Classification of the disease
Alopecia areata is autoimmune in nature. The human body begins to perceive healthy hair as a threat and at the same time tries to get rid of foreign formations.
There are several provoking factors for its development.
1. Genetic predisposition. If there were relatives in the family suffering from a similar illness, then the likelihood of its occurrence increases. The hereditary transmission of the defect has been proven by scientists. 2. Psychological factor. Experiencing stressful situations contributes to the launch of genetic mechanisms. 3. Disorders of the peripheral nervous system. Problems in the functioning of nerves are manifested by insufficient blood flow. Hair follicles do not receive the proper amount of nutrients, which causes their depletion. As a result, their growth stops completely. 4. Autoimmune problems. Pattern baldness can occur as a result of an immune failure. Cells that protect the body from foreign bodies begin to perceive their own as a potential threat to life and health. The trigger for such a factor is often an acute infection, injury, chronic infection (tonsillitis, rhinosinusitis, caries, etc.). 5. Endocrine disorders, improper functioning of the adrenal gland, pituitary gland, hypothalamus, and thyroid gland can increase the level of testosterone (male hormone). This failure provokes hair loss with increased sensitivity to changes.
Risk factors for developing androgenetic alopecia
When studying the causes of androgenetic alopecia, experts identified several factors leading to the development of pathology:
- Gender. Men suffer from androgenic pattern baldness 4–5 times more often than women.
- Age. Every second man and fourth woman over 50 years old finds signs of androgenetic alopecia.
- Hormonal imbalance. Hormonal imbalance in women usually occurs after pregnancy or during treatment with medications containing male hormones. In men, the cause of alopecia can be the use of drugs that activate testosterone production, for example, various types of doping agents.
- Heredity. If androgenetic alopecia was identified in previous generations, or if relatives suffered from severe hair loss for no apparent reason, then the probability of this pathology occurring in subsequent generations is close to 80%.
- Various types of tumors and damage to the glands that produce sex hormones.
- Hyper- or hypofunction of the pituitary gland.
- Oncological formations in the adrenal glands or increased function due to certain diseases.
- Decrease or increase in the level of hormones produced by the ovaries and testicles in orchitis, polycystic disease, ovarian sclerocystosis, ovarian disease.
If the patient has at least one of the listed risk factors and his hair has noticeably thinned, then you should not postpone a visit to the dermatologist. After examination, the doctor will either decide that it is androgenetic alopecia or diagnose another cause of hair loss.
Genesis
In medicine there are 3 main stages:
1. the first one is spicy. It is accompanied by uncomfortable sensations, which manifest themselves as itching, burning, redness and inflammation of the skin at the source of development. This entails complete degeneration of the hair follicles;
2. second - subacute. The patient does not experience any discomfort, and the inflammatory process is minor;
3. third - regression. The process of baldness stops, and the affected areas begin to become covered with “fluff”. Over time, the strands return to normal and resume their growth.
Please note that when checking for symptoms of bald patches, it is necessary to undergo an examination and tests from a number of specialists: an endocrinologist, trichologist, dermatologist and gastroenterologist. Only an integrated approach will provide a holistic picture of the ongoing violation. Monitoring the presence of sexually transmitted infections and disruptions in the functioning of the nervous system will exclude related diseases.
Directions for future research
Current areas of research and future therapeutic modalities include:
- stem cells of follicular origin,
- as well as technology for culturing hair follicle tissue.
Accurate identification and effective delivery of appropriate protective and triggering mechanisms that will stimulate the activation of quiescent stem cells can make prevention and reversal of hair loss possible.
Recorded based on the report of Ovcharenko Yu.S., Associate Professor of the Department of Dermatovenerology of KhMAPO, member of the board of the European Hair Research Society (EHRS), head of the Institute of Trichology clinic (Kharkov) at the VI scientific and practical conference of the non-profit partnership “Professional Society of Trichologists”.
Symptoms
The manifestation of alopecia areata varies among several clinical forms.
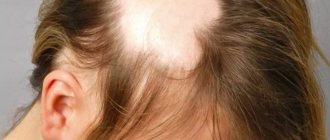
1. Local. The sources of baldness are scattered on the head, have rounded outlines and do not intersect with each other. 2. Ribbon-shaped (serpentine). Based on its name, it is clear that baldness looks like a ribbon that meanders towards the temples from the occipital area. Most common in children. It differs in that the hair does not fall out completely, and the borders of the bald spot will be covered with fluff for a long period of time. 3. Subtotal. In this case, areas of vegetation loss can merge together and thereby form large areas of bald patches. 4. Total. Loss occurs around the circumference of the head, including facial hair (eyelashes, eyebrows) and other areas with natural hair (groin, face, armpits). 5. Universal. It is a malignant form that causes hair shedding in all parts of the body. 6. Spot. It is expressed in the form of small sources of baldness that are in contact with each other. The diameter of the dots reaches only 1–2 mm. 7. Shearing. Complete hairlessness of the affected areas on the body. Often found on the frontal or parietal region of the head. In this case, the vegetation looks broken off, and the length is no more than 15 mm. 8. With a negative effect on nails. A complex manifestation of the disease, in which skin derivatives (nails, teeth) suffer.
The most noticeable developmental symptom is loss of hair on the head. The number of plots is not limited, and the area may vary. The progression of the condition provokes a total loss of follicles on the body.
Characteristic features include:
● detection of pathologies accompanying the disease; ● the skin turns red and wounds form on it; ● presence of areas with thinning hair; ● inflammatory processes on the surface, accompanied by itching, pain, discomfort; ● decrease in the elasticity of the cover; ● violation of the shade and structure of nails, increased fragility; ● one or two-sided loss of eyelashes and eyebrows.
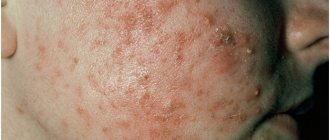
It is important to distinguish alopecia from infection with fungus, mycoses or ringworm. A distinctive feature is the unforeseen nature of the further course. The return of curl growth can occur without therapeutic intervention, and also form new areas.
Alopecia
Fungus
Syphilis
Chicken pox
20392 November 16
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Alopecia: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Alopecia is a pathological partial or complete loss of hair on the head, face and/or other parts of the body, resulting from damage to the hair follicles.
Normally, a person loses up to 100 hairs per day. Losing more hair is considered pathological and can lead to partial or complete baldness.
Hair consists of a visible part (shaft) and a root located in the hair follicle (hair follicle). There are approximately 100,000-150,000 follicles on the human head, in which hair growth occurs.
It is customary to distinguish three stages of hair growth:
1st phase - anagen, when the hair grows continuously; the duration of this phase is from 2 to 5 years;
2nd phase - catagen, when hair growth stops and the hair follicle prepares to enter the resting stage; the duration of this phase is 3-4 weeks;
3rd phase - telogen, when the hair separated from the root moves to the surface and falls out, and the follicle rests and prepares to produce new hair; The duration of this phase is 2-4 months.
Normally, approximately 80-90% of human hair is in the anagen phase, 1-2% in the catagen phase and the rest in the telogen phase.
Classification of alopecia
It is customary to distinguish scarring and non-scarring alopecia.
Scarring alopecia is characterized by complete destruction of hair follicles with the formation of fibrous tissue in their place and the impossibility of hair regrowth.
Non-scarring alopecia:
- nested
- manifested by hair loss in a limited area (usually on the scalp) without the formation of scar tissue in the affected areas. Alopecia areata can be local (focal), band-like (marginal), subtotal, total and universal - with damage to the nail plates; - diffuse
(symptomatic, toxic alopecia) - a disease characterized by widespread diffuse hair loss associated with a violation of the physiological change in the phases of their growth; - androgenetic
- a disease associated with a genetically determined disorder of androgen metabolism in the scalp; usually baldness affects the parietal and frontal areas; - seborrheic
- occurs against the background of seborrhea (an inflammatory disease caused by an increase in sebum secretion and a change in its composition).
Causes of alopecia
The causes of scarring (irreversible) alopecia may be hereditary disorders; mechanical or thermal injuries to the skin; fungal (trichophytia, favus), bacterial (tuberculosis, syphilis, etc.), protozoal (leishmaniasis) or viral (shingles, chicken pox) diseases; neoplasms (squamous cell carcinoma); various dermatoses (scleroderma, Hoffmann's folliculitis, etc.).
Alopecia areata can be a consequence of diseases such as malaria, syphilis, shingles, fungal infection, HIV infection. With mycobacteriosis, even a minor injury contributes to infection of the scalp, and after 2–3 weeks the hair becomes brittle. Staphylococcal skin lesions are determined when hair grows into the skin.
Diffuse alopecia develops during pregnancy and lactation, with hypothyroidism, malignant neoplasms, and syphilis. Stress plays a significant role in the formation of the disease. Etiological factors contributing to the occurrence of diffuse alopecia include radioactive radiation, chemotherapy, exposure to strong poisons, long-term use of medications (antibiotics, antipsychotics, antidepressants, etc.).
With insufficient nutrition, the body can develop a deficiency of not only protein, but also essential microelements: iron, zinc, copper, chromium, sulfur, selenium, magnesium, potassium, silicon, which also does not have the best effect on the condition of the hair.
Androgenetic alopecia is associated with dysfunction of the endocrine glands (diseases of the adrenal glands, sclerocystic ovarian syndrome, etc.) and genetic factors.
Seborrheic alopecia is a complication of seborrhea. It develops in approximately 25% of people, usually beginning during puberty and reaching its maximum severity by age 25.
Alopecia symptoms
Scarring alopecia begins with the appearance of small patches of baldness in the parietal or frontal areas. The process may be accompanied by redness of the skin. In unaffected areas, hair is usually not changed, but is easily removed along the periphery of the lesions. At a later stage, significant fibrosis is observed in the dermis.
Another type of cicatricial alopecia is Hoffmann's abscess folliculitis. The disease is characterized by multiple deep and superficial abscesses, which, when healing, turn into rough, often keloid scars.
Alopecia areata is manifested by rounded lesions of varying sizes, devoid of hair. The process is most often localized on the scalp, but can affect eyebrows, eyelashes and other areas of the skin (in men, the beard and mustache growth area). At first, the areas of baldness are small (up to 1 cm in diameter) with normal skin (sometimes short-term redness is observed). Then they enlarge, new ones appear, merge with the old ones, forming large areas of baldness, along the periphery of which there is hair in the form of an exclamation mark - narrowed at the base and thickened towards the end. After a few weeks or months, hair growth may resume in the original lesion, which does not exclude the appearance of new lesions. The growing hair is initially thin and unpigmented, but gradually it regains its structure and color.
Androgenetic alopecia is characterized by the replacement of normal hair in the temporo-frontoparietal region with gradually thinning vellus hair, which shortens over time and loses pigment. First, bald patches appear in the temple area, then the parietal region is involved in the pathological process. The Norwood scale is used to determine the degree of male pattern baldness, and the Ludwig scale is used to determine the degree of hair thinning in women.
With seborrheic alopecia, the hair becomes oily and sticks together. Yellowish scales can be seen on the hair and skin. A person often complains of itching. The disease is characterized by a shortening of the anagen stage, which causes premature hair loss, thinning and replacement with vellus hair. Baldness usually begins from the edges of the forehead to the back of the head or from the crown to the forehead and back of the head. Along the edges of the bald spot there are always tightly-set hairs.
Diagnosis of alopecia
Laboratory and instrumental research of alopecia includes a wide range of tests:
- clinical blood test: low levels of hemoglobin and red blood cells indicate the presence of anemia, an increase in the red blood cell index indicates B12 and folate deficiency conditions; an increased level of leukocytes and neutrophils can be observed in the presence of an infectious focus in the body;
Diagnosis
In order to determine the type of baldness, a standard examination of the location of the disease will suffice for the doctor. In some situations, a dermatoscope is used during examination. If during the study a diagnosis of alopecia areata is made, then the causes and treatment will be interconnected in order to achieve the desired result. Accurate determination of the factors of its occurrence requires the patient to undergo research:
● blood and urine sampling (checking the body for the presence of inflammatory processes); ● monitoring immunity for increased activity; ● monitoring of hormonal levels; ● Trichogramma (determines the quality and volume of vegetation); ● examination of the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms
Thinning begins gradually
Excessive hair loss occurs when combing and other manipulations
· thinning of hair in any area (on the top of the head, along the central parting, on the temples, etc.)
appearance of round lesions without hair
· in some cases, the disease begins with redness of the skin, the formation of scales, and itching
If you notice excessive hair loss on the scalp, you need to consult a specialist to rule out possible diseases or begin treatment immediately if the diagnosis requires it.
How to cure the cause of alopecia areata
Only a specialist - a dermatologist or trichologist - can stabilize the condition. At the first symptomatic signs, you should not delay a visit to the doctor in order to avoid progression of the disease to more complex stages of clinical manifestation.
The procedure is divided into 2 stages:
1. Psychological assistance, in which a specialist will explain the complexities of the disease and the need for individual selection of medications. 2. Drug therapy, accompanied by the use of drugs to correct pathologies of the body and eliminate the entire range of concomitant diseases.
The most popular methods of therapeutic influence on the affected boundaries are a combination of several areas:
1. The use of ointments containing strong corticosteroid hormones. They can slow down the production of protective cells and are effective for autoimmune conditions. However, you should not apply ointments over a long course, as this may lead to the development of unwanted side effects. 2. Corticosteroid injections. Using an injection, a concentrated drug is injected into the affected area, restoring hair growth. For a large area, it is irrational to use this method, due to the formation of atrophic phenomena of the scalp. 3. Hormonal pills. The corticosteroids included in the composition will actively affect the entire body. 4. Complex drugs. The greatest effect is achieved with simultaneous stimulation with medicinal agents in several directions: tablet form from the inside, spray, lotion from the outside. A typical representative of this group of drugs is Selencil. It is able to stop the loss of vegetation, eliminate its causes, accelerate growth and increase density. 5. Phototherapy. The procedure is carried out using ultraviolet radiation, which promotes hair restoration. 6. Vitamin complex containing adaptogenic and biostimulating components. 7. Preparations to improve skin microcirculation (Sermion, Trental, Troxevasin ointment). 8. Immunomodulators.
Treatment of focal baldness in women
Regardless of what the cause is, alopecia is treated comprehensively. The treatment regimen includes basic drugs and additional drugs:
- external therapy, low-intensity laser therapy;
- injection methods of treatment: mesotherapy, ozone therapy, fractional microneedling therapy;
- correction of mineral metabolism disorders and deficiency conditions;
- vitamin-mineral complexes;
- corticosteroid therapy (in some cases).
The course of treatment takes from 4 to 12 months (depending on the form, stage and course of the disease).
An important part in the complex treatment of focal baldness in women is proper care of the scalp and hair, scalp peelings of various types, massage of the back and cervical-collar area. If necessary, consultations with related specialists (endocrinologist, therapist, hematologist, gastroenterologist, neurologist, psychotherapist) are recommended to identify and eliminate possible causes of the disease.
Looking for where to go for effective treatment? Alopecia can be overcome, but for this you need to use proven methods and means. An-Tech Research Laboratories offers:
- guaranteed treatment results;
- pleasant service without queues or waiting;
- customer focus;
- advanced methods in treatment;
- professional approach to the work of all specialists;
- attention and care for everyone within the walls of the clinic.
Back to list of articles
Alopecia areata: how to treat with auxiliary means
Bald patches are effectively combated using physiotherapeutic methods: 1. PUVA therapy; 2. Electrophoresis; 3. Dansorval; 4. Cryomassage; 5. Mesotherapy; 6. Laser therapy; 7. Iontophoresis; 8. Massage.
In this case, there is a specific effect on the bald area and nutrition of it with useful substances.
The use of folk remedies is not recommended due to their low effectiveness and the possibility of causing more undesirable consequences. Only a doctor knows how to treat alopecia areata and selects an individual course of treatment based on the results obtained during examinations.
It is worth paying attention to the fact that the treatment process is time-consuming and quite expensive, and it may not always lead to a positive resolution of the problem. If conservative therapy is ineffective, baldness can be cured only by transplanting strands.
Treatment of androgenetic alopecia with traditional methods
Since ancient times, traditional medicine has offered various ways to strengthen hair, increase the density of curls, and reduce the rate of baldness. But all of them will give the expected effect only when used together with medications.
- Onion rub. At the first signs of thinning, it is recommended to rub a mixture of chopped onion into the hair roots. Leave the mask on for an hour and a half, then wash off with strengthening or regular shampoo. If you add crushed garlic and a little honey to the onion mass, the procedure will be even more effective.
- Pepper tincture. Grind the pepper, pour in 100 ml of vodka and leave for 24 hours. Then rub the tincture into the scalp and after an hour and a half, wash your hair thoroughly.
- Onion-cognac tincture. Grind a medium onion through a meat grinder and pour 200 ml of cognac into it. The mixture should sit for several hours. To achieve a positive result, the tincture must be rubbed into balding areas of the head daily.
- Mustard mask with castor oil. Take one tablespoon of dry mustard, mix it thoroughly with 30 ml of castor oil and let it brew for 20-30 minutes. To reduce the amount of hair falling out, a mustard mask should be applied to the scalp for 40–50 minutes. The session is carried out before each hair wash 1-2 times a week.
- Nettle lotion. The therapeutic effect is obtained by using nettle for androgenetic alopecia. In a saucepan with 5 tbsp. spoon leaves, pour 450 ml of water, add 2 tbsp. spoons of vinegar and put on the stove. Bring the mixture to a boil, keep on low heat for half an hour, then remove and cool. The product should be rubbed into the scalp every day before bed.
- Salt mask. Good results are obtained by rubbing regular or sea salt into the scalp 30–40 minutes before washing it.
- Mask with vitamins and Dimexide. Mix 2 tbsp. spoons of castor and burdock oil, add to them 1 teaspoon of vitamins A, E and 1 tbsp. spoon of Dimexide. The prepared mixture is rubbed into the roots of thinning hair and left for one hour.
- Tincture to strengthen follicles. Pour 1 tbsp into a jar. spoon of nettle and crushed burdock root, pour a glass of alcohol, add 1 bottle of alcohol tincture of mint and propolis. Close the jar tightly and put it in a cool place for a week. Then filter the composition and pour into a container with an airtight lid. Rub the resulting lotion daily before bed.
- Mask with sea buckthorn oil. Mix 1 teaspoon of sea buckthorn oil with 6–8 drops of grapefruit oil, 1 teaspoon of vitamins A, E and heat in a water bath. Then add 1 spoon of Dimexide to the mixture. Apply the mixture to the hair roots and leave for an hour.
Due to the fact that androgenetic alopecia is difficult to treat, some medications will have to be used throughout life, taking short breaks between courses. Otherwise, baldness will progress.
Why clients choose Veronika Herba Beauty and Health Center:
- This is a beauty center where you can take care of yourself at a reasonable cost, while your face and/or body will be treated not by an ordinary specialist, but by one of the best in Moscow. This is a completely different, higher level of service!
- You can receive qualified help at any time convenient for you. The beauty center is open from 9:00 to 21:00, seven days a week. The main thing is to agree with your doctor in advance on the date and time of your appointment.
Sign up for a consultation with a specialist by phone +7 (495) 085-15-13
, and you will see for yourself!
Proper nutrition
In addition to the main method of eliminating the disease, the patient needs to eat well. Many products contain essential macro and microelements that help strengthen and stabilize the hair follicle.
In case of acute and recurrent illness, it is worth eating food with a high content of protein, fat (animal, vegetable) and nutrients. The daily diet should always contain natural fresh foods of various types in unlimited quantities: vegetables, berries, seeds.
Patients who have previously suffered from nested baldness should not follow strict diets. A normal psychological atmosphere also plays a special role. You need to avoid stressful situations and overwork. Additional walks in the fresh air will help restore the health of the human body.
Prevention
Knowledge of what alopecia areata is will help prevent its development and apply effective preventive measures. These include: ● Rinsing with decoctions or herbal infusions that help strengthen and improve the condition of hair. ● Protection from adverse environmental factors - sun, low temperatures in the cold season. ● Minimizing traumatic mechanical effects - avoiding blow-drying hair and using styling tools. ● Use of natural gentle care shampoos and conditioners. Monitoring the level of vitamins and microelements, maintaining sufficient quantities in the body - groups A, E, B, C, calcium, zinc and iron.
In addition, you need to undergo timely diagnosis when the first symptoms are detected, and take the treatment of concomitant diseases and pathological conditions seriously. They are a potential cause of the disease. Proper nutrition, hormonal control, and comprehensive care will provide reliable protection against baldness.
Diagnostics and necessary tests
First of all, an experienced specialist will collect anamnesis, study medical history, and conduct a visual examination. A trichologist determines hair density and examines the skin for the presence of foci without vegetation.
It is necessary to study hormonal levels (thyroid function, hormone levels), as well as a complete blood test.
In addition, it is important to exclude the presence of infectious diseases and disorders of the immune system.
The scalp and hair shaft are also examined under a microscope.
In order to determine a treatment regimen, it is necessary to identify the cause of the disease, which only an experienced doctor can do.
Forecast
In this article, we looked at what alopecia areata is and how to treat it. Manifestations of the disease are individual, so the prognosis will depend entirely on the patient’s personal characteristics: age, medical history. In childhood and adolescence, the disease usually heals faster.
We can talk about an unfavorable prognosis in severe forms of loss of vegetation throughout the body. According to statistics, in more than 80% of people, hair growth resumes and returns to normal. However, 90% of those who have suffered from the disease can relapse again within the first year. The chances of further hair restoration depend on the speed of focal hair loss.
In rare cases (about 18% of the total mass), the loss of vegetation is immediate. In just a few weeks, the patient can completely lose their integument, and the follicles stop functioning.
Treatment
After a relatively short time (an average of 2-3 years), irreversible atrophic changes form in the structures of the hair follicles. The sooner treatment is started, the greater the chance of restoring the previous hair thickness!
The choice of treatment tactics for alopecia depends on:
- duration of the disease,
- degree of severity of clinical manifestations,
- the presence of chronic diseases,
- effectiveness of previous therapy.
The institute provides treatment for patients with hair loss and thinning of the scalp!
- A diet for alopecia requires adequate nutrition: the patient’s diet should contain animal proteins. Those. Vegetarianism and veganism are strictly contraindicated for them!
- Proper care of hair and scalp is necessary: delicate combing, individual selection of hygiene products (shampoos, balms), avoidance of hair coloring and perms during the period of active hair loss, etc.
- In parallel with the examination of patients, complex therapy is carried out, including the prescription of systemic medications and external therapy that stimulates hair growth and stops intense hair loss.
If such local treatment does not have an effect within 1 month, then it is necessary to immediately move on to more effective methods. This is due to the fact that after a relatively short time (on average 2-3 years), irreversible atrophic changes form in the structures of the hair follicles. Therefore, the sooner treatment is started, the greater the chance of restoring the previous hair thickness!
Sometimes the degree of thinning and the intensity of hair loss are so pronounced that mesotherapy or PRP therapy of the scalp must be started as early as possible (without using lotions first).