Nicotinic acid is a truly wonderful product for the beauty of your skin, which is very easy to use at home. It costs very little, is sold in every pharmacy, and is suitable for all skin types. In general, there is no reason not to buy. You can make a lot of cool masks with nicotinic acid. It contains as many as 15 recipes, quickly choose the one you like.
In this article:
With aloeNourishing maskWith honeyYolk + honeyRejuvenating maskBrightening maskAnti-greasy Vitamin maskFor sensitive skinAdvanced alginate maskGlycerin moisturizing maskSoothing maskNight maskAnti-wrinkleFor radiance
With aloe
Photo by KoolShooters: Pexels
A universal recipe that will suit absolutely everyone. The aloe mask is made from just two ingredients and is easy to prepare.
It is best to use natural aloe gel, extracted directly from the plant that grows on the windowsill. In general, if this is not found, ready-made aloe gel from one of the well-known brands will do.
How to prepare the mask:
- aloe gel – 1 tbsp;
- nicotinic acid - half an ampoule.
Mix everything and apply to the skin. After 15 minutes, rinse with water. This mask will moisturize your skin, improve your complexion, keep your pores clean, and at the same time provide a good rejuvenating effect.
Side effects
The drug stimulates the release of histamine , which in some cases may be accompanied by:
- redness of the skin (mainly the upper half of the body and face) with a burning and tingling sensation;
- hypotension;
- orthostatic hypotension (with rapid injection into a vein);
- increased secretion of gastric juice;
- dyspepsia;
- dizziness;
- feeling of a rush of blood to the head;
- hives;
- itching.
Side effects associated with long-term use of high doses of vitamin B3 are expressed as:
- anorexia;
- impaired liver function and obesity;
- vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- irritation of the mucous membrane of the digestive canal;
- ulceration (ulceration) of the gastric mucosa;
- transient increase in the activity of alkaline phosphatase, aspartate aminotransferase, lactate dehydrogenase;
- paresthesia;
- arrhythmias;
- decreased glucose tolerance;
- hyperglycemia.
Nourishing mask
Surely you already know about the super powers of an ordinary egg yolk. This simple product perfectly nourishes the skin, has a rejuvenating effect, and all due to the record content of beneficial amino acids.
Yolk is most often added to masks for dry and tired skin. We offer a universal recipe that will suit all types. To do this, mix 1 yolk with half an ampoule of nicotinic acid and add 1 capsule of vitamin E to the composition. Apply to the face for 15 minutes.
The mask is perfect as a means for express recovery, when you urgently need to soothe the skin and speed up regeneration.
Vitamins in dermatology. Review article
Vitamins include a group of organic compounds that are present in small quantities in cells and catalyze various chemical reactions. It is known that almost all hypovitaminosis is accompanied by certain changes in the skin and its appendages. In dermatovenerology, vitamins and their various complexes are used for nonspecific immunomodulatory therapy, which changes the body’s relationship with etiopathogenetic factors and drugs used to treat this disease.
Vitamins are divided into two classes:
- water-soluble: thiamine, riboflavin, nicotinic acid, pantothenic acid, pyridoxine, folic acid, cobalamin, ascorbic acid, biotin,
- fat-soluble: retinol, calciferol, tocopherol, phylloquinone.
Water-soluble vitamins
Thiamine (vitamin B1) controls the most important processes of energy production and biosynthesis of living cell substances. This vitamin is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids. The action of thiamine is characterized as hyposensitizing, analgesic, antipruritic, anti-inflammatory; it stimulates the detoxification function of the liver and has a beneficial effect on the state of the central nervous system. Thiamine stimulates melanogenesis, as well as the synthesis of connective tissue elements. Changes in lipid peroxidation in the body of thiamine have been reported; in particular, an increase in the permeability of lysosomal and plasma membranes of leukocytes has been established. There are observations about the participation of thiamine in immunological reactions. The action of this vitamin is realized by activating the biosynthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, which underlies the proliferation of both thymocytes and bone marrow cells. With thiamine deficiency, both cellular and humoral immunity are inhibited.
Thiamine is recommended for eczema, psoriasis, lupus erythematosus, for diseases with photosensitivity - photodermatoses: porphyrin disease, lupus erythematosus, pellagra; as well as neurodermatitis, pruritus, chronic urticaria, skin itching, seborrhea, lichen planus, when the peripheral nervous system is involved in the pathological process in patients with herpes zoster, leprosy, as well as in the complex treatment of vitiligo, circular and seborrheic hair loss, chills, cheilitis , acne vulgaris, pyoderma, candidiasis.
On the other hand, a dermatologist in his practice may encounter negative effects of vitamin B1 caused by allergic reactions: urticaria, skin itching, Quincke's edema, erythroderma. A manifestation of increased sensitivity to thiamine under conditions of its production is contact dermatitis.
Riboflavin (vitamin B2) is involved in energy metabolism processes. It is part of tissue respiration enzymes and affects the metabolism of nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. This vitamin has a beneficial effect on the processes of growth, regeneration and trophism of tissues, is closely related to the metabolism of a number of other vitamins, and stimulates phagocytosis and melanogenesis.
If there is a deficiency of riboflavin in the body, wounds and trophic ulcers do not heal well.
Riboflavin preparations are effective in combination with other drugs for cheilitis, angular and aphthous stomatitis, glossitis, cracked lips, seborrheic dermatitis, alopecia, rosacea, photodermatoses, psoriasis, eczema, neurodermatitis, prurigo, acne vulgaris, streptoderma. Vitamin B2 is indicated for long-term use of antibiotics, sulfonamides, hormones, and antimalarial drugs, which are often used in dermatology. The stimulating effect of riboflavin in trophic disorders in tissues, as well as its participation in the regeneration process, make it possible to use this vitamin for the treatment of burns.
Nicotinic acid (vitamin PP or B3) is part of the enzymes of redox reactions, affects the metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, reduces blood glucose, improves the functional state of the central nervous system, liver and stomach, and participates in the reparative processes of the skin.
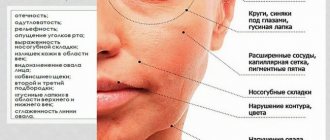
With a lack of nicotinic acid, pellagra develops (Italian pelle - skin, agro - rough). The main manifestations of pellagra are photodermatitis and inflammatory lesions of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and tongue. Dermatitis is located mainly in open areas. Erythematous in the acute period, it is accompanied by itching or burning. Then, within 2 - 3 weeks, it becomes dry and scaly, and the skin thickens. Collar of Kasal is a term used to describe sharply defined skin lesions that form around the neck, resembling a necklace. Skin lesions also occur on areas of bony prominences and on the face. When nicotinic acid is added to the diet, the skin symptoms of pellagra quickly disappear centrifugally. A decrease in the content of nicotinic acid in the body has been established in psoriasis, eczema, and photodermatoses.
Due to the vasodilating effect of nicotinic acid, it is successfully used to treat chills, chronic acrodermatitis atrophicus, Raynaud's disease and scleroderma, and due to its beneficial effect on the nervous system and liver function, it is used to treat eczema, neurodermatitis, prurigo, lichen planus, and psoriasis. The photodesensitizing effect of vitamin PP allows it to be used for photodermatoses, and its beneficial effect on the functional state of the digestive tract allows it to be used for erythematosus. Due to the ability of this vitamin to prevent and reduce toxic effects, it is recommended to prescribe it for long-term use of high doses of antibiotics, sulfonamides, antimalarial drugs, as well as in combination with other drugs - for cheilitis, stomatitis. The use of nicotinic acid gives a good effect on sluggishly healing wounds and ulcers. Nicotinic acid is prescribed to obtain the phenomenon of inflammation in the diagnosis of syphilitic roseola and erythema leprosum.
Patients suffering from allergic dermatoses during periods of severe allergic conditions (allergic dermatitis, eczema, urticaria) should not be prescribed the drug. Side effects include redness of the skin of the face and upper half of the body, increased skin temperature, sometimes itching and urticarial elements.
Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5). It has been established that pantothenic acid takes part in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and participates in redox processes and in melanogenesis.
Pantothenic acid is used in dermatological practice as a dermatoprotector, because it has a regenerating and anti-inflammatory effect. It is used in the treatment of atopic dermatitis, eczema, trophic ulcers, burns, herpes, alopecia and dermatoses of various etiologies.
Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) catalyzes processes that regulate the metabolism of nucleic acids, proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Pyridoxine deficiency leads to the development of anemia, functional changes in the central nervous system, seborrheic dermatitis, glossitis, cheilitis, and hair loss.
Vitamin B6 is used to treat dermatoses in which there is a significant lack of pyridoxine in the body - seborrhea, stomatitis, psoriasis, scleroderma, herpes zoster, photodermatoses, atopic dermatitis.
The drug is indicated for patients suffering from neurodermatitis and eczema. Pyridoxine prevents and reduces toxic effects in people taking high doses of antibiotics, antimalarial and antituberculosis drugs for a long time.
A positive clinical effect was established in patients with acne vulgaris, for the treatment of which a cosmetic cream containing 0.5% pyridoxal phosphate was used.
The use of the drug in dermatological practice for psoriasis, eczema, and neurodermatitis is associated with its ability to stimulate metabolic processes in the skin and mucous membranes. In patients with psoriasis, the use of pyridoxal phosphate is pathogenetically justified by a deficiency of pyridoxine and a violation of tryptophan metabolism at the level of the B6-dependent enzyme.
Allergic reactions to pyridoxine are possible - skin itching, urticaria, toxicoderma.
Folic acid (vitamin B9). Folic acid plays an important role in the metabolism of serine, glycine, histidine, and the biosynthesis of DNA and RNA molecules. It is also essential for the normal course of the processes of growth, development, tissue proliferation, and melanogenesis.
The administration of folic acid is accompanied by a clinical effect for psoriasis, solar urticaria, pruritus, porphyria cutanea tarda, rosacea, cheilitis, hyperkeratosis, dermatitis herpetiformis, pyoderma, acne, radiation damage to the skin, as well as with prolonged use of cytostatics, antibiotics, sulfonamides. Thus, the combination of methotrexate with folic acid in the treatment of patients with psoriasis significantly reduces the incidence of such serious side effects as anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Folic acid is classified as a vitamin that is characterized by severe toxicity, since even a single administration of it to a person in a dose of more than 100 mg causes symptoms reminiscent of histamine poisoning - severe redness of the face, an itchy maculopapular rash, etc. Positive skin tests in some cases indicate about the allergic nature of such phenomena.
Cobalamin (vitamin B12). The ability of cobalamin to increase nonspecific resistance to bacterial infections has been established. One of the basis of the mechanism of the immunomodulatory action of this vitamin is considered to be its effect on the exchange of nucleic acids and proteins.
Vitamin B12 is successfully used for psoriasis, photodermatoses, dermatitis herpetiformis, and neurodermatitis.
When cobalamin is administered, allergic reactions in the form of urticaria and Quincke's edema are possible. The combined use of cobalamin with thiamine more often causes the development of allergic reactions than separate use. In case of a pronounced hyperergic state during the period of exacerbation of eczema and neurodermatitis, the administration of cobalamin can enhance allergic reactivity, therefore, in the acute stage of dermatoses, the use of this vitamin should be avoided. A similar tactic is advisable for the progressive stage of psoriasis, psoriatic erythroderma and its arthropathic form.
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is involved in the formation of connective tissue, the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, the synthesis of adrenal hormones, nucleic acids, has a beneficial effect on regenerative processes, regulates pigment metabolism in the skin, stimulates the antitoxic function of the liver, the activity of the endocrine glands, promotes adaptive abilities of the body. Ascorbic acid preparations are characterized by antitoxic, hyposensitizing, anti-inflammatory, and antihyaluronidase effects. In vitro, the bacteriostatic and bactericidal role of vitamin C in relation to staphylococcus and streptococcus was revealed.
Vitamin C deficiency leads to disruption of the T-immune system and less significant deviations of humoral immunity. The fact of melasma due to vitamin C deficiency is widely known. Violation of collagen synthesis with vitamin deficiency is reflected in poor wound healing.
The positive effect of ascorbic acid has been noted in inflammatory, degenerative and other pathological processes of the skin. The administration of ascorbic acid is advisable for toxicoderma, allergic dermatitis, eczema, neurodermatitis, prurigo, chronic urticaria, lichen planus, photodermatoses, vasculitis, pemphigus, stomatitis, glossitis, chronic atrophic acrodermatitis, chronic pyoderma, acne vulgaris, alopecia alopecia, mycoses of the feet, a also with prolonged use of corticosteroid drugs and antimalarials. In the treatment of diseases manifested by vascular pathology of the skin, the effectiveness increases with the combination of ascorbic acid and rutin.
Biotin (vitamin H) is an organic acid that participates in numerous carboxylation reactions. Biotin deficiency is accompanied by alopecia, dryness, scaly skin (seborrhea), skin hyperesthesia, swelling and atrophy of the tongue papillae.
Used in the treatment of atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, alopecia, seborrhea. A good clinical effect was obtained when treating acne vulgaris with high doses of biotin.
Fat-soluble vitamins
Vitamin A (retinol). In terms of the variety of reactions in which retinol is involved, it ranks first among vitamins. Retinol affects the processes of reproduction and growth, redox processes, the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, the synthesis of corticosteroids and sex hormones, nucleic acids. Retinol is involved in the regeneration of epithelial tissues and regulates the processes of keratogenesis. The important function of retinol has been established as maintaining the stability of plasma and subcellular membranes. At the same time, retinol hypervitaminosis leads to shifts in the activity of phospholipases, which play an important role in changes in the composition of biomembranes. The antioxidant properties of retinol have been established. The ability of the vitamin to have an immunomodulatory effect is noted. This vitamin causes a relative and absolute increase in the content of B-lymphocytes in the peripheral blood. With retinol deficiency, antibody formation is inhibited. The ability of this vitamin to relieve the immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids is known.
Retinol deficiency in the body naturally manifests itself as a violation of the processes of keratinization of the skin and mucous membranes, especially the oral cavity; brittle nails, hair loss, phrynoderma (Greek Phrynos - toad) - follicular keratosis, in which areas of keratinization are surrounded by a zone of depigmentation on the skin of the upper arms and legs, are noted. Then it moves to the torso, back, stomach and neck. Lesions on the face may resemble comedones due to inflammation of the sebaceous glands of the hair follicles.
The beneficial effect of retinol in inflammatory, degenerative and other pathological processes of the skin serves as the basis for its widespread use in dermatological practice. This vitamin is effective for diseases accompanied by hypertrophy of the stratum corneum of the epidermis (all forms of ichthyosis, follicular keratosis, hyperkeratosis of the palms and soles). It is used in the treatment of dermatoses, which are characterized by disturbances in the processes of keratinization (psoriasis), the secretory function of the sebaceous glands (seborrhea, seborrheic alopecia, acne vulgaris), with damage to the mucous membranes (leukoplakia), nail dystrophy, hair growth disorders (dryness and increased fragility, monilethrix (Latin monile necklace + Greek thrix hair; - hereditary hair dystrophy, manifested by alternating spindle-shaped thickenings of the hair shaft with areas of thinning, dryness, fragility and hair loss. In combination with other agents, retinol is useful in the treatment of eczema, chronic ulcerative pyoderma, trophic ulcers, Raynaud's disease. Taking into account the pronounced antioxidant properties of retinol, its combination with tocopherol acetate and 0.5% selenium ointment has been successfully used in the treatment of psoriasis and baldness.
Hypervitaminosis A is also characterized by dermatological manifestations: rash, itching, pigmentation, yellow discoloration of the skin of the palms and soles, delayed wound healing, hair loss. Seborrheic rashes and bleeding of the mucous membranes of the mouth may be observed on the skin.
Retinoids, being synthetic derivatives of vitamin A, have significantly expanded therapeutic options for a number of dermatoses, including severe ones and those resistant to other medications. Synthetic retinol derivatives - aromatic retinoids - are hundreds of times less toxic than their natural predecessor, so they can be used in the clinic in fairly large doses for a long time. Etretinate (tigazone) and 13-cis-retinoic acid (isotretioin) have found use in clinical practice.
The influence of retinoids is characterized by an amazing variety of biological effects. In practical terms, the most significant is their antitumor and immunostimulating effect; When these drugs are prescribed in patients, the total number of lymphocytes in the blood and the number of T cells significantly increases.
Isotretinoin (the commercial name of the drug is “Roaccutane”), which has a sebostatic effect (inhibits the secretion of the sebaceous glands), is used in the treatment of various forms of acne. Among the side effects during the period of taking maximum doses of Roaccutane, in some cases, increased dryness of the skin is observed, especially around the mouth, mucous membranes of the oral cavity, as well as dermatitis of the facial skin, weeping, itching, and reversible alopecia.
Another retinoid, tigazone, due to its antiproliferative effect, has been effective in the treatment of psoriasis. The effectiveness of treatment increases significantly when etretinate is combined with photochemotherapy. The authors recommend such an integrated approach in the treatment of patients with widespread, often recurrent psoriasis.
There is evidence of a favorable clinical result of the use of tigazon in the treatment of patients with lichen planus of the oral mucosa, subacute lupus erythematosus, hyperkeratotic eczema of the hands and feet, palmoplantar hyperkeratosis, pustulosis of the palms and soles, and ichthyosis of various forms.
The most common complications of taking tigazone include dry mucous membranes, itching, hair loss, and excessive peeling of the palms and soles.
Calciferol (vitamin D). The skin plays a major role in the production of vitamin D, where it can be actively synthesized by keratinocytes, fibroblasts and macrophages under the influence of UV rays.
The action of the vitamin is realized by regulating phosphorus-calcium metabolism; it also has a regulating effect on the state of the autonomic nervous and vascular systems, increases sweating and sebum secretion, improves hair growth, and normalizes water metabolism in the skin. Many tissues have receptors for calcitriol, so it is thought to have a variety of functions that are not yet understood. Thus, its active influence on cell differentiation in normal and tumor tissues has recently been established.
Due to the wide range of biochemical activity of calciferols, they are used in the treatment of tuberculous lupus, scrofuloderma, and chromomycosis. The literature describes a case where the administration of vitamin D for senile osteoporosis led to regression of concomitant psoriasis in the patient, which served as the basis for the use of vitamin D in the treatment of this disease.
Calciferol can cause acute poisoning with symptoms of hemorrhagic vasculitis. With prolonged use of high doses of the vitamin, pustular and acne-like rashes and general sweating may occur. These phenomena are reduced with the combined use of calciferol with retinol, thiamine and ascorbic acid.
Tocopherol (vitamin E) affects the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids and steroids, promotes the accumulation of retinol and other fat-soluble vitamins in the body, exhibits anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic effects, reduces the permeability of the vascular wall, and acts as an antioxidant. Protecting lipids from peroxidation is one of the most studied functions of vitamin E. Since unsaturated lipids are a component of biological membranes, this function of tocopherol is very important for maintaining the structural integrity and functional activity of lipoprotein cell membranes and subcellular structures. The immunostimulating properties of tocopherol are realized by inhibiting the activity of T-suppressors. At the same time, vitamin E significantly increases the activity of natural killer cells.
The use of vitamin E is indicated for ichthyosis, dermatomyositis, scleroderma, Raynaud's disease, photodermatoses, psoriasis, ulcerative stomatitis, poorly healing leg ulcers, X-ray ulcers, acne vulgaris, seborrhea, nested hair loss, as well as for dermatoses associated with dysfunction of the gonads. Good clinical results have been established with the combined administration of tocopherol acetate, retinol and 0.5% sodium selenite ointment to patients suffering from psoriasis and alopecia alopecia.
Vitamin E is also used externally in dermatology - in the form of an oil concentrate or an ointment containing 3% tocopherol acetate.
Vitamin K (phylloquinone) is involved in blood clotting, enhances the anti-inflammatory effect of steroid hormones, affects tissue regeneration, increases resistance to infections, and has an analgesic effect. Vitamin K deficiency leads to the development of hemorrhagic syndrome.
The use of vitamin K is indicated for burns and frostbite, radiation injuries, dermatoses with a hemorrhagic component, ulcerative stomatitis, gingivitis, and dermatomyositis.
Vitamin-like compounds
Lipoic acid (vitamin F) is part of a multienzyme complex involved in the decarboxylation of pyruvic acid, exhibits a pronounced hepatotropic and weak hypoglycemic effect, activates the consumption of glucose and pyruvate by tissues, reduces the content of cholesterol and total lipids in the blood serum, stimulates phosphorylation and protein biosynthesis in the liver.
The effectiveness of lipoic acid in psoriasis and dermatoses accompanied by impaired liver function and lipid metabolism has been established.
With prolonged use of lipoic acid, allergic skin reactions are possible.
Calcium pangamate (vitamin B15) affects lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, increases the activity of respiratory chain enzymes, and therefore significantly increases the absorption of oxygen by tissues. Due to the lipotropic effect of the vitamin, the total content of lipids in the liver, as well as cholesterol, decreases, the production of glucocorticoids increases, and a detoxifying effect is observed.
Calcium pangamate is successfully used for psoriasis, pruritus, skin itching, toxicoderma, as well as to improve the tolerability of corticosteroid and sulfonamide drugs.
Rutin (vitamin P). The vitamin P group includes a number of substances - bioflavonoids, which have the ability to reduce the permeability and fragility of capillaries.
The physiological effect of the vitamin is realized through the endocrine glands, through its influence on the enzyme systems involved in tissue respiration. Vitamin P preparations exhibit antihistamine effects and antioxidant properties. Rutin regulates free radical homeostasis through several mechanisms. Firstly, it neutralizes the most dangerous radicals (peroxynitrite and hydroxyl), and secondly, it controls the production of physiologically important radicals (superoxides) by cells. In addition, rutin stimulates the release of nitric oxide, the main stimulator of relaxation of the muscles of the vascular wall.
With vitamin P deficiency in the body, characteristic changes are noted in the form of small intradermal hemorrhages (petechiae), which occur spontaneously, especially in areas of pressure, and disappear after the administration of bioflavonoids.
The use of vitamin P is advisable in case of increased permeability of blood vessels and their fragility (hemorrhagic diathesis, capillary toxicosis). The effectiveness of vitamin P has been noted for toxicoderma, allergic dermatitis, eczema, urticaria, vasculitis, exudative form of psoriasis, erythroderma, Dühring's dermatosis, and radiation dermatitis.
Along with vitamin P, it is advisable to prescribe ascorbic acid.
Methylmethionine sulfonium chloride (vitamin U), being a donor of methyl groups, is involved in the biotransformation of various xenobiotics, as well as the methylation of histamine, which provides an antihistamine effect. When studying the autoflora of workers involved in the production of methylmethionine sulfonium chloride, a significant increase in the number of microbes was found, an increase in the number of hemolytic forms of microorganisms and yeast-like fungi. Such changes are regarded as evidence of the possibility of a nonspecific effect of vitamin production products on the general reactivity of the body.
Vitamin U has proven to be somewhat effective in the complex treatment of patients with psoriasis, especially patients with concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
The material was prepared by dermatocosmetologist S.N. Lyshkanets
Yolk + honey
That's right, another nourishing mask in our selection, this time with all the nourishing ingredients you can find in the refrigerator. You will need:
We erase wrinkles from the face with nicotinic acid
- yolk;
- a tablespoon of honey;
- a tablespoon of milk;
- ampoule of nicotinic acid.
Mix everything and apply generously to the face. After 20 minutes, rinse off, wipe the skin with toner and apply your favorite cream. The recipe has proven itself as a remedy for dry skin.
Rejuvenating mask
A mask with argan oil will help get rid of wrinkles, tighten your skin, and at the same time improve your complexion. This is one of the best anti-aging products that can be used even in its pure form. If you add half an ampoule of nicotinic acid to it, you will get a real elixir of youth.
But we have slightly expanded the recipe so that the skin gets even more benefits. Prepare the mask like this:
- shea butter – 1 tbsp;
- argan oil – 10 drops;
- nicotinic acid – ½ ampoule.
Heat the shea butter a little. It should be warm, not hot. Add the rest of the ingredients to it and apply to the skin. You can leave it overnight if your skin “eats” the oil, or you can wash it off after 20 minutes if you feel a film on your face - it all depends on the characteristics of your skin.
Interaction
N. acid enhances the effect of vasoactive drugs (in particular, ganglion blockers), which may be accompanied by attacks of orthostatic hypotension .
Bile acid sequestrants (for example, colestipol or cholestyramine ) reduce the bioavailability of acidic drugs, including n. acid, so the drug should be taken at least one hour before or no earlier than four hours after taking these medications.
When conducting an analysis to determine the level of glucose in urine, the drug may provoke a false-positive reaction with Benedict's reagent (copper sulfate solution).
N. acid has hyperglycemic potential and can significantly reduce the activity of acarbose, which can cause the development of decompensation of diabetes mellitus .
Due to the ability of N. acids cause hyperglycemia , patients who are prescribed the drug in combination with “ metformin + saxagliptin ” or “metformin + sitagliptin ” should constantly monitor their glycemic control parameters.
In patients taking nadroparin calcium, it is necessary to keep hemocoagulation parameters under control.
With simultaneous use of n. acids and combinations “ amlodipine + atorvastatin ”, n. acid and simvastatin , n. acid and lovastatin may increase the risk of developing myopathy . Combination n. acid with simvastatin can also provoke rhabdomyolysis .
Myopathy and rhabdomyolysis are also possible when using the combination “n. acid in lipid-lowering doses and Simvastatin + Ezetimibe .”
The risk of developing myopathy also increases when lipid-lowering (exceeding 1 gram per day) doses of n. acids in combination with Rosuvastatin . In this regard, treatment with Rosuvastatin should be started at 5 mg/day.
The combination “Nicotinic + Ascorbic acid ” should be used with caution.
The possibility of drug interaction with sodium heparin .
High doses n. acids reduce the effectiveness of the combination “ Glibenclamide + Metformin ”, the hypoglycemic effect of Gliclazide and the effectiveness of the combination “ Gliclazide + Metformin ”, as well as the hypoglycemic effect of Glimepiride .
When used simultaneously with n. acid reduces the effect:
- Glipizide;
- hypoglycemic effect of Gliquidone ;
- Insulin Lispro (including biphasic);
- Metformin;
- Repaglinide;
- hypnotic effect of Phenobarbital .
It is forbidden to mix n in one syringe. acid and Thiamine .
Despite the fact that the simultaneous use of n. acids with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors can provoke myopathy , with simultaneous administration of the drug with Fluvastatin , the bioavailability of the latter, as well as the bioavailability of n. acid does not change. However, this combination should be used with caution.
For sensitive skin
Nicotinic acid promotes regeneration, so it is also suitable for sensitive skin. To prepare a mask that will relieve flaking, soothe and speed up regeneration, take the following ingredients:
- cereals;
- half a banana;
- half an ampoule of nicotine;
- spoon of milk.
Pour milk over about a spoonful of oatmeal and let stand for a couple of minutes. At this time, mash half a banana with a fork and add it to the oatmeal. At the end, add nicotinic acid, mix everything and apply to the skin for 5-20 minutes.
Since the mask is thick and tends to slide off the skin, it is better to apply it while lying down.
Indications for use
Indications for the use of Nicotinic acid are:
- hypo- and avitaminosis caused by insufficient intake of vitamin B3 from food, exclusively parenteral nutrition, malabsorption syndrome (including against the background of pancreatic ), Hartnup disease, rapid weight loss, gastrectomy , diseases of the digestive system ( persistent diarrhea , including tropical , celiac enteropathy , Crohn's disease );
- conditions accompanied by an increased need for vitamin PP (diseases of the hepatobiliary system, prolonged fever, hyperthyroidism , prolonged stress, chronic infections, pregnancy, lactation, cancer);
- hyperlipidemia (including triglyceridemia and hypercholesterolemia );
- atherosclerosis;
- obliterating diseases of the vessels of the lower extremities (for example, Raynaud's disease );
- ischemic cerebral circulatory disorders;
- spasm of the urinary and biliary tract, vessels of the extremities;
- microangiopathy;
- diabetic polyneuropathy;
- hypoacid gastritis;
- colitis and enterocolitis ;
- facial nerve neuropathy;
- trophic ulcers and non-healing wounds.
Glycerin moisturizing mask
A glycerin mask will help quickly get rid of dryness and restore the water balance of the epidermis. Glycerin can be purchased at a pharmacy. While you're there, grab aloe extract in ampoules at the same time - we'll need it too.
So, the recipe:
- a tablespoon of glycerin;
- a teaspoon of aloe extract;
- teaspoon of nicotinic acid.
Mix everything and apply to the skin. This is difficult to do, the mask leaks, so use a cotton pad. Apply several layers of this liquid and wait until it dries. Then be sure to wash your face and apply moisturizer on top.
Night mask
Surely you have a cream that seems to be suitable, but doesn’t seem to do anything special to the skin. Know that you can give it a second life as a night mask.
To do this, take a portion of the cream and mix it with half an ampoule of nicotinic acid. Prepare your skin for bed as usual: wash your face, wipe your face with toner or apply toner, then a layer of serum. As soon as the serum is absorbed, seal it with nicotine cream - this will be your new night mask.
In the morning, be sure to wash your face with foam or gel; any night mask must be washed off.
What is nicotinic acid
This is a B vitamin (PP). Other names: nicotinamide, niacin, pyridine-3-carboxylic acid, C₆H₅NO₂. Trichologists recommend it for hair loss, to increase hair density, strengthen hair follicles, and also if you want to grow long hair.
Available in:
- solution for intramuscular/intravenous injections (in glass ampoules);
- tablets,
- liquids for local rubbing (sprays, plastic capsules).
More often, the latter option is used for hair treatment. But the effectiveness of the drug has not been fully studied. With regular rubbing of the contents of the ampoules, the condition of the curls really improves.
But it is not clear whether this happens due to vitamins or as a result of massage manipulations. It is possible that one complements and enhances the effect of the other.