Endocrinologist, nutritionist, nutritionist
Evdokimova
Elena Viktorovna
14 years of experience
Endocrinologist, nutritionist, nutritionist, member of the Russian Association of Endocrinologists. Member of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD)
Make an appointment
Pathology in the form of breast enlargement in men is called “gynecomastia”. Its main cause is hormonal disorders in the body, which cause intensive growth of fatty and glandular tissue in the chest area. In addition to the undesirable cosmetic effect, in the absence of medical control and treatment, the disease can have serious consequences in the form of the development of neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature.
Etiology
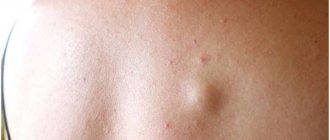
Literally translated from Latin, “gynecomastia” means female breasts. The pathology is observed in men and has the appearance of a benign formation, the structure of which is formed due to the cells and ducts of glandular tissue or the growth of the fat layer. In the first case, they talk about the so-called true gynecomastia, and in the second, about a false type of disease. The increase can reach 12 cm, which causes the patient severe psychological discomfort and significant inconvenience in everyday life. Unilateral enlargement of the glands is rare; more often the disease affects both glands. Externally, it manifests itself in the form of sagging tissues, reminiscent in shape of a woman’s breasts.
Reasons for development
The intensive growth of adipose and glandular tissue has serious internal reasons. Among the influencing factors it is worth noting:
- uncontrolled long-term medication use;
- exposure to toxic substances on the body;
- hormonal imbalances;
- diseases with systemic symptoms.
Each of these phenomena triggers the process of intensive production and entry into the blood of female sex hormones - estrogens. Against the background of a stable or reduced amount of the male hormone androgen, hormonal imbalance is observed, which is expressed in the impact on the so-called target organs that are most sensitive to changes in the body. Among them is the mammary gland, the growth of which is sharply activated. The mechanism of development of gynecomastia, taking into account the influence of the hormonal factor, is completely similar to the process in the body of young girls during adolescence, when a sharp increase in female hormones stimulates the process of breast growth.
In the body of a healthy man, the hormone content is balanced, and the amount of estrogen cannot affect the growth of breast tissue. In addition, their volume is controlled by another hormone - testosterone, which determines the characteristics of the male figure and the functioning of the body of representatives of the stronger sex. But in the event of a hormonal imbalance and a weakening of the influence of testosterone, estrogens trigger a process of external and physiological changes, including the process of development of secondary sexual characteristics characteristic of the opposite sex.
Forms and stages of development
The gradual growth of breast tissue allows us to talk about the gradation of the disease. To establish the degree of its manifestations at a specific point in time, a histological examination of the cells of the pathological formation is carried out. Experts distinguish:
- proliferating stage. The duration is approximately 4-6 months, and the main symptoms include intense tissue growth.
- an intermediate stage lasting about a year. The formation of the “female” gland is completed, its size stabilizes.
- fibrous stage. Its main symptom is the proliferation of glandular and connective tissue, which gives the breast a characteristic appearance.
Based on the diagnostic report on the stage of the detected disease, the doctor selects the optimal form of therapy, taking into account the age and general condition of the patient’s body.
In order to further clarify the nature of the disease, the following classification of gynecomastia has been adopted:
- physiological - considered normal in infancy, adolescence or old age, therefore at these stages of the patient’s life it does not require strict monitoring and intensive treatment. There are subtypes of pathology based on age: transient gynecomastia of newborns, adolescent form and gynecomastia of older patients. Transient gynecomastia occurs in 70-80% of babies and goes away within the first three weeks of life. Its cause is the entry of estrogen from the mother into the fetus through the placenta. Pubertal gynecomastia is observed in teenage boys aged about 13-15 years, which is associated with hormonal changes, a sharp increase in the number of estrogens and the maturation of the body. Signs of the disease disappear on their own approximately a year after their appearance. The cause of gynecomastia in elderly patients is suppression of testosterone, against the background of which the amount of estrogen begins to predominate and influence physiological processes in the body.
- false gynecomastia. The disease is characterized by intense growth of adipose tissue. more often observed in patients suffering from various forms of obesity. The degree of breast enlargement varies depending on the constitution of the body and other diseases.
- True gynecomastia is caused by a hormonal imbalance that causes breast growth.
- idiopathic pathology. The diagnosis is made when it is impossible to accurately indicate the cause of the disease.
Some experts refuse the proposed classification, combining physiological, idiopathic and true forms of the disease based on the similarity of their histological picture. However, most doctors use the accepted official form of describing gynecomastia due to their differences in their nature and characteristics of the course. In addition, women are diagnosed with gynecomastia. This usually happens when it is necessary to note in the anamnesis the fact of breast growth during a period of the patient’s life, which is not characterized by such changes.
How to cure gynecomastia
Physiological forms of the disease do not require medical intervention or correction with drugs.
In rare cases, with severe symptoms in adolescence, hormonal drugs are prescribed that can reduce the concentration of estrogen in the body. If medications do not help reduce the size of the glands, plastic surgery is used to remove gynecomastia. During the intervention, excess glandular tissue is excised, and fat in the surrounding areas is also removed. The treatment regimen for pathological gynecomastia depends on the primary disease that provoked the proliferation of glandular tissue. Conservative hormonal therapy, during which the ratio of estrogen and testosterone is normalized, is effective during the first four months of development of the pathology Source: Modern ideas about the epidemiology, etiology and pathogenesis of gynecomastia. Yashina Yu.N., Rozhivanov R.V., Kurbatov D.G. Andrology and genital surgery, 2014. p. 8-15.
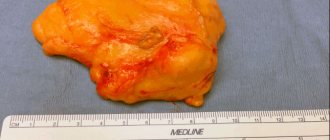
If conservative treatment does not bring results or is obviously not used (for example, in the presence of malignant tumors), surgical removal is prescribed. The surgical operation involves excision of excess tissue and restoration of the normal contours of the area. To do this, the following types of operations are performed:
- subcutaneous mastectomy, in which the areolas are preserved and access is provided through their circumference (periareolar);
- subcutaneous mastectomy combined with liposuction;
- endoscopic mastectomy (effective only with slight magnification).
Patients tolerate these types of interventions well. Fast rehabilitation allows you to return to your normal rhythm of life within a week, and even to training in the gym after a month.
Signs
External signs of gynecomastia are determined by the stage of its development:
- At the proliferation stage, there is a slight increase in the size of the mammary glands. If the pathology is detected at this stage and the patient is offered treatment, the disease goes away within a short time;
- at the intermediate stage, breast tissue grows rapidly, and milk secretion is released from the nipple. This condition causes significant discomfort to the patient. Most cases of gynecomastia are diagnosed at the second stage, because symptoms of the disease become obvious;
- at the fibrotic stage, intensive proliferation of adipose and connective tissue causes characteristic lumps to appear in the breasts. Its structural changes are considered irreversible even with prolonged intensive treatment.
Symptoms of gynecomastia are often observed in athletes taking steroid drugs. The main signs of the disease include itching, burning, discomfort in the nipple area, and the release of a small amount of milk secretion.
Postoperative period
Mastectomy is usually well tolerated, patients fully recover within a month to a month and a half. The patient stays in the hospital for no more than three days, then undergoes outpatient treatment. For 2 – 3 weeks, you need to wear special underwear with a tightening effect so that the skin shrinks better.
During the rehabilitation period, it is recommended to avoid excessive physical exertion and overwork. If your professional activity does not involve hard work, you can return to work in about a week. When the wound heals, you should immediately begin exercising and doing exercises to strengthen the pectoral muscles.
Diagnostics
Characteristic external symptoms allow the doctor to accurately make a diagnosis and prescribe additional measures to clarify the nature of the disease. You can get a comprehensive picture:
- interviewing the patient with a request to describe his own feelings and complaints of malaise;
- external examination of the mammary glands with palpation of the contents, as well as studying the condition of other organs, signs of pathology of which can be detected visually;
- biochemical blood test for gynecomastia, on the basis of which the doctor can easily determine the fact of hormonal imbalance;
- mammography, the image of which clearly shows the structure of the tissue and the features of its development;
- computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, thanks to which it is possible to determine the cause of development and the type of overgrown tissue;
- biopsy of overgrown tissues with their mandatory histological examination, necessary for the timely detection of a malignant process.
The sooner the correct diagnosis is made to the patient, the greater the chance of achieving significant treatment results and completely eliminating the external manifestations of the pathology.
Forecast
The prognosis for gynecomastia is usually favorable. In the majority of adolescents (75%), the disease regresses on average within a year or two after manifestation. After 2.5 - 3 years, the breasts acquire normal shape in the remaining 25% of young men.
The prognosis largely depends on the cause of the disease. The least favorable prognosis is hypertrophy caused by systemic pathologies - diabetes, cirrhosis, etc.
At the Euromedprestige clinic they will help you find a solution to any health problem. Our specialists will conduct a full diagnosis and draw up an optimal treatment regimen for true and false gynecomastia. If necessary, it can always be adjusted to achieve maximum effect.
Treatment methods
Depending on the severity of the disease according to the diagnostic results, the age and condition of the patient, the doctor decides on the choice of drug or surgical treatment.
A course of taking medications allows you to adjust your hormonal levels and eliminate the imbalance in favor of female hormones. It is possible to achieve good results by taking medications no later than 4 months from the moment the first symptoms appear. The basis of the course is anti-estrogenic drugs and vitamin complexes.
Surgical treatment is possible only in the absence of contraindications: acute infections, third degree obesity or cardiovascular diseases. The main method of surgery for gynecomastia is mastectomy, which allows you to completely or partially remove overgrown tissue. The priority is considered to be endoscopic or subcutaneous methods, which are characterized by minimal trauma and a good cosmetic effect.
A separate group includes cases where gynecomastia can be treated without surgery and a long course of medications. In this case, treatment is designed to reduce risk factors: reduce the content of fatty tissue in the body, normalize hormonal levels. Fats, fried and smoked foods, table salt, all types of alcohol, as well as coffee and chocolate are excluded from the diet. Dynamic observations allow us to evaluate external changes in the body and make a decision on the advisability of choosing a different treatment option for gynecomastia.