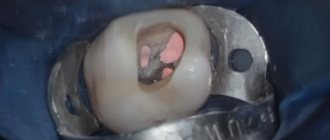
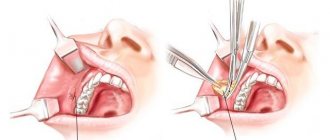
The simplest manipulation for which sedation can be used?
Sedation in dentistry has its own peculiarities.
All the manipulations are, in fact, simple for a professional in his work and his field; for him there is no difficulty in carrying out the same work without sedation. At the moment, the main factor why sedation is performed in dentistry is the patient’s fear. And if the patient has fear, treatment begins with sedation. If the patient has no fear, if he trusts the doctor, then the same can be done under local anesthesia, and the patient is only conscious. And the doctor can carry out the same amount of treatment for 4-5 hours, while he can take a break and the patient can rest, and then continue to treat teeth under local anesthesia.
Minimum time for a patient to be under sedation?
The minimum time for dental treatment under sedation is the local implementation of one manipulation. It’s just that when sedation is chosen, they try not only to minimize the time, but, on the contrary, to maximize it, in order to do a larger volume due to the fact that the patient is afraid. So that in this short time, sedation allows you to carry out as much therapeutic work as possible with an adult patient.
By the way, in the next video you can see how the implantation operation takes place under sedation
— installation of two Astra Tech implants. And the patient is me, the chief physician of the German Implantology Center, implant surgeon Dakhkilgov Magomed Umatgireevich. Implantation is carried out by my colleague, implant surgeon at the National Research Center Kolushev Gleb Valerievich:
How safe is sedation for human health?
Is sedation dangerous? Properly selected sedation cannot cause harm. If the patient has indicated all the features of his health and has undergone tests before the procedure, then the risk is minimized and there will be no harm to the patient’s health.
How often can sedation be used?
Depending on age, dental treatment with sedation can be done every week, but again, we are talking about the fact that doctors try to reduce its use to a minimum in frequency. “Better less, but better” - that is, it is better to do as much dentistry as possible under one-time sedation over a certain period of time, so as not to regularly put the patient into a state of half-asleep and not to increase the number of drugs and manipulations under sedation.
Maximum time under sedation per visit
This is determined by the anesthesiologist-resuscitator and, of course, the characteristics of the patient are taken into account. Sedation allows optimal treatment of teeth for about 4-5 hours. This is a comfortable time, despite the fact that the patient does not get very tired, because he lies in one position, and for the doctor this is also a comfortable time for work, because then there is a slight accumulation of fatigue, both for the doctor and the assistant, and at the patient. When the treatment time is more than 5 hours, the back and muscles become a little numb, and only after cooling it becomes less comfortable, the patient may begin to experience real discomfort.
Advantages and disadvantages
For simple surgical interventions, local anesthesia is indispensable; it has advantages over other types of sensitivity suppression. The drug that is used, an anesthetic solution, acts strictly at the injection site, which helps to avoid severe complications and adverse reactions.
The blockade of pain sensitivity develops on average in 10-15 minutes. The effect lasts for an hour or more, so local anesthesia can reduce pain in the area of the postoperative wound. The patient’s consciousness does not suffer from the action of the local anesthetic, so after the manipulation he can leave the clinic and not be in the ward.
But local anesthesia has its drawbacks. Just a few years ago, it was widely used for operations on superficial tissues and extremities; methods for intravenous administration of drugs with simultaneous application of a tourniquet were developed. Intraosseous anesthesia was widely used. But due to the large number of adverse reactions and complications, these methods began to be used less frequently. And after receiving high-quality drugs for anesthesia, dangerous methods of pain relief were practically abandoned.
The disadvantage of the local method is its limited scope of application. It is effective for anesthesia of mucous membranes, skin and superficial tissues, but is not used for operations on the abdominal and pelvic organs, neck and head.
The infiltration type of local anesthesia cannot be used when operating on malignant tumors due to the possibility of tumor cells entering beyond the wound into other tissues. This increases the risk of developing metastases.
Complications after sedation
Do nausea and fainting occur after sedation, or can such nuances be clarified before it begins? Of course, the characteristics of patients may be different: for some it may be nausea, for others it may be dizziness, etc. All this, of course, is discussed in advance in consultation with an anesthesiologist-resuscitator. It determines the patient’s health characteristics and determines the reactions that are possible due to the action of the drug. Any sedative drug can cause:
- drowsiness throughout the day after the manipulation, especially if the treatment was carried out in the morning,
- weakness,
- mild nausea
- It may make some people feel hungry, while others may feel the opposite.
There may be peculiarities, and this is not something pathological or something negative, this is the norm.
Types of local anesthesia
Several types of local anesthesia are used in surgical practice, but some of them already have historical significance. The main methods of pain relief are the following:
- superficial anesthesia - pain sensitivity is suppressed after the anesthetic comes into contact with the surface of the tissue, most often used to anesthetize the mucous membranes. The anesthetic solution is applied by lubrication or irrigation, the effect lasts for 10 minutes;
- infiltration anesthesia - anesthesia by impregnation, or infiltration of tissue layers with a local anesthetic. The technique allows you to control the depth and width of the drug injection, depending on the intended incision. The medicine is injected carefully first into the subcutaneous area until the lemon peel effect appears, then the needle is gradually moved inward and an additional dose of the drug is injected;
- anesthesia according to Vishnevsky is an improved version of the infiltration method. A weak anesthetic solution is injected layer by layer under high pressure. A tight creeping infiltrate forms in the tissues. It spreads through the interfascial spaces and disrupts the conduction of impulses along the nerves passing through them. After cutting the wound, the liquid gradually flows out of the wound, so there is no risk of its absorption into the systemic circulation and the development of toxic reactions;
- conduction anesthesia is the essence of the method in anesthetizing a specific area of the body innervated by the nerve trunk. An anesthetic drug is injected into the tissue around the nerve; the technique is used for operations on the limbs;
- spinal anesthesia - the analgesic effect is achieved by injecting an anesthetic drug under the choroid of the spinal cord, the main place of drug administration is the lumbar region, and pain sensitivity in the pelvic organs and lower extremities disappears. But tactile sensitivity does not suffer;
- epidural anesthesia is a type of anesthesia in which a local anesthetic is injected into the space over the dura mater of the spinal cord, and a puncture is also performed in the lumbar region. Sensitivity is lost after 15-20 minutes, but the effect lasts for 3-4 hours. The use of this type of anesthesia allows you to resume activity early after surgery;
- bone anesthesia is a type of anesthesia in which an anesthetic solution is injected into spongy bone. Currently, it is practically not used; previously it was used for operations on the limbs.
Are there complications with anesthesia?
Complications during anesthesia may be related to the technique of administering anesthesia or the effect of anesthetic agents on vital organs.
- One of the complications is vomiting
- Breathing complications may be associated with airway obstruction
- Complications from the circulatory system - hypotension - a decrease in blood pressure both during the period of induction of anesthesia and during anesthesia - can occur due to the effect of narcotic substances on the activity of the heart or on the vascular-motor center; - heart rhythm disturbances (ventricular tachycardia, extrasystole, ventricular fibrillation); — cardiac arrest is the most dangerous complication during anesthesia
Preparations for local anesthesia
Local anesthetics are drugs from the group of neurotropic drugs that completely or partially block the flow of signals along nerve fibers from the site of painful manipulation or surgery to the central parts of the nervous system.
The peculiarity of the action of drugs is related to their spectrum of action. They suppress the transmission of signals along myelinated type A nerve fibers, which transmit feelings of pain, smell, and temperature. Tactile sensations are carried out through type B fibers, and anesthetics do not affect them. Therefore, when using local anesthesia, the patient does not feel pain, but feels the touch of the doctor and the surgical instrument.
Local anesthetic drugs are divided into 3 groups depending on the duration of action:
- short-acting - the effect lasts 30-50 minutes, these include Novocain;
- average duration - up to 90 minutes, these are drugs Lidocaine, Trimecaine, Ultracaine;
- long-acting – the effect lasts more than 90 minutes, typical for Bupivacaine.
Local anesthetic drugs affect the electrochemical processes of ion exchange in nerve endings. Medicines work effectively in an alkaline environment and tissues rich in lipids, which include nerves. But the analgesic effect decreases with severe tissue inflammation, which is associated with a transition of pH to the acidic side.
The effect of local anesthetics is enhanced by drugs that affect vascular tone. Therefore, they are often combined with adrenaline to prolong the effect. This allows you to reduce the dose of pain medication and avoid toxic reactions.
How to treat teeth without pain?
Today, all therapeutic and surgical procedures performed by a dentist with the risk of causing pain to the patient are carried out exclusively after the use of painkillers. Dentists use different types of anesthesia, which means reducing the sensitivity of the injection site to any external influences. The administered medication prevents the “pain impulse” from entering the brain, so the person “feels nothing.” Anesthesia in dentistry is necessary so that the patient avoids unpleasant sensations when a specialist performs treatment. When the patient is not in pain, he can remain at rest for a long time. These are optimal conditions under which the dentist can perform manipulations more efficiently and effectively.
What is operated under local anesthesia in mammology?
The mammary glands are located superficially, they do not have muscles and large nerve trunks. Breast tissue is loosely located; in young women, glandular tissue predominates, which is replaced by fatty tissue with age. Therefore, for numerous manipulations and operations, local anesthesia can be used.
In mammology, anesthesia is used to perform invasive diagnostics, which include breast tissue biopsy. To do this, a local anesthetic is injected with a thin needle into the area of the intended puncture. After 10-15 minutes, the doctor can take breast tissue for examination without fear of causing pain to the patient.
Local infiltration anesthesia in mammology is used for small, minimally invasive operations. A woman can undergo puncture of a breast cyst after preliminary infiltration anesthesia. A similar approach can be used when removing small benign breast tumors.
In men, anesthesia is used during surgery for type 1 gynecomastia, when the size of the gland is still small. Infiltration of tissues increases hydrostatic pressure in them, thanks to which the doctor can easily separate pathological tissues from healthy ones.
Other applications
Local anesthesia may also be used to diagnose some chronic conditions and to relieve pain after surgery.
Research has shown that local anesthesia may be more useful than opioids such as morphine for treating pain after total knee replacement surgery.
In 2010, results from a rodent study in Turkey showed that local anesthetics may reduce some symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Anyone administering any type of anesthetic should be appropriately trained and qualified.
Is it painful to do local infiltration anesthesia?
When performing anesthesia, a standard disposable syringe with a thin needle is used. Whether local anesthesia is painful depends on your general pain threshold. The patient feels the moment of the first puncture of the skin and a slight feeling of fullness when the drug is administered. After the medication begins to act, sensitivity disappears. The doctor checks how effective the injection is by tapping the skin. In response, there is a feeling that the injection site has become woody.
After the end of anesthesia, sensitivity gradually increases, and a slight tingling sensation may appear. If anesthesia was performed for surgery, pain in the wound area begins to bother you, which can be reduced with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Benefit
Local anesthesia provides pain relief for dental surgery and other outpatient procedures.
Local anesthesia is used when:
- the operation is minor and does not require general or regional anesthesia
- the procedure can be performed quickly and the patient does not have to stay overnight
- the operation does not require muscle relaxation or loss of consciousness of the patient
Examples include dental surgery, removal of warts, moles or cataracts, and biopsy.
Contraindications for local anesthesia
Local infiltration anesthesia is a relatively safe method of pain relief. But to reduce risks during and after surgery, it is necessary to take into account contraindications to the use of the method. The main ones are the following:
- allergy to anesthetic - if earlier during dental treatment under local anesthesia an allergy to an anesthetic appeared, then during breast surgery the effect will repeat, and may be more pronounced, up to anaphylactic shock;
- psychomotor agitation and mental illness, reaction to the administration of an anesthetic and the surgical procedure itself can cause unpredictable behavior of the patient;
- during operations on malignant tumors - when infiltration anesthesia does not allow compliance with the ablastic rule;
- during long operations that require the use of microsurgical equipment;
- during interventions on areas of the body with a pronounced vascular network, for example, on the neck.
If local anesthesia is contraindicated, general anesthesia is preferred.
How to improve the quality of pain relief?
The patient, for his part, can also prepare for the upcoming intervention and thereby improve the quality of pain relief. To do this you need to follow these simple rules:
- Postpone a visit to the dentist if you have infectious diseases or (for women) during menstruation.
- Be sure to inform your doctor about allergic reactions to medications.
- The day before visiting the dentist, refrain from drinking alcohol and visiting the sauna.
- The evening before your visit, you may take a small dose of a sedative to relieve tension.
What is meant by the term “Anesthetic care”?
Anesthetic care for patients includes:
- assessment of the condition of patients before surgery, determination of anesthetic and surgical risks
- determining the feasibility and carrying out, if necessary, intensive therapy in order to prepare the patient for surgery
- prescribing premedication (drug preparation for anesthesia)
- selection of anesthesia method and necessary funds
- anesthesiological support for planned and emergency operations, dressings and complex diagnostic studies
- monitoring the condition of patients during anesthesia and conducting corrective therapy in order to prevent and eliminate life-threatening functional and metabolic disorders
- awakening patients after general anesthesia, if there are no indications for prolonged maintenance of drug-induced sleep
- elimination of pain caused by various causes (including incurable diseases) using special methods