Ways to eliminate imperfections of the lower eyelid without surgery
Our clinic performs a range of procedures to correct the area under the eyes. Let's look at which options best help with different problems.
Puffiness under the eyes (photo 1)
Swelling can be eliminated using procedures that improve lymphatic drainage . These include vacuum diamond peeling or gas-liquid peeling jet peel. Treatment consists of a course of procedures, from 4 to 10 or more, depending on the manifestation and cause of the problem, if we are talking specifically about swelling caused by stagnation in the lower eyelid area.
Some formations that look like swelling are actually lower eyelid hernias . They are formed as a result of the redistribution and sliding of adipose tissue and a decrease in skin tone.
How to determine - edema or fatty hernia? If the size of the “bags” under the eyes varies: in the morning/evening, after the weekend/on weekdays, then most likely it is swelling.
Mesotherapy can also be used for swelling. Various meso-cocktails can strengthen the skin and remove dark circles, but a course of treatment is needed, since the effect of mesotherapy is cumulative. The course includes 3-5 procedures.
Hernia of the lower eyelid (photo 2,3)
Small hernias, as in photo 2, can be corrected using contour plastic surgery, provided that the problem is not advanced. The area of the nasolacrimal groove is filled with hyaluronic acid filler. The bags are “leveled out”, unevenness and wrinkles are smoothed out almost immediately, and the effect lasts 10-12 months. There is no rehabilitation period!
Large hernias (photo 3) often cannot be repaired using non-surgical methods. If the formation under the eyes “hangs” strongly and is a complete semicircle, from the medial to the lateral edge, then only plastic surgery will help.
During surgery, fat packets are removed or redistributed to make them less noticeable. The operation is not a pleasant thing, but it gives 100% results for a long time.
After surgery, you can recover for weeks. Therefore, it is better to prevent such situations in time. To do this, we recommend undergoing preventive procedures to strengthen the skin of the eyelids after 30 years.
Nasolacrimal groove (photo 4.5)
The deep furrow under the eyes is smoothed out using a combination of contouring with fillers and mesotherapy.
If the problem is advanced, then it can only be dealt with through comprehensive correction. These are fillers + laser correction + mesotherapy. Additionally, IPL may be required - a technique of so-called photorejuvenation. You and I will have to “sweat”, but if we do not eliminate the problem at this stage, then it will only get worse.
Plastic surgery / Blepharoplasty (Eyelid surgery)
| Section: Blepharoplasty Articles: History of blepharoplasty Anatomy of the upper and lower eyelids Ideal proportions of the eye Age-related changes in the upper and lower eyelids Aging of the eyelids. Causes and manifestations Classification of age-related changes in the eyelids | Modern blepharoplasty techniques. Indications and contraindications Preparing for blepharoplasty Blepharoplasty. Options and surgical techniques After blepharoplasty Complications and risks of blepharoplasty The most frequently asked questions about blepharoplasty Blepharoplasty: results (before and after photos) |
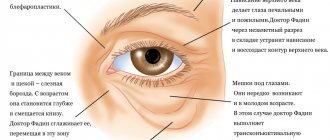
The key to a good result when performing plastic surgery on the eyelids is an accurate knowledge of the anatomy of the eyelids. The eyelids and periorbital region are a single anatomical complex, consisting of many anatomical structures that undergo changes during surgical manipulation, and all new and most effective methods of eyelid surgery have a clear anatomical justification and allow obtaining the best possible aesthetic and functional results.
1 - Upper eyelid fold 2 - Upper eyelid groove 3 - Internal canthus 4 - Nasolacrimal groove 5 - Eyelid-cheek division 6 - Lower eyelid fold 7 - Horizontal axis of the eye 8 - Lateral canthus 9 - Upper eyelid
The skin of the eyelids is the thinnest on the body. The thickness of the eyelid skin is less than a millimeter. This thin skin heals better than skin on any other part of the body because it has a very good blood supply, so the scar after a properly performed blepharoplasty is usually almost impossible to see.
Unlike other anatomical areas where fatty tissue lies under the skin, just under the skin of the eyelids lies the flat orbicularis oculi muscle, which is conventionally divided into three parts: internal, median and external. The internal part of the orbicularis oculi muscle is located above the cartilaginous plates of the upper and lower eyelids, the middle part is above the intraorbital fat, the external part is located above the bones of the orbit and is woven above into the muscles of the forehead, and below into the superficial musculofascial system of the face (SMAS). The orbicularis oculi muscle protects the eyeball, performs blinking, and functions as a “tear pump.”
1 - Frontalis muscle 2 - External part of the orbicularis oculi muscle 3 - Median part of the orbicularis oculi muscle 4 - Internal orbicularis oculi muscle 5 - Internal canthus 6 - Nasalis muscle, 7 - Levator labii superioris muscle 8 - Levator labii superioris muscle 9 - Depressor septum muscle nose 10 — Zygomaticus major muscle 11 — Zygomaticus minor muscle 12 — Infraorbital nerve 13 — External canthus
The musculoskeletal system of the eyelids performs a supporting function and is represented by thin strips of cartilage - tarsal plates, lateral canthal tendons and numerous additional ligaments. The superior tarsal plate is located on the lower edge of the upper eyelid under the orbicularis oculi muscle, and is usually 30 mm in length and 10 mm in width, it is firmly connected to the inner part of the orbicularis oculi muscle, the aponeurosis of the levator superioris palpebral muscle, Müller's muscle and the conjunctiva. The inferior tarsal plate is located on the upper edge of the lower eyelid, is usually 28 mm long and 4 mm wide, and is attached to the orbicularis muscle, capsulopalpebral fascia and conjunctiva. The lateral canthal tendons are located under the orbicularis oculi muscle and are firmly connected to it. They connect the tarsal plates to the bony edges of the orbit.
1 - Müller's muscle 2 - Internal canthus 3 - Lacrimal sac 4 - Ligaments 5 - Inferior tarsal muscle 6 - Lockwood's ligament 7 - External canthus
Under the orbicularis muscle also lies the orbital septum - a thin but very strong membrane; one edge is woven into the periosteum of the bones surrounding the eyeball, and the other edge is woven into the skin of the eyelids. The orbital septum retains the intraorbital fat within the orbit.
1 - Orbital septum 2 - Internal canthus 3 - Intraorbital fat - central portion 4 - Ligaments 5 - Intraorbital fat - outer portion 6 - External canthus 7 - Lacrimal gland
Under the orbital septum there is intraorbital fat, which acts as a shock absorber and surrounds the eyeball on all sides. Portions of the upper and lower intraorbital fat are divided into internal, central and external. Next to the upper outer portion is the lacrimal gland.
1 - Intraorbital fat - central portion 2 - Dividing septum 3 - Intraorbital fat - internal portion 4 - Internal canthus 5 - Intraorbital fat - internal portion 6 - Intraorbital fat - central portion 7 - Ligaments 8 - Intraorbital fat - external portion 9 - External canthus 10 - Intraorbital fat - external portion 11 - Lacrimal gland
The muscle that lifts the upper eyelid opens the eye and is located in the upper eyelid under the cushion of fat. This muscle is attached to the superior tarsal cartilage. The skin of the upper eyelid is usually attached to the levator palpebrae superioris muscle. At the site of attachment of the skin to this muscle, when the eye is open, a fold forms on the upper eyelid. This supraorbital fold varies greatly from person to person. In people from Asia, for example, it is weakly expressed or not at all; in Europeans, it is well expressed.
1 - Muller's muscle, 2 - Levator superioris muscle 3 - Superior rectus muscle 4 - Inferior rectus muscle 5 - Inferior oblique muscle 6 - Orbital bones 7 - Orbital margin 8 - SOOF - infraorbital fat 9 - Orbital ligament 10 - Orbital septum 11 - Intraorbital fat 12 - Capsulopalpebral fascia 13 - Inferior pretarsal muscle 14 - Inferior tarsal plate 15 - Superior pretarsal muscle 16 - Superior tarsal plate 17 - Conjunctiva 18 - Ligaments 19 - Levator superioris muscle 20 - Orbital septum 21 - Intraorbital fat 22 - B level 23 - Eyebrow fat 24 - Orbital bones
Behind these structures is the eyeball itself, which is supplied and innervated through the posterior part of the orbit. The muscles that move the eye are attached at one end to the eyeball and lie on its surface, and at the other end they are attached to the bones of the orbit. The nerves that control the muscles are small branches of the facial nerve and enter the orbicularis oculi muscle on all sides from its outer edges.
The anatomical structures of the lower eyelid and midface are closely related, and changes in the anatomy of the midface affect the appearance of the lower eyelid. In addition to portions of periorbital fat, two additional layers of fatty tissue exist in the midface.
Beneath the outer part of the orbicularis oculi muscle lies the infraorbital fat (SOOF). The greatest thickness of SOOF is on the outside and sides. The SOOF is deep to the superficial musculoaponeurotic system of the face (SMAS) and envelops the zygomatic major and minor muscles. In addition to SOOF, malar fat pad is an accumulation of fat in the form of a triangle or so-called. “painting” fat is located under the skin, above the SMAS. Aging of the midface is often accompanied by sagging of the malar fatty tissue, which results in noticeable zygomatic or so-called “painting” bags on the face.
1 - Orbital septum 2 - Orbital ligament 3 - SOOF - infraorbital fat 4 - Zygomatic ligament 5 - Prezygomatic space 6 - Zygomaticus major muscle 7 - Subzygomatic space
The main supporting structure of the midface is the orbitozygomatic ligament, which runs from the bones almost along the edge of the orbit to the skin. It contributes to the formation of the zygomatic “painting” bag and the eyelid-cheek separation visible with age.
1 — Fatty “hernia” 2 — Painter’s “bag” 3 — Nasolacrimal groove
Wrinkles and skin bags in the lower eyelid area
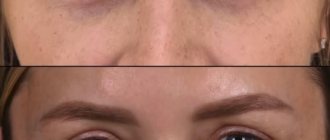
Laser resurfacing or laser blepharoplasty of the lower eyelids is a unique and very effective non-invasive procedure that helps with sagging skin of the lower eyelid (Fig. 6).
Non-surgical blepharoplasty (that is, eyelid lift) can only be performed with a laser. Other procedures (including those listed above) cannot be called blepharoplasty, since they do not in any way affect the area of eyelid skin .
Effect of laser resurfacing:
- will help eliminate skin ptosis;
- the eyelid will tighten, followed by the surrounding skin;
- wrinkles will smooth out or become less pronounced;
- the overall appearance of the skin will improve, dark circles will disappear;
- skin tone will increase.
In combination with injections, laser blepharoplasty works wonders. This can be seen in the photo: you can completely transform your face and maintain youth for a long time.
What definitely won't help?
Collagen injections, biorevitalization, various creams for bags under the eyes - all this cannot eliminate bags and even out the skin on the lower eyelid. The same applies to acid and chemical peels. They only help improve the condition of the skin, but they cannot tighten it or remove bags.
Trust the beauty of your eyes to our doctors and maintain your youth for the next 10 years!
Our trump cards : experience, education, licensed drugs and equipment and, of course, the results of our patients!
Carry out the procedure with a 15% discount!
We have many promotional offers, the main one: 15% discount on your first visit! We will select the best for you!
I want a discount!
Thank you!
Information has been sent to the clinic administrators!
Get a 15% discount on your first visit to our clinic! You can write to this number on WhatsApp!
The information in the article is of a general educational nature. It is important to understand that treatment cannot be prescribed over the Internet. It must be selected individually, based on a medical examination.
Therefore, sign up for a consultation with one of the doctors at our clinic, and then it will be clear in which direction you and I should move.