The birth of a baby is always a very important event. And although nature took care of everything itself, it can be quite difficult for a woman to return to her previous appearance. These problems especially appear when childbirth involves surgical intervention. The usual contours of the body can be returned with the help of a special procedure - abdominoplasty, which has become a real salvation for the fair sex after a caesarean section. To understand the From and To procedure, it is best to familiarize yourself with it in theory in order.
What is abdominoplasty
Abdominoplasty after cesarean section is a surgical procedure that helps to get rid of excess skin fat and restore the body to its original appearance. During abdominoplasty, diastasis of the abdominal muscles is sutured, thus returning to natural proportions very quickly. This procedure is indicated to achieve aesthetic goals, but in some cases it is also necessary for medical reasons: for the treatment of abdominal hernia, plastic surgery is prescribed as a therapeutic agent.
Abdominoplasty after cesarean section is a fairly popular procedure, but it is also used by those who have suddenly lost weight and are experiencing sagging skin. With the help of this procedure, both women and men can quickly restore their appearance and get rid of complexes.
Postpartum endometritis
Treatment should be comprehensive and aimed at localizing the inflammatory process, fighting infection, activating the body's defenses, detoxification and correction of homeostasis. Before starting treatment, material from the uterine cavity and vagina is taken for culture to determine the nature of the causative agents of the complication and their sensitivity to antibiotics.
Integral components of complex conservative treatment of postpartum endometritis are antibacterial, infusion and detoxification therapy, the use of uterine contractions, desensitizing and restorative therapy. To limit inflammation and activate the body's defenses, a therapeutic and protective regimen and sedative therapy are prescribed, which helps to normalize the state of the central nervous system. The patient must be protected from negative emotions and pain. A nutritious diet with a high content of proteins and vitamins is important.
Antibacterial therapy. When prescribing antibacterial therapy, it should be taken into account that infection with bacterial associations leads to the development of postpartum endometritis. It must be remembered that there are a number of strains of resistant bacteria, and in this regard, prescribe those drugs to which resistance is low. When obtaining the results of microbiological studies, it is necessary to use those antibiotics to which the detected microflora is most sensitive. At the site of infection, a concentration of the drug should be created that suppresses the growth and development of microflora.
Antibacterial therapy regimens are as follows.
The main regimen: lincomycin group (lincomycin or clindamycin) in combination with aminoglycosides (gentamicin, etc.).
Alternative modes:
- II-IV generation cephalosporins (cefuroxime, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, cefoperazone) in combination with metronidazole or antibiotics of the lincomycin group (lincomycin or clindamycin).
- Fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin or ofloxacin) when combined with metronidazole or lincomycin group antibiotics (lincomycin or clindamycin).
- Carbapenems.
For late endometritis, additional oral administration of doxycycline or macrolides (azithromycin once, erythromycin, clarithromycin or spiramycin) is necessary.
Treatment can be completed 24-48 hours after clinical improvement. Further oral administration of drugs is not required, except in cases of late postpartum endometritis.
Breastfeeding during antibiotic therapy is not recommended in most cases.
- Combination of penicillins with β-lactam antibiotics: augmentin in a single dose of 1.2 g is administered intravenously 4 times a day. During hysteroscopy, 1.2 g is administered intravenously;
- unasin in a single dose of 1.5 g is administered intramuscularly 4 times a day.
- cefuroxime (zinacef, cefogen, ketocef) in a single dose of 0.75 g is administered intravenously 3 times a day;
During hysteroscopy, the following is administered intravenously: 1.5 g of cefuroxime and 0.5 g of metrogil.
- First generation cephalosporins in combination with nitroimidazoles and aminoglycosides: cefazolin in a single dose of 1 g is administered intramuscularly 3 times a day;
- metrogil in a single dose of 0.5 g 3 times a day, intravenously;
- Gentamicin in a single dose of 0.08 g is administered intramuscularly 3 times a day.
During hysteroscopy, 2 g of cefazolin and 0.5 g of metrogil are administered intravenously.
In severe cases of endometritis, thienam is prescribed intravenously at a dose of 500 mg 3-4 times a day.
To prevent candidiasis and dysbacteriosis, the treatment regimen for postpartum endometritis includes nystatin 500,000 units 4 times a day, levorin 250,000 units 4 times a day.
After the end of antibacterial therapy, it is necessary to correct the biocenosis of the vagina and intestines with therapeutic doses of probiotics (bifidumbacterin, lactobacterin, acylact, 10 doses 3 times a day for 7-10 days), growth stimulators of normal intestinal microflora (hilak forte 40-60 drops 3 times per day for a week), enzymes (festal 1-2 tablets, mezim forte 1-2 tablets with each meal).
Surgery. Surgical treatment of the uterine cavity includes hysteroscopy, vacuum aspiration of the contents of the uterus, washing its cavity with cooled solutions (8-10 ° C) of antiseptics (furacilin, 1% dioxidine, sodium hypochlorite in a volume of 1200 ml).
Rinsing the uterine cavity with antiseptic solutions is recommended to reduce the absorption of decay products and toxins in case of severe disturbances in the processes of involution, the presence of copious and purulent discharge or when the latter is delayed. The procedure is performed no earlier than 4-5 days after vaginal delivery and 5-6 days after cesarean section.
Contraindications for washing the uterine cavity are:
- postpartum endometritis after cesarean section with signs of suture failure on the uterus;
- beginning or developing peritonitis;
- the presence of purulent-inflammatory diseases in the pelvic area outside the uterus;
- extremely serious general condition of the patient, septic shock.
Before the procedure begins, the postpartum woman is placed on a gynecological chair; perform treatment of the external genitalia; the cervix is exposed using speculum and treated with Lugol's solution; the contents of the uterine cavity are sucked out using a Brown syringe for bacteriological examination; carry out careful probing to determine the length of the uterine cavity; drainage and inflow tubes connected together are inserted through the cervical canal into the uterine cavity. It is important that the inflow tube is inserted to the fundus of the uterus, which facilitates complete and uniform irrigation of the endometrial surface. In patients with postpartum endometritis after cesarean section, the tubes should be passed with extreme caution along the anterior wall of the uterus so as not to damage the sutures in the lower segment. After inserting the inflow tube to the fundus of the uterus, the outflow holes on the drainage tube should be located above the area of the internal os. A bottle with a sterile solution of furatsilin diluted 1:5000 is placed in the freezer 2-3 hours before use until the first ice crystals form in it, which indicates a decrease in temperature to +4 °C. The first portion of the cooled solution is administered in a stream over 20 minutes to quickly remove the liquid contents of the uterine cavity and achieve a hypothermic effect. After the washing liquid has cleared, the solution injection rate is set to 10 ml/min. One procedure requires 2.5-3.5 liters of solution. The total duration of lavage is 1.5-2 hours. During the procedure, the patient’s general condition and hemodynamic parameters (pulse, blood pressure) should be monitored. It is necessary to constantly monitor the free outflow of fluid from the uterine cavity. After completing the administration of furatsilin, 20-30 ml of a 1% solution of dioxidine or a single dose of the antibiotic used in this patient with novocaine (0.25% solution) or with a 0.9% solution of sodium chloride can be introduced into the uterine cavity through the inflow tube.
The general course ranges from 2-3 to 5 procedures, which can be performed daily or after the 3rd procedure - every other day. Against the background of lavage of the uterine cavity, in a number of observations, the use of only a 3-5-day course of antibacterial therapy with antibiotic-synergists is sufficient. The main criteria for deciding whether to cancel the procedure are improvement of the patient’s well-being, reduction of tachycardia, normalization of body temperature, blood parameters, cessation of pain and progressive contraction of the uterus. After the rinsing is cancelled, the postpartum mother continues to undergo restorative and nonspecific anti-inflammatory therapy for 3-5 days. The absence of relapse of the disease, progressive improvement in the patient’s condition, the disappearance of local signs of the inflammatory process against the background of normalization of laboratory parameters indicate the patient’s recovery.
When parts of the fertilized egg are retained in the uterus and become further infected, there is a danger of toxins and biologically active substances entering the patient’s body from the source of infection, which contribute to an increase in intoxication and aggravation of the course of the disease. In this case, measures should be taken to remove them by curettage or vacuum aspiration. The latter is preferred due to the lower risk of intervention. It is advisable to remove parts of the placenta in patients with a limited inflammatory process while the infection is within the uterus. If the process is more widespread and the infection is generalized, instrumental exposure is contraindicated. Removal of parts of the placenta is carried out under general anesthesia, under the control of hysteroscopy, against the background of complex use of antibiotics, infusion, detoxification and desensitizing therapy.
In the absence of a significant amount of contents in the uterine cavity, one can limit oneself only to expansion of the cervical canal under anesthesia to create a reliable outflow.
Surgical treatment of the uterine cavity for postpartum endometritis after spontaneous birth can reduce bacterial contamination of the uterine cavity. The effectiveness of surgical treatment is practically independent of the degree of initial bacterial contamination.
Infusion and detoxification therapy. Infusion therapy is designed to restore normal hemodynamics by eliminating hypovolemia, which often occurs in postpartum purulent-inflammatory diseases, and especially in postpartum women who have suffered preeclampsia, increased blood loss during childbirth or surgery.
It is advisable to compare the volume and composition of infusion therapy with colloid osmotic pressure data and osmogram indicators. On average, the volume of intravenous infusions is up to 1000-1500 ml per day for 3-5 days.
The following are used as components of infusion therapy:
- crystalloids and electrolyte metabolism correctors (5% and 10% glucose solutions, lactasol, isotonic sodium chloride solution, disol, acesol);
- plasma-substituting colloids (hemodez, rheopolyglucin, gelatinol, infucol HES 6% or 10%);
- protein preparations (FFP, 5%, 10% and 20% albumin);
- drugs that improve the rheological properties of blood (trental 10 ml, chimes 4 ml, adding to infusion media).
In a hyperoncotic state, the ratio between colloid and crystalloid solutions should be 1:2-1:3.
In normooncotic and hypooncotic conditions, this ratio should be 1:1. In the latter case, preference should be given to more concentrated solutions of albumin. The total volume of infusion therapy per day is 2.0-2.5 liters. When body temperature increases by more than 37 °C for each degree, it is recommended to increase the volume of infusion therapy by 10%.
Water and electrolyte balance should be monitored, taking into account the amount of fluid administered under the control of diuresis.
Treatment of intestinal paresis and prevention of paralytic obstruction. A special place among these therapeutic measures is occupied by the restoration of electrolyte balance. Elimination of hypokalemia, improvement of hemocirculation due to moderate hemodilution and the use of vasodilators allows one to avoid a serious outcome. Early and ongoing intervention should be nasogastric intubation. If intestinal paresis has developed, the use of hypertonic solutions in an enema is contraindicated. By replacing potassium ions, sodium aggravates hypokalemia and contributes to the progression of paresis. To restore intestinal function and empty it, the safest thing is to suction its contents through a tube, which is first inserted into the stomach and then passed into the small intestine.
Extracorporeal methods. In severe forms of postpartum endometritis, plasmapheresis may be used. The main mechanism of its therapeutic action is considered to be the removal of pathological plasma ingredients, cryoglobulins, microbes and their toxins. In addition, there is a pronounced positive effect on the hemostatic system, rheological properties of blood, and the state of the immune system, which significantly improves the course of the postpartum period in women with postpartum endometritis and accelerates reparative processes in the uterus.
Desensitizing and antihistamine therapy. In purulent-inflammatory diseases, the content of free histamine and histamine-like substances increases in the body. In addition, antibacterial therapy may also be accompanied by allergic reactions. In this regard, it is recommended to include antihistamines in the treatment of postpartum endometritis. Diphenhydramine is used 0.05 g 2 times a day orally or 1 ml of a 1% solution 1-2 times a day intramuscularly. Suprastin 0.025 g 2 times a day orally or 1 ml of a 2% solution 1-2 times a day intramuscularly.
Uterotonic drugs. Considering that in the presence of postpartum endometritis, the contractile activity of the myometrium is disrupted, it is necessary to prescribe uterine contractions. This also promotes better outflow of lochia, reduction of the wound surface, and reduces the absorption of decay products during the inflammatory process. For this purpose, it is necessary to administer 1.0 ml (5 units) of oxytocin intramuscularly 2-3 times a day or intravenously drip with 5-10% glucose solution 200.0 ml or with isotonic sodium chloride solution.
Immunocorrective drugs. Prescribe Thimalin or Taktivin 10 mcg daily for 10 days, Viferon rectal suppositories 500,000 units 2 times a day for 5 days.
Vitamin therapy. Considering that purulent-inflammatory diseases are accompanied by the development of hypovitaminosis, and also that the use of antibiotics against the background of an infectious process leads to a decrease in the content of vitamins in the body, appropriate therapy is carried out with vitamins C 250-300 mg and group B (B6 - 50 mg).
Drugs that accelerate reparative processes. Use Actovegin 5-10 ml intravenously or solcoseryl 4-6 ml intravenously drip for 5 days.
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment. Interference current therapy according to Nemec. It is based on the use of low and medium frequency currents (about 4000 Hz) in two independent circuits using four electrodes. Low-frequency interference currents have a distinct, quickly-onset analgesic effect, improve the functional state of the neuromuscular system and peripheral circulation, promote vasodilation, accelerate and improve metabolism. In addition, rapid resorption of edema of various origins, including traumatic ones, is ensured. Carrying out physical prevention of uterine subinvolution and postpartum endometritis with interference currents according to Nemec after a cesarean section allows one to achieve the same results as when prescribing uterotonic drug therapy. However, the possibility of reducing the drug load on the body of postpartum women and reducing the overall cost of treatment makes the use of physical methods for the prevention of uterine subinvolution more justified.
Low-frequency pulse currents, galvanization of the mammary gland area, and a constant low-frequency magnetic field are recommended to be used after stopping the inflammatory reaction of the body for the purpose of early rehabilitation, eliminating the asthenic condition, and strengthening the contractility of the uterus.
Acupuncture. Recently, the method has become increasingly widespread. The beneficial effect of acupuncture on the hemostatic system in postpartum women with postpartum endometritis has been proven; a positive effect on the state of activity of factors of nonspecific resistance of the body and an immunostimulating effect have been noted.
External and intracavity irradiation using a low-intensity laser. Laser irradiation has the following beneficial properties: general stimulating, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, immunostimulating, helps normalize microcirculation, reduces intracellular and interstitial tissue edema, stimulates metabolic processes and local protective factors, reduces the pathogenicity of individual strains of microorganisms, expands the spectrum of sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics.
The effectiveness of complex intensive therapy for postpartum endometritis should be assessed no earlier than 7 days after the start of treatment. If the therapy is not effective, even against the background of satisfactory health of the patient, but clinical and laboratory signs of inflammation persist, it is necessary to decide on the removal of the uterus.
Types of abdominoplasty
There are several techniques that are used to perform abdominoplasty:
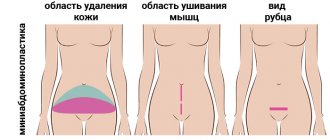
- Full or classic consists of a fairly extensive correction of the abdomen and includes transfer of the navel. This type of plastic surgery is used in cases of ptosis of the soft tissues of the anterior abdominal wall, hernia and diastasis of the abdominal muscles. This type of abdominoplasty is the most difficult: access occurs through the suprapubic area, using a horizontal incision.
- Mini abdominoplasty involves removing excess skin in the area below the navel. This procedure can be combined with liposuction. It is believed that such an intervention is not as traumatic as in the case of classic abdominoplasty, since a large incision is not required. Recovery after such a procedure will also be twice as fast.
- Endoscopic abdominoplasty is used if it is necessary to close diastasis and tighten the anterior abdominal wall. This type of procedure eliminates incisions, and all interventions occur through punctures in the abdomen. This type of plastic surgery differs from others in its very fast recovery time.
Indications and contraindications
It is important to understand that the operation is performed solely according to indications. They are determined at an appointment with a surgeon: the doctor will examine you and offer correction options - full abdominoplasty, mini abdominoplasty, endoscopic technique. If necessary, navel transfer and hernia removal are performed.
- Indications:
- Excess skin, subcutaneous fat in the abdominal area (fat apron, etc.);
- Diastasis;
- Stretch marks
- Hernia of the anterior abdominal wall with excess skin and subcutaneous fat;
- Rough scar or folds in the abdominal area after a cesarean section.
The presence of contraindications may be a reason for refusing surgery. It is necessary to inform the doctor about all the diseases you have, as well as undergo a preoperative examination. You can find a list of tests for general anesthesia in the “Patients” tab, and get a memo about the operation in the doctor’s office.
- Contraindications to abdominoplasty:
- Diabetes;
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- Obesity;
- infectious, inflammatory diseases;
- Pregnancy planned in the near future (it is better to perform the operation 6-9 months after birth);
- Scars and postoperative scars above the navel (individually, upon examination).
Indications for the procedure
It is worth understanding that abdominoplasty after cesarean is a serious surgical intervention. You cannot undergo the procedure without indications that can only be given by a doctor. The main pathologies for which you can undergo the abdominoplasty procedure:
- Diastasis. This problem is faced by mothers who cannot restore their figure. Neither exercise nor diet helps. In this case, the cause is stretching of the abdominal muscles along the white line. With the help of abdominoplasty, they are sutured.
- Sudden weight loss can also be an indication for abdominoplasty. As a rule, in people who are obese and have lost weight in a short time, characteristic folds of the skin can be seen. Abdominoplasty allows you to get rid of these excesses and improve your body shape.
- Abdominoplasty after childbirth is used to suturing the hernial ring, tightening the soft tissues and preserving the navel.
At home or in the hall
Light exercises after a caesarean section can be done at home. Physical education can also be done outdoors to increase the flow of oxygen into the blood and speed up tissue regeneration.
More complex workouts that require special conditions can be carried out in the gym or swimming pool. Women after childbirth often need the help of a trainer. A specialist will be able to suggest the intensity of training and develop a weight loss program without harm to health, which will help achieve results in a short time.
When compiling a set of training, the instructor takes into account not only the general condition of the woman, but also her goals:
- breast reconstruction;
- pumping up the press;
- elimination of sagging skin;
- strengthening the smooth muscles of the uterus;
- elimination of lower back pain.
You can use the trainer’s recommendations not only in the gym, but also at home. When switching to complex workouts, you should not forget about light exercises in the morning.
Contraindications
Like any serious procedure, abdominoplasty has its contraindications, under which surgical intervention will be refused. Below is the list:
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels, as well as the nervous system.
- Presence of neoplasms.
- Diabetes mellitus, regardless of degree.
- The presence of inflammatory processes.
- Pregnancy and childbirth.
- Blood clotting disorder.
- Immunodeficiency states.
In order to obtain permission to perform abdominoplasty, you must consult with a doctor, take urine and blood tests, perform an ultrasound of the abdominal organs and undergo fluorography.
Is it possible to do yoga
You are allowed to start practicing classical yoga after 4-6 months from the date of surgery. Sessions begin with breathing exercises. When choosing asanas, you need to adhere to positions that do not create additional stress on the seams.
It is recommended to attend yoga classes in groups with women in the same situation. An instructor will help you recover faster after surgery and ensure safe exercise.
With the right choice of asanas, metabolic processes are normalized. A person becomes cheerful, gets rid of stress and strengthens the nervous system.
Rehabilitation and result
Rehabilitation is a very important stage, the rules and recommendations of which must be strictly followed by patients. Physical labor is contraindicated for 3-5 months. Moderate dynamic loads are indicated with a slow increase as the sutures heal. Compression garments must be used and must be worn continuously for 2 to 4 weeks. After this, it is recommended to wear it during exercise.
Abdominoplasty helps people regain their self-confidence by improving their appearance and body shape, but dieting and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are also very important. Improper nutrition can lead to unwanted reactions and gas accumulation. So, in addition to wearing compression garments and avoiding stress, you will also have to take care of what’s in your refrigerator.
Diet after CS for a nursing woman to lose weight and remove belly fat
During lactation, it is almost impossible for women to lose weight, this is due to the protective functions of the body. The body accumulates vitamins and useful substances to transfer them along with milk to the baby. The emotional state of a young mother is important, since stress contributes to the appearance of extra pounds. Hormonal levels should also be kept under control.
What foods should be included in the diet and which ones should be excluded in order to lose weight for a nursing woman:
| Healthy foods | Harmful products |
| Natural yoghurts, kefir, fermented baked milk | Chocolate products |
| Low-fat cheeses | Citrus |
| Chicken, turkey, lamb, rabbit | Fast food |
| Bananas, carrots | Smoked products |
| Buckwheat, rice | Mushrooms |
| Green apples | Fried meat and vegetables |
| Green tea | Carbonated drinks |
To lose weight during lactation, it is necessary to adjust your diet and physical activity, since the body during this period is able to increase weight due to protective functions. An integrated approach is necessary; the body cannot be rushed, since the recovery process takes a different amount of time for each woman.
Abdominoplasty after caesarean section in Kaliningrad
If you are determined to improve your figure with abdominoplasty in Kaliningrad , have tried all the options, but have not achieved the desired results, then we invite you for a consultation at a plastic surgery clinic, where experienced surgeons will take care of you. Thanks to their extensive experience and knowledge in the field of abdominoplasty, they are able to find the best solutions and achieve the best results.
Only a modern approach and innovative techniques for the beauty of your body in the Ivanov Pavel plastic surgery clinic.
Physical activity intensity
Any physical activity, including physical therapy to strengthen the muscles of the uterus, should be done carefully. The intensity of exercise should be increased gradually.
At the initial stage of training, you do not need to spend more than 10 minutes for 1 session; it is not recommended to repeat the movements more than 5 times .
Every 2-3 days you should increase the frequency of approaches and duration of exercises. In this case, you need to focus on your well-being - it is important that the exercises do not turn out to be harmful and do not pose the risk of seams coming apart.