Causes Symptoms Diagnostics Treatment Advantages of treatment at MGK Prices
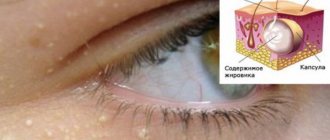
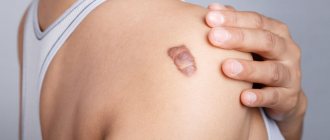
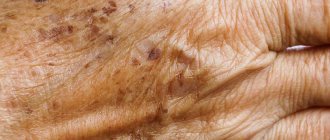
Xanthelasmas of the eyelids look like small single or multiple flat yellowish plaques located at the inner corner of the upper (usually) or lower eyelid. Xanthelasmas are benign formations that are not prone to malignancy; their appearance is associated with general disorders of lipid metabolism.
General information
Xanthelasma (xanthoma) of the skin of the eyelids is a benign formation in the form of a flat, slightly raised yellowish plaque on the skin.
The predominant localization of the pathological formation is the inner corner of the upper eyelid. Formations can be either multiple or single, symmetrical, varying in consistency and shape - soft/hard, even flat or nodular. Eyelid xanthelasmas are a type of xanthomas that appear on the eyelids when they are absent elsewhere on the body. Histologically, eyelid skin xanthoma consists of xanthoma cells (histiocytes), which contain intracellular fat deposits, that is, they contain vacuoles that are filled with partially esterified cholesterol . They are located predominantly in the upper reticular layer of the dermis/perivascular region, less often in the area of the appendages. These formations are not prone to malignant degeneration and do not pose a threat to life.
Xanthelasma of the eyelids (a type of xanthoma) is the most common manifestation of xanthomatosis. It occurs more often in females (1.1%) and much less frequently in males (0.3%) aged 15-75 years with a peak at the age of 30-50 years. Xanthomatosis is a disease characterized by multiple deposits of lipid substances, mainly in the skin (elbows, buttocks, thighs), less often in tendons, bones, dura mater), caused by hyperlipidemia .
Advantages of xanthelasma treatment and prices at MGK
By contacting the Moscow Eye Clinic, you can be assured of a quick and reliable diagnosis of xanthelasma of the eyelid and its effective treatment. Removal of xanthelasma of the eyelid can only be performed by a specialist with appropriate professional skills. To avoid possible complications, this procedure should be entrusted to an experienced doctor. At the Moscow Eye Clinic you will be able to undergo all the necessary tests, based on the results of which the attending physician will recommend you the most effective treatment methods. The Clinic employs specialists with extensive professional experience who enjoy well-deserved respect both among colleagues and among patients.
Removal of xanthelasma of the eyelid is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. During the operation, sterile instruments and disposable consumables are used, which eliminates the risk of infectious complications.
Author:
Yakovleva Yulia Valerievna 5/5 (1 rating)
Honey. portal:
Causes
The development of xanthelasmas is based on a disruption of the process of lipid metabolism with the gradual development of a state of hyperlipidemia, in which the content of lipoproteins of various fractions in the blood significantly increases. They are associated both with genetically determined (primary) disorders - primary hyperlipidemia types 2 and 4, and with fat metabolism disorders, which are based on various types of disorders/diseases - increased blood cholesterol ; hypothyroidism , diabetes mellitus , pancreatitis , cirrhosis , lipoid nephrosis , severe hepatitis .
In some cases, the cause of xanthelasma is age-related changes in the body, taking certain medications ( estrogens , corticosteroids , anabolic steroids , cyclosporine , antihypertensives , retinoids ), as well as abuse of cholesterol/fat-rich foods and alcohol-containing drinks.
Primary forms of xanthomatosis occur predominantly in persons under 40 years of age, including children, while secondary forms occur mainly in older/elderly people. However, xanthomas and xanthelasmas can also appear against the background of a normal lipid profile due to an inflammatory process on the skin, allergic contact dermatitis and erythroderma .
Wide range of results
Polygenic familial combined hyperlipidemia: type IIb
- Mixed genetic and life history causes
- Elevated total cholesterol levels
- Elevated triglyceride levels
- Low HDL (High Density Lipoprotein) Cholesterol
- Elevated LDL cholesterol levels
- LDL may be normal levels but denser and more likely to cause atheroma (sebaceous cyst)
Moderate hypertriglyceridemia
- Often also associated with high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, high insulin levels, high uric acid levels
- This may be due to alcohol or medications such as systemic steroids, isotretinoin, acitretin
- Triglycerides 2_10 mmol/l
- Often associated with low HDL cholesterol levels
Severe hypertriglyceridemia: Types 1 and V
- Mixed genetic and life history causes
- Diabetes
- Familial LPL (lipoprotein lipase) deficiency
- Triglycerides > 10 mmol/l
- Elevated total cholesterol levels
- Raised chylomicrons
- Elevated LDL cholesterol levels
Wide beta hyperlipoproteinemia: type III
- Rare mutation of the apo E gene
- Triglycerides 5-20 mmol/l
- Total cholesterol 7-12 mmol/l
The reason for the appearance of xanthoma with normal levels of fat in the blood is currently unclear.
Symptoms
Xanthelasma is a light orange/yellow plaque that slightly protrudes above the unchanged surface of the skin, with a predominant localization on the upper eyelid (at the border of the fixed/moving part), sometimes at the inner corner of the eye. On palpation, the formation has a soft consistency and is painless. They can be single/multiple, located on one or both eyelids. In some cases, xanthelasmas merge to form a solid yellow stripe with an uneven contour or lumpy elements.
Characterized by slow, steady development, a tendency toward slow fusion of neighboring elements and the absence of spontaneous healing. There are no subjective sensations on the part of the patient. The formation can grow to the size of a large bean, but does not transform into a malignant neoplasm. In cases where xanthelasmas are symptoms of xanthomatosis, they can also be located on the lower eyelid and other parts of the body: on the face, elbow/knee joints, neck, buttocks, etc.
The resulting xanthelasmas do not regress on their own and persist throughout life. In some cases, their number continues to gradually increase. Below is a photo of xanthelasma.
Xanthelasma or flat xanthoma of the eyelids?
A flat xanthoma is a slightly raised fatty formation that can form on any part of the body: face, neck, shoulders, skin between the fingers, palms. Flat xanthoma or xanthelasma differs in location on the body: flat xanthoma located on the eyelids is called xanthelasma.
Enlargement of xanthelasma or flat xanthoma of the eyelids over time can cause discomfort when blinking and therefore needs to be removed. Psychological discomfort is also an indication for removal of eyelid xanthelasma.
Tests and diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by examining the patient based on the location/characteristic appearance, color and consistency of the mass. During examination, diascopy is used - pressing on the neoplasm with a glass slide, which allows you to bleed the formation and clearly determine their yellow color and the contours of the formation. If necessary, a lipid profile study is prescribed: determination of lipoprotein/cholesterol and triglyceride fractions in the blood serum. Differential diagnosis must be carried out with dermal cysts, wen, elastic pseudoxanthoma, syringoma and other skin tumors.
Eruptive xanthoma
- Lesions usually appear as seedlings of small red-yellow papules
- They most often occur on the buttocks, shoulders, arms and legs, but can occur throughout the body
- Rarely the face and inside of the mouth are affected
- Lesions may be tender and usually itchy
- Lesions may resolve spontaneously within a few weeks
- Associated with hypertriglyceridemia (increased levels of triglycerides in the blood) often in patients with diabetes mellitus (diabetes mellitus)
Diet
Diet for vascular atherosclerosis
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 2 months
- Dates: no data
- Cost of products: 1700-1800 rubles. in Week
In the diet it is necessary to exclude/significantly limit:
- Saturated fats (all animal fats, butter, and coconut and palm oils).
- Foods rich in cholesterol (egg yolks, liver, kidneys, butter, high-fat fats, ghee, fish roe, shrimp).
- Simple carbohydrates (various sweets, confectionery, sweet carbonated drinks, ice cream, condensed milk).
Olive oil, legumes and plenty of vegetables (Mediterranean diet) should form the basis of a cholesterol-lowering diet. A diet low in animal fats, simple carbohydrates and high in fiber can normalize slightly elevated lipid levels. To do this, you need mainly dishes from vegetables in any form, fish, legumes and grains. If you are obese or overweight, it is important to reduce your intake of high-calorie foods and at the same time increase physical activity.
Methods for removing xanthelasma
There are many methods for removing formations, such as chemical cauterization, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation, etc. However, these methods do not guarantee the total elimination of xanthelasma and the prevention of relapse, but only stop the development of this disease. The most effective methods are:
- laser removal is a safe method of layer-by-layer removal of tumor tissue using a laser beam, in which only affected tissue is removed and healthy areas of the skin are not damaged, which significantly reduces the duration of the rehabilitation period; after laser removal there are no scars left, another advantage is the immediate cauterization of the affected capillaries;
- surgical excision - removal under local anesthesia using a scalpel; this method is suitable for eliminating large xanthelasmas and involves the application of cosmetic sutures; The duration of the rehabilitation period is determined by the area of the affected tissue.
Xanthelasma
Laser removal of xanthelasma
Consequences and complications
Xanthelasmas are not dangerous because they are a benign formation and there is no possibility of their degeneration into a malignant tumor. They also do not affect vision. Removal of formations is carried out for aesthetic reasons. In isolated cases, especially with injury, inflammation (suppuration) may develop. If we consider the consequences after surgical treatment, we can note frequent relapses of the disease. To avoid such consequences, the patient must strictly follow a diet (vegetable-protein diet) and take medications prescribed by the doctor. Also, a scar (hypertrophic or keloid) may form at the site of surgical removal of the formation. Most often this is noted with a predisposition to the development of keloid scars.
Prices for treatment for xanthelasma
The cost of surgical treatment of xanthelasma starts from 2000 rubles. (in the presence of a single formation up to 5 mm). The final cost of removal will depend on the number and size of formations, as well as the volume of therapeutic and diagnostic procedures performed.
You can find out the cost of a particular procedure by calling (499) 322-36-36 or online using the appropriate form on the website; you can also read the “Prices” section.
Go to the "Prices" section
Make an appointment
List of sources
- Surkichin S.I., Gryazeva N.V. Xanthelasma of the eyelids: management tactics / Medical alphabet 2022 No. 7 /, volume No. 1, pp. 63-64.
- Trukhan D.I., Viktorova I.A., Bagisheva N.V. Skin changes in somatic diseases // International Journal of Applied and Fundamental Research. 2016. No. 8. pp. 736–740.
- Cronenberg G. M. et al. Obesity and lipid metabolism disorders / Translation from English, ed. I. I. Dedova, G. F. Melnichenko. M.: Read Elsiver LLC, 2010. 264 p.
- Vizir V.A., Berezin A.E. Modern approaches to the treatment of hyperlipidemia / Zaporozhye Medical Journal. - 2011. - volume 13, no. 1, pp. 108-117.
- Machekhin V.A. Clinical and histological analysis of tumors of the eye and its protective and auxiliary apparatus // PRACTICAL MEDICINE. - 2012. - T. 2, No. 59. - P. 255-259.
Treatment of xanthelasma of the eyelids
Since xanthelasmas and xanthelomas in most cases accompany lipid metabolism disorders, liver disease, etc., it is imperative to treat the underlying disease. It is recommended to follow a diet limiting the consumption of animal fats and replacing them with vegetable fats. If hypercholesterolemia is detected, drugs that normalize lipid metabolism (statins, lipoic acid, berlition) are prescribed. The use of drugs that normalize liver function (choleretic agents, Essentiale, multivitamins) is indicated.
There is no drug treatment for xanthelasma of the eyelid; the formation (at the request of the patient) is removed using a laser, electrocoagulation or surgery. The intervention is performed under local infiltration anesthesia. During removal, a specialist uses tweezers and miniature scissors to separate the base of the plaque, then treats the skin in the wound area with an antiseptic. If the size of the lesion to be removed is not large, the edges of the wound are treated with a solution of iron albuminate, which promotes effective healing. In the case of a more extensive wound surface, its edges are treated with electric current (diathermy) or cosmetic sutures are applied.
How to remove xanthelasmas
As noted earlier, the most atraumatic and safe method of eliminating tumors is laser removal. At the beginning of the session, the affected skin area is treated with an antiseptic; if necessary, if the patient has a low pain threshold, a local anesthetic can be used. Then the doctor begins targeted heat treatment of the plaque, making a sufficient number of “passes” with the laser to completely remove it. Having evaporated the tumor completely, the doctor re-treats the skin with an antiseptic, and the patient can go home.
Contraindications
If you have xanthelasma of the eyelids, you should consult a specialist before removing them with a laser. Laser therapy should absolutely not be carried out if the following disorders are detected in the patient:
- herpetic type skin lesions;
- infectious diseases;
- diabetes mellitus;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- oncological diseases;
- neurological disorders;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system.
It is also not recommended to carry out the procedure during pregnancy and lactation.
During the initial examination, the doctor will reliably assess the patient’s physical capabilities and make a decision on the possibility or impossibility of the operation.