We invite you to familiarize yourself with the most important things on the topic: “crusts under the beard” with a full description and recommendations.
Some men wonder why the skin under the mustache and beard peels and what to do in this case? This doesn’t happen often, but so that you know how to act in such a situation, we will tell you in detail the reasons and ways to combat the skin defect.
Why does the skin under my beard peel?
In most cases, the skin under the beard and mustache peels off in people with dry skin type, but those with other skin types are not immune either. Some of the most common causes of flaking beard skin include:
- using inappropriate shaving products;
- weakening of immune defense;
- chronic skin diseases;
- frequent consumption of fried and salty foods;
- allergy;
- alcohol abuse.
We looked at why the skin under the beard peels, but what to do if these unpleasant symptoms occur.
How to deal with flaking beard?
When a person has peeling skin on his face under his beard, it is better not to delay treatment so that the situation does not worsen. You must select one or more of the following methods:
- contact a cosmetologist or dermatologist;
- resort to traditional medicine;
- start taking medications;
- change your diet;
- cure diseases that cause the skin under the mustache and beard to peel.
Treatment with medications
For dry beard skin that is already flaking, you can use pharmaceutical products, one of which is a cream containing hydrocortisone. It is applied to problem areas daily for two weeks.
If there is severe peeling of the skin under the beard, which cannot be cured with moisturizing products, you can resort to drugs based on dexapanthenol. The remedies are effective when the causes of the disorder are associated with a deterioration in the protective and regenerative functions of the epidermis.
Pharmacies sell the effective product Panthenol in the form of a spray. It should be sprayed on the chin several times a day, and after 10 minutes from the moment of application, remove the excess with a napkin. Instead of a spray, you can use a cream.
Bepanten is considered a good drug if the skin under the beard is peeling. It not only combats dryness, but also relieves irritation on sensitive skin. In winter it is sometimes used to prevent flaking.
About nutrition rules
Having figured out why the skin under your mustache and beard peels, you must understand the role of proper nutrition. It is important to supply the body with a sufficient amount of minerals and vitamins, especially group B. Include eggs, fish, dairy products, whole grain bread, more fresh vegetables and fruits, brown rice, which is as rich in vitamins as possible, as well as nuts.
Additionally, vitamin complexes from the pharmacy will help you. If all this does not help get rid of flaking skin under your beard, do not panic, but go to a doctor who will identify the cause of the problem and prescribe treatment.
Peeling skin in a child
In some children, peeling skin may be present until adolescence. Therefore, it is worth knowing that the structure of the skin in children differs significantly from the structure of the skin in adults, because in children it is thinner, especially in the stratum corneum. Because of this, the skin's moisture is retained for a short time, causing dry skin.
The following factors can cause peeling skin in a child:
- External irritants such as humid wind, cold air and hot weather in summer.
— Various fungal infections, seborrheic dermatitis, scarlet fever and chickenpox.
— Diseases of internal organs, for example, intestinal dysbiosis, pathology of the liver and kidneys, can act as serious reasons for the appearance of peeling skin in a child.
It should be noted that intestinal dysbiosis can provoke peeling of the skin in newborns, because children at this age are very susceptible to changes in the composition of the intestinal microflora.
Vitamins also play a certain provoking role. Their deficiency, as in adults, in children provokes peeling of the skin.
Allergies very often cause skin peeling. In children, allergies can manifest themselves to food allergens (gluten, lactose, fructose, etc.). Therefore, to prevent the occurrence of food allergies, the expectant mother follows a certain diet (limiting baked goods, citrus fruits, etc.). And, of course, natural feeding of a child is also an important factor for the prevention of allergies in a baby.
Peeling of the skin in newborns often occurs in the head area due to physiological “scabs”. They are somewhat reminiscent in appearance to seborrheic dermatitis, but their differences are that such scabs go away on their own during the newborn period - within 2-3 weeks after birth.
Failure to maintain sufficient hygiene when caring for a child or, conversely, excessive care of his skin provokes peeling of the skin.
It is also important to take into account the fact that helminthic infestations (worm infestations, roundworms, roundworms, toxocara and giardia) are quite common in children. It happens that the only sign of their presence in the child’s body is peeling of the skin
This often puts parents off going to a specialist because they try to cope with skin peeling on their own, thinking that it is just the influence of an external factor.
In this case, when peeling appears on the child’s cheeks, hands and forearms, it is important to pay attention to the presence of other symptoms characteristic of worm infestation. As a rule, these are: stool disorders, dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting), drooling at night. Also: bruxism (teeth grinding at night), unmotivated increase in body temperature to low-grade levels, cough (as with bronchitis)
Loss of appetite is also a characteristic sign of the presence of parasites in a child. And it is worth remembering that parasitic infestations contribute to the development of vitamin deficiency and, as a result, decreased immunity. The child becomes more susceptible to viral and bacterial infections. The nervous system also undergoes significant changes - the child becomes more irritable and whiny
Also: bruxism (grinding teeth at night), unmotivated increase in body temperature to low-grade levels, cough (as with bronchitis). Loss of appetite is also a characteristic sign of the presence of parasites in a child. And it is worth remembering that parasitic infestations contribute to the development of vitamin deficiency and, as a result, decreased immunity. The child becomes more susceptible to viral and bacterial infections. The nervous system also undergoes significant changes - the child becomes more irritable and whiny.
Treatment of skin peeling in children should be carried out only after examination by a pediatrician. The main thing is to find out the cause of its occurrence, because external factors can only be a “cover” for the correct diagnosis of the cause of peeling skin. Applying protective and nourishing creams will help to alleviate the child’s condition beforehand.
Peeling skin in newborns also causes them a lot of discomfort.
When treating it, it is important to use certain creams. It is considered a permanent condition to apply such a cream under the diaper.
Bathing the baby must be done every day, since personal hygiene for a newborn is the prevention of many skin problems, as well as air baths.
Forms
Depending on the characteristics of the manifestations, the following forms of seborrheic eczema are distinguished.
- Fat. Liquid: secretion of liquid sebum when pressing on the hair root (on the skin in the area of the nasolabial folds);
- pustules may appear on the affected skin;
- more common in girls 10-14 years old;
- The scalp is flaky and the hair quickly becomes greasy after washing.
- sebum is thick, difficult to remove, has an unpleasant odor, so complications often arise - ulcers, as sebum accumulates and becomes inflamed;
- on dry skin there are many small white-gray scales, after removal of which reddened skin is exposed;
- with this form, oily seborrheic eczema is detected on the face, dry or thick on the scalp;
Causes
Seborrheic eczema occurs when a combination of various factors:
- yeast-like fungi - found on the skin of most healthy people, concentrated around the sebaceous glands, feeding on sebum;
- decreased immune activity (decreased body resistance due to lack of vitamins, poor nutrition);
- diseases of the nervous system, including stress and emotional stress;
- hormonal imbalance (increased amount of male hormones in the blood);
- increased sweating;
- the presence of foci of infection (carious teeth, inflammation of the tonsils (tonsillitis), etc.);
- genetic predisposition (tendency to increased oily skin).
In the winter season (including due to wearing hats) in the cold, the manifestations of the disease (flaking, redness, itching) intensify. In summer, the manifestations of seborrheic eczema become less intense.
LookMedBook reminds: the sooner you seek help from a specialist, the greater your chances of maintaining health and reducing the risk of complications:
Peeling skin on the face in men: causes and treatment
Peeling of the facial skin most often occurs around the eyes and mouth in people who have naturally dry skin. At the initial stage, this condition is characterized by slight detachment of the epidermal scales. After some time, the situation worsens, burning and itching appear. If peeling occurs for a short period, then you can cope with it using folk remedies. If the skin dries constantly, this indicates the presence of serious diseases.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to determine the cause of such defects. According to the nature of manifestation, all factors can be divided into internal and external.
Among the main internal reasons are the following:
- Irregular food intake, violation of the regime, resulting in a deficiency of beneficial microelements in the body. Peeling skin on the face may indicate a lack of B vitamins.
- Allergic dermatitis, liver dysfunction due to alcohol abuse.
- Atherosclerosis, which causes plaque to form in the blood vessels.
- Bacterial, viral, fungal infection.
- Heredity.
- Constant stress, chronic fatigue, regular lack of sleep, which leads to a malfunction of the nervous system and affects the condition of the skin.
Peeling on the face in men can occur due to health problems such as:
- obesity, high sugar levels, endocrine system diseases;
- liver dysfunction;
- reduced acidity of gastric juice;
- neurodermatitis;
- dermatitis;
- mycosis;
- eczema;
- psoriasis;
- seborrhea.
Peeling near the nose can occur due to colds, demodicosis, allergic reactions, seborrheic dermatitis, seborrheic psoriasis.
Among the external factors causing the disease are:
- 1. Weather conditions. Cold, ultraviolet radiation, and wind damage the skin. Therefore, peeling and dryness are most often seasonal.
- 2. Low quality cosmetics. Symptoms may occur when using products that are not suitable for your skin type. Cheap hygiene products contain oils and alkali, which wash off the top layer of skin. During recovery, it is exposed to bacterial attack.
- 3. Shaving. As a result of frequent procedures, microscopic damage to the skin of the face occurs. In addition, tap water is used, which contains large amounts of iron, chlorine and other impurities that create a feeling of “tightness” and provoke peeling.
Diagnostics
- Analysis of the medical history and complaints of the disease: how long ago did the first changes on the skin appear (foci of peeling and redness, pustules);
- Is skin itching bothering you, does it intensify during the cold season;
- Has anyone in the family had similar complaints?
Prevention of seborrheic eczema
- Hygiene of the scalp and face with shampoos containing ketoconazole (an antifungal component), zinc, etc.
- Taking vitamins (groups A, B, D, E, zinc, sulfur) - to maintain immunity and improve skin restoration.
- A balanced and rational diet (eating foods high in fiber (vegetables, fruits, herbs), avoiding canned, fried, spicy, hot foods).
- Treatment of concomitant diseases (nervous, cardiovascular systems).
Mycosis is a disease caused by a fungal infection. Mycosis with skin lesions in the area of beard growth in most cases is provoked by fungi of the genus T. mentagrophytes var. and T. verrucosum. These fungi belong to the zoophilic group, that is, they parasitize mainly animals. Much less often, mycosis of this type, as well as mycosis of the feet and mycosis of the legs, is provoked by fungi that are part of the anthropophilic group - T. rubrum, T. schonleinii, etc.
Mycoses caused by fungi from the zoophilic group are most often diagnosed in people living in rural areas. The risk group includes livestock industry workers who, due to their professional duties, are constantly in contact with animals.
What to do to prevent peeling
The skin needs proper cosmetic care. Avoid using alkaline cleansers. Buy foams and gels designed to cleanse sensitive epidermis.
- Make moisturizing and softening masks regularly.
- Once a week, remove dead skin cells with soft scrubs.
- Use hypoallergenic cosmetics.
- Lubricate the dermis with nourishing cream every day.
- When going outside, protect your face from ultraviolet radiation, wind and cold.
To prevent flaking, stay hydrated. Drink at least 2 liters of liquid throughout the day, dividing it into even portions.
Adjust your diet. Include in your diet:
- fresh herbs;
- fruits;
- vegetables;
- fiber;
- dairy products;
- red fish;
- beef liver;
- eggs.
Minimize the consumption of smoked lard, sweets, marinades, and pickles.
On a note. Give up bad habits, play sports, worry less and rest more. A healthy lifestyle strengthens the immune system and improves the condition of the skin.
Reasons for development
The cause of the development of mycosis with skin lesions in the area of beard growth is a fungal infection. Most often, the sources of infection are animals - cats, dogs, cows, etc. However, rodents (mice) can also spread a fungal infection.
In urban residents, beard skin mycosis and facial mycosis in general most often develop when infected from a sick person. Infection, as a rule, occurs through close contact or through the use of common objects - towels, razors, etc. The risk of contracting mycosis especially increases among members of the same family or within organized groups.
Clinical picture
Mycosis of the skin in the area of beard growth in its clinical course has much in common with trichophytosis, which occurs in an infiltrating-suppurative form. Mycosis rashes are located symmetrically, usually affecting the skin of the chin, neck, and lower part of the neck. The skin above the upper lip is rarely affected.
On the skin affected by mycosis, bluish, sharply limited nodes of elastic consistency are formed. The surface of the nodes is covered with a large number of follicular pustules. The pustules quickly merge, leading to the formation of large abscesses.
When the pustules are opened, pus is released, after which the skin becomes covered with crusts. When abscesses are opened, fistulas and purulent cavities are formed.
The hairs growing in the affected area are brittle, they are easily pulled out or fall out without external influence.
Despite the fact that the course of mycosis has a pronounced purulent character, the pain of the nodes is little pronounced.
When mycosis occurs in a severe form, general symptoms may develop - regional lymphadenitis, fever.
In mycoses caused by infection with fungi of the genus M. canis, the disease can occur with symptoms of severe pyoderma with the formation of abscesses. Mycoses caused by infection with E. floccosum often give an atypical clinical picture, manifested by the formation of warty growths.
Mycoses caused by fungi belonging to the anthropophilic group often occur in a mild form. In this case, mycosis is clinically manifested by the formation of ring-shaped or round erythema. The skin in the affected area peels off. With this course of mycosis, many patients consider the manifestations of the disease to be a common irritation, but at the same time, they are spreaders of a fungal infection.
Mycosis with skin lesions in the beard growth area lasts for several months, after which the nodes resolve, even if the patient has not received treatment. In most cases, no scar changes remain on the skin, and hair growth is completely restored.
Herpes
Viral infection. Infection occurs through contact. The pathogen is activated when the immune system is weakened, and causes itching and tingling in the skin. Then groups of watery blisters appear on the pubis, which soon burst. In their place, erosions and particles of a thin film similar to scales remain. Then the sores become crusty. The whole process is accompanied by itching and burning. Although symptoms usually disappear without treatment, therapy is still necessary. It will help avoid complications and relapses and significantly alleviate the patient’s condition. For herpes, antiviral ointments and tablets are used.
Diagnostic methods
The basis for diagnosing all types of mycosis is laboratory diagnostics. If mycosis is suspected, the following is prescribed:
- Microscopic examination of skin and hair scrapings taken from the affected area.
- Cultural studies - inoculation of material on special media to identify the fungal culture.
- Blood biochemistry (analysis is necessary if systemic antifungal therapy is planned).
- Additionally, an analysis is carried out to exclude syphilis infection.
To make a preliminary diagnosis, an examination under a Wood's lamp may be prescribed. Skin affected by mycosis in the rays of this lamp acquires a greenish color and clearly stands out against the background of unaffected skin.
When conducting diagnostics, it is important to exclude diseases such as:
- Impetigo;
- Secondary syphilis;
- Seborrheic eczema.
Treatment
To treat mycosis of the beard, antifungal drugs are used, which the doctor selects individually for each patient. Taking the medications must be continued until control tests for the presence of fungi give a negative result.
For external treatment of mycosis, an alcoholic tincture of iodine is used, as well as ointments containing antifungal substances. If the focus of mycosis is single, and treatment is started in the early stages, then you can limit yourself to only external treatment.
Hair growing in areas of mycosis should be carefully removed (cut or plucked with tweezers). When large abscesses form, it is recommended to open them (in a hospital setting) and treat the surfaces with a disinfectant solution, for example, chlorhexidine.
Treatment with traditional methods
For mycoses of the skin in the area of beard growth, you can also use traditional methods of treatment.
Beetroot decoction for mycosis. Boil peeled beets in a small amount of water. Mix the decoction with an equal amount of honey. Lubricate the sore skin with the product every half hour.
Sulfur helps well in the treatment of cutaneous forms of mycosis. Yellow sulfur should be mixed with vegetable oil until a thick paste is obtained. Apply to skin affected by mycosis three times a day. After an hour, remove the sulfur with a dry cloth; do not wet the affected area with water.
Prepare a decoction of horsetail, celandine and string grass (ingredient ratio 1: 2: 4). Brew two tablespoons of the mixture with a glass of boiling water. Use the infusion as a lotion for skin affected by mycosis.
Another remedy for treating fungal skin infections in the beard area is an ointment made from fish broth and garlic. You need to prepare a rich broth from any unscaled fish. For 200 grams of strained broth, take three large heads of garlic and 100 grams of melted butter or fat (you can take goose fat, butter, etc.). The garlic is ground into a paste and mixed with broth and fat. The resulting creamy product is applied to the affected skin overnight. The product does not have the most pleasant smell, but it helps well in the fight against skin mycosis.
How to get rid of peeling skin on a man's face?
sometimes cosmetic antifungal antihistamine
Diathesis
in case of secondary infection they suppress the immune response have an anti-inflammatory effect plasmapheresis in the form of tablets, that is, they are prescribed both in the form of ointments and in the form of tablets. medications, tobacco smoke, mold, etc.
Psoriasis
improve blood circulation reduce the body's hypersensitivity remove toxins from the body hepatoprotectors protect liver cells from damage reduce or remove symptoms for a while, for example, the severity of psoriasis, its form, patient contact with certain provoking agents, etc.
Adverse external factors
which occurs when the skin is exposed to unfavorable external factors, for example, changing cosmetics, medications, using protective clothing when working with dyes, solvents, moving to a different climate zone, etc. that is, skin suppuration
Avitaminosis
if the patient has such products Products rich in certain vitamins
| Vitamin name | What foods contain this vitamin in large quantities? |
| Vitamin B2 | Vitamin B2 is present in significant quantities in liver, mushrooms, almonds, eggs, brewer's and baker's yeast, milk, cottage cheese, and cabbage. |
| Vitamin B3 | Vitamin B3 is rich in milk, meat (chicken, beef), sunflower seeds, peanuts, pine nuts, mushrooms (honey mushrooms), soybeans, peas, beans, buckwheat. |
| Vitamin B6 | Vitamin B6 is found in large quantities in fish, eggs, meat, peas, beans, fresh green peppers, whole grains of cereals and their bran, walnuts, and spinach. |
| Vitamin B7 | A lot of this vitamin can be found in liver, egg yolk, wheat flour, rice bran, soybeans, cauliflower, peanuts, and walnuts. |
| Vitamin A | Vitamin A is found in sufficient quantities in fish oil, caviar, liver, butter, milk, cottage cheese, sour cream, and eggs. Plant foods are rich in provitamin A (carrots, sweet peppers, pumpkin, parsley, green onions, peaches, apricots, apples, etc.). |
| Vitamin E | Vitamin E is present in significant quantities in vegetable oil, lettuce, cabbage, eggs, rose hips, nuts (peanuts, almonds, hazelnuts, walnuts), sea buckthorn, and fish. |
Mycosis
lichen versicolor, dermatophytosis antifungal agents fluconazole ketoconazole traconazole repetitions of the disease when, for example, not only the skin of the face is affected, but also other areas of the body tablets
Seborrheic dermatitis
ketoconazole, fluconazole, miconazole, clotrimazole, voriconazole, zinc pyrithione and other topical glucocorticoids B1, B2, B6, B12, B9, A, Edoxy-chem, xanthinol nicotinate redness, peeling, swelling, itching in the presence of itching and burning in the affected areas
Ichthyosis
acitretin, isotretinoin and other keratolytic agents for the separation of uric acid and glucocorticoids, that is, with suppuration of flaky skin, ultraviolet irradiation, oxygen, mud, sea baths, etc.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for mycosis affecting the skin of the beard is good. Prevention of the development of mycoses involves eliminating risk factors:
- It is strictly not recommended to pick up or pet stray dogs or cats;
- If you suspect a fungal infection in your pets, you should contact your veterinarian. If suspicions are confirmed, the sick animal should be isolated until complete recovery.
- It is not recommended to use other people's shaving accessories, towels and other hygiene items. In hairdressing salons, shaving instruments, scissors and combs must be placed in the sterilizer after each client.
- If there is a person with mycosis in the family, it is necessary to provide him with separate hygiene items and thoroughly disinfect them after use.
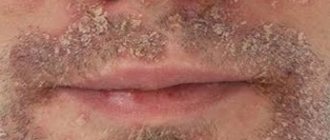
Fungus on beard photo
One of the serious pustular skin diseases is mycosis, which affects the area of beard and mustache growth. Among specialists, it is called “infiltrative-suppurative trichophytosis of the mustache”, and more often – “parasitic sycosis”. This type of mycosis is an inflammation of the hair follicles on the face caused by certain types of fungi.
Choosing a doctor
A trichologist, a specialist who does approximately the same thing as a dermatologist, will help solve the problem of flaky and flaking facial skin. However, his specialty is not the problems of the whole body, but only the scalp.
After the appearance of seborrhea, the patient may need to see other doctors:
- gastroenterologist, for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- immunologist, for psoriasis or lupus erythematosus;
- endocrinologist and gynecologist to stabilize hormonal levels.
Sometimes you have to contact a therapist to identify the source of the disease and prescribe the correct treatment. The same doctor will issue a referral to a neurologist or neurologist if the causes of dandruff are associated with stress or disorders of the nervous system.
Mycosis of the beard and mustache: causes
Parasitic sycosis is referred to as purulent skin lesions on the face. It is most often provoked by fungi of the genus Staphylococcus aureus or white, a combination of several strains. The spores enter the hair follicle and begin to actively grow in comfortable conditions.
People encounter this type of mycotic pathogens everywhere. Yeast fungus on the face may be present on the skin or mucous membranes of the nose in a “dormant” state. The fungus on the beard begins to show its activity against the background of certain factors:
- microtrauma of the skin after shaving;
- chronic prolonged runny nose;
- various inflammations and rashes on the chin;
- infections of the maxillofacial area.
Mycosis on the face photo
Predisposing factors are prostatitis and hormonal changes associated with deterioration in the activity of the gonads. More often than others, the disease occurs in people who constantly abuse alcohol or work in dusty industries or farms. The latter is due to the natural ability of cattle to carry certain types of fungus and staphylococcus.
This fungal inflammation of the mustache and beard growth area is most often diagnosed in men, but occurs in middle-aged and older women. It can develop against the background of greatly reduced immunity, which is provoked by diseases of internal organs, severe stressful situations, and problems with the nervous system.
Why do skin problems occur under the beard?
The source of problems with the skin on the chin, covered with well-grown hairs, can be anything:
- hormonal imbalance or prolonged abstinence;
- experienced stress;
- hot humid weather;
- changing the diet with a predominance of meat and hot spices;
- incorrectly selected products for washing and caring for the beard.
For the first time, discomfort occurs at 2-3 weeks of growing a beard, when the hairs reach a length of 10 mm or more and put a certain load on the skin. If you carelessly wash and dry your facial hair with a towel, single hair “breaks” may occur, to which the skin reacts with inflammation.
Also, hair shafts provide additional area for various microflora. Particles of sebum, dead epidermis, food, and dust particles accumulate on their surface. All this is a favorable substance for bacteria and fungi. The slightest injury on the surface of the integument, and they rush into the dermis, provoking pustular inflammation.
Mycosis of the beard and mustache: main symptoms
Mycosis on the chin
Parasitic mycosis damages the bulbs on the chin and upper lip, along the area of beard hair growth, and on part of the neck. The disease begins as an irritation or rash. Small boils resemble irritation after shaving, gradually grow and merge on the skin. The main symptoms of mycosis of the beard and mustache:
- the skin on damaged areas of the face becomes bluish;
- infiltration oozes from the inflamed bulbs;
- there are thick purulent crusts on the chin;
- hairs in affected areas become dull and break off easily.
Once parasitic sycosis is activated, the entire lower part of the face may be covered with inflamed skin with a constant clear discharge. When they are removed, open eczema and painful wounds are found under the crust. All rashes are located asymmetrically to each other, practically do not affect the cheeks and greatly increase in the area of the lower jaw.
At the initial stage, mycosis of the beard and mustache resembles the consequences of careless shaving, and many men do not attach importance to the appearance of imaginary irritation. Depending on the state of the entire immune system, the problem gradually develops over several months without obvious pain. With prolonged symptoms, the skin on the face becomes swollen and hypersensitive, and the overall body temperature may rise. A thorough shave becomes impossible and from the outside the man gives the impression of a sloppy person.
Demodicosis
A rather rare infectious disease, it is caused by microscopic mites that parasitize human skin. The pathogen itself is often found in nature; the entire population of the globe comes into contact with it in everyday life. But a normally functioning immune system provides reliable protection against the disease.
But if it weakens significantly, the disease develops rapidly. And the skin around the nose is the first to suffer from the disease; the skin in this place is very vulnerable. In addition to redness in various areas of the skin, it is also characterized by a number of other symptoms:
- peeling in affected areas,
- dryness around the nose,
- itching
We suggest you read: Which powder is best for problem skin?
Diagnostic technique
Correct treatment and choice of medications can be made only after identifying the main type of fungus that provoked mycosis of the facial hair growth area. A dermatologist takes skin particles and fluids for analysis in a laboratory setting, which allows them to grow colonies and understand the root cause.
The basis of parasitic sycosis is always infection with a fungus, to which staphylococcus is attached. Therefore, in addition to identifying the type and type of pathogen, a study is carried out for resistance to antibiotics. This helps you choose the right treatment options. Additionally, beard hair tests and several skin tests with trichophyton are carried out.
Infection with zoophilic species of dermatophytic fungi is more often detected in people living in urban settlements, villages, hamlets and among workers on livestock farms. The problem associated with anthropophilic fungi can arise from poor hygiene of shaving accessories and contact with a sick person.
Mycosis of the beard and mustache: treatment
Synthomycin ointment for nail fungus
Therapy for mycotic lesions of the facial hair growth area is usually quite long. It includes a combination of treatment of fungal and staphylococcal pathogens using different methods. All appointments are made by a qualified dermatologist or mycologist. In case of exacerbation of internal diseases, consultation with a surgeon, neurologist or urologist is necessary.
To relieve skin inflammation and reduce the secretion of pus, it is recommended to treat the chin several times a day alternately:
- syntomycin ointment;
- gentamicin solution;
- a mixture of boric acid and potassium permanganate.
This helps reduce the exacerbation and move on to the main antimycotic treatment. The patient takes antibiotics orally or by injection:
- Oxytetracycline;
- Chlortetracycline;
- Augmentin;
- Cephalexin.
Additional intake of these drugs helps to effectively fight staphylococcus from the inside. The course of treatment can be up to three weeks and is constantly accompanied by monitoring the patient’s health.
In parallel, antifungal therapy is carried out using local and internal medicines. To treat trichophytons that cause mycosis of the beard and mustache, dermatologists use:
- Ketonazole;
- Fluconazole;
- Itraconazole capsules;
- Griseofulvin.
They can be used in the form of light emulsions and creams. Beforehand, the hair must be trimmed as much as possible; shaving is strictly prohibited during an exacerbation and treatment. Applications of an antifungal composition can be combined with skin treatment with an alcohol solution of regular iodine.
A good addition to the main treatment is irradiation of the affected areas of the skin with ultraviolet radiation and doses of ultraviolet radiation on purulent wounds. The patient should take a course of multivitamins and immunostimulants that help the body cope with the disease faster.