Consultation with plastic surgeons with over 20 years of experience – free! Sign up by phone. Waiting for you! Re-endoprosthetics or re-mammoplasty is an operation to replace breast implants. Breast implant replacement can occur for a variety of reasons, but the most common is fibrous capsular contracture (constrictive fibrosis). In the first months after breast augmentation with implants, a capsule of connective tissue is formed around the endoprosthesis, the density and thickness of which depends on the individual characteristics of the body’s reaction to a foreign body and the quality of the implant.
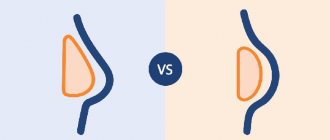
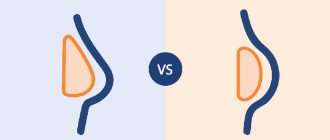
Around modern textured implants of the fourth and fifth generations, a barely noticeable capsule is formed, more like a “web”, which cannot be said about the smooth implants of the first generations. A dense, hard capsule around a smooth implant often leads to fibrous capsular contracture, compresses the endoprosthesis and causes deformation of the mammary glands.
Capsular contracture – a capsule of dense fibrous tissue compressing the implant
Indications
In addition to aesthetic reasons and complications, re-endoprosthetics may also be necessary in cases where an implant was previously installed that requires replacement after a few years.
Removal of implants due to complications includes the following:
- capsular contracture (formation of scar tissue around the implant);
- asymmetry of the mammary glands;
- displacement of the endoprosthesis;
- violation of the integrity of the implant;
- inflammation;
- contouring or wrinkling of the implant;
- loss of sensation;
- accumulation of fluid in the chest;
- ptosis (drooping) of the breast.
Types of accesses in mammoplasty when installing breast implants
Endoprosthesis replacement is performed in three access options. After consultation and examination, the plastic surgeon decides which way is best to insert endoprostheses.
Submammary (submammary) access
This is the first and well-developed type of plastic surgery, which is now operated using new techniques and technologies. The incision is made along the natural fold located under the breast. A pocket is formed under the breast or muscle into which the implant is placed. The endoprosthesis looks more natural under the muscle.
The advantages of the inframammary approach include:
- correction techniques brought to perfection;
- easy recovery period;
- possibility of prosthetic implants of large volumes;
- universality of the method;
- maintaining the integrity of the mammary gland.
This method also has disadvantages. Due to the need to transfer the own submammary fold, there is a possibility of implant prolapse.
Plastic surgeons recommend this method to all women who have a pronounced submammary fold under the breast. It is not done for girls with small and high breasts, which after plastic surgery will not hide the postoperative scar.
Periareolar access
This is a method of installing an implant through the areola. To do this, at the border with the skin, along the lower edge of the areola, a small incision is made into which the implant is inserted. It can be installed behind a muscle or gland.
From an aesthetic point of view, this is the most acceptable method.
With mammoplasty with periareolar access, you can not only increase the size, but also correct other breast defects:
- reduce the size of the areola,
- restore the symmetry of the mammary glands;
- pull up the nipples;
- perform a mini gland lift;
- move the nipples to the periphery or closer to the center.
This access also has disadvantages, and quite significant ones:
- the possibility of the formation of a keloid scar cannot be excluded;
- discomfort during the rehabilitation period when installing an implant under the muscle;
- possible loss of sensation in the nipple;
- there is a possibility of the formation of pericapsular contracture - excessive formation of fibrous tissue around the endoprosthesis and deformation of the mammary glands;
- there is a possibility of retraction of the scar under the areola.
Surgeons do not recommend this method for women planning to breastfeed for a year after plastic surgery. It is not suitable for patients with light-colored nipple areolas, as well as those who have a tendency to form a keloid scar.
Transaxillary access
This is an endoscopic method of installing an implant through the armpits. An incision is made along the posterior edge of the pectoralis major muscle, in the armpit area. It can be vertical or horizontal. Under the control of endoscopes, surgeons form a cavity, place an endoprosthesis, quickly eliminate bleeding, and control all risks. At the same time, the doctor, using a video camera, sees the correct installation of the implant.
In some clinics, this operation is performed “blindly”, but this method is too traumatic and there is a high risk of bleeding under the muscle. Now it is practically not used. Optics reduced the risk of hematomas, massive bleeding and other complications.
The endoprosthesis is inserted without injuring the mammary gland, since its tissue is not affected during surgery. This is important for women who want to breastfeed their baby. This access is one of the most aesthetic methods, in which it is easiest to hide traces of surgical intervention.
This method has other advantages:
- recovery time after surgery does not exceed two weeks;
- the scar completely resolves within five months and does not form a keloid;
- these methods provide the possibility of fixing the implant and reduce the risk of displacement after correction;
- The duration of the surgical intervention does not exceed 40 minutes.
The disadvantages of the method include the impossibility of plastic breast correction during surgery. This type of access is not used when it is necessary to eliminate the asymmetry of the glands and shift the inframammary fold. The method does not exclude the possibility of the formation of fibrous contractures, in which excessively overgrown fibrous tissue deforms the endoprosthesis and the breast.
After correction with axillary access, scars do not require special care. Physical activity is not excluded, you can raise your arms.
According to plastic surgeons, this method of access gives excellent results on a “boyish figure” with small breasts.
Contraindications
The list of contraindications for surgery to remove implants includes the same reasons as any other operation:
- problems with blood clotting;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- systemic organ damage;
- diabetes;
- internal inflammation;
- oncological diseases;
- pregnancy and lactation period.
Other contraindications may be identified during examination of the patient and based on test results.
Rehabilitation after breast implant replacement
During the rehabilitation period for repeated breast correction (mammoplasty with endoprostheses or removal of implants with a one-stage breast lift), wearing compression garments for 1.5 months, regular dressing visits and compliance with all instructions of the plastic surgeon are required. For 2-3 months after the operation, it is necessary to refrain from increased physical activity and sports, avoid stress on the upper shoulder girdle, and do not visit the bathhouse, sauna, or solarium.
The cost of replacing breast implants depends on many factors, in particular on the principle of the operation: removal of implants with a lift or replacement of implants. The latter option is more expensive, since the cost of new breast endoprostheses (about 60,000 rubles) is added to the cost of surgical procedures to remove implants. The complexity of the situation itself is also assessed, whether there is inflammation, contracture, etc. To find out the current prices for surgery, contact our administrators by phone numbers listed on the website.
Recovery
After the operation, the patient must spend 1-2 days in the hospital. If necessary, a course of antibiotics may be prescribed. The drainage system will be removed after 1 day, the sutures will be removed after 7-10 days. A compression bra should be worn for at least a month, and the same amount of time should be abstained from physical activity, visiting bathhouses and solariums, as well as swimming pools.
The duration of rehabilitation depends on the type of surgery and the individual characteristics of the body. In order for the recovery to proceed without complications, you need to come regularly for examinations and strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions.
If, after removing the old endoprosthesis, a new one is not installed, then over time the bed formed for the implant becomes tightened. However, often to restore the shape of the breast after removal of implants, a lift or re-installation of endoprostheses may be required. The need for additional procedures will become noticeable after a period of rehabilitation and complete recovery, which takes at least 3 months.
Medical in St. Petersburg offers surgery to remove breast endoprostheses. The clinic’s specialists will perform the operation and also accompany the patient in the pre- and postoperative period. Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely eliminate the risk of complications after surgery, but they can be minimized if you turn to professionals. Schedule a consultation with a medical plastic surgeon to learn more about the implant removal procedure.
| Author of the article Dmitry Konstantinovich Yakimov |
Replacing or removing breast implants is a simpler operation than breast augmentation. There may be some slight discomfort after surgery. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia and lasts about 1-2 hours. If the patient's condition is satisfactory by evening, she can go home.
Removal of breast implants: tests and surgery
The preoperative examination includes a full list of tests for general anesthesia, as well as additional ultrasound and MRI of the mammary glands. A more detailed list of preoperative tests can be found here.
In the case of breast re-endoprosthetics, new implants are usually installed, and it is possible to increase or decrease the volume of the endoprostheses at the request of the patient, and in the case of removal of the implants, a breast lift is performed (circular pexy, mastopexy). Revision breast surgery is performed in such a way as to minimize scarring and maintain the natural appearance of the breast. The duration of the operation is up to 2 hours, and the removal of the old implant takes no more than 15 minutes, but the complete removal of capsular contracture and the formation of a new breast shape is a labor-intensive process that takes up most of the time.
Angelina Jolie is not the first
June 22, 7:27
“We are not cutters”: a plastic surgeon - about the request “like Jolie” and the difference in price
Why going to Moscow for new breasts is no longer relevant, what are the features of male plastic surgery and what you definitely won’t be able to change about yourself
About 10 years ago, Angelina Jolie had her breasts removed and implants inserted for preventive purposes - she had a very high risk of developing cancer. This operation - subcutaneous mastectomy - has been performed in Barnaul for several years now.
“Angelina Jolie once drove everyone crazy with this operation. In fact, she was not the first. For example, in Barnaul such operations have been performed for more than 20 years,” the specialist commented.
Such operations are performed for certain indications: a high risk of inherited cancer, the presence of multiple benign tumors, and even treated distant cancer in the adjacent breast.
“There are times when a patient, who has already had one breast removed due to cancer, asks to have the second one removed out of fear. This puts a lot of moral pressure, and women want to play it safe,” explains the doctor.
We do not perform such operations free of charge within the framework of compulsory medical insurance.
How are implants and oncology related?
Discussions about whether implants can cause breast cancer have been going on for a long time, says the doctor. Research conducted by scientists and doctors since the late 1980s suggests that there is no connection between breast enlargement and cancer. Moreover, observations have shown that women who have implants have a lower risk of developing cancer.
“It cannot be said that having implants prevents the development of cancer. The research data can be explained by the fact that women who decide to install implants and invest a lot of money in their breasts more often visit a mammologist, have an ultrasound scan and carefully monitor their health,” explains the surgeon.
Breast implant placement sites
Before surgery, the plastic surgeon decides how to insert the prosthesis and in which layer of the breast the pocket for the implant will be formed. In mammoplasty, installation is performed in four main ways:
- subglandular;
- subfascial;
- subpectoral;
- submuscular (axillary).
The choice of method depends on several factors. One of them is the position of the glands on the chest. They can be located low or low, occupy a middle position. During the consultation, the surgeon evaluates ptosis (sagging) of the glands. Other factors are skin elasticity and subcutaneous fat thickness. The shape of the chest, the presence of rib deformities, and anatomical features of the muscles are assessed.
Subglandular location
The implant is installed under the gland. The pocket is formed by separating the glandular tissue from the connective tissue of the pectoral muscle fascia. This method is suitable for patients with well-developed and dense mammary glands, good muscles and elastic skin. In this case, the endoprosthesis will look as natural as possible.
This plastic option has many advantages:
- short rehabilitation period due to minor tissue trauma;
- the natural contours of the mammary gland are preserved;
- breast ptosis can be eliminated during plastic surgery;
- minimal risk of bleeding after surgery;
- slight pain during scar healing;
- deformation of the implant during physical activity is excluded.
Disadvantages include the likelihood of infection of the gland during surgery, the formation of capsular contractures, and implant rejection.
When placing an implant under the mammary gland, muscle fibers are not injured, so rehabilitation is better, and the prosthesis does not cause discomfort. However, complications are more common. For example, if you lose weight, the implant may become noticeable. During the recovery period, fibrous tissue forms around a foreign body, such as breast implants. Its excessive formation leads to contracture: it compresses the endoprosthesis and deforms the breast. Although this complication occurs in 1% of cases, contracture most often occurs when an implant is installed under the gland. Sometimes, under the influence of the mass of a large implant, the breast moves downward. Its aesthetic appeal is lost.
Subfascial location
With this method, the implant is placed under the fascia. It is a plate of connective tissue covering the muscle. During plastic surgery, the surgeon separates it from the underlying pectoral muscle and forms a pocket in which the endoprosthesis is installed.
In this way, only small implants can be placed for the first or second breast size, since the fascia will not cover large prostheses. Its advantage over the previous method is more reliable fixation of the implant.
Subpectoral location
A combined method in which implants are inserted partly under the pectoralis major muscle and partly under the mammary gland. When forming a pocket, the lower part of the pectoral muscle is cut. This method of implantation turns out to be the only possible one for minor breast sagging. It combines the advantages of the submuscular and subgladular methods of placement of the endoprosthesis.
Submuscular (axillary) location
The implants are placed under the pectoralis major muscle. When creating a pocket, the plastic surgeon peels away the muscle from the rib cage, separating it partially at its attachment to the ribs. Most of the endoprosthesis after installation is under the muscle tissue, only the lower segment is located under the mammary gland. Unlike the subpectoral placement, with this type of installation the lower part of the muscle fibers is not cut.
All other things being equal, preference is given to placing the implant under the muscles, because it is in this place that the endoprosthesis is securely fixed and the likelihood of capsular contracture formation is reduced. Recovery with this installation method is more difficult: new endoprostheses cause discomfort at first. Painful sensations occur when moving the arms, and their mobility is limited throughout the entire recovery period. In the postoperative period, there is a high probability of implant deformation.
Lift or reduction?
If the breasts are sagging and a woman is no longer satisfied with their shape, a breast lift can be done. Doctors work only with the skin, and do not touch the gland tissues themselves. After a breast lift, the breasts retain their beautiful shape for quite a long time. And even breastfeeding, provided all conditions are met (compression garments and normal weight), does not particularly affect its shape.
However, this is an individual question: no one can promise that breasts will retain their shape forever after a lift. Repeat surgery may be required.
Reduction – breast reduction – is one of the most difficult operations in mammoplasty. Doctors recommend stopping breastfeeding after such an intervention. The fact is that during reduction, the doctor removes part of the glandular tissue, and the ducts may be damaged. The milk may arrive, but there will be nowhere for it to go, and this is fraught with serious complications, the doctor explains.