that if the disease is neglected, it can lead to quite deep cracks in the feet, pain and bleeding. In addition, in such cases, the risk of infection and inflammation increases, since an open wound is formed in the areas of cracking.
The most common complication of hyperkeratosis is calluses, which can be of the following types:
- Core callus.
This type of neoplasm from the dry stratum corneum occurs when connective tissue begins to grow in places where this should not happen.
A callus is called that because it has the appearance of a growth that, like a spike or rod, penetrates into the deep layers of the skin. The place of localization, as a rule, is either the sole of the foot or the area between the toes. Such calluses cause a person quite severe pain and are dangerous.
- Soft callus.
The appearance of soft type defects occurs when mechanical stress is supplemented by high humidity. Such neoplasms are considered a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic microorganisms. Like cracks, they become a hotbed of fungal infections.
- Subungual hyperkeratosis.
This type of pathology is called onychogryphosis and is the growth of rough tissue under the nail plate.
- Fibrous callus.
With excessive loads on the foot and constant friction, compression of the nerve endings occurs, accompanied by pain. This type of complication is the most severe with hyperkeratosis, since a person is not able to wear shoes, because it gives him severe discomfort and burning.
How to treat foot hyperkeratosis
Therapy for hyperkeratosis is always complex, using medications and traditional medicine.
Which treatment method to choose depends mainly on the cause of the disease. If a person has diseases of internal organs, then he needs to consult such specialists as a dermatologist, endocrinologist, phlebologist, or orthopedist. As for the feet, problems related to them are dealt with by a podiatrist. After examination and diagnostic measures, the doctor prescribes an effective method of therapy to the patient.
Treatment of hyperkeratosis of the skin of the feet at home.
A person diagnosed with Hyperkeratosis needs to pay more attention to their feet and provide them with careful care.
With this disease, skin softening medications and too frequent hygiene procedures are unacceptable. An effective method in the fight against hyperkeratosis of the feet is the use of traditional medicine based on oils of mountain pine, lavender, and rosemary. To achieve a positive result, the following set of procedures is suitable: medicine is applied at night, a special tonic or lotion is applied in the morning, and all this is supplemented with foot baths once or twice a week.
To soften the rough layer of dermis, you can add sea salt to the bath.
Soda has a similar effect. Additionally, you can use essential oils, for example, peach or tea tree, which have a healing effect on cracks and also soften the dry stratum corneum.
There is nothing complicated about preparing a medicinal composition. Although it may not be able to overcome the cause of hyperkeratosis, it will relieve itching, pain and other symptoms that cause discomfort to a person.
We recommend
Anti-wrinkle facial massage: 10 effective techniques Read more
- Potato compress.
Prepare potato pulp by grinding the pre-peeled tubers on a fine grater. Then you should place it on gauze and apply it to the problem area for 60 minutes, then change it to a fresh mixture. This procedure is repeated three times in a row. In order for maximum effectiveness, compresses should be done every day.
- Onion peel tincture.
The solution is prepared as follows: pour the husk (1 glass) with vinegar (150 ml) and place in a dark place for two weeks. After this, you need to take it out and strain.
Gauze soaked in onion tincture is applied to the affected areas for 30–60 minutes. However, this method is unacceptable if there are cracks in the feet.
- Agave juice.
Aloe is used to treat many diseases, including foot hyperkeratosis.
In the case of this disease, agave is used as follows:
- Cut off the leaves that are located at the very bottom of the plant.
- Wrap them in cotton cloth.
- Place in the refrigerator for three days.
- Next, cut the leaves into thin slices.
- Apply to the affected areas and wrap with a bandage overnight.
- Remove the compress in the morning.
- Treat your feet with a weak solution of alcohol (salicylic acid).
The following method is no less effective: mix eucalyptus and castor oil with aloe juice in a 1:1:1 ratio. Apply the resulting mixture to problem areas, wrap them in plastic and put on socks.
There are certain requirements for the drugs used to treat foot hyperkeratosis. They should moisturize the skin, since dryness is quite common in this pathology, and at the same time have a pronounced keratolytic effect. For hyperkeratosis of the feet, treatment with ointments containing urea, which is included in most moisturizing preparations, is indicated.
This substance has been used for about 100 years and is very effective, especially in the field of dermatology. Depending on the concentration, urea can be used to treat wounds, treat increased dryness, hyperkeratosis, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, keratosis, eczema, ichthyosis, keratoderma, keratosis Pilaris, ingrown and traumatic nails.
For the treatment of inflammatory dermatoses, 2–10% urea is used, and 40% or more is part of complex therapy together with antifungal medications.
At home, you need to ensure proper hygienic foot care, which includes removing the stratum corneum using pumice. However, this must be done in such a way as not to affect healthy layers:
- You should use a pumice stone every day after steaming your feet. This will stop the thickening of the epidermis. After each procedure, the instrument must be thoroughly rinsed and dried.
- After this, using a file or scrubs purchased in a store, the problem areas and heels in general are polished. The use of these tools is not mandatory, but they will achieve better results.
- Finally, the feet should be treated with a nourishing cream designed specifically for feet. For maximum effect, it is better to do this before going to bed and not get up after at least half an hour.
Thanks to pumice and its daily use, you can control the thickness of the epidermis and prevent the growth of the stratum corneum. In order to prevent the development of hyperkeratosis, it is enough to run it a couple of times over the entire foot. Pumice should only be used on pre-washed feet. However, the skin should not be allowed to dry completely; the surface should be damp.
If you follow all the rules regarding foot care at home indicated above, you can prevent the appearance of hyperkeratosis, and if it already exists, then alleviate the symptoms accompanying it.
Treatment of hyperkeratosis of the skin of the feet in the podiatrist's office.
As mentioned above, foot problems are dealt with by a podiatrist; he is the one who will determine the causes and prescribe treatment for foot hyperkeratosis. Today, there is a treatment regimen for this disease that has already been proven by many years of practice, and it includes several stages: softening the stratum corneum, its removal, and skin resurfacing.
In order to soften the hard stratum corneum (stratum corneum), several methods are used. Water in its pure form or with the addition of flavors and salts is a classic remedy. However, chemical solutions, foaming preparations and gels with a softening and disinfecting effect are often used, which are highly effective and cost-effective.
To remove iron ore, the doctor uses a scalpel or removable blades of different sizes. Moreover, all instruments are disposable. Areas of skin on the soles of the feet, on the phalangeal joints and between the toes, affected by hyperkeratosis, look like grains of rice or narrow ribbons. To clean them from the stratum corneum, the specialist uses hollow blades.
Removal of rough skin is done very carefully so as not to touch the healthy pink dermis in the process. If the procedure is carried out correctly, the iron ore tissue is completely removed without damaging the soft tissue.
At the end of the session, the surface is polished using files or special devices with disposable ceramic attachments. The latter option is more effective, faster and more hygienic.
Treatment of hyperkeratosis of the skin of the feet with medications.
Patients with foot hyperkeratosis are usually prescribed drugs that accelerate the rejection of dead skin flakes and ensure tissue regeneration at the cellular level. These are products from the group of retinoids and those that contain vitamin D. Next we will talk about the most effective and popular medications.
- "Neotigazon".
This drug from the group of retinoids normalizes the regeneration of skin tissue. It contains vitamin A. Contraindications to the use of this product are liver and kidney failure, pregnancy, allergic reaction, and excessive amounts of vitamin A in the body.
You must strictly adhere to the instructions regarding the rules of administration and dosage. The drug is prescribed in courses of two to three months, 0.5–1 mg per 1 kg of weight every day.
An overdose of a drug can cause the following symptoms:
- dry lips or mucous membranes, as well as their inflammation;
- constant feeling of thirst;
- hair loss (after the drug is completed, the symptom goes away);
- inflammation of the cuticle.
In addition, people suffering from alcoholism, diabetes, obesity and some other diseases may experience an increase in blood cholesterol while taking the drug.
- "Calcipotriol".
This drug is an analogue of vitamin D, but only of the synthetic type. Its action is aimed at slowing down the synthesis of keratinocytes. It is prescribed to patients with hyperkeratosis of the feet and nails to treat the affected areas.
The procedures must be performed twice a day, and one dose should not exceed 15 g. If we talk about the weekly norm, then this is no more than 100 g. Treatment is carried out in a course lasting 6–8 weeks, but the result is noticeable after 14 days.
You need to be careful because when using the drug in excess of the indicated dosage, hypercalcemia may develop.
Contraindications in this case are age under 18 years and pregnancy. Some people may experience skin irritation at the application sites.
- Thioctic acid.
The drug is part of a group of drugs intended to normalize metabolic processes in the body. Thioctic acid, which is similar in properties to lipoic acid, allows you to restore the balance of carbohydrates and fats in the body.
This drug is contraindicated if the patient has the following diseases:
- allergic reaction to the drug;
- duodenal or gastric ulcer;
- convulsions;
- gastritis;
- diabetes.
This drug should not be used for the treatment of hyperkeratosis of the feet by women who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or children under six years of age.
If you do not comply with the dosage, that is, exceed it, side effects may appear in the form of the following symptoms:
- skin rashes;
- feeling of nausea;
- vomit;
- change in taste sensations;
- itching of the skin;
- diarrhea;
- headache;
- dyspnea;
- shock;
- hemolysis;
- eczema;
- stomach ache.
Taking the drug with alcohol is unacceptable, otherwise severe intoxication of the body is possible. It must be borne in mind that throughout the entire course of the drug you need to constantly monitor the level of glucose in the blood. Since thioctic acid is aimed at reducing it, there is a possibility of developing hypoglycemia.
We recommend
How to get rid of blackheads: the most effective methods Read more
As for the dosage and duration of use, they are selected individually for each patient, taking into account his state of health.
For minor lesions of the feet with hyperkeratosis, a fairly effective treatment is the use of fatty ointments.
These drugs contain the following active substances:
- panthenol;
- urea;
- lactic and salicylic acid;
- corticosteroids.
With their help, the hard stratum corneum is softened and the skin is moisturized.
- "Belosalik."
This is a fairly effective remedy in the fight against hyperkeratosis of the feet, since it relieves inflammation well and has keratolytic properties. It should be used twice a day by applying a thin layer of ointment to the affected areas. If the disease is at an early stage, then just a few applications will be enough. If it has gone far, you will have to undergo a course of treatment that lasts one month.
- "Solcoseryl".
Thanks to its softening effect, the product prevents the formation of cracks. In addition, it also has antiseptic properties due to the presence of salicylic acid in the composition, and urea helps soften iron ore.
If long-term treatment is required, it is better to use Solcokerasal, since it does not contain steroids.
- Hydrocortisone ointment.
One of the most inexpensive drugs for the treatment of hyperkeratosis of the feet is considered to be “Hydrocortisone”. It allows you to relieve inflammation and irritation, as well as normalize the regeneration of epithelial tissue. The glucocorticosteroids it contains begin to act quite quickly, but their effect does not last long. Most often, this ointment for hyperkeratosis of the feet is prescribed in combination with other drugs.
Apply the product in a circular motion without effort twice a day. The duration of use depends on how far the disease has progressed.
Hardware treatment of foot hyperkeratosis.
If symptoms of foot hyperkeratosis appear, you should consult a podiatrist. After the examination is completed, the specialist will prescribe the necessary tests and then make a final diagnosis.
Treatment of hyperkeratosis of the feet is as follows:
- Using chemical compounds, which can be in the form of gels or ointments, the doctor softens the hard stratum corneum.
- Using a blade or scalpel, the specialist removes the skin that was treated at the previous stage. This is done as carefully as possible so that the soft tissues are not affected, that is, to the “fresh” epidermis.
- Finally, grinding is carried out using files or a device with ceramic attachments.
This method of treatment is considered classic, however, in addition to it, there are more modern methods of combating foot hyperkeratosis, which involve the use of hardware technologies.
- Using a laser, the stratum corneum is dried out, leaving a small scar in its place.
- When using liquid nitrogen, single lesions affected by hyperkeratosis are frozen.
- For small keratomas, excision using an electric knife is considered a less traumatic method compared to the traditional one.
- The radiosurgical method allows you to get rid of keratomas without leaving scars, and involves the use of pulses of a certain frequency.
- A pedicure, performed at an appointment with a podiatrist, consists of medical grinding of the stratum corneum of the skin using devices with high-speed cutters and burs.
- Elimination of manifestations of hyperkeratosis of the feet by bactericidal action. When ulcers or cracks form, photodynamic therapy is performed, which consists of a targeted effect on individual areas of the skin with irradiation with a simultaneous antimicrobial effect. In this case, if we compare this method of therapy with antibiotics, there are completely no side effects.
Only the attending physician can select the most effective treatment option for foot hyperkeratosis. It should be taken into account that any hardware technique has side effects and contraindications.
Risk factors:
- Age over 40 years;
- Living in hot countries;
- Frequent tanning and sunburn;
- Light skin type, blond or red hair, blue or green eyes;
- Previous actinic keratosis or skin cancer;
- Weak immune system due to chemotherapy, leukemia, AIDS, or previous organ transplantation.
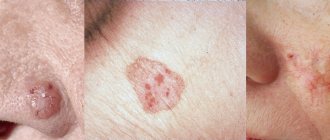
Rice. 3a. Actinic keratosis capitis
Rice. 3b. Actinic keratosis on the nose
Rice. 3c. Actinic keratosis on the face
Rice. 3g. Actinic keratosis on the forehead
Rice. 3d. Actinic keratosis at the corner of the eye
Leather and its features
Human skin is a multifunctional organ, the condition of which is in close relationship with other organs and systems of the body. It has 3 layers, the thickness of which differs in different parts of the body. This:
- epidermis;
- dermis;
- subcutaneous fat tissue.
The epidermis is the top and thinnest layer of the skin. Moreover, it itself has a multilayer structure and is formed:
- stratum corneum;
- glassy or shiny layer (present only in the skin of the palms and soles);
- granular layer;
- spinous layer;
- basal layer.
The epidermis is 85% composed of keratinocytes - cells that contain keratin and successively undergo stages of differentiation, shifting from the basal layer to the spinous, granular and gradually losing water, the nucleus and turning into prismatic scales of the stratum corneum. The latter are called corneocytes. At the same time, the epidermis is constantly renewed due to the desquamation of corneocytes of the uppermost stratum corneum and its replacement by other keratinocytes, which also transform over time into corneocytes and are ultimately desquamated.
Thus, the skin is constantly renewed. If this process is disrupted due to the action of certain factors and desquamation slows down with thickening of the granular and stratum corneum of the skin or excessive formation of creatine is observed, hyperkeratosis develops.
Treatment of actinic keratosis
Foci of actinic keratosis must be removed.
Removal can be done in several ways:
- Medicines - Aldara cream, etc.;
- Surgically -
- Cryotherapy. Actinic keratoses can be removed by freezing the lesions with liquid nitrogen.
- Curettage. The surgeon scrapes off the keratosis and treats it with an electrocoagulator. Curettage is carried out after injecting an anesthetic under it.
- Photodynamic therapy. A light-sensitive substance is applied to the keratosis lesion, and then treated with a special light.
- Laser removal. The keratosis lesion is removed with a laser.
Diagnostics
A dermatologist will help you determine what type of tumor it is, as well as select treatment methods. Differential diagnosis is very important - keratoses resemble other skin diseases. For this purpose, the following is carried out: - Visual inspection. — Laboratory studies - histology is carried out during surgical treatment and if there is a possibility of keratoma degeneration. — Instrumental diagnostics – dermatoscopy (examination under magnification), biopsy (sampling of material), ultrasound examination.