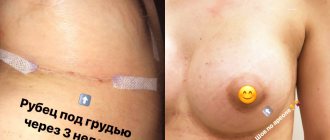
Sometimes situations arise when the threads used to stitch wounds have to be removed independently. In the “Instructions” section we will tell you how to remove sutures at home without problems, pain and complications, and in which cases it is better to consult a specialist.
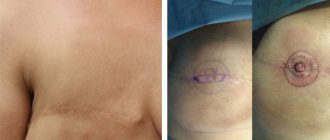
Classification of postoperative sutures
How quickly the sutures heal after surgery largely depends on the nature of their application and the materials used. In this regard, post-surgical procedures are usually classified as follows.
- Bloodless (the edges of the wound are glued together with a special plaster) and bloody (a classic suture that is applied manually with a medical instrument). In turn, the latter are divided into:
- simple knots (applied at a distance of 1–2 cm from each other, after which the knot is tightened until the edges of the incision touch);
- intradermal continuous (considered the most effective, since after their healing there are no traces left);
- mattress (applied after abdominal surgery);
- purse string (used in plastic surgery, as well as in operations to reduce the volume of the stomach);
- entwining (circular sutures that are used to sew together blood vessels and hollow organs).
- Manual (applied with a needle, thread and other special tools) and mechanical (performed with a medical stapler).
- Submersible (applied during operations on internal organs with threads that are absorbable or implanted into living tissue) and removable (they are used to stitch the skin, and after the edges of the wound have fused, the threads are removed).
Absorbable sutures are made in cases where long-term fixation of the edges of the incision is required, for example, when cutting the uterus during a cesarean section. As a rule, they are performed with threads from purified connective tissue, which is subsequently rejected into the organ cavity. To apply removable sutures, threads and other fasteners made of cotton, silk, metal and other non-absorbable materials are used (more than 30 varieties in total).
Hand stitching tools
WHEN DISSORBABLE THREAS ARE USED
This type of medical materials is used when suturing surgical wounds: such manipulations are carried out both on the surface of the skin, during cosmetic operations, and in deep layers of tissue, for example, during transplantation of internal organs.
The main function of such sutures is to maintain internal tissues in a stable condition until they grow together and begin to function without outside support.
It is advisable to use absorbable sutures in cases where the patient does not have the opportunity to return to the surgeon to remove the applied staples, clamps or sutures made of durable materials.
The most common use of absorbable sutures in gynecology is for suturing the perineum, tears in the vagina or cervix during natural childbirth. Studies have shown that during the postpartum period, the threads removed themselves within 2-4 months.
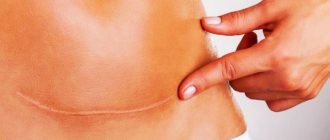
How to care for the suture after surgery?
Once the edges of the incision tighten, there will be no need for additional support. Removal of sutures in the head, face and neck area occurs already on the 5th day after the operation. If they were applied in the area of the torso or limbs, then it will take at least 10 days for the wound to heal. Daily dressings are necessary for the first few days. The patient usually spends this time in the hospital. After discharge, tight bandages are usually no longer needed. But if necessary, you can always change the dressing at the nearest hospital or medical center.
Caring for the suture after surgery consists of daily treating the incision area with an antiseptic and taking medications that accelerate tissue regeneration. All medications for home therapy are used strictly according to the doctor’s recommendation!
Treatment of sutures is usually carried out with ready-made pharmaceutical preparations or homemade antiseptics, such as solutions of iodine, potassium permanganate, brilliant green or hydrogen peroxide. To avoid getting a chemical burn when performing such procedures, the liquid for disinfection should be prepared only according to a prescription issued by a doctor.
To speed up regeneration processes, external agents with wound healing and antibacterial effects are used. These include balsamic liniment (better known as Vishnevsky ointment), levomekol, ichthyol ointment and many others.
Pain of varying intensity after surgery is absolutely normal. If discomfort is severe, analgesics approved by your physician may be used.
How to remove suture threads from a tooth socket
Many people associate the removal of sutures with unpleasant pain. Pain occurs only in people with a low pain threshold, increased sensitivity, or when there is inflammation in the tooth socket. Usually the patient experiences only discomfort.
Stages of removing suture material:
- treating the patient's oral cavity with an antiseptic;
- examination of the mucous membranes for hyperthermia, swelling, suppuration;
- the use of topical anesthesia to prevent even minimal pain;
- cutting the threads with a special dental instrument - the stitches are divided in half, especially in the case of an intermittent suture line;
- removing pieces of thread with tweezers;
- checking the density of the scar and the quality of wound healing.
Next, the patient will be asked to rinse his mouth with an antiseptic composition.
The first three days after the stitches are removed, stiffness of movements and discomfort when opening the mouth are possible.
Additional recommendations for suture care after surgery
In addition to medical procedures, certain lifestyle adjustments are also necessary in the postoperative period. In particular, the following rules must be adhered to:
- Limit physical activity. Any high and medium intensity exercise (running, aerobics, etc.) during this period is strictly contraindicated.
- Avoid heavy lifting. As a rule, a person who has undergone surgery should not lift more than 2–2.5 kg. This rule is especially relevant when caring for a suture on the abdomen after surgery.
- Limit mobility in the waist area (avoid sharp and high-amplitude bends and turns of the body) after abdominal surgery.
- Carry out water procedures with great care. Before the stitches are removed, or better yet, before a scar forms, it is strongly recommended not to wet the wound.
- Avoid any pressure on the wound. When it comes to how to care for a suture after surgery, this is one of the main rules.
- In cases where surgery was performed on an arm or leg, the injured limb should be placed above the level of the heart (for example, placed on a pillow) during sleep. If the wound is above the level of the neck, then it is better to sleep with the head of the bed raised by 45° (two pillows are enough for this).
- During abdominal operations, observe bed rest until the doctor allows you to break it. To avoid bedsores and improve blood circulation, you can perform simple movements such as lifting your limbs and performing light self-massage.
- Strictly follow the diet prescribed by your doctor (especially after abdominal surgery).
- Protect the wound from exposure to direct sunlight. After the tissue has healed and until a full-fledged skin forms in this area, you can use sunscreen.
Operation methods
In the classic case, laparotomy involves the doctor making a vertical incision in the abdominal wall, bypassing, above or below the navel. The length of the incision line depends on the indication for the procedure.
Main types.
- Median laparotomy. It is used more often in gastroenterology. The surgeon gains access to the organs by making a cut with a scalpel in the center of the abdomen from the bottom of the chest to the womb.
- Pararectal laparotomy. It is carried out primarily for the treatment of gynecological pathologies. The specialist begins the operation with a dissection along the outer zone of the rectus abdominal muscle.
Techniques for directing cutting lines:
- transverse;
- longitudinal;
- corner;
- oblique;
- combined.
In gynecology, transverse and longitudinal techniques are used.
There is also exploratory laparotomy, which is used in surgery to open the abdominal cavity in order to diagnose the characteristics of the development of an oncological tumor.
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
Seeking help from a doctor during the healing process of a suture is a completely normal practice, even in the absence of serious problems. And in the event of adverse reactions due to a violation of the treatment regimen or any unforeseen circumstances, it is absolutely impossible to delay it. First of all, it is dangerous to ignore the following symptoms:
- bleeding that cannot be stopped by conventional means;
- high temperature (more than 38 degrees);
- weakness, chills;
- increasing pain or other progressive discomfort that cannot be relieved with medications;
- purulent discharge of a bright yellow or green color with a thick consistency and very often with an unpleasant odor;
- severe redness, swelling, or swelling in the wound area;
- the skin at the site of injury is hard and hot to the touch;
- the appearance of a rash or blisters;
- Suspicion of seam dehiscence.
Precautionary measures
If you feel severe pain or see blood while removing a suture, stop immediately. This means that the wound has not yet healed and it is dangerous to touch it, otherwise the edges will separate. Pain, tissue inflammation, suppuration or increased temperature after removal of the threads are a dangerous sign. It indicates that the tissue has become infected and requires immediate medical attention.
We categorically do not recommend removing stitches at home, especially if you are not confident in your abilities. Contacting specialists Dr. Mos will relieve you of discomfort and unwanted consequences of the procedure.
Author: Ph.D. surgeon Samsonova G.S.
How long does it take for a wound to heal after surgery?
The rate of healing of a postoperative wound depends on many conditions. Among them:
- age;
- body mass;
- state of immunity;
- state of the cardiovascular system.
On average, it takes about 3 months from the moment of surgery to the formation of a scar. Depending on the complexity of the operation and if there are complications, this period may last 12 months. Tissue regeneration takes place in 4 stages.
- Inflammation (5–7 days). The body's standard defense reaction to damage. During this period, there is an increased production of substances that stimulate blood clotting.
- Polyferation (from 10 days to 1 month). At this stage, the formation of young connective (granulation) tissue, penetrated by a dense network of microvessels, occurs. At first it is bright red in color and grainy in consistency, but as the wound heals it becomes pale and smooth, and its bleeding decreases.
- Epithelization (from 1 to 3 months). The connective tissue is finally formed. Skin begins to form at the site of the wound. The number of vessels decreases, a scar forms.
- Scar formation (from 3 to 12 months). Temporary vessels completely disappear. Fibers of collagen and elastin - elements of connective tissue - form the scar.
Suturing the gums after tooth extraction: when required
On the eve of a surgical operation, patients are often interested in whether it is necessary to apply sutures after removing a tooth - wisdom, canine, incisor. There are certain indications for gum suturing:
- Dental implantation. When choosing a one-stage tooth restoration protocol, the patient must undergo two surgical interventions at once. This is tooth extraction and immediate implantation. In order for the dental implant to take root in the bone tissue without any problems, the doctor will apply sutures and leave the implant in the tooth socket.
- Removing eights. Wisdom teeth are characterized by enlarged roots, an uncomfortable position in the jaw row, and difficulty in extraction. When third molars are removed, soft and bone tissues are severely damaged, heavy bleeding begins, and severe pain is possible. To reduce unpleasant consequences, the doctor places a hemostatic sponge in the hole and sutures the gums after tooth extraction.
Sutures are also indicated when there is a threat of severe bleeding, extraction of dystopic and impacted teeth. The manipulation is also performed at the patient’s personal request.
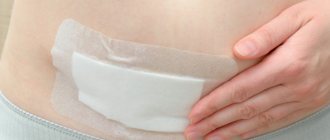
How to care for a wound when the stitches are removed after surgery?
It would be useful to remind you that stitches should only be removed by a specialist - a doctor or nurse. It is strictly forbidden to perform this procedure yourself, due to the high risk of causing infection in the wound or causing bleeding.
Treatment of the incision site after removal of the sutures is carried out using the same means as before. Treatment procedures last until the wound is completely healed. This usually takes about 1 week.
Why did you sew up the hole after tooth extraction?
If stitches were applied after wisdom tooth removal, this will only be beneficial. Repeated studies have proven that a sutured socket is:
- reducing the risk of infection and complications - by 90%;
- rapid stop of bleeding;
- preservation of the blood clot and natural healing of the wound;
- minimal pain after surgery;
- rapid fusion of tissues thanks to sutures.
Sutures are placed on the socket immediately after the removal operation. After which the doctor gives recommendations for accelerated healing and rapid normalization of the general condition.
Professional care for postoperative sutures at Stoletnik MC
If in any matters related to taking care of your own health, you prefer to trust professionals, you are welcome at the medical office. To help those who are not sure how to properly care for a suture after surgery, a wide range of post-operative services is available. Among them:
- dressing large and small;
- removal of stitches up to 5 cm;
- removal of sutures 5–10 cm;
- removal of stitches more than 10 cm;
- sanitation of the wound surface;
- scar excision;
- and much more.
The responsibility and high professionalism of the clinic’s staff is the key to the safe and speedy recovery of our patients. And the affordability of the services provided will eliminate the need to waste time and nerves on trips to the clinic. Sign up for procedures by phone: +7 (8412) 999-395, 76-44-20. We are waiting for you at the address: Penza, st. Chaadaeva, 95 (Shuist microdistrict).
Preparation for laparotomy surgery
Laparotomy is not a full-fledged operation, but is considered a method of gaining access to more serious surgical intervention. The preparatory stage involves following the doctor’s recommendations regarding laparotomy and a specific method for performing a full-fledged operation. The purpose of preparation is to prevent complications that may arise during the operation or after its completion.
Doctors' recommendations.
- 2-3 days before surgery, foods that cause gas, solid foods and alcohol should be excluded from the diet. On the day when the laparotomy is performed, do not eat or drink anything.
- Hygiene procedures are performed the day before or on the day of the operation.
- Stop taking medications that affect blood clotting.
You must inform your surgeon about taking any medications before setting the date for laparotomy. You may need to stop taking medications.
Literature
- Belyaev A.N., Kozlov S.A., Taratykov I.B., Novikov E.I. Patient care in a surgical clinic: textbook. allowance. – Saransk: Mordovian University Publishing House, 2003. – 136 p.
- Buyanov V. M. Egiev V. N. Udotov O. A. Surgical suture. – M.: Antis, 2000. – 92 p.
- Zoltan J. Operating technique and conditions for optimal wound healing. – Budapest: Publishing House of the Academy of Sciences of Hungary, 1983. – 175 p.
- Mironova E. N. Fundamentals of physical rehabilitation. – M.: MOO “Academy of Safety and Survival”, 2016 – 310 p.
- Semenov G.M., Petrishin V.L., Kovshova M.V. Surgical suture - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2001. - 256 p.
Author: Korolev E. S.
Reviewer: reflexologist Kurus A. N.
How is laparotomy performed?
At the Yusupov Hospital, laparotomy surgery is performed in the surgery clinic, where qualified surgeons work. Laparotomy can be performed only after consultation with the attending physician and anesthesiologist, diagnosis, preliminary conservative therapy and preparation.
Laparotomy is performed under local spinal anesthesia (in gynecology) or under general anesthesia. Before the operation begins, the surgeon treats the abdominal area with an antiseptic solution. Then an incision is made with a scalpel into the skin and subcutaneous fat. The surgeon uses a coagulator to seal the vessels and stop bleeding. Using special instruments, the doctor separates the edges of the wound, dissects the aponeurotic layer and peritoneum.
After completing all the manipulations, the surgeon alternately stitches all layers of tissue. To exclude internal bleeding, fluid accumulation or purulent process, drainage is installed. The seam area is treated with an antiseptic. A bandage is applied on top.
The duration of the operation depends on the purpose of its implementation. Laparotomy can last from 30 minutes to 2 hours or more.
Sinus lift
Osteoplasty, which is performed in the lateral parts of the upper jaw, is called sinus lifting. The operation time in professional hands will be about 15 minutes. And here it’s not a matter of haste, but of the level of the specialist. The operation is carried out as follows:
- The membrane of the maxillary sinus is lifted with a special instrument;
- The doctor inserts a previously prepared graft into the newly formed space;
- End of surgery.
After surgery, the volume of the maxillary sinuses decreases slightly in size, but this does not interfere with breathing function. There are two types of sinus lifting: open type and closed type. Open involves cutting and folding back a flap of soft gum tissue, and subsequent drilling of the maxillary sinuses. Finally, stitches are placed on the gums for effective wound healing. The closed sinus lift method is a more gentle method that does not require subsequent stitches. But there is a condition that is important to comply with. The height of the bone must be at least 4 mm at the site proposed for implantation.
Sutures after bone grafting and sinus lifting are always placed tightly and firmly using special threads. They are divided into 2 types:
- Absorbable;
- Non-absorbable.
The first includes the legendary catgut, the sutures of which can remain in the oral cavity for up to 2 weeks. To prevent them from coming undone, they are tied with surgical and conventional knots. It happens that it can cause a local inflammatory reaction, as it is a foreign protein-containing material. But it is better not to use catgut threads if a local inflammatory reaction is possible. For example, this is bone tissue transplantation, the use of membranes that have tissue restoration properties in dental implantology.
Synthetic sutures for bone grafting and sinus lifting are made of Dexon and/or Vicryl. They are easier to use than catgut, but require knowledge in tying surgical knots. Resorption usually occurs after 1 month, they do not cause inflammation, but they need to be removed a maximum of 10 days after surgery.
The non-absorbable material primarily includes silk, which is produced from a protein secreted by the silkworm. This thread is easy to tie, it is strong and pliable, it is better to use surgical knots. But there is also a drawback - such threads often cause inflammation of the oral mucosa. It's all about a foreign protein that causes an inflammatory-allergic reaction. The next type of thread is braided polystyrene thread; its strength is comparable to silk, but does not cause tissue inflammation.
For fixation, a few knots are sufficient, which are tied on opposite sides and supplemented with surgical ones. Such threads are coated with silicone, polybugylate or polytetrafluoroethylene solutions, which reduce inflammatory reactions and give them elasticity. Monofilament sutures are another type of non-absorbable sutures that are a single thread made from polytetrafluoroethylene. They have good mechanical, anti-inflammatory and adaptive properties. They are often used in the application of periodontal membranes. But the ends of the threads must be covered with a bandage, as they have hard ends that can damage the mucous membranes of the lips and cheeks.
How they are treated at the Yusupov Hospital
At the surgery clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, laparotomy is performed by qualified surgeons with many years of experience, which allows us to be confident in the results and the absence of medical errors.
Our advantages:
- use of modern technology and tools;
- use of safe anesthetic drugs;
- high-quality diagnostics;
- 24-hour hospital;
- monitoring the patient’s condition until complete recovery;
- affordable prices.
Laparotomy surgery for diagnostic and treatment purposes at the Yusupov Hospital is performed in modern operating rooms by qualified surgeons with many years of experience. Our specialists are always ready to provide professional assistance at the highest level.
Healing time for external sutures on the perineum
It's no secret that all mothers who have just given birth are interested in the question of how long postpartum sutures last. The healing process is directly related to the size of the wound surface, the correctness of care during the recovery period, the general condition of the woman’s body, and the techniques and materials used when suturing. If self-absorbable threads (natural or synthetic) were used during suturing, healing will take about two weeks, and scar formation when using metal staples or non-absorbable threads takes longer - 15-30 days; in the latter case, the sutures are removed in the maternity hospital before discharge, approximately on the seventh day after birth.
Suture removal technique
Following the correct algorithm for removing sutures and maintaining sanitary conditions allows you not only to avoid infection of the wound, but also to speed up healing. Specialists explain the procedure to the patient before performing it and place him on the couch. The procedure has the following algorithm:
- Removing the protective bandage.
- Inspect the wound and determine the number of stitches to remove.
- Treating the wound with an antiseptic. It must be carried out 2 times to prevent infection, near the wound and inside.
- The suture knot is grabbed with tweezers and lifted.
- The thread that appears after pulling is cut.
- The suture is pulled back with tweezers and the knot is removed.
- Checking the integrity of the skin.
- Treating the wound with an antiseptic.
- The area is covered with a sterile napkin and then fixed with either a bandage or adhesive tape.
This procedure is performed in a hospital, but it is now quite common for postoperative sutures to be removed at home by a specialist.
Types of suture materials and suturing methods in modern medicine
An ideal suture material should have the following characteristics:
Be smooth and glide without causing additional damage. Be elastic, stretchable, without causing compression and tissue necrosis. Be durable and withstand loads. Tie securely in knots. Be biocompatible with body tissues, inert (do not cause tissue irritation), and have low allergenicity. The material should not swell from moisture. The period of destruction (biodegradation) of absorbable materials must coincide with the time of wound healing.
Different suture materials have different qualities. Some of them are advantages, others are disadvantages of the material. For example, smooth threads will be difficult to tighten into a strong knot, and the use of natural materials, so valued in other areas, is often associated with an increased risk of developing infection or allergies. Therefore, the search for the ideal material continues, and so far there are at least 30 thread options, the choice of which depends on specific needs.
Suture materials are divided into synthetic and natural, absorbable and non-absorbable. In addition, materials are manufactured consisting of one thread or several: monofilament or multifilament, twisted, braided, having various coatings.
Non-absorbable materials:
Natural – silk, cotton. Silk is a relatively durable material, thanks to its plasticity it ensures the reliability of knots.
Silk is a conditionally non-absorbable material: over time, its strength decreases, and after about a year the material is absorbed. In addition, silk threads cause a pronounced immune response and can serve as a reservoir of infection in the wound.
Cotton has low strength and is also capable of causing intense inflammatory reactions. Stainless steel threads are durable and produce minimal inflammatory reactions. Used in abdominal surgeries, when suturing the sternum and tendons.
Synthetic non-absorbable materials have the best characteristics. They are more durable and their use causes minimal inflammation. Such threads are used for matching soft tissues, in cardiac and neurosurgery, and ophthalmology.
Absorbable materials:
Natural catgut. The disadvantages of the material include a pronounced tissue reaction, the risk of infection, insufficient strength, inconvenience in use, and the inability to predict the timing of resorption. Therefore, the material is currently practically not used.
Synthetic absorbable materials. Made from degradable biopolymers. They are divided into mono and polyfilament. Much more reliable compared to catgut. They have certain resorption times, which differ for different materials, are quite durable, do not cause significant tissue reactions, and do not slip in the hands. Not used in neuro and cardiac surgery, ophthalmology, in situations where constant strength of sutures is required (for suturing tendons, coronary vessels).
Materials used in osteoplasty
Osteoplasty uses both natural implants and artificial ones (allosynthetic materials). Natural ones include:
- Autogenous grafts are those that were taken from the same patient and transplanted into him. This material survives better than all other grafts, but you need to understand that another operation will be performed to remove tissue from the donor site.
- Allografts are material that has been taken from a donor's dead body for medical purposes. The material is carefully processed, disinfected, it perfectly restores bone tissue and is used in osteoplasty with great success.
- Xenografts are material taken from certain species of animals and corals. It is also carefully processed, sterilized and prepared for further use in invasive dental procedures associated with implantation.
Synthetic (alloplastic) implants are made on the basis of calcium phosphate or hydroxyapatite; they are also widely used by all specialists around the world.
What thread are used to stitch the stitches?
Now there are quite a few types of threads that surgeons use; they can be classified both by brand and by characteristics. There are these types of threads:
- Absorbable. Able to be independently excreted from the body, incapable of rejection. These types of threads are used if the tissue is able to grow together quickly.
- Non-absorbable. Used for stitching tissues of internal organs or if long-term (permanent) stitching of tissues is necessary.
Absorbable threads are created from materials such as:
- nylon;
- polypropylene;
- catgut;
- lavsan.
When using this type of thread, it is necessary to accurately determine the rate of tissue fusion, since if the thread is removed from the body earlier than necessary, this can cause a number of problems.
Non-absorbable threads consist of the following materials:
- cotton;
- linen;
- silk.
This type of thread has a number of disadvantages. The most important thing is the ability to form microbes in tissue. When choosing, the doctor is guided not only by the purpose of the thread, but also by his own experience, and the patient’s preferences are not taken into account.
Techniques used in bone grafting
- Alveolar process resorption is used for horizontal bone splitting when it is necessary to increase the density of the alveolar process. It is performed on both jaws, and today is the most popular method for increasing the volume of the alveolar process, while having a low cost compared to more expensive procedures. Again, there are variations of this technique, but it’s worth paying attention to “Split Control”. The technique makes it possible to simultaneously expand the space and install an implant.
- To increase the volume and length of the alveolar process, a bone block transplantation technique is used. Autogenous material is more often used here. The principle is to screw a bone block taken, for example, from the maxillary region of the zygomatic-alveolar ridge to the bone, using medical mini-screws made of titanium alloy. Then it’s all covered with bone shavings and covered with a connective tissue membrane, which is secured. Subsequently, the surgical wound is tightly sutured with synthetic thread. The disadvantages of autogenous material were discussed above, which should be taken into account when choosing therapy.
- Guided tissue regeneration is a method in which it is possible to both increase the height and expand the volume of the alveolar processes. This technique also involves the simultaneous installation of an implant.
The guided bone regeneration technique includes two components:
- implanted bone material;
- a special barrier membrane that protects against the effects of various infectious agents and other unpleasant factors.
It is important to understand and take into account that the technique of directed bone regeneration does not always provide a sufficient effect. When using this method, bone material is “planted” on the outside of the cortical plate of the upper or lower jaw. The bone structure is very different from its own and is prone to incomplete splitting. Therefore, such an operation should be performed by an experienced doctor who knows all the nuances of the technique and can adequately assess further treatment tactics.