Types of pathology
Proper distribution of gynecomastia into types and forms allows you to select the correct treatment regimen, taking into account the characteristics of a particular type of disease.
First of all, there are two basic forms of pathology:
- True – accompanied by the proliferation of glandular tissues.
- False – characterized by an increase in fatty tissue. Getting rid of false gynecomastia allows you to fight excess weight, as a result of which massive deposits of adipose tissue will decrease in size Source: Gynecomastia. Beltsevich D.G., Vanushko V.E., Kuznetsov N.S., Kats L.E. Endocrine surgery, 2012. p. 18-23.
In some cases, true pathology is a variant of the physiological norm. Depending on the age at which physiological gynecomastia occurs, the disease is divided into three main types:
- Newborn period. In 60-90% of newborns, the mammary glands swell. The process is associated with the action of maternal hormones, which enter the child’s body inside the womb. Treatment is not required; within 2-4 weeks the condition of the glands returns to normal.
- Puberty. It is observed in adolescents aged 13-14 years in 30-60% of cases. Caused by the formation of the male reproductive system, an imbalance of female and male sex hormones. Within 1-2 years, the pathology regresses.
- Elderly. Diagnosed in men over 50 years of age. Associated with a decrease in testosterone production in the body.
The listed types of physiological abnormalities in most cases do not require treatment.
At the same time, pathological gynecomastia is also distinguished, the causes of which lie in serious diseases of the body. In this case, recovery is possible only with competent medical care.
Possibility of cure without surgery
In addition to an increase in the size of the mammary glands, gynecomastia is characterized by constant discomfort, pain, lumps, and burning in the chest area. A frequent question that worries sick men and women is: how to get rid of the disease at home with the help of drugs, without resorting to surgery.
Experts note that getting rid of the pathology at home, without resorting to surgical procedures, is only possible if the patient has physiological gynecomastia.
This type of disease is characterized by the growth or hypertrophy of the connective or glandular tissue of the mammary gland within the medical norm.
Reasons for development
In normal condition, the male mammary glands are a vestigial organ that consists of glandular and fatty tissues, ducts and nipples.
The female sex hormone estrogen and the pituitary hormone prolactin are responsible for their development. Due to a number of reasons, the production of testosterone in the male body may decrease. In this case, under the influence of estrogen, the mammary glands begin to develop in the same way as happens in the female body.
The causes of hormonal imbalance determine the further treatment plan for gynecomastia. Among the most common causes of the disease are:
- Malignant neoplasms in the body. These can be tumors of the pituitary gland, testicles, stomach, pancreas, adrenal glands, lungs.
- Hypogonadism, or insufficient functioning of the gonads. The disease can be primary or age-related.
- BPH.
- Hyperprolactinemia is a disease in which the body experiences increased secretion of prolactin. Most often it is a concomitant disease with hypothyroidism and pituitary cancer.
- Violation of metabolic processes. Often occurs as a result of the development of diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis, and obesity.
- Diseases that do not affect the endocrine system. In some cases, the causes of gynecomastia are cardiovascular or renal failure, adrenal insufficiency, liver cirrhosis, and HIV infection.
- Taking medications. There is a category of medications that act on the receptors of the mammary gland, increase the production of prolactin and estrogen, and affect the testicles. As a result of their intake, hormonal imbalance occurs. These can be anabolic steroids, corticosteroids, ranitidine, captopril, nifedipine, antidepressants, estrogen creams and many other drugs.
- Drug use - drug addiction, alcoholism Source: Etiology and age-related factors of gynecomastia. Akimov D.V. Tumors of the female reproductive system, 2012. p. 34-38.
Signs of gynecomastia
The main and most pronounced symptom of gynecomastia is an enlargement of the male mammary gland with a diameter of 2 to 15 centimeters.
The mass of the gland can reach 160 grams. Together with the surrounding tissues, the nipple also enlarges, the areola becomes more pigmented and expands by 2-3 centimeters in diameter. Most often, an enlarged gland does not cause pain, but if the disease is caused by a hormonally active tumor, there will be soreness and a feeling of fullness. The sensitivity of the nipples may also increase, which causes discomfort when the skin rubs against clothing. Occasionally, the pathology is accompanied by discharge from the nipple, which looks like milk.
Symptoms increase as gynecomastia develops. There are three stages of its formation :
- Developing - minimal severity of signs, symptoms are reduced to minor tissue proliferation. The duration of the stage is about four months. At this stage, the disease can be cured with medications.
- Intermediate – glandular tissues mature and grow more actively, increasing rapidly. The stage lasts from four months to one year. If the disease is caused by excessive production of prolactin, impotence, oligospermia, and damage to the nervous system may occur.
- Fibrous – fatty and connective tissues develop in the breasts. The highest probability of developing a malignant tumor. Treatment requires surgical intervention Source: Pathomorphological and molecular biological characteristics of gynecomastia. Mnikhovich M.V., Ben Ammar M.A., Kulikov E.P., Zhakota D.A. Bulletin of Volgograd State Medical University, 2016. p. 32-37.
Diagnostics
If the first symptoms of the disease appear, the breasts become slightly enlarged or the sensitivity of the nipples worsens, you should immediately consult a doctor. A comprehensive examination, which is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis, includes the following procedures:
- initial examination of the patient (examination of the glands, testicles, assessment of the severity of sexual characteristics, study of family history, heredity, chronic pathologies and medical history);
- laboratory blood tests for testosterone, prolactin, estradiol, creatinine, nitrogen and other substances that affect the growth of glands;
- X-ray of the lungs;
- computed tomography of the brain, adrenal glands and other organs to exclude the presence of tumor processes;
- ultrasound examination of the scrotum and mammary glands, axillary lymph nodes;
- mammography;
- biopsy (performed only if there is suspicion of a malignant tumor).
One of the main tasks of the doctor at the diagnosis stage is to discover the root causes of gynecomastia, identify its type, distinguish the growth of fatty tissue from glandular tissue, and also exclude or confirm the presence of cancer processes in the body.
Which doctors and clinics specialize in the treatment of gynecomastia?
Men with breast enlargement first need to find out the cause. The first point of contact here is usually the family doctor. If malignant breast cancer or hormonal disorders are suspected, the patient may be referred to a specialist in gynecology, urology or endocrinology. After this, if the interested person wants to undergo surgery to remove gynecomastia, he should contact a specialist in plastic and aesthetic surgery. They specialize in male breast reduction.
We will help you find a specialist to treat your disease. All of the listed doctors and clinics have been checked by us for their high qualifications in the field of gynecomastia surgery. They are awaiting your inquiry or application for treatment.
How to cure gynecomastia
Physiological forms of the disease do not require medical intervention or correction with drugs.
In rare cases, with severe symptoms in adolescence, hormonal drugs are prescribed that can reduce the concentration of estrogen in the body. If medications do not help reduce the size of the glands, plastic surgery is used to remove gynecomastia. During the intervention, excess glandular tissue is excised, and fat in the surrounding areas is also removed. The treatment regimen for pathological gynecomastia depends on the primary disease that provoked the proliferation of glandular tissue. Conservative hormonal therapy, during which the ratio of estrogen and testosterone is normalized, is effective during the first four months of development of the pathology Source: Modern ideas about the epidemiology, etiology and pathogenesis of gynecomastia. Yashina Yu.N., Rozhivanov R.V., Kurbatov D.G. Andrology and genital surgery, 2014. p. 8-15.
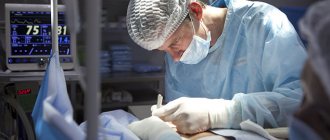
If conservative treatment does not bring results or is obviously not used (for example, in the presence of malignant tumors), surgical removal is prescribed. The surgical operation involves excision of excess tissue and restoration of the normal contours of the area. To do this, the following types of operations are performed:
- subcutaneous mastectomy, in which the areolas are preserved and access is provided through their circumference (periareolar);
- subcutaneous mastectomy combined with liposuction;
- endoscopic mastectomy (effective only with slight magnification).
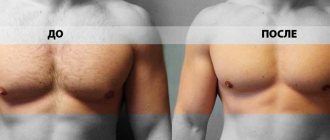
Patients tolerate these types of interventions well. Fast rehabilitation allows you to return to your normal rhythm of life within a week, and even to training in the gym after a month.
What should you consider after gynecomastia surgery?
If breast reduction was performed using liposuction only, outpatient treatment is possible. However, if a mastectomy has been performed, a hospital stay is required. When a severe or moderate course of the disease is diagnosed, the patient is operated on under general anesthesia.
As with any surgery, there may also be general risks and complications such as infections, bruising, bleeding or impaired wound healing, although these are rare. Sports activities are prohibited for six weeks after surgery. In addition, a compression vest is mandatory, especially early after surgery, to prevent or minimize swelling, effusion, and bruises.
Prevention
Prevention of physiological gynecomastia is difficult due to the fact that it is part of normal biological processes in the body. This condition depends on natural hormonal fluctuations and quite often goes away on its own, requiring neither prevention nor treatment.
To prevent pathological gynecomastia, it is necessary to carefully monitor the hormonal system, avoid taking drugs that affect the production of hormones, give up alcohol and drugs Source: Risk factors, the role of steroid hormones and their receptors in the development of gynecomastia. Vovchuk I.L. Scientific notes of the Crimean Federal University named after V.I. Vernadsky. Biology. Chemistry, 2014. Prevention of the disease is complicated by the fact that most often it is not the cause, but a consequence of the development of other diseases in the body.
Sources:
- Gynecomastia. Beltsevich D.G., Vanushko V.E., Kuznetsov N.S., Kats L.E. Endocrine surgery, 2012. p. 18-23
- Etiology and age factors of gynecomastia. Akimov D.V. Tumors of the female reproductive system, 2012. p. 34-38
- Pathomorphological and molecular biological characteristics of gynecomastia. Mnikhovich M.V., Ben Ammar M.A., Kulikov E.P., Zhakota D.A. Bulletin of Volgograd State Medical University, 2016. p. 32-37
- Modern ideas about the epidemiology, etiology and pathogenesis of gynecomastia. Yashina Yu.N., Rozhivanov R.V., Kurbatov D.G. Andrology and genital surgery, 2014. p. 8-15
- Risk factors, the role of steroid hormones and their receptors in the development of gynecomastia. Vovchuk I.L. Scientific notes of the Crimean Federal University named after V.I. Vernadsky. Biology. Chemistry, 2014
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.