Dermatologist-oncologist
I'm drowning
Angelina Georgievna
18 years of experience
Oncologist, member of the Russian Society of Dermatoscopy and Optical Diagnostics of the Skin, member of the Russian Society of Dermatovenereologists and Cosmetologists (RODVK), member of the Russian Society of Clinical Oncologists (RUSSCO)
Make an appointment
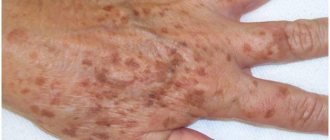
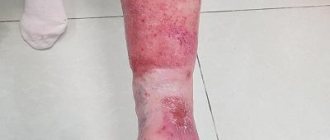
Skin basal cell carcinoma, also known as basal cell carcinoma, is a neoplasm in the form of skin ulcers. Mostly such formations occur on the face (up to 90% of all cases); much less often they appear on the arms, legs or torso. The location of this type of cancer on the head varies. It can manifest itself in the nose area, near the eye, etc. The tumor grows both outside and inside.
Basalioma is a slowly progressing tumor, and it does not metastasize to other parts of the skin. Because of these characteristics, the formation is often classified as borderline: at the junction of malignant and benign. For the patient, this means that the prognosis in his case will be quite favorable, and the chances of recovery are high.
Causes
As in many other cases associated with cancer, clear and unambiguous reasons for the development of the disease have not yet been identified. But there are a number of factors that, according to doctors, contribute to this disease.
So, the probable causes of basal cell carcinoma include the following:
- prolonged exposure of the skin to sunlight, abuse of solarium;
- regular interaction with substances containing arsenic;
- consumption of liquids that contain a high content of arsenic and heavy metals;
- xeroderma pigmentosum virus;
- skin damage associated with burns, scar development, etc.;
- precancerous diseases that are not treated in time and are left to chance;
- predisposition to the disease due to light skin and hair color, mature age, etc.;
- serious immune disorders.
Obviously, none of these reasons is decisive, but each of them individually or several in combination can contribute to the development of basal cell carcinoma.
Are you experiencing symptoms of basal cell carcinoma?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
At the moment, there are two most common forms: superficial and nodular
Superficial (newly identified) BCC:
- most often develops on the skin of the trunk and limbs;
- less common: head and neck;
- in younger patients, with a predominance of women.
Important!
The main development factor is genetic - this is a hereditary mutation that is transmitted to descendants or arises in connection with environmental or other adverse effects of the external environment. Nodular form (first identified) of BCC:
- most often develops on the scalp
- in elderly and senile patients
Types of disease
Based on the type of formation and its characteristics, several types of skin basal cell carcinoma are distinguished.
- Nodular-ulcerative. This is a red or pink nodule that appears mainly on the face, grows very slowly and becomes covered with ulcers over time. Over time, the shape becomes deformed and adjacent tissues are affected and destroyed.
- Solid. Light pink or yellow formation in the form of a semicircle. It grows slowly, capillaries are visible under the surface.
- Warty. Multiple node, shaped like a cauliflower. No ulcers.
- Perforating. Grows faster than others, completely covered with ulcers. It mainly appears in areas that are constantly damaged.
- Cylinder. The purple-pink multiple tumor is a basal cell carcinoma of the scalp and scalp.
- Scleroderma-like. Resembles a superficial nodule that may or may not develop an ulcer.
- Flat scar (also pigmented). In the process of development, it looks like a mole surrounded by various formations (like a necklace). Then ulcers appear, and after healing, a scar remains on a dark background.
- Superficial. Resembles a flat plaque surrounded by small formations. It grows for a long time and may not manifest itself for years and not bother the patient.
- Adenoid. Formed in the area of the tonsils, it consists of many cyst-like nodules.
Like other forms of cancer, basal cell carcinoma has its own stages.
How common is this skin growth?
- Skin tumors occupy the second place in the cancer incidence of the world's population. And BCC is the most common malignancy among them.
- BCC accounts for almost 80% of all newly diagnosed malignant skin tumors.
However, in reality, a significant number of basal cell carcinomas are not diagnosed in the early stages due to the duration of the development of the process, the latent course of the disease in elderly and senile patients who do not want to consult a specialist, as well as due to the lack of metastasis and severe complications.
Unfortunately, the incidence of BCC increases annually by 4-8%. According to the National Medical Research Center of Oncology named after. N.N. Petrova, in 2016, among all identified malignant neoplasms, skin cancer was 9.93% in women and 7.05% in men, while in 1995 these figures were 5.5% and 3.9%, respectively.
You will be curious that according to WHO (2017), in Australia, the country with the highest incidence of skin malignancies, two thirds of the population will develop BCC during their lifetime. And in the USA, 1/3 of all cancers are skin cancer, of which 80% are BCC.
It is also necessary to note significant fluctuations in skin cancer incidence rates in the structure of malignant neoplasms in different regions of the world and Russia in particular, depending on national, climatic characteristics and urbanization in general.
Most often, BCC is found in the southern regions, although high population mobility has recently led to the fact that the incidence rates of northern peoples are also steadily increasing, and in women they are consistently higher than in men. The incidence of BCC reaches its maximum in people over 60 years of age. However, in recent decades, the number of young patients has increased significantly. Their share will continue to grow, due to an increase in life expectancy, migration of people across regions of the planet, an increase in the intensity of natural UV radiation due to environmental factors and the more frequent use of artificial ultraviolet radiation.
However, despite the high incidence, age-adjusted metastasis and mortality rates are estimated to be only 0.0028% to 0.5% and 0.12% per 100,000 population, respectively.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma on a leg, arm, face or other place involves a number of diagnostic measures. This:
- detailed examination by a doctor and medical history;
- dermatoscopy. It is usually not enough for an accurate diagnosis;
- blood and urine tests;
- histology of the diseased area;
- cytology;
- CT, ultrasound, radiography. These studies are carried out if the tumor has already grown into cartilage or bone tissue.
Be careful! Since there are many forms of this disease, and some of its manifestations are similar to wounds, ordinary moles and nevi, only a doctor can make a diagnosis after a thorough examination! If you notice something suspicious and unusual on your skin, be sure to consult a specialist.
During a general examination of the patient, an oncodermatologist
EVERYONE is watching! Skin on the torso, face, neck, limbs, mucous membranes, scalp.
- Dermatoscope.
- SIAscopically.
- Cytologically.
- Histologically!!
Biopsy of a skin tumor
A mandatory diagnostic step for skin tumors is morphological verification of the process; for this, a biopsy
. The oncologist takes cells or tissues from the site of the tumor and submits them for examination to pathologists, who form their conclusion.
The morphological report contains information about the tumor:
- localization of the process (where the tumor is located);
- diameter (what size is the tumor);
- growth type;
- characteristics of the resection margin (the tumor was completely removed or not).
The oncologist makes a final diagnosis and forms a treatment plan only after receiving the results of the biopsy.
Prognosis and prevention of basal cell carcinoma
The extremely slow growth of the tumor and the low probability of metastasis of basal cell carcinoma give a good prognosis in terms of complete recovery. Metastatic forms of basal cell carcinoma are extremely rare, so it is difficult to talk about accurate survival prognosis here. According to world literature, the average life expectancy of such patients is 4.5 years.
Prevention of cutaneous basal cell carcinoma involves regular protective measures against the aggressive effects of carcinogenic factors:
- Do not expose your skin to direct sunlight. At a minimum, use creams with sunscreen properties. Do not overuse tanning or visiting a solarium.
- When working with chemical irritants in hazardous production conditions, use personal protective equipment - clothing, gloves, masks.
- Do not neglect protective equipment when working with household chemicals.
In order to detect skin cancer in time and carry out treatment with minimal losses, it is recommended to undergo annual preventive examinations using dermatoscopy.
At Euroonko, this procedure is carried out using special German PhotoFinder technology. It involves drawing up a map of moles and neoplasms of the entire body, followed by tracking the dynamics of their changes. The resolution of the optical system allows visualization of skin tumors measuring only 0.9 mm.
When basal cell carcinoma is detected, we use treatment methods recommended by modern protocols. They give good clinical and cosmetic results. If you have any questions, please contact our specialists.
| Price : | |
| Oncologist consultation | 5,100 rub. |
| Dermatoscopy | 4,600 rub. |
| Histological examination | 5,200 rub. |
| PDT without contrast cost | RUB 39,600 |
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Treatment
It is advisable to determine treatment tactics according to the prevalence of the tumor process, its localization, risk factors, and the general somatic condition of the patient. Due to the high incidence of the disease in elderly patients, functional reserves and the presence of concomitant pathology are often of significant importance in determining treatment algorithms for skin tumors.
Surgery
The main treatment method for localized forms of skin tumors is surgical excision.
Radiation therapy
If there are contraindications to surgical treatment (or the patient refuses surgical treatment), radiation therapy is recommended. The choice of the type of radiation therapy (close-focus X-ray therapy, gamma and electron therapy) depends on the capabilities of the medical institution and the patient’s condition. It should be remembered that radiation therapy should not be given to patients with genetically determined skin cancer (for example, Gorlin-Goltz syndrome), xeroderma pigmentosum or scleroderma, since radiation therapy can worsen the course of the disease.
Laser destruction. Photodynamic therapy for basal cell carcinoma
In addition to two fairly well-studied and widely used in clinical practice areas of laser application - low-intensity stimulating laser radiation and high-energy damaging radiation, a third area is rapidly developing - photodynamic therapy of tumors (PDT). Interest in it is due to the fact that tumor destruction is achieved by irradiating it with low-intensity laser radiation, eliminating the risk of uncontrolled thermal damage to the organ wall.
Photodynamic therapy (PDT)
- part of photochemotherapy, in which, in addition to light and drug, oxygen is needed.
Cryogenic therapy
Cryodestruction
- the process of destruction of biological tissues under the influence of extremely low temperatures.
Locally acting therapy
If there are contraindications for surgical or radiation treatment for adults without immunodeficiency (HIV, hepatitis B and C, organ transplantation), it is advisable to use locally acting drugs (ointments). having antitumor activity. Use ointment as recommended by an oncologist.
Indications for use:
- presence of a primary focus of BCC (not relapse);
- size no more than 2 cm;
- superficial spreading form;
- localization on the trunk, neck or limbs (except hands and feet).
Treatment of patients with metastatic and unresectable skin cancer (stage IV)
It is recommended to make a decision on the management tactics of patients with metastatic and unresectable skin cancer within the framework of a multidisciplinary consultation with the participation of a surgeon, chemotherapist and radiation oncologist. Currently, systemic treatment regimens have been developed and are being used in patients with unresectable skin cancer.
The most effective drugs for the treatment of locally advanced basal skin cancer are targeted drugs (target literally translated from English is translated as a target or goal) - that is, this is a treatment when the drug acts specifically on a mutation in the tumor tissue, like a shot at a target. In 2022, one of these drugs was included in the list of vital and essential drugs (VED).
Chemotherapy is selected individually in each specific case.