Almost every athlete who regularly exercises in the gym knows about gynecomastia or has even observed this disease in reality. This phenomenon is a benign increase in the size of the mammary gland in representatives of the stronger half of humanity. It is usually caused by hypertrophy of adipose tissue and glands. Most often, the development of gynecomastia is typical for those bodybuilders who take anabolic steroids. The disease can be caused by other reasons.
Breast enlargement in bodybuilders is provoked by: varying degrees of obesity, taking steroid drugs, teenage transition, various diseases accompanied by a decrease in testosterone concentration against the background of an increase in estrogen. Gynecomastia is often called “gyno” in bodybuilding. Most bodybuilders are afraid of the development of this disease. This is due to the fact that it becomes the main obstacle for every bodybuilder competing in competitions.
Classification of gynecomastia
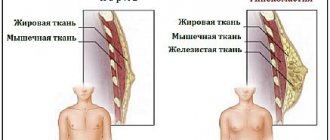
There are two types of gynecomastia: false and true.
False is not a real disease, but only the deposition of adipose tissue in the chest area. With true, pathological growth of glandular tissue occurs.
True gynecomastia can be of the following types:
- Idiopathic
- Physiological (neonatal, pubertal, senile)
- Pathological
- congenital (with Klinefelter's Syndrome, anorchia, hermaphroditism, androgen resistance syndrome, enzymatic defects in testosterone synthesis, increased aromatase in peripheral tissues)
- endocrine (for castration, mumps, Cushing's syndrome, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, panhypopituitarism, hyperprolactinemia)
- symptomatic (for tumors of the testicles; adrenal glands; pituitary adenoma; breast cancer; tumors that secrete human chorionic gonadotropin)
- medicinal (when using hormones; antiandrogens; prolactin stimulants; when using drugs; anti-tuberculosis drugs)
- metabolic (with thyrotoxicosis; renal failure; liver cirrhosis; fasting; alcoholism)
- other (for HIV, chest wall trauma, cystic fibrosis, physiological stress)
Signs
External signs of gynecomastia are determined by the stage of its development:
- At the proliferation stage, there is a slight increase in the size of the mammary glands. If the pathology is detected at this stage and the patient is offered treatment, the disease goes away within a short time;
- at the intermediate stage, breast tissue grows rapidly, and milk secretion is released from the nipple. This condition causes significant discomfort to the patient. Most cases of gynecomastia are diagnosed at the second stage, because symptoms of the disease become obvious;
- at the fibrotic stage, intensive proliferation of adipose and connective tissue causes characteristic lumps to appear in the breasts. Its structural changes are considered irreversible even with prolonged intensive treatment.
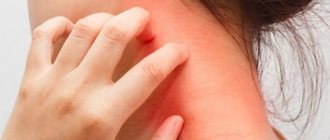
Symptoms of gynecomastia are often observed in athletes taking steroid drugs. The main signs of the disease include itching, burning, discomfort in the nipple area, and the release of a small amount of milk secretion.
Diagnostics
A thorough medical history is important to determine the underlying cause of gynecomastia and rule out breast cancer and other tumors. On the other hand, it should be noted that about 25% of cases of gynecomastia may be idiopathic (the cause is unknown).
Must be taken into account during examination
- patient's age,
- onset and duration of breast augmentation,
- symptoms of associated pain,
- recent weight change and
- possible endocrine disorders.
It is necessary to establish whether any medications or drugs are being taken, as they can cause up to 10–20% of cases of gynecomastia.
On physical examination, gynecomastia is defined as overgrown glandular tissue under the nipple-areolar complex and can vary in size.
True gynecomastia must be differentiated from pseudogynecomastia, or false gynecomastia, which is manifested by hypertrophy of adipose tissue without proliferation of the gland itself.
Breast cancer is rare and accounts for less than 1% of malignant neoplasms in men (according to UK and US data). It usually appears on one side and is felt as a hard mass located outside the nipple-areolar complex.
As part of a systematic review, the physical examination should include a search for signs of chronic disease of the thyroid gland, kidneys or liver, or genital organs. When examining the genitals, it is also important to monitor testicular weight or testicular atrophy. Sometimes liver enlargement may occur.
Laboratory research
Biochemical evaluation includes tests to determine liver, kidney and thyroid function, as well as serum levels of testosterone, prolactin, follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone.
Additional tests may be necessary in cases of recent or symptomatic gynecomastia to rule out tumors. For example, serum levels of estrogen, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), dehydroepiandrosterone and 17-ketosteroids in urine.
Routine mammography and breast ultrasound with or without biopsy are usually not recommended unless breast cancer is suspected or the patient has unilateral breast enlargement.
Similarly, a testicular ultrasound or CT scan of the abdomen may be performed if the testicle or adrenal gland becomes enlarged.
Diagnostic evaluation of gynecomastia
- Lab tests: testosterone
- estrogen-β-human chorionic gonadotropin
- prolactin, follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone
- urea and electrolytes
- ± dehydroepiandrosterone or 17-ketosteroids in urine
- Ultrasound of the breast
Patient selection
Various clinical and histological classifications have been proposed for gynecomastia. The Simon classification is the most practical because it takes into account not only breast size, but also the amount of excess skin.
Causes of breast hypertrophy
True gynecomastia in men, which is treated without surgery in various ways, occurs due to disorders in the body. This pathology may appear as a result of increased secretion of prolactin. This usually happens with hypothyroidism and pituitary tumors.
But the most common cause of gynecomastia in men is a malfunction in the ratio of estrogen and testosterone in the body. A similar condition is observed with inflammation in the testicles, Addison's disease, prostate adenoma, as well as with hormonally active tumors or age-related hypogonadism.
Pathologies of a non-endocrine nature can also lead to breast enlargement in men: trauma or herpetic lesions of the chest, cardiovascular or renal failure, HIV infection, cirrhosis of the liver.
Gynecomastia is often caused by diseases that are accompanied by metabolic disorders, such as pulmonary tuberculosis, excess weight or diabetes.
Gynecomastia in the stronger sex often occurs due to the use of certain drugs that negatively affect the receptors of breast tissue. In addition, they increase the production of prolactin and estrogen, and can also have a toxic effect on the body. These drugs include Amiodarone, Cimetidine, anabolic steroids, Theophylline, antidepressants, corticosteroids or creams containing hormones.
Breast hypertrophy in some situations occurs due to alcohol abuse or drug use.
At the same time, many are interested in whether, if gynecomastia is diagnosed in men, treatment without surgery in young men and adolescents is possible or not. It is worth understanding that surgical intervention can be avoided only in the early stages of the disease.
Indications for removal of gynecomastia
- Persistent increase after puberty (>2 years)
- Inadequate response to treatment
- Severe breast enlargement
- Significant asymmetry or unilateral condition
- Patient request
- Post-massive weight loss
- Special clinical conditions
The boundaries between categories are not clearly defined, which leads to subjectivity. Therefore, in our practice, we classify gynecomastia into three stages:
- small to moderate in size with no or minimal excess skin (Grades I and IIA)
- medium to large in size with moderate to severe excess skin (grades IIB and III).
Lifestyle, nutrition, exercise
For the drugs to work:
it is important to eliminate stress; rest more; ensure a good night's sleep.
It is advisable to increase physical activity.
Walking in the fresh air, jogging, swimming, cycling are useful. It is also possible to exercise in the gym without overexertion. You should start your morning with exercise, which triggers metabolic processes and improves the general condition of the body. It is important to strengthen the muscles of the chest and shoulder girdle, as well as the back and abs. Exercises with dumbbells, an expander, or a rubber band are suitable. The patient’s task is to develop muscles and reduce body fat, which stimulates the production of estrogen
This will help both hide gynecomastia and improve your well-being.
The patient’s task is to develop muscles and reduce body fat, which stimulates the production of estrogen. This will help both hide gynecomastia and improve your well-being.
A mandatory item is giving up bad habits. Alcohol inhibits testosterone production and causes severe hormonal imbalance. Innocuous at first glance, beer contains phytoestrogens, which cause an increase in body weight with the deposition of fat according to the female principle.
If there is a predisposition, even small doses of ethyl alcohol can accelerate the development of pathology and greatly weaken the effectiveness of medications.
Men involved in professional sports and bodybuilding should completely avoid drugs containing steroids.
Now you know exactly how to get rid of gynecomastia at home. Don’t forget about another very important point – a balanced diet. Overweight men need to lose weight by consuming no more than 2,500 kilocalories per day (subject to average physical activity).
It is necessary to exclude:
- smoked meats;
- pickles;
- hydrogenated fats and sweets.
The menu includes foods that lower estrogen levels.
These include:
- broccoli;
- green beans;
- soybeans
Fresh tomatoes, as well as tomato sauces and juices rich in lycopene, are useful. As you can see, gynecomastia can be treated without surgery.
Treatment of gynecomastia
Drug treatment
Most cases of gynecomastia do not require treatment as they are benign and self-limiting.
Weight loss should be recommended first for patients with pseudonecomastia. Particular attention should be directed to eliminating any identified cause.
Drug therapy is mainly aimed at correcting androgen and estrogen imbalance. Medicines are most effective during the active, proliferative phase of gynecomastia. In patients with prolonged gynecomastia for more than 1 year, drug treatment is often ineffective, since the breast tissue progresses to irreversible dense fibrosis and hyalinization during this time.
Treatment of gynecomastia without surgery involves taking medications. Antiestrogenic drugs are often prescribed.
The most common drugs:
- Tamoxifen
- Clomiphene citrate
- Proviron
- Progestogel.
Taking medications must be agreed with your doctor. It is he who prescribes the treatment regimen, determines the required dosage and duration of medication. You should not self-medicate, as this can greatly worsen the patient’s health.
Surgery
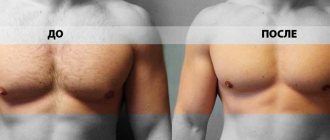
The mainstay of treatment for gynecomastia is surgical treatment, the goal of which is to restore the normal-appearing contour of the male breast with minimal scarring while maintaining the viability of the nipple-areolar complex.
Surgical treatments for gynecomastia include various forms of liposuction, breast excision, skin tightening, and a combination of these.
Liposuction is now a major surgical technique because it is minimally invasive, improves contouring by smoothing the contours, and is often successful as a stand-alone technique.
Various types of liposuction have been described, including conventional, mechanical, ultrasound, laser and vibration assisted (VASER). The most common types are conventional and ultrasonic liposuction.
Anesthesia and infiltration
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. All patients undergo preoperative photography. All patients receive antibiotic prophylaxis.
Patients are marked before surgery in a vertical position, indicating the inframammary fold, the boundaries of the mammary glands, and the planned incision sites.
The breast tissue is infiltrated through an incision in the inframammary fold, and a special raster for liposuction is introduced.
Liposuction allows you to achieve good breast contours with minimal scarring. Special cannulas for liposuction are used.
Open gland removal
Open removal of gland tissue is performed through the lower areolar approach. Various other incisions are also described, such as circumvertical, periareolar, transareolar, anchor, t-inverted.
Liposuction is often not effective for removing dense glandular tissue. Excisional techniques are effective for these patient populations, although they are associated with a high complication rate with the potential for gross scarring and contour deformities.
We use open excision combined with liposuction. Liposuction serves several purposes, such as pretunneling to facilitate resection, reduce bleeding and bruising, and partially destroy breast tissue. After liposuction, tissue can be removed through several small incisions.
We prefer the time-tested method of open excision, where the breast tissue is excised through a semicircular incision along the lower edge of the nipple-areolar complex. At least 1 cm of breast tissue is left under the areola to prevent depression of the nipple-areolar complex.
Open excision, even in combination with liposuction, sometimes does not completely correct large and ptotic breasts for which skin tightening is indicated. Some surgeons recommend avoiding skin resection, allowing the skin to shrink on its own for 6-8 months. We prefer to remove excess skin during the first operation. This has practical advantages such as reduced cost, single operation, and reduced operating time.
Skin tightening
There are a number of techniques used to tighten the skin of gynecomastia. Although most of them are similar to those used for mastopexy in women, there are still some differences.
Although skin tightening techniques may result in larger scars compared to liposuction and simple removal, they are indicated for patients with large breasts, significant ptosis, or poor skin turgor. Therefore, in patients with obvious excess skin or very large breasts, skin tightening techniques should also be planned in advance and should be performed simultaneously with open breast tissue removal or in a second stage, at least 4-6 months later.
However, there is no consensus on when and how to perform skin tightening. We base this decision on skin elasticity, presence of ptosis and excess skin, skin type, and the patient's willingness to accept a potential two-step procedure. Surgeon preference also plays a role in the choice of technique. Whenever there is excess skin or ptosis, we prefer to address the excess skin at initial surgery, especially in cases of poor or borderline skin elasticity.
The choice of skin tightening method also largely depends on the surgeon's preference. It is possible to perform a lift
- circular
- vertical
- without vertical scar with transposition of the nipple-areolar complex
- anchor
Periareolar mastopexy
Periareolar skin tightening is a preferred method over other skin tightening methods, mainly because it avoids additional scarring.
We prefer to use the periareolar technique due to less noticeable scarring.
Vertical mastopexy according to Le Jour
In patients with true ptosis or very large breasts, skin tightening and tissue resection can be undertaken using the LeJour vertical lift. The skin and underlying breast tissue are resected in a vertical ellipse, and then the wound edges are approximated.
However, a vertical scar may be noticeable. This technique is used as a last resort, especially in those patients who want to avoid a T-scar.
Other skin tightening methods
Lateral wedge, elliptical and inverted T-shape excision are sometimes used.
Patients with very large or ptotic breasts are suitable candidates for elliptical mastectomy and free nipple transfer.
This also avoids the characteristic scarring associated with mastopexy in women.
In patients at high risk of developing keloids or hypertrophic scarring, we often use a non-vertical scar technique with Lalonde breast reduction. After deepithelialization, liposuction is performed before open removal of the glands and through a horizontal incision. Once hemostasis is achieved, the nipple areolar complex is perfectly transposed and brought into a new position.
Gradual skin reduction
Patients with mild ptosis sometimes do not need to undergo gland removal with simultaneous skin tightening. The operation can be performed in two stages. We start with liposuction followed by skin tightening after at least 4-6 months.
Sometimes patients scheduled for two-stage surgery are satisfied with the initial results and refuse a second skin tightening procedure because they can experience gradual skin tightening on their own.
However, the skin may still not shrink, in which case we perform one-stage skin tightening and excisional techniques for severe gynecomastia with significant excess after liposuction.
How to treat at home?
Treatment for men and women at home includes procedures that are recommended to be performed on an outpatient basis, without the need for hospitalization.
Even if the symptoms do not cause the patient to doubt the diagnosis, it is almost impossible to independently cure the disease at home, since it is associated with hormonal changes. Treatment is prescribed by a doctor
It is important!
Any therapy is carried out under the supervision of the attending physician and depends directly on the form of the disease. Most often, pathology occurs as a result of hormonal imbalance in the body. Among the folk remedies and medications, there are proven remedies that allow you to reduce or completely eliminate the internal and external manifestations of the disease at home, in both men and women.
Positive dynamics in treatment with folk remedies and methods are observed in both men and women.
The duration of treatment with thyme is 3 weeks. It consists of using a decoction. Prepare the product as follows:
- 2 tbsp. spoons of thyme herb are dipped in 1 liter. boiling water and, without removing from heat, leave for another 8 minutes.
- Then the resulting liquid is cooled, passed through cheesecloth and drunk 1 tbsp. once a day at any time.
Strengthening the body, treating hormonal imbalances, improving digestion - these are some of the positive effects that the plant has on the patient’s body.
- Wash a handful of roots, dry them, chop them, pour in 0.75 liters of red wine.
- Place on the fire until a film appears (boiling does not preserve the beneficial properties!).
- Leave in a dark place for 3 days.
- Strain the finished wine and take 50 g after dinner.
- 2 parts ginseng root;
- 1 part Siberian ginseng root;
- 1 part licorice root;
- 1 part raspberry leaves.
- Mix the dried ingredients, take 1 tbsp. l. mixture pour 2 tbsp. hot water.
- Leave covered for half an hour until cool.
- Strain and take in small portions throughout the day.
When choosing a conservative drug therapy, the doctor prescribes one of the drugs listed below.
| No. | Drug name | Description | Instructions | The cost of the drug in Moscow | The cost of the drug in St. Petersburg |
| 1. | Tamoxifen (tablets) | An effective remedy for suppressing the production of estrogen, which affects the growth of the mammary glands. Used for gynecomastia and malignant tumors of the mammary glands. The effect of taking it is long-lasting, up to 4 months. | The dosage is selected individually. Use only as prescribed by a doctor. If side effects occur, urgent consultation with a specialist is necessary. | 734 rubles | 580 rubles |
| 2. | Testosterone propionate (solution for intramuscular administration) | Promotes an increase in the level of male sex hormone. Taking the drug leads to normalization of hormonal levels, which as a result has an effect on the reduction of mammary glands. | The dosage is selected individually. It is used only for patients under 50 years of age, otherwise recovery will not be observed. | 785 rubles | 877 rubles |
| 3. | Anastrozole (tablets) | An effective remedy for a patient who was on a course of steroids to increase body weight. The drug also acts as an antitumor agent. | The dosage is prescribed by the doctor individually. Should not be used simultaneously with estrogens. | 7187 rubles | 1519 rubles |
| 4. | Proviron (tablets) | The drug helps reduce estrogen levels. | The drug is prescribed for pain and lumps in the chest, which are accompanied by burning and redness. After 2 months of treatment, positive dynamics are noticeable. | 900 rubles | 784 rubles |
| 5. | Progestogel 1%. (ointment) | The effect of the medicine is to reduce fluid in the breast tissue, putting pressure on the milk flow. | The drug contains progesterone, which blocks estrogen synthesis and reduces prolactin levels. | 908 rubles | 787 rubles |
In addition to the medications listed above, to increase the effectiveness of treatment, it is necessary to take a course of vitamins A and E, which have a beneficial effect on the hormonal balance of the entire body.
Recovery after gynecomastia removal
Drains are not usually used except in major resections or when skin resection is performed, such as in patients with massive weight loss. Patients are advised to wear a special compression bandage for gynecomastia day and night for 4-6 weeks.
Oral antibiotics are taken for a total of 5 days. Painkillers should be used, as a rule, for 2-3 days.
Outcomes, prognosis and complications
Only an integrated approach can lead to predictable results in the surgical treatment of gynecomastia. Our starting point for all cases of gynecomastia is liposuction, even in those with hard subareolar glands, as it facilitates subsequent open excision. It is also technically easier to perform liposuction at the beginning of the operation rather than after removal. We use conventional liposuction only when ultrasonic liposuction is not available.
In patients in whom open excision is not necessary due to appearance and consistency, we always agree to open excision if liposuction leaves significant residual stromal tissue.
Whenever there is excess skin and/or ptosis, we prefer to treat the excess skin with primary surgery, especially in cases of poor or borderline skin elasticity. This is done to avoid post-operative excess skin.
The choice of skin reduction technique largely depends on the surgeon's preference.
Possible consequences of gynecomastia
- Bleeding and hematoma formation
- Seroma formation
- Infection
- Skin/nipple necrosis
- Contour deformity such as nipple inversion or depression
- Altered nipple sensation
- Redundancy of skin
- Residual asymmetry
- Unfavorable scars (wide, hypertrophy, keloid, pigmentation)
- Overcorrection, undercorrection
- Occasional need for revision surgery: asymmetry, residual tissue, depressed nipples
Recurrence of gynecomastia
Patients with gynecomastia in general are a surgically challenging group of patients, not least because of their high expectations from surgery. In patients who have undergone surgical treatment, it is sometimes necessary to undergo revision surgery several months after the initial surgery for various reasons. These include inadequate correction, patient dissatisfaction, painful residual lumps, asymmetry, and recurrence (often associated with weight gain). Overcorrection is rare.
Lipofilling of the pectoral muscle.
Photo before surgery:
| Before surgery without markings | Before surgery with markings | Fat harvesting area for lipofilling |
Video before and after surgery:
Recommendations
It is often difficult for even experienced surgeons to choose the most appropriate treatment. Sometimes a combination of these methods is necessary. Surgical treatment of gynecomastia consists of three main stages, which may not all be necessary for a given patient: liposuction, open excision and skin tightening.
Liposuction should always be used for diffuse or large breast enlargement. It may not be necessary when correcting small breasts with a hard subareolar nodule, but facilitates subsequent open removal. Our results with ultrasonic liposuction have led us to the conclusion that, when available, it is preferable to conventional liposuction because it is more effective and stimulates better skin contraction. Additionally, there may also be less bruising. After liposuction, the consistency of the breast is again assessed and open excision is performed if residual gland tissue is present.
Skin tightening is indicated if there is noticeable excess skin after removal. The choice between a concentric, vertical scar (LeJour technique) and an elliptical skin excision largely depends on the amount of excess skin to be removed, as well as the experience of the surgeon.
How to treat at home?
Treatment of gynecomastia at home, like “blepharoplasty” without surgery, as well as otoplasty at home, include procedures that can be performed without hospitalization.
Conservative therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis under the supervision of the attending physician and depends directly on the form of the disease.
However, it is worth noting that the treatment of gynecomastia in adolescence has some features:
- wait-and-see approach - after 2-3 years, in case of teenage disease, regression of mammary gland growth begins. In this case, medications with a low degree of effectiveness are prescribed;
- operational approach - a diagnosis is determined and treatment is prescribed with medications that regulate the balance of hormones.
Drugs
For gynecomastia, the doctor prescribes medications that are aimed at regulating estrogen and testosterone in the patient’s blood.
Medicines are usually prescribed at the first stage of the disease - the first four months after the mammary glands have increased in size.
First degree of gynecomastia
The effectiveness of treatment using such drugs is low, and to increase it, pathogenetic drugs that stimulate the secretion of lutein are prescribed.
They are used for six months.
Attention! Medicines used to treat gynecomastia are prescribed exclusively by the attending physician. Your doctor may prescribe the following medications:
Your doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- “Testosterone” – is prescribed only to those men in whose bodies the level of this hormone is low;
- “Clomiphene” is an anti-estrogen, which is prescribed only if the level of female hormones exceeds the permissible level;
- "Nolvadex" - prescribed in the later stages of the disease when the patient refuses surgical intervention;
- Danazol is a synthetic drug that reduces the synthesis of estrogens in the testicles. This drug is used to treat gynecomastia less frequently than the above drugs.
"Nolvadex"
It is important to know! If gynecomastia is caused by diseases of the internal organs or organs of the endocrine system, treatment of the underlying disease is required. If the changes become malignant or irreversible, urgent surgical intervention is required
If the changes become malignant or irreversible, urgent surgical intervention is required.
Diets
How to get rid of gynecomastia with diet?
The adult human body contains about 1.5 grams of zinc, which is mainly found in the liver, muscle tissue and skin (epidermis).
With gynecomastia, these zinc reserves begin to be used up, which is why the disease develops.
To prevent this, it is necessary to replenish the zinc content in the body.
To do this, you need to include in your diet such foods as:
- beef liver;
- fruits and berries: citrus fruits, dates, figs, raspberries, black currants;
- sunflower and pumpkin seeds, nuts;
- mushrooms;
- legumes: peas, beans, chickpeas;
- vegetables: cabbage, asparagus, onions, garlic, beets, green leafy vegetables;
- unrefined brown rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, barley, wheat bran;
- honey;
- green tea;
- seafood, fish,
- beef, rabbits, young lamb, chicken meat;
- mustard.
Diet for gynecomastia: cereals and nuts
In addition to the above products, overweight men should lose extra pounds, since obesity is one of the reasons for the development of gynecomastia.
Attention! To normalize your diet and choose a suitable diet and exercise plan for you, it is recommended to consult a nutritionist
Physical exercise
Exercise can be used to treat gynecomastia collectively.
They are not able to eliminate the consequences of the disease, but in combination with other therapeutic methods, physical education will give a positive result.
Some of the most useful activities include:
- Push-ups: Patients are advised to do as many push-ups as possible in the morning and evening.
- Jogging: It is recommended to jog in the morning and evening.
- Swimming: This is an effective technique for developing and strengthening the pectoral muscles, which is recommended to be used at least three times a week.
- Cycling: Strengthens your core muscles.