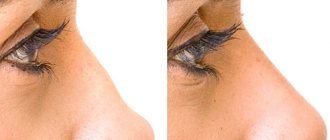
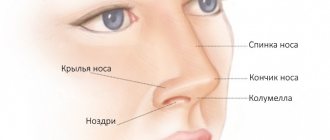
A nasal fracture is a common facial injury, typical causes of which are sports, domestic conflicts, road accidents, and violations of industrial safety regulations.
The treatment scenario is determined by the nature and intensity of the damage: from simple suturing for a non-displaced fracture to a complex surgical operation to reposition bone fragments for a multiple displaced fracture. When the bones have fused and the soft tissues have healed, the consequences of the fracture appear: a crooked nasal septum, distortion of the contours, disruption of the skin texture.
Post-traumatic defects not only spoil a person’s face, but also harm their health. Many chronic pathologies of the ENT organs develop as a result of injury. In such cases, the solution to the problem is plastic surgery.
If you are concerned about the consequences of a recent injury or are interested in the question “How to straighten a long-broken nose?”, make an appointment with a plastic surgeon.
More about the operation
Nasal fractures account for almost 40% of the total number of facial injuries.
The causes of damage can be a traffic accident, a fall, household injuries, some sports, etc. Repositioning is a surgical procedure aimed at restoring the functionality and anatomy of the nose. The doctor compares bone fragments in an anatomically correct position, helping them to heal faster. The method of surgical intervention depends on the type of injury and its severity. Restoring the shape of the organ is carried out in the following ways:
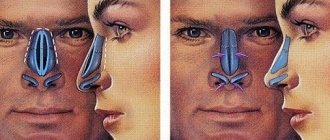
- finger – used when it is necessary to eliminate lateral deformation. The doctor presses with his fingers on the area of asymmetry until there is a click, which is evidence that the bones are in place. A control x-ray examination is performed both before and after the manipulation;
- instrumental - performed using special instruments (Volkov elevators), which the surgeon inserts into the nasal canals and lifts bone fragments with them, restoring the shape of the organ. A control x-ray examination is performed both before and after the manipulation;
- finger-instrumental – is carried out in the presence of retraction of the back of the nose and displacement of the bones to the side. The otolaryngologist expands the nasal passages with special dilators, returning the displaced fragments to their place and fixes them in their normal position with dense turundas (anterior nasal tamponade), which simultaneously perform a hemostatic function. A control x-ray examination is performed both before and after the manipulation.
In cases of severe open fractures or fractures of all lateral cartilages, open reconstruction of the nasal skeleton is used. This is a full-fledged operation that involves cutting tissue, comparing bone fragments under visual control, and applying sutures. To fix the fragments put in place, tamponade, special plate devices, metal, plastic or plaster splints, etc. can be used.
Cost of repositioning nasal bones for fractures
The prices indicated in the price list may differ from the actual prices. Please check the current cost by calling +7 495 104 8605 (24 hours a day) or at the GMS Hospital clinic at the address: Moscow, st. Kalanchevskaya, 45.
| Name | Price |
| Closed reduction of the nasal bones | RUB 47,096 |
| Reposition of a closed fracture of the nasal bones with PSO wound | RUB 36,901 |
| Reposition of an open fracture of the nasal bones with PSO wound | 70,000 rub. |
| Reposition of bone fragments in a closed fracture | RUB 20,978 |
Dear Clients! Each case is individual and the final cost of your treatment can only be found out after an in-person visit to a GMS Hospital doctor. Prices for the most popular services are indicated with a 30% discount, which is valid when paying in cash or by credit card. You can be served under a VHI policy, pay separately for each visit, sign an agreement for an annual medical program, or make a deposit and receive services at a discount. On weekends and holidays, the clinic reserves the right to charge additional payments according to the current price list. Services are provided on the basis of a concluded contract.
Plastic cards MasterCard, VISA, Maestro, MIR are accepted for payment. Contactless payment with Apple Pay, Google Pay and Android Pay cards is also available.
Western standards of treatment (evidence-based medicine)
Continuous staff development
Regular interaction with leading Russian and foreign medical institutions
Modern medical equipment and advanced diagnostic and treatment methods
Unified standard of service
We work around the clock 24/7/365
Make an appointment We will be happy to answer any questions Coordinator Oksana
Why surgery is needed
If reduction is not carried out in a timely manner, serious complications may arise. The most common of them is a deviated nasal septum, which causes:
- disturbances of normal nasal breathing;
- constant inflammation of the mucous membrane and paranasal sinuses (chronic rhinitis, sinusitis);
- disorder of smell perception, up to complete anosmia.
Another common complication is a hematoma of the nasal septum, which in turn leads to narrowing of the nasal canals, difficulty breathing, and in some cases, suppuration or melting of the cartilage.
You need to understand that not a single untreated fracture goes away without a trace. Timely reposition allows not only to avoid such problems, but also to do without subsequent plastic surgery. The intervention lasts only a few minutes, does not require hospitalization, and postoperative recovery is about 2 weeks.
Why you shouldn't ignore the problem
The younger a person is, the faster recovery processes occur in his body. If you do not seek help in a timely manner after a fracture, after 2-3 weeks the bones will not heal properly, and in order to correct the curvature they will have to be broken. And this is more expensive, much more painful and requires much more recovery time than timely intervention. Or suffer from chronic runny nose and breathing problems for the rest of your life.
Particularly dangerous is a septal hematoma. In the absence of timely medical care, suppuration will begin in the damaged area. This will be followed by an abscess and subsequent melting of the cartilage. As a result, the nose will take on an extremely unattractive shape.
If you want to avoid such consequences, the otorhinolaryngologists of Doctor Grishin’s Clinic will be happy to help. Make an appointment and we will get your nose in order quickly and without problems.
Advantages of nasal bone repositioning at GMS Hospital
Experienced otolaryngologists at GMS Hospital perform all types of repositioning of nasal bones in case of a fracture. In our surgical center, such manipulations are carried out using minimally invasive methods, which eliminates surgical scars and scars.
A team of highly specialized specialists works on each clinical situation, which allows us to evaluate it from all sides and select the most optimal method of therapy. And the use of modern diagnostic equipment makes it possible to reliably determine the extent of damage to soft and hard tissues and carry out the procedure with precision.
The manipulation is performed within an hour if there are no contraindications (no severe swelling, concussion, etc.). The surgery center of the GMS clinic operates 24 hours a day. An appointment with an ENT surgeon can be made by phone or online.
Types of nasal reposition
Timely implementation of this simple procedure allows you to avoid many unpleasant consequences (constant inflammation of the mucous membrane, difficulty breathing, dullness of smell). Depending on the degree of damage that may be required during this manipulation, there are:
- closed reduction of the nasal bones after displacement. It involves maintaining the integrity of the skin during the procedure.
- open reduction of the nasal bones , where the doctor makes incisions to provide access to the damaged area.
During the entire rehabilitation period (normally about 6 months) after injury and straightening of the nose, after a fracture or displacement of bones, it is necessary to avoid certain actions:
| Action | Cause |
| Taking warming water and solar treatments (hot bath, sauna, sauna, hot compresses on the face, visiting the beach and solarium). | Increased blood pressure and risk of bleeding. |
| Intense sports, significant physical activity. | Rapid breathing creates stress on the post-traumatic area, causing the risk of rupture of the mucous membrane and bleeding. |
| Inclusion of alcohol in the diet, consumption of spices, spicy and hot dishes. | Increased blood circulation, which threatens hemorrhage. |
| Wearing goggles, heavy respiratory protection, diving masks | The load on the fragile nasal septum threatens repeated fracture or displacement of the bones |
Indications for surgery
Direct indications for surgical manipulation are:
- closed fractures of the nose - the outer integument is not damaged or the damage is expressed by superficial abrasions;
- open fractures, with damage to superficial tissues and bone fragments in the wound;
- fractures with displacement (there is a pronounced deformation of the nasal skeleton, disrupting the asymmetry of the face).
Fractures are often confused with severe bruises. But there are several signs that unconditionally indicate serious organ injury:
- nosebleeds (external, internal);
- pain around the nose, the intensity of which increases when trying to feel the site of injury;
- swelling of the mucous membrane and soft tissues, leading to difficulties with nasal breathing;
- visible change in the shape of the organ (retraction of the back, pressing inward, displacement to the side);
- crepitus of bone fragments (a characteristic crunch is heard when trying to feel the organ) - this symptom is checked only by specialists, otherwise serious damage can be caused.
If you are injured and have even one of the above symptoms, do not delay, go to the doctor immediately.
Preparation, diagnostics
Although the reduction of the bones of the nasal skeleton is an outpatient procedure, it is necessary to prepare for it in advance. Diagnostic measures are aimed at clarifying the nature, type and degree of the fracture, as well as identifying other disorders. Preoperative preparation includes:
- X-ray of the nose and paranasal sinuses;
- rhinoscopy;
- CT, MRI of the skull;
- blood and urine tests;
- consultation with an anesthesiologist.
The procedure is carried out in the first few hours after the injury, before tissue swelling occurs, or after 2-5 days, when the swelling subsides.
If more than 10 days have passed after the injury, it will be much more difficult to realign the nose, and after 3 weeks a callus will begin to form at the fracture site and repositioning can only be done with a complex operation. Therefore, it is extremely important to seek qualified help in a timely manner. An experienced surgeon will perform the procedure according to indications quickly and with minimal discomfort. After a short time, nothing will remind you of the trauma you suffered.
Treatment methods
Immediately after the injury (within 3-4 hours, before the development of soft tissue edema), manual reposition of the bones is performed - manual adjustment of bone fragments under local anesthesia (irrigation of the mucous membrane with lidocaine solution and injection of anesthetic). In case of lateral displacement of the bones, the shape of the nose is restored without the use of instruments. If the back of the nose is damaged, a so-called “elevator” is used, which is inserted into the nasal cavity to lift the sunken bone. Manual repositioning of the nasal bones is quite painful and does not always lead to the desired result. If more than 10 days have passed since the fracture, persistent impairment of respiratory and aesthetic function may occur. In this case, it is recommended to carry out reposition with the help of surgery, since a bone callus has already formed at the fracture site, leading to fusion of the bones. The operation is called rhinoseptoplasty, and if the correction affects only the septum, then septoplasty.
How is the operation performed?
Reduction of the bones of the nasal skeleton is performed in an outpatient operating room using local anesthesia. No hospitalization required. The reduction technique is selected individually, depending on the type of fracture. For closed fractures with bones displaced to the side, the finger method is used - the surgeon presses with his thumbs on the deformed area until a characteristic click is heard, indicating that the fragments have moved into place.
In case of injuries accompanied by retraction of the nasal bridge, reposition is carried out using special instruments. The doctor inserts them into the nasal canals, lifting the displaced bones and returning them to their place. Next, fixes the fragments in the desired position with dense tampons.
For mixed injuries, simultaneously accompanied by displacement of the bones to the side and retraction of the nasal dorsum, the finger-instrumental method is used. If necessary, for better fixation of bone fragments, anterior tamponade is supplemented by applying a pressure bandage or plaster splint to the nose.
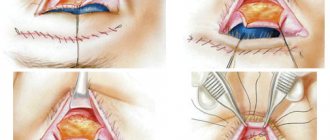
Open fractures have their own characteristics. Since in these cases there is damage to the skin and soft tissues, the doctor first treats the wound with an antiseptic and only then restores the nasal skeleton. GMS Hospital specialists try to preserve all bone fragments, even the smallest ones, during the intervention. This makes it possible to restore the anatomical shape of the organ as much as possible. The procedure ends with suturing. If the wound is dirty or inflamed, additional treatment is prescribed.
Reposition lasts 10-40 minutes (depending on the nature of the fracture and the extent of the intervention); after the manipulation, the patient can immediately go home. However, in the presence of heavy or recurrent bleeding, severe deformation of the nasal skeleton and injuries complicated by infection or inflammation, hospitalization is required.
You have questions? We will be happy to answer any questions Coordinator Tatyana
Injuries
There is no need to dwell on the mechanism of nasal injury - it is understandable. The mildest injuries are bruises and abrasions; they do not carry serious consequences and quickly pass without treatment. Antiseptics should be used to treat abrasions, as abrasions can become inflamed, which can cause infection of the skin and other tissues. For wounds of the external nose, they are treated with antiseptics and sutured.
Stitches are usually left in place for 7 days. For deep wounds with cartilage damage, the cartilage is first sutured, if possible through the perichondrium, and then the skin is sutured. Wound treatment is carried out in a gentle manner, and suturing is carried out in a cosmetic way, in order to maintain a good cosmetic effect in the future.
Fracture of the nasal bones
It occurs rarely in children, especially at an early age. This is due to the fact that the bony pyramid in children is small, and the cerebral part of the skull is more developed than the facial part, so the blow falls on the frontal area, which “protects” the olfactory organ from fracture. But fractures still happen.
Symptoms of a fracture requiring medical intervention:
- deformation of the nose (it may move to the side, the back or one of the slopes may become retracted);
- difficulty in nasal breathing (this can occur due to swelling of the mucous membrane or the formation of a septal hematoma);
- nosebleeds (if it is intense and prolonged, then it needs to stop);
- prolonged nasal discharge (very rare, but after trauma to the nose and facial bones, nasal liquorrhea occurs - the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from the nasal cavity. This occurs due to a fracture of the bottom of the anterior cranial fossa and rupture of the dura mater).
Fractures often occur without displacement, which does not require additional treatment; it is enough to maintain mechanical rest of the damaged organ. Often, a patient consults a doctor when there is severe swelling of the soft tissues, and it becomes difficult to assess the degree of deformation. In such cases, it is recommended to wait until the swelling subsides, about 5-7 days. The deformity is assessed primarily clinically, even if a fracture is clearly identified on an X-ray or CT scan, and the nose is straight, without signs of deformation—reposition is not required.
Repositioning of the nasal bones
What is the time frame for repositioning? There is an early reposition, when swelling of the soft tissues has not had time to develop, this is the first 6-12 hours, and a late one, after the swelling has subsided, on days 5-7. The nasal bones can be realigned in up to three weeks. After reposition, their fixation is required; for this, tamponade is performed and a plaster or adhesive fixing bandage is applied.
The nasal tamponade is left for 3-5 days. Tampons cause noticeable discomfort, but they are still preferable because they support the nasal bones from the inside and also have hemostatic properties. After removing the tampons, you need to be observed by a doctor for some more time, since after tamponade the formation of synechiae (scar adhesions) in the nasal cavity is possible.
Reduction and tamponade are difficult to achieve in children. Due to fear and reluctance to participate in unpleasant procedures, for children, if necessary, the operation is performed under anesthesia.
Subluxation of the quadrangular cartilage
With nasal injuries, subluxation of the quadrangular septal cartilage often occurs. With this injury, as a rule, the lower parts of the cartilage are torn from the bottom of the nasal cavity. This injury is rarely diagnosed because it is not always clear whether the septum was previously deviated. Subluxation of the quadrangular cartilage can occur together with a fracture or independently.
Symptoms of this injury are nosebleeds, septal hematoma, changes in the position of the septum and collumella, and increased mobility of the quadrangular cartilage. The quadrangular cartilage is not reduced because it is difficult to fix. If the septum is deformed and nasal breathing is impaired, septoplasty is performed - surgical correction of the curvature of the nasal septum.
Almost all cases of deviated septum in adults are associated with trauma to the quadrilateral cartilage in childhood. Even minor trauma can result in rupture of the perichondrium or disruption of the connections of the quadrangular cartilage to surrounding structures.
Nosebleed due to injury
Occurs when the vessels of the nasal septum are damaged or when bones are broken with rupture of the skin and mucous membrane in the nasal cavity. Depending on the diameter of the vessel and the clotting ability of the blood, bleeding can be profuse, prolonged and lead to significant blood loss.
The main way to stop nosebleeds is with tamponade for several days. Sometimes, if the source of bleeding is clearly visible, electrocoagulation of the bleeding vessel is possible.
Hematoma of the nasal septum due to trauma
It occurs when blood vessels rupture in the thickness or under the mucous membrane of the septum, and blood, leaving the vascular bed, peeling off the mucous membrane, forms a cavity filled with blood. It may be on one side or both. Hematoma of the septum can accompany a fracture of the nasal bones, subluxation of the quadrangular cartilage, or occur independently.
The main symptom is difficulty in nasal breathing, which does not improve over time or by taking vasoconstrictor drops. Upon examination, a sharp thickening and cyanosis of the septum are determined; when pressing on the mucous membrane, its pliability is determined, with the adoption of the previous form - fluctuation.
Treatment of hematoma
In the first hours, a puncture of the cavity is performed and the blood is aspirated with a syringe, followed by anterior tamponade. After 9-12 hours or later, an incision is made along the front edge of the hematoma and the cavity is cleared of blood, since clots have already formed and it is not possible to aspirate them with a syringe. A graduate is placed into the incision and anterior tamponade is performed.
Subsequently, the nasal cavity is subjected to care several more times. A frequent complication is the development of suppuration of “old” blood with the formation of a septal abscess, so it is recommended to treat all hematomas.
Foreign bodies
Injuries to the olfactory organ can also include foreign bodies. This happens especially often in children, who, while playing, can stick various objects into their noses. Often parents do not know about this, but after some time they notice that the child cannot breathe in one nostril (much less often two) and a liquid with an unpleasant odor is released from it. The depth of the foreign body varies; it can be the vestibule of the nasal cavity or the cavity itself.
Sometimes foreign bodies can remain in the nasal cavity for years, gradually becoming overgrown with mineral layers of mucus, which forms rhinoliths, which can remain there for decades. If a foreign body is suspected, an examination by an ENT doctor is required with endoscopy, and sometimes a computed tomography scan of the paranasal sinuses.
Features of the rehabilitation period
For several days after the intervention, minor pain may occur, which is eliminated with painkillers prescribed by the surgeon. Fixing tampons are removed from the nasal passages after 3-4 days, the plaster is removed 7-14 days after the intervention.
Recovery time depends on the extent of the intervention and the nature of the injury. On average, the recovery period lasts from 3 to 6 weeks. All this time you need to adhere to the following recommendations:
- any load on the organ is eliminated - you cannot wear glasses, sleep on your side or stomach, or touch your nose with your hands from the outside or inside;
- sports and physical activity should be postponed until recovery;
- Any thermal exposure is prohibited - hot baths, visits to saunas, solariums, beaches, baths must be excluded;
- avoiding alcohol, spicy and hot food and drink - this increases blood circulation and can cause bleeding.
Final fusion of the bones usually occurs 2-3 months after the injury.
Recovery period
The duration of rehabilitation depends on the type of fracture - open or closed. But in both cases, the patient will experience pain for the first few days. Swelling and bruising will subside in about two weeks. If a cast was applied, it is also removed 10-12 days after the operation.
Throughout this entire period, the patient is contraindicated in physical activity and visiting places with elevated air temperatures (baths, saunas, etc.), as this may cause the patient to experience nosebleeds and the recovery process will be delayed. It is also necessary to avoid any strain on the nose (do not touch it, do not wear glasses, a mask, etc.).