Asymmetrical breasts of different sizes are one of the most common phenomena. According to statistics, 90% of girls have a difference between the right and left mammary glands, and in 45% the bust size differs by half a standard cup. Another question is how to approach this? Some people notice this difference and feel complex, while others perceive it as a common occurrence and do not pay attention.
So what to do if your breasts are different sizes? Let's figure it out.
Why do breasts come in different sizes?
True asymmetry, when breasts are different sizes and differ from each other by one cup. The reasons can be very diverse. They can be divided into 2 groups.
Congenital causes:
- hypoplasia (delayed development) of glandular tissue
- Poland syndrome is a congenital disease characterized by atrophy of the pectoralis major muscle
- hormonal problems during puberty
- micromastia - one mammary gland is significantly reduced in size compared to the other
- problems with the endocrine system
- prolonged incorrect body position, which leads to poor posture
- hereditary predisposition
- individual feature
Typically, congenital breast asymmetry is noticeable in girls aged 9-10 years. During this period, the ovaries already produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone, which are responsible for the development of glandular tissue. The bust can become disproportionate if hormones are in short supply or excess. If there is disproportionality, then you need to contact an endocrinologist or mammologist. Usually this problem is leveled out by the age of 18-19. If it persists into adulthood, then it can only be corrected by a plastic surgeon.
Acquired reasons:
- Breast-feeding. In this case, breast asymmetry is the so-called post-lactation involution of the mammary gland, which also manifests itself in disproportion. It depends on hormonal changes, and not on the duration of lactation, as many young mothers think. However, asymmetry can actually develop if you feed your baby on only one side.
- Mastopathy (fibroadenomatosis). Benign breast tumor. A characteristic sign of mastopathy is palpable lumps in the breast. The main reason is hormonal imbalance. Often, all types of mastopathy lead to visible asymmetry.
- Neoplasms. After their removal, the breast requires restoration.
- Sagging and drooping breasts. With age, the mammary gland loses elasticity and volume, and the muscles become less elastic. Because of this, the bust loses its former attractiveness and symmetry. This often happens when a woman crosses the threshold of menopause.
- Chest injuries. At risk are female athletes who play basketball, volleyball and other sports where there is a risk of physical injury.
Etiology
All reasons for the development of asymmetry can be divided into two large categories - congenital and acquired.
Congenital causes:
- genetic disorders;
- fetal malformations;
- fetal trauma.
Acquired reasons:
- hormonal diseases;
- consequences of surgical operations for partial or complete mastectomy;
- consequences of surgical infection of the mammary glands;
- the result of aesthetic breast surgery;
- breast injuries;
- age-related changes;
- neoplasms;
- lactation changes;
- problems with posture.
These factors can lead to uneven growth, enlargement or underdevelopment of one organ in relation to another, asymmetry of the areolas, as well as discrepancy between the glands in shape and size.
Classification of breast asymmetry
It is important to understand: there is no absolute symmetry - people are asymmetrical. Our right and left sides of our faces, legs, arms and, of course, chest are different. This is absolutely normal. A pathological fixation on symmetry often results in complexes and self-doubt.
We can talk about asymmetry when it is visible to the naked eye. Differ:
- bust shape and volume
- position and outline of the nipple and areola.
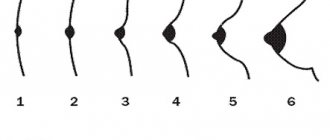
Doctors distinguish 3 degrees of breast asymmetry:
- light. The breasts are practically no different from each other. They come in one bra size;
- average. The difference between the mammary glands reaches 0.5 sizes. This is visually noticeable, but usually does not interfere with everyday life;
- heavy. One breast can be 1.5-2 times larger than the other. In this case, there are problems with the selection of underwear and clothes.
Note that there is no exact way to measure asymmetry, so in this matter you should rely only on the experience of the selected specialist.
Main symptoms of asymmetry
Asymmetry itself can be a symptom of various diseases, but quite often it is a variant of the norm. Clinical manifestations are divided into aesthetic, functional, psychosocial, and concomitant.
Aesthetic symptoms:
- absence of nipples and areolas;
- the presence of additional nipples and pigmentation;
- multi-level location on the chest wall;
- mismatch of shape and size;
- deformation of the shape of one breast in relation to the other;
- absence of part or all of an organ;
- one woman having more than two breasts.
Functional manifestations
- inability to lactation;
- altered lactation process;
- temporary dysfunction of lactation capacity;
- complete absence of lactation function.
Associated symptoms
Manifestations vary and depend on the clinical picture of the underlying disease:
- symptoms of cancer: the presence of a pathological formation, nipple retraction syndrome, weight loss, weakness;
- signs of hormonal disorders: dysmenorrhea (pain during menstruation, amenorrhea (lack of menis), galactorrhea (pathological process of milk secretion from the breast);
- congenital symptom complex: absence of any pectoral muscle, decrease in the subcutaneous fat layer in the bust area, deformation of the ribs or absence of several bones, shortening of the fingers, partial or complete fusion of the fingers, lack of hair growth in the armpits.
Psychosocial manifestations
In many ways, this symptomatology is determined by the woman’s age, her upbringing and environment. There are temporary and permanent ones.
Temporary symptoms include:
- changes in different periods associated with the hormonal dependence of the organ.
Constant symptoms:
- individual ideas about the ideal visualization of the shape and size of the bust;
- social and aesthetic prejudices;
- national and racial characteristics of worldview.
Regardless of whether asymmetry is acquired or congenital, women’s psycho-emotional status is often disturbed, which can lead to changes in social status and serious mental disorders.
Prevention of breast asymmetry
Is it possible to prevent breast disproportion? Yes, if we are talking about acquired asymmetry. Here are some examples:
- During breastfeeding, place your baby alternately on both breasts. Avoid “preferring” one breast. If the baby loves one breast more, then be sure to express the second;
- wear a corrective bra to prevent breast sagging after lactation;
- do a contrast shower to improve blood circulation;
- physical exercise will strengthen your posture and pectoral muscles.
Contraindications to surgical treatment
With surgical plastic surgery, general restrictions apply for operations:
- chronic decompensated pathological processes;
- pregnancy and lactation period;
- the post-lactation period is less than six months;
- acute inflammatory and bacterial infections;
- pathology of the blood coagulation system;
- active oncological process;
- age up to 18 years (for severe psychosocial disorders - before puberty).
Also, operations are not performed for acute mental disorders and with an established status of incapacity.
What to do if your breasts are different sizes?
It is necessary to start with an objective analysis and answer the questions: how asymmetrical are the breasts and does this affect the aesthetic appearance?
If there is a slight difference in bust size, it can be adjusted using underwear. It is also worth trying conservative methods - correcting posture, physical exercises to strengthen the pectoral muscles.
If the asymmetry is significant and causes discomfort to the girl, then it is worth contacting a plastic surgeon for surgical correction.
Possible complications
About 90% of women have asymmetry of varying severity; in the vast majority of cases, the differences are normal and do not lead to complications.
In girls with clear manifestations of congenital pathology, complications associated with other systems are of decisive importance. Hence, only a small part of women perceive asymmetry as a serious problem. And then they may actually develop complications, which are primarily related to their psycho-emotional and social status. Most often, manifestations occur in the form of anxiety, hysteria, excitability, aggression, pessimism, various complexes and loneliness.
Surgical methods for correcting breasts of different shapes
Surgical correction techniques vary depending on the degree of asymmetry. In such cases, the plastic surgeon offers breast lift, augmentation or reduction.
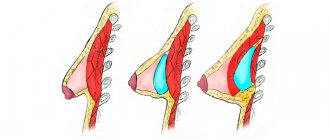
- Breast augmentation. The most popular plastic surgery, which solves not only issues of asymmetry, but also gives ideal forms. It is performed using silicone implants. The size and volume are selected individually during consultation. The following are taken into account: the patient’s height and weight, the initial condition of the mammary gland. A plastic surgeon can install identical implants if the asymmetry is minor. If there is a significant difference in breast size, implants of different volumes are installed. Breast augmentation surgery lasts about 1 hour. No longer a consultation, the patient sees the result of the upcoming operation thanks to fitting sizers and 3D modeling.
- Mastopexy (breast lift). Asymmetry, which is caused by significant sagging of the breasts, is eliminated by removing and tightening excess skin and glandular tissue. The bust is not only tightened, but also a new symmetrical shape is created. If the difference between the mammary glands is insignificant, then a breast lift is performed using a periareolar approach around the areola. Please note: in this case, the scar is located on the border of dark and light skin, and is as invisible as possible, and there are no additional scars on the chest. In case of severe ptosis, either vertical mastopexy is performed (the scar runs from the areola to the inframammary fold) or anchor (the scar is located along the areola, vertically to the inframammary fold and along the line of this fold).
- Reduction mammoplasty (breast reduction). If there is a significant difference between the mammary glands, breast reduction can be performed.
- Lipofilling. Correction of mammary glands using own fat tissue transplantation. Your own fat is taken from the so-called “depot” areas - the abdomen, hips, back flanks and injected into the problem area. Lipofilling allows you to enlarge one of the breasts to the desired size.
The technique is always determined individually during consultation. During an individual meeting, the plastic surgeon will select the optimal technique for you, which will allow you to achieve the ideal breast shape.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of asymmetry most often does not cause difficulties; DS can be diagnosed by the woman herself during a visual examination. Complex diagnostic methods are aimed at identifying the causes of pathology in congenital origin or as a manifestation of another disease. With acquired changes, instrumental diagnostics may be required to identify the relationship of glandular and connective structural tissue in the breast, to determine the organic or functional pathological process.
Laboratory methods:
- genetic analysis to detect changes in gene structure;
- blood for hormones;
- UAC;
- biopsy.
Instrumental methods:
Most often performed:
- Ultrasound;
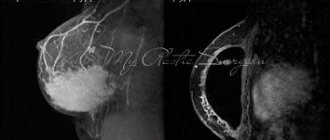
- mammography;
- less often - Rg, CT, MRI.
When performing these studies, a quantitative determination of glandular tissue, the degree of its distribution, as well as the presence or absence of a tumor process is carried out.
Prevention and prognostic measures
The prognosis for life is favorable, the percentage of disability is zero, all problems are of an aesthetic nature, which can be removed using the most optimal technique for each specific case.
Prevention consists, first of all, in preventing congenital pathologies. You should be gentle with your breasts during surgical treatment of infectious lesions of the gland and chest wall. Any surgical intervention on the mammary gland must comply with the rules of plastic surgery.
More or less?
There is almost always a tendency to form smaller breasts into larger ones, but often better symmetry is achieved by reducing the larger breast. If there is pronounced asymmetry, you should not chase a larger breast size. Better symmetry should be preferred to larger volume .
Although you may like the shape of one of your breasts better, you should remember that surgery may have to be performed on the other side. Everything will depend on the individual characteristics of your figure and breasts.
General principles of preparation for surgery
Preparation for surgical correction consists of the following points:
- consultation with a plastic surgeon;
- clarification of the patient's requirements;
- choice of type of surgical intervention;
- selection of implants;
- consultation with an oncologist and anesthesiologist;
- passing clinical minimum tests (including blood group and Rh);
- performing mammography;
- hair removal in axillary areas;
On the day of surgery, you are prohibited from eating or drinking water. Without getting out of bed, a woman needs to wear category 1 compression stockings to prevent thromboembolism.
Still have questions? Ask them to a specialist
Plastic surgeon Vladimir Krugly will answer all your questions
Ask a Question
Is it possible to pick your ears with cotton swabs?
Without getting carried away. Despite its unsightly appearance and repulsive smell, earwax is actually beneficial because it protects the eardrums from dirt, bacteria and mechanical damage. So there is no point in trying to get rid of it completely. Of course, excess of this substance does not look hygienic, but it tends to dry out, fall out, or be washed away when you take a bath. If not, grab a cotton swab. But it can only be used on the outer part of the ear and under no circumstances should it be inserted deep into the ear! Firstly, you will only push the wax deeper and can cause an infection, and secondly, you risk simply damaging the eardrum.
It happens that too much sulfur is released, a plug forms, and this can even affect hearing. But in this case, cotton swabs will not help. Contact an ENT specialist, he will solve your problem with a few simple manipulations.
Is it possible to squeeze pimples?
Not a good idea. Pimples are formed when sebum mixes with dead epidermal cells and bacteria begin to multiply in this “quagmire.” If you try to extract the pus, unsightly scars may remain on the skin, plus there is a chance of introducing even more infection into the wound.
To avoid the appearance of ulcers, wash your face more often to remove excess sebum, and use a scrub to exfoliate. If pimples pop up despite all your efforts, consult a dermatologist: there are also cures for this scourge.