WHY DOES THE DISEASE DEVELOP?
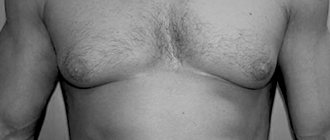
Hypertrophy (enlargement) of male breasts occurs precisely when testosterone levels drop significantly and the secretion of the female hormone (estrogen) increases, which is the most common cause of its appearance, very often this happens in adolescence, when a person’s hormonal system is not stable.
Other causes of gynecomastia may be: diabetes mellitus, tumors of various organs (adrenal glands, prostate gland, etc.), sudden increase in body weight, use of steroid drugs (medicinal gynecomastia, can occur in athletes)
At the Yuhelp clinic in Ufa you will receive accurate medical advice and surgical treatment.
Why does gynecomastia occur?
It is possible to count about 30 reasons for the formation of pathological gynecomastia. But all the reasons can be divided into 3 groups:
- An increase in female hormones in the male body.
- Decreased levels of male sex hormones (testosterone).
- Use of certain medications.
In almost all cases, gynecomastia progresses spontaneously and therefore does not cause any discomfort to a man. However, if it persists for a long time, gynecomastia increases the risk of breast cancer. This disease is rare in men. But it can lead to consequences such as breast cancer, similar to breast cancer in women. This suggests that treatment for gynecomastia cannot be delayed. Symptoms characteristic of breast cancer: the appearance of a lump, bloody discharge from the nipple, the appearance of ulceration, skin changes at the site of formation, enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes.
HOW IS SURGICAL TREATMENT PERFORMED?
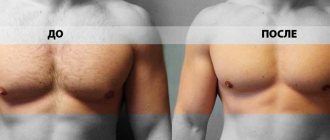
To begin surgical treatment, first of all, you need to undergo a consultation with a surgeon (plastic surgeon) at the Yuhelp clinic. After consultation with the doctor, an examination plan is formed to clarify the diagnosis. Upon completion of all procedures (usually 1-2 days), our specialists will determine the date and tactics of the surgical operation. Tactics depend on the results of the ultrasound examination. If the gynecomastia is false (only adipose tissue), we use minimally invasive access, removing adipose tissue through small incisions (0.5 cm) - liposuction . For true gynecomastia, use the classic method with access (incision) along the border of the areola. Each method can be used either separately or in combination.
Gynecomastia - symptoms and treatment
Which doctor should I contact for treatment?
Patients with gynecomastia should consult a surgeon experienced in such operations. It is extremely important that the clinic has a license for plastic surgery and a hospital, since a full-fledged operation to correct gynecomastia may require not only the removal of the mammary glands, but also liposuction of the breast area, as well as a lift or plastic surgery.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment of gynecomastia is possible only in the early stages of the disease, when the use of estrogen receptor blockers or aromatase can stop the proliferation of glandular tissue. This approach is justified when the cause of gynecomastia is known (hormonal disorders or drug-induced gynecomastia).
Surgery
If the disease exists for a long time, then its spontaneous regression is impossible, and drug treatment will not be effective, since fibrosis of the mammary glands develops.[21] Therefore, with established gynecomastia, only surgical treatment is possible.
Treatment of gynecomastia stages 1-2
A full-fledged operation to remove gynecomastia consists not only of a mastectomy - the removal of glandular breast tissue, but also of creating an anatomically correct shape of the male breast. Therefore, the surgeon must take into account both medical and aesthetic aspects, as well as listen to the wishes of the patients. Some of them strive to get rid of not only hypertrophied glands, but also to emphasize the lower edge of the pectoralis major muscle. Others want to leave excess fatty tissue, which, in their opinion, visually increases the volume of the pectoral muscles.
The main aesthetic criterion for an adequately performed surgical operation is the absence of areola inversion (“dropping” of the nipple). In foreign medical literature there are descriptions of methods for preserving part of the gland under the areola, which supposedly prevents its retraction. However, this approach is unacceptable, since it sharply increases the chances of developing a relapse of the disease: surgical trauma to the glandular tissue, if preserved, can trigger the process of secondary growth, which will lead to a partial or complete relapse of gynecomastia.
To form a smooth surface and prevent areola inversion, in 2012 we proposed a method for reconstructing fatty tissue. It involves the formation of a fat pad under the areola due to the movement of vascularized fat flaps. This technique is successfully used in men with unexpressed fat tissue, when liposuction is not necessary.
An unnoticeable postoperative scar is an important aesthetic criterion. For this reason, mastectomy should be performed through the areolar approach, and the incision itself should be made along the lower border of the areola strictly along the line of transition of the pigmented skin of the areola into the skin of the anterior chest wall. The length of the incision should not exceed 1/3 of the circumference of the areola to avoid circulatory problems. And although the removal of large mammary glands through mini-areolar access can be a certain technical difficulty, however, as personal experience shows, it is possible to remove glands of any size through the areola without increasing the surgical access.
Surgical approaches along the submammary fold (under the breast), as well as lateral vertical and transareolar approaches that extend beyond the areola should be considered unaesthetic and therefore unacceptable.
Liposuction of the breast area plays an important role in the treatment of gynecomastia. This technique, in combination with mastectomy, gives the best aesthetic results in men with true gynecomastia due to excessive deposition of fatty tissue in the chest area. Like breast removal, liposuction is performed through the areola without the need for separate accesses.
Treatment of gynecomastia stages 3-4. Breast lift
Long-term gynecomastia of large size leads to stretching of the skin and sagging breasts. For this reason, it is impossible to limit yourself to just removing the mammary glands and liposuction; to top it off, breast skin tightening is required.
Paraareolar pexy—tightening the skin around the areola—is necessary for men with grade III gynecomastia. During circular marking surgery, excess skin is excised while preserving the fascia that nourishes the areola. After liposuction and removal of glandular tissue, a padded suture is placed around the outer circumference, which tightens the skin around the areola. This technique allows you to achieve a good aesthetic result, since the postoperative scar turns into a pale texture along the border of the areola.
Amputation breast surgery with free transplantation of the nipple-areolar complex is a standard treatment method for stage IV gynecomastia with severe breast ptosis. The technique involves excision of a complex of tissues (gland/subcutaneous tissue/skin) to form a long linear scar on the anterior chest wall from the sternum to the mid-axillary line. The areola itself is transplanted above the linear scar to an area of de-epidermalized skin.
Lateral mastectomy (lateral breast lift) is our original patented technique that avoids amputation of breast surgery in cases of severe ptosis.[24] The operation combines the benefits of an areola lift with elements of amputation surgery, where a linear scar is formed from the side of the areola to the midaxillary line. The advantage of the technique is the absence of a scar on the anterior chest wall.
Treatment of gynecomastia in adolescents
Gynecomastia in adolescents usually resolves spontaneously, so in most cases no specific treatment is required.
Non-drug treatment. Folk remedies
Honey compresses, fish oil, herbal remedies and other popular methods of traditional medicine are not effective in the treatment of gynecomastia.
Diagnosis of gynecomastia
After an appointment with a doctor, the patient will need to take a blood test for estradiol, testosterone, LH, prolactin, FSH, thyrotropin, liver enzymes, human chorionic gonadotropin, nitrogen, creatinine, urea.
The examination can be supplemented with instrumental methods in order to find out the cause of gynecomastia. For example, for breast cancer, additional procedures such as mammography, biopsy, and ultrasound examination of the axillary lymph nodes and breast are prescribed.