Traditionally, it was believed that gynecomastia ( ICD-10 N62 ) is a pathology that occurs only in men. But most practitioners argue that this disease is a cross-sex disease, although it is registered more often in representatives of the stronger sex. It can occur in children, adolescents and adulthood. In this case, breast hypertrophy can reach 10 cm.
In this article you will learn what are the causes of gynecomastia, how treatment is carried out at home, how the removal operation is performed and the prices for it, and you will also be able to see photos.
General information
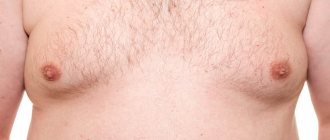
Gynecomastia is a pathology of the development of mammary glands in men, which is based on a dishormonal hyperplastic process, manifested by an increase in their size, due to a wide range of proliferative/regressive changes in glandular/adipose tissue.
Clinically manifested by enlargement and thickening of the mammary gland, painful sensations on palpation and a feeling of heaviness. Pathophysiologically: violation of the ratio of connective tissue and epithelial components. ICD-10 code for gynecomastia: N62. Normally, the mammary gland in men is rudimentary and formed by glandular/fatty tissue, short ducts and the nipple. However, with hormonal imbalances (increased levels of the female hormone estrogen against the background of a decrease in the level of the male hormone testosterone), men begin to develop/grow the mammary glands according to the female type, mainly with intensive development and compaction of glandular tissue. Bilateral gynecomastia is more common and much less common - unilateral.
There are false and true gynecomastia:
- False gynecomastia (syn. pseudogynecomastia) is not associated with hormonal disorders. It develops as a result of passive excess deposition of adipose tissue in the mammary gland, which is accompanied by a visually detectable increase in the volume of the mammary glands. As a rule, false gynecomastia occurs in men with constitutional exogenous obesity, developing against a nutritional-hypodynamic background.
- True gynecomastia is based on the growth of glandular tissue directly from the mammary glands themselves. At the same time, a distinction is made between physiological and pathological gynecomastia.
Physiological gynecomastia in men
It occurs at any age and has a three-phase distribution with a peak during the newborn period, in teenage boys and men after the age of 50 years:
- Gynecomastia of the newborn period is caused by the residual effect of maternal/placental estrogens and is transient, disappearing 2-3 weeks after birth.
- Pubertal gynecomastia . Gynecomastia in adolescents 12-15 years old occurs in 50-70% of boys during puberty; in most cases, it spontaneously regresses after 1-2 years. Gynecomastia in adolescents develops against the background of an increase in the concentration of estradiol , as well as a lack of free testosterone . Laboratory tests show an increase in the estrogen/androgen ratio in the blood serum. In some cases, teenage gynecomastia can develop due to certain genetic diseases, while taking medications/nutritional supplements.
- Gynecomastia in older adult men develops due to a decrease in the concentration of free testosterone . Gynecomastia of varying severity occurs in almost 60% of men aged 50-80 years, mainly in overweight individuals, which is caused by the conversion of androgens into estrogens in adipose tissue. Currently, abdominal fat is considered as an independent endocrine organ in which various biologically active substances are synthesized, including estrogens . The latter contribute to the deposition of female-type fat on the hips, buttocks and mammary glands.
Pathological gynecomastia
androgen deficiency , due to excessive production of estrogens , disruption of the process of conversion of androgens into estrogens, while taking medications, etc.
Gynecomastia in women, as such, is diagnosed extremely rarely, since the growth of mammary glands in women is a normal variant. We are talking about pathology if the volume of the mammary gland exceeds 400 cm3, otherwise excessive enlargement is considered as mammary gland hypertrophy .
The observed increase in the number of patients with true gynecomastia is due to many factors:
- general aging of the population;
- environmental problems;
- increase in endocrine diseases in the male population;
- uncontrolled use of medications, increased drug addiction;
- low stress resistance.
Considering the fact that gynecomastia is a heterosexual symptom and a pronounced cosmetic defect, its development in adolescents is accompanied by severe pressure on the psyche, causing chronic stress, decreased personal self-esteem, which often disrupts the adaptation of young people in society and leads to changes in behavioral intersexual reactions with the development of impotence , mental depression , sometimes suicidal tendencies . In addition, long-term gynecomastia is a favorable background for breast cancer , which in 30-70% of cases develops against the background of gynecomastia.
What methods are applicable for home therapy for gynecomastia?
This pathology does not require hospitalization of the patient, which is why the treatment course is carried out at home. In this case, the principle of complex therapy is observed, and the patient is recommended to use:
- Medicines;
- Traditional medicine recipe;
- Diet restriction with increased physical activity.
Use of drugs
A course of testosterone is a common practice for gynecomastia in the initial stages
. The use of hormonal drugs in therapy requires contacting a medical institution. The use of these drugs without medical prescription, in addition to negative manifestations, can cause the opposite effect.
To eliminate signs of pathology, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Hormones . They are the medications of the main choice. Most often the appointment occurs:
- Testosterone is prescribed in all cases when there is a lack of it in the body (adolescents and the elderly);
- Clomiphene has a pronounced antiestrogenic effect;
- Tamoxifen allows you to cope with the disease in an advanced form;
- Danazol is a synthetic testosterone derivative that suppresses the production of estrogen;
- Androgel is applied externally to accelerate the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics.
- Diuretics . To speed up the removal of fluid from the body, Furosemide, Lasix or Mannitol are prescribed.
- Antioxidants . They improve trophism in tissues, thereby accelerating regeneration processes. For this purpose, Actovegin, Yantavit and mineral complexes containing vitamin E are used.
- Immunomodulators . To increase the immune status of the body, Cycloferon, Laferon or Thymogen are used.
Folk recipe
Adherents of the use of medicinal infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs need to know that they can be used as an addition to therapy only after consultation with the attending physician.
This is due to their ability to cause allergic reactions. The following medicinal compositions are usually prescribed:
- Infusion of lovage rhizomes;
- Using liquid honey to apply compresses at night;
- Pharmacy tincture of ginseng or eleutherococcus;
- Infusion of Echinacea purpurea;
- Dietary supplements with yohimbe bark.
Changing your daily routine for a healthy lifestyle
First of all, it is necessary to correct the diet. A complete taboo applies to smoked foods, pickles and marinades, as well as the use of lean meat (chicken, turkey or rabbit). Positive dynamics in the treatment of gynecomastia are provided by products that reduce estrogen activity (soybeans, green beans, tomatoes and broccoli).
Physical activity should begin immediately after waking up, for which it is necessary to perform gymnastic exercises, focusing on the muscles of the chest, shoulder girdle, back and abdominals. of push-ups from the floor (starting from a minimum and working up to a maximum number of times) will be especially useful In addition, during the day it is recommended to visit the pool, go walking or cycling.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenetic mechanisms of gynecomastia are quite diverse and have not been sufficiently studied to date. According to the leading theory, the pathogenesis of this phenomenon is based on:
- impaired sensitivity of steroid receptors to sex hormones;
- change in the ratio of androgenic-estrogenic hormones.
Testosterone (androgen with high biological activity) is secreted by Leydig cells located in the testicles. Free androgens, penetrating into the target cell, bind to androgen receptors, which are localized in the cytosol and in the cell nucleus. Testosterone, when interacting with a target cell under the influence of a tissue enzyme, is converted into 5α-dihydrotestosterone, which has the highest androgenic activity.
The formation of estrogens in the male body occurs through the transformation of testicular/adrenal androgens under the influence of the aromatase , mainly in adipose tissue. Breast development is determined by androgen/estrogen stimulation. Thus, with an excess of estrogen in the body against the background of low androgen activity, the glandular tissue of the mammary gland grows. The same process occurs when androgen levels decrease against the background of normal estrogen levels. Thus, the development of gynecomastia is based on an imbalance in the ratio of androgenic-estrogenic hormones.
Plastic surgery
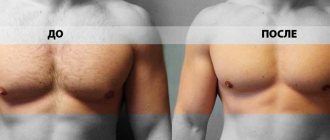
If “nothing helps,” how to get rid of “female” breasts? This is where plastic surgeons come to the rescue. The results of their work can be seen in the before and after photographs of their intervention.
How to treat the pathology promptly will depend on its type. If adipose tissue predominates, the doctor may suggest liposuction. An operation to remove excess connective and glandular tissue and restore the breast contour can be performed as:
- subcutaneous mastectomy using pariareolar access, while the areola is preserved;
- the same operation with additional liposuction;
- endoscopic version of “truncation” of the mammary glands, with slight hypertrophy.
Usually all types of procedures are well tolerated by patients; they go home after 2-3 days. Complete rehabilitation requires 4 weeks. After the operation, in the first 10-20 days (as the doctor says), you need to wear special underwear. It will allow you to form the correct contour of the breast, allow the skin to shrink well and protect post-operative sutures from damage.
After a week, the man can return to intellectual and light physical work. In a month, return to full physical labor and sports training.
With this we say goodbye to you until new articles. Share information with friends via social networks and read our new articles.
Classification
According to the etiology, there are several forms of gynecomastia:
- Physiological (juvenile/pubertal/senile age);
- Gynecomastia of endocrine origin ( hypothyroidism , thyrotoxicosis , true hermaphroditism , hypogonadism , testicular tumors , hyperprolactinemia , estrogen-secreting tumors , diabetes mellitus , adrenal cortex dysfunction , Prader-Willi syndrome and other genetically determined syndromes).
- Drug-induced gynecomastia. Medicines that cause gynecomastia include psychotropic drugs ( Haloperidol , Clozapine , Sonapax , Aminazine , etc.), hormonal drugs (glucocorticoids, human chorionic hormone, estrogens, anabolic, androgens), antitumor drugs, marijuana, opiates, etc.
- Gynecomastia is not of endocrine origin ( liver cirrhosis ; long periods of fasting; intoxication; renal failure , unfavorable environment; alcoholism , long-term use of cosmetics containing plant estrogens, for example, lavender, tea tree oil; contraceptives, estrogen-containing foods, etc.).
- Idiopathic.
Based on histological characteristics, they are distinguished:
- Parenchymal gynecomastia caused by proliferation of milk ducts with the formation of lobules. As a rule, it develops under the influence of hormones - estrogens , progesterone and testosterone .
- Interstitial gynecomastia caused by proliferative processes of periductal/interlobular tissue with fat deposition and proliferation of connective tissue. It is based on enhancing the effects of prolactin .
Based on the level of proliferative activity of the epithelium, gynecomastia is distinguished without proliferation, with proliferation, and with atypical proliferation of the epithelium. Fundal and bilateral gynecomastia and diffuse/nodular enlargement of the mammary glands are also distinguished.
Treatment methods
Gynecomastia of physiological types does not require specialized treatment in men and resolves without surgery or medication.
Drug therapy involves the use of hormonal drugs. If there is no improvement in their background, plastic surgery is performed:
- mastectomy combined with liposuction;
- mastectomy, preserving the contour of the areola;
- endoscopic mastectomy performed with small increases in size.
A similar approach to treatment is practiced in women.
Causes
The development of true pathological gynecomastia is based on a whole complex of factors, the main of which are:
- A violation of the estrogen/testosterone ratio in the male body, which develops with hormonally active tumors of the adrenal glands, testicles, pituitary gland, pancreas, stomach, lungs, insufficiency of the gonads, inflammatory diseases in the testicles, prostate adenoma, etc.
- Increased secretion of prolactin (hyperprolactinemia) with hypothyroidism , pituitary tumors .
- Diseases with metabolic disorders ( obesity , toxic diffuse goiter , pulmonary tuberculosis , diabetes mellitus , etc.
- Diseases of non-endocrine origin - HIV infection , intoxication, liver cirrhosis , cardiovascular / renal failure .
- Taking medications that act on breast tissue receptors, blocking gonadotropin receptors, increasing the production of prolactin / estrogens .
- Alcoholism /drug use (heroin, marijuana, opiates).
Stages of the disease
During the pathological process (this does not mean physiological gynecomastia), there are 3 stages:
- Proliferation (development).
- Intermediate period.
- Fibrosis.
In the first 4 months of the development of the pathological process, a reverse development of the symptoms of the disease is possible if you choose the right medications. At the next stage, the overgrown tissues are already maturing. The stage lasts from 4 to 12 months approximately.
At the last stage, with the development of stromal tissues, the reverse process is not possible; removal of hypertrophied areas is required. The process is accompanied by bloody discharge from the nipple, enlarged lymph nodes in the axillary area, and skin ulcerations, raising suspicion of malignancy.
Symptoms
With pathological gynecomastia, the most significant symptom is a visually detectable enlargement of the mammary glands. The degree of enlargement/weight of the mammary glands can vary widely and reach 15 cm in diameter and up to 200 grams in weight. Visually - enlargement of the nipple, pigmentation and swelling of the areola area and its increase in diameter up to 3-4 cm. Palpation - the mammary glands are painless; when the nipple/areola is squeezed, exudate may be released. The patient may complain of a feeling of fullness, a feeling of constriction, hypersensitivity of the nipples (a feeling of friction when wearing clothes).
There are three stages of gynecomastia:
- proliferating (developing) – the first 4 months, changes are not pronounced, with appropriate conservative treatment the process may reverse;
- intermediate – occurs over a period of 4-12 months, the glandular tissue of the gland matures;
- fibrous – characterized by the appearance of connective/fatty tissue in the mammary gland; as a rule, regression of the pathological process at this stage is almost impossible.
Which specialist prescribes treatment for gynecomastia?
If the first signs of pathological changes in the mammary glands appear, then first of all you need to consult a therapist .
An initial examination, collection of anamnestic data and the appointment of the necessary types of research will allow us to find out the cause of the development of gynecomastia. If dysfunction of the endocrine glands plays a major role in the genesis of the pathological process, then the patient is prescribed a consultation with an endocrinologist .
Breast enlargement as a result of problems in the reproductive system requires subsequent treatment under the supervision of an andrologist .
In some situations, you may need to consult a mammologist , surgeon or oncologist .
Tests and diagnostics
Diagnosis of gynecomastia does not present any particular difficulties and is established on the basis of anamnesis and objective examination (rate of mammary gland enlargement, elasticity, density, mobility of glandular tissue to surrounding tissues; presence/absence of nipple discharge, etc.). Additionally, laboratory and instrumental examinations are carried out:
- Laboratory tests: determination of blood serum levels of estradiol , prolactin , testosterone , LH, FSH and thyroid-stimulating hormone , indicators of kidney/liver function.
- Instrumental examinations: ultrasound of the mammary glands/scrotal organs; if the presence of hormonally active tumors is suspected, MRI of the pituitary gland, CT/MRI of the adrenal glands, and chest X-ray are prescribed.
- If cancer is suspected, breast biopsy
Consequences of gynecomastia
Gynecomastia, which is not treated in time, will progress, the tissue will undergo scarring and it will no longer be possible to remove it with medications. In this case, you will have to resort to surgery to remove the overgrown mammary glands.
Since gynecomastia occurs due to dysfunction of the hormonal system due to disruption of the functioning of certain organs, prolonged absence of treatment can lead to the development of tumors, the formation of metastases and other diseases of organs and systems.
Also, patients with gynecomastia may experience psychological problems, this is especially common in adolescents.
Diet
There is no special diet. However, correction of the diet is indicated with a limitation of table salt, beer, chocolate, chips, coffee, ketchup, mayonnaise, spicy seasonings/dishes, sweet carbonated water, refractory fats (lard), butter, fried foods/smoked meats, and alcoholic beverages. If there is a significant excess of body weight - Diet for obesity . Such nutrition has a number of pathogenetic advantages: reduction of peripheral estrogenogenesis in adipose tissue; disinhibition of the process of gonadotropin production, improvement of liver function, reduction of swelling of breast tissue.
List of sources
- Beltsevich D.G., Kuznetsov N.S., Vanushko V.E., Kalinchenko S.Yu. Gynecomastia // Endocrine surgery. 2008. No. 1(2). pp. 25-27.
- Endocrinology: national guidelines. Ed. I.I. Dedova, GA. Melnichenko. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2012. P. 872-8.
- Manusharova R.A., Cherkezova E.I. Gynecomastia (pathophysiology, clinical picture, diagnosis, treatment). Med Council 2008; 7-8: 48-52.
- Ivanov V. A., Ozerskaya I. A., Akimov D. V. Diagnosis and treatment of gynecomastia: Methodological recommendations. M.: Vidar, 2013. 64 p.
- Yashina Yu. N., Rozhivanov R. V., Kurbatov D. G. Modern ideas about the epidemiology, etiology and pathogenesis of gynecomastia // Journal “Andrology and Genital Surgery”. 2014. pp. 8-15.
Types of pathology
Proper distribution of gynecomastia into types and forms allows you to select the correct treatment regimen, taking into account the characteristics of a particular type of disease.
First of all, there are two basic forms of pathology:
- True – accompanied by the proliferation of glandular tissues.
- False – characterized by an increase in fatty tissue. Getting rid of false gynecomastia allows you to fight excess weight, as a result of which massive deposits of adipose tissue will decrease in size Source: Gynecomastia. Beltsevich D.G., Vanushko V.E., Kuznetsov N.S., Kats L.E. Endocrine surgery, 2012. p. 18-23.
In some cases, true pathology is a variant of the physiological norm. Depending on the age at which physiological gynecomastia occurs, the disease is divided into three main types:
- Newborn period. In 60-90% of newborns, the mammary glands swell. The process is associated with the action of maternal hormones, which enter the child’s body inside the womb. Treatment is not required; within 2-4 weeks the condition of the glands returns to normal.
- Puberty. It is observed in adolescents aged 13-14 years in 30-60% of cases. Caused by the formation of the male reproductive system, an imbalance of female and male sex hormones. Within 1-2 years, the pathology regresses.
- Elderly. Diagnosed in men over 50 years of age. Associated with a decrease in testosterone production in the body.
The listed types of physiological abnormalities in most cases do not require treatment.
At the same time, pathological gynecomastia is also distinguished, the causes of which lie in serious diseases of the body. In this case, recovery is possible only with competent medical care.