According to the World Health Organization, 20–33% of people worldwide live with painful musculoskeletal diseases, and musculoskeletal diseases are the second leading cause of disability[1].
This situation forces doctors to look for new ways to treat such diseases. One of them is intra-articular plasma lifting, or autoplasmotherapy (in accordance with the nomenclature of medical services approved by Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated October 13, 2022 No. 804n - intra-articular administration of drugs). In simple terms, this is treatment with your own blood plasma. The method not only helps relieve pain, it relieves inflammation, improves joint mobility and accelerates the process of restoration of cartilage tissue in it.
Reinfusion of autologous blood Reinfusion of autologous blood into the joint area can help combat pain and inflammation. More details
Plasmolifting technology was developed relatively long ago and was initially used in dentistry, but in the course of research conducted by Russian doctors, it turned out that the patient’s own plasma can work in almost any tissue of the body. Thus, plasma lifting entered the arsenal of traumatologists and orthopedists[2].
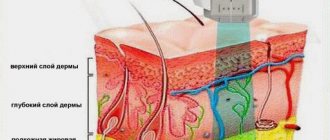
The essence of plasmolifting is that the patient’s platelet-rich blood plasma (PRP) is injected into the damaged areas of the joints. Cartilage tissue has a very weak ability to regenerate independently, especially in older people, and the introduction of plasma starts the recovery process - treatment is much faster and more effective. Platelets contain biologically active substances that stimulate healing processes, the so-called growth factors. They activate fibroblasts - connective tissue cells located in the deep layers, causing them to actively synthesize elastin, collagen and hyaluronic acid. As a result, the patient’s microtraumas heal, blood supply improves, pain decreases, joints become more mobile, and the process of restoring the structure of bone tissue at the site of cracks begins.
Plasma is injected directly into the joint itself, which means that the method works in a targeted manner without affecting other tissues and organs. Another feature of plasmolifting is that it uses the restorative resources of the body itself, is completely hypoallergenic and does not cause the side effects that can occur during drug therapy.
Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint Intra-articular administration of drugs can be used in the treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint. To learn more
In addition, the plasma lifting procedure is minimally traumatic. Despite the fact that the method is injection, there is practically no pain during the procedure, and there is no need for subsequent rehabilitation of the patient. Literally the next day after the injection, a person can return to their usual lifestyle.
We recommend reading:
- Plasmolifting in orthopedics and traumatology
- Plasmolifting in the treatment of the spine
- Plasmolifting of joints
- Plasmolifting of the knee joint
- Plasmolifting: how many procedures are needed
- Recommendations before the plasma lifting procedure
- Plasmolifting for arthrosis
- Plasmolifting for coxarthrosis
- Plasmolifting for arthritis
- Plasmolifting for osteochondrosis
- Plasmolifting how much does 1 procedure cost?
- Plasmolifting preparation for the procedure
- Plasmolifting of the hip joint
- Plasma therapy for the treatment of joints
More articles →
Principle of the method
The PRP method in the treatment of knee joints is based on enhancing the regeneration of intra-articular tissues. Thanks to platelet-rich plasma, cartilage, menisci, ligaments and other tissues are restored faster.
Even in ancient times, doctors drew attention to the fact that traumatic injuries accompanied by the formation of a hematoma heal much faster. The reasons for this have been established only in recent decades. It turned out that platelets secrete a number of substances that accelerate regeneration. These are the growth factors:
- epidermal;
- epithelial growth;
- endothelium;
- fibroblasts;
- insulin-like;
- transformative.
These substances have a polypeptide (protein) structure. They have different purposes. But all of these compounds take part in tissue regeneration. They stimulate the mitotic activity of cells, accelerate their growth and division.
PRP therapy for the knee joint makes it possible to significantly increase the intensity of reparative processes of both soft and bone tissues. In medicine, platelet-rich plasma is increasingly used. It is used for any injuries: soft tissue damage, muscle and ligament ruptures, bone fractures. All types of tissues regenerate faster if a sufficient number of platelets are present.
Why do they contact us?
- No queues
No need to wait, we work by appointment
- All in one day
Doctor's appointment, diagnosis and treatment on the day of treatment
- Let's relieve the pain
We relieve pain in just 1-2 visits to us
- We guarantee
Professional approach, affordable prices and quality
- Doctor's appointment 0 RUB!
If the cost of treatment is more than 30,000 rubles
- Three treatment options
We will select several methods and offer optimal treatment
Indications
Among knee joint diseases, the following diseases and conditions are considered indications for the use of PRP:
Arthrosis of the knee joint or gonarthrosis. A degenerative disease associated with the gradual degradation of articular cartilage. The use of PRP at stages 1-2 can improve regenerative processes in cartilage tissue. Thanks to this effect, a significant slowdown in the development of the pathological process is achieved. With the help of PRP, doctors are able to eliminate many symptoms of arthrosis, delay the need for knee replacement, or even abandon the operation completely if an effective conservative therapy regimen is used, in which PRP is one of the elements.
Injuries. The knee is often injured by athletes. Most often these are ligament ruptures and meniscus damage. Intra-articular fractures occur. If the doctor determines that conservative treatment is sufficient, he or she may use PRP to speed up the healing of the lesions. Otherwise, they can take a very long time to recover. This process takes weeks, or even months.
Operations. After arthroscopic surgery on the knee, a rehabilitation period follows. It continues until all tissue damage is restored. PRP can be used to speed up this process.
Defects of the articular surface. PRP is used for cartilage deficiency of articular surfaces of any origin. The cause may be injuries, arthrosis, inflammatory diseases of the knee, metabolic pathologies, psoriasis, systemic connective tissue lesions and other diseases. With a small defect, it is possible to enhance the regenerative processes of PRP. If there is a significant area of cartilage thinning, surgical treatment is indicated.
Safety
PRP therapy for the knee joint is one of the safest treatment methods. There is no risk of complications. The exception is the human factor. The doctor may miss the needle into the joint or cause an infection if he does not follow the rules of asepsis and antisepsis.
But if you turn to a highly qualified specialist who has extensive experience in performing this type of medical manipulation, the procedure will go smoothly. If a joint is deformed, if it is difficult for a doctor to get into its cavity, ultrasound can be used. Therefore, there is no risk of damage to healthy tissue during PRP therapy.
The drug itself for injection into the joint cavity is prepared from the patient’s blood. Therefore, the risk of transmission of infection or allergic reactions is eliminated. Your own blood does not carry an antigenic load. It is completely safe.
How do they do it?
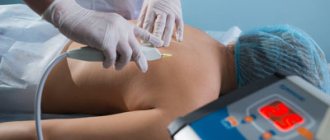
Blood is taken from the patient from the cubital vein. He then waits for 20 minutes for the intra-articular injection. During this time, the drug is prepared. Centrifugation is used. It can be one- or two-stage. In the first case, it is possible to better preserve the integrity of platelets, in the second, their higher concentration is obtained.
After preparing PRP, the resulting plasma is administered intra-articularly. The injection site is numbed with an anesthetic. Therefore, the patient does not feel significant pain during the procedure. In terms of tolerability, it can be compared to an intramuscular injection - unpleasant, but quite tolerable.
Some patients feel a feeling of fullness inside the joint. Especially in cases where a large volume of plasma is administered. After the injection, the doctor asks the patient to perform flexion and extension movements in the knee joint so that the plasma is better distributed in the joint cavity. After 10 minutes the patient goes home. He does not require hospitalization or additional observation.
Plasma can be used in courses of varying durations. Most often, PRP is administered once a week. A total of 3 to 7 injections are required. The treatment regimen is selected individually. The doctor forms it based on the clinical situation and the purposes of using platelet-rich plasma.
Effectiveness for arthrosis
When to expect results depends on the purpose of using PRP and the indications for treatment. In any case, it does not develop instantly. PRP is not a pain reliever. Platelet-rich plasma only enhances tissue regeneration, and this process takes quite a long time.
For arthrosis of the knee joint, the maximum effect develops 3-6 months after the start of treatment. Only a few patients report a decrease in pain after the first injection. For others, the first results are achieved within a month from the start of therapy.
In comparative studies, PRP shows much better results than intra-articular glucocorticoids. These differences are especially noticeable in grade 3 gonarthrosis. Pain syndrome in patients with this method of treatment is less pronounced. In addition, PRP has a more beneficial effect on cartilage - plasma stimulates its regeneration, while glucocorticoids, on the contrary, have a chondrotoxic effect.
According to E.Kon, 80% of people were satisfied with the results of the treatment after a series of injections of platelet-rich plasma for osteochondrosis. Results were assessed after 5 weeks. Another study found that treatment results were rated as positive by 67.3% of patients six months after undergoing PRP therapy for knee arthrosis. In the control group this figure was only 4.3%.
Another study calculated the average amount of time that elapses from the first injection until the therapeutic result is obtained. Patients considered this to be a reduction in clinical symptoms. This period was 17.63 days.
It should be noted that PRP has two main effects: anti-inflammatory and reparative. When surveying patients, only short-term symptomatic effects are taken into account. It develops more quickly after administration of platelet-rich plasma, but goes away more quickly after completion of the course of therapy. The first results of treatment are due to hyperplasia of the synovial membrane and modulation of the level of cytokines in the articular cavity.
At the same time, the main effect of PRP is chondrogenesis. But this process is happening too slowly. Patients cannot feel it. Only by comparing the symptoms and radiological parameters of the main and control groups are researchers able to obtain data on the effectiveness of PRP therapy for the knee joint several months after the course of treatment.
How is plasma therapy used in orthopedics?
The introduction of a concentrate of one’s own plasma reduces symptoms and restores joint mobility. Lost functions are restored 2-3 times faster than with conventional drug therapy.
The use of prp therapy in orthopedics is based on the ability to initiate the process of regeneration of cartilage and ligaments. This is a proven fact. Therefore, the duration of the effect after the course exceeds the period of remission from traditional methods.
Particularly high results are achieved in the treatment of degenerative diseases of the joints and spine - arthritis, arthrosis, osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia, etc. Injections are given once every 1-2 weeks for several months. If there are no contraindications, plasma therapy for joints is used without restrictions.
PRP for knee diseases
Knees are more often exposed to adverse effects - cold, injury and overload during long walking. Indications for use are:
- Osteoarthritis, arthritis of the knee joint begins due to a decrease in metabolic processes. Due to the low supply of nutrients, cartilage tissue is destroyed. There is pain, stiffness and swelling of the knee.
- Bursitis - damage to the synovial bursa is manifested by pain with swelling of the knee.
- Injuries and fractures lead to damage to soft tissues, hematomas, wounds, and disruption of the integrity of bones and ligaments. This is accompanied by redness, swelling and acute pain.
- After operations, the healing process can be accelerated if these injections are included in the treatment complex.
- With atrophy (drying, deformation) of cartilage associated with various changes - inflammatory, degenerative, autoimmune, crunching, friction, and pain occur in the knee.
Treatment of joints with plasma therapy reduces pain, restores mobility and reduces the use of painkillers. But, a stable effect is achieved after 4-6 months of continuous course.
Plasma injection into the knee joint
The manipulation is unpleasant, but it can be tolerated. The sensations are comparable to a regular injection. Some patients feel bloating at the injection site. It is important to move your knee after administration so that the liquid is well distributed.
PRP for hip diseases
The largest bone joints in humans. They can withstand quite heavy loads. But, with age, their condition worsens. There is a crunching and stiffness, as well as pain when moving.
Progression leads to a decrease in the functions of the hip joint. Initially, this is associated with metabolic disorders, drying out of cartilage, and a decrease in the amount of synovial fluid.
Intra-articular administration of plasma concentrate is used for inflammatory and degenerative changes:
- Coxarthrosis occurs mainly after 40 years. Caused by deterioration of nutrition of articular structures. As a result, they become deformed and destroyed, which leads to inflammation, pain, and immobility.
- Injuries, including intra-articular fractures, are more often diagnosed in athletes and older people. They are associated with severe pain, prolonged limitation of movements, and increased body temperature.
- Loss of mobility occurs due to inflammatory processes and injuries. Due to its structure, it quickly loses the ability to move freely. In severe cases, surgery is prescribed.
- Recovery after surgery requires serious rehabilitation. To shorten this period, plasma therapy sessions are included in the therapeutic complex.
The manipulation is carried out in a lying position on the side opposite the injection site. A painkiller is injected at the puncture site. After the injection, the patient will be asked to move - raise, lower his leg and perform other movements.
The composition with bioactive components does not have analgesic properties. Therefore, one cannot expect an immediate effect. Like all natural remedies, plasma therapy will bring tangible results only after a few injections.
PRP for shoulder diseases
The use of the drug is indicated for the following conditions:
- Arthritis and arthrosis are inflammatory diseases that become chronic. They are characterized by excruciating acute pain when moving the arm, a feeling of stiffness, swelling and redness.
- Injuries, dislocations, and fractures are accompanied by damage to surrounding soft tissues, bones, muscles and ligaments. There is pain in the injured area, redness, increased body temperature, and numbness in the hand.
- Bursitis - damage to the synovial bursa causes acute pain in the shoulder area and stiffness of movement.
Plasma injection into the shoulder joint
An injection into the shoulder is painful and unpleasant. It is carried out after preliminary anesthesia. The result of the course will be a rapid restoration of the motor ability of the hand.
PRP for elbow diseases
Some of the most mobile joints are rarely susceptible to disease. But they often suffer from injuries and sprains. The use of unusual injections is indicated for the following conditions:
- Epicondylitis is a periarticular inflammation affecting the muscles and humerus. Manifested by acute pain and decreased mobility. If the situation drags on, it leads to atrophy of muscle fibers, sometimes to disability.
- Inflammatory pathologies - bursitis, arthritis, tendinitis, are manifested by pain, increased body temperature, redness and stiffness.
- Injuries, fractures, ligament ruptures are accompanied by acute pain, numbness of the hand, and impaired motor functions.
After using PRP, pain and inflammation gradually disappear, and functions are completely restored. The earlier treatment is started, the better the result. The procedure is carried out in any position - sitting, lying down. Then the patient is asked to move his elbow - straighten and bend. Usually, 3-5 sessions are enough.
PRP for ankle problems
Large joints that support body weight. If one of them is damaged, the second suffers from increased stress. Without timely measures, the patient will develop disease in both legs. The technique is used to eliminate the following ailments:
- A sprained ligament in the ankle area is accompanied by prolonged aching pain and lameness.
- Inflammatory diseases - arthritis and arthrosis, are associated with degenerative changes. In this case, the ability to move is lost.
- Bone necrosis is accompanied by severe pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
- Destruction of cartilage for various reasons - chondromalacia provokes excessive friction of the joint structures. This causes nearby tissues to become inflamed and swollen.
The PRP therapy technique is also used to prevent joint damage. This is true for athletes and people engaged in heavy physical labor.
Advantages and disadvantages, complications
The benefits indicate the significant safety of this treatment for patients. This is complete compatibility between the administered substance and the patient, since everything that is administered to a person is taken from him. Accordingly, there is no risk of infecting the patient with HIV infection or viral hepatitis through blood. The plasma lifting session has a prolonged effect and does not require daily repetitions.
Own blood components, unlike non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, do not harm the gastrointestinal mucosa. Finally, there is no allergy and no harmful systemic effects.
Despite all the advantages, the method is invasive; the needle must be brought as close as possible to the affected intervertebral disc. In fact, if we slightly change the operating factor, and do not inject platelets, but use a laser LED, then we already get a modern minimally invasive neurosurgical intervention.
There is a certain danger of infection of medical personnel, although the patient is usually not concerned about this disadvantage. If the patient has a blood pathology, thrombocytopenia and thrombocytopathy, hemorrhagic syndrome, then this method cannot be used.
There are no optimal data on platelet concentrations, and modern randomized trials have not yet been able to show a precise correlation between clinical effects and platelet concentrations. There are also difficulties in preparing plasma, in which red blood cells can get into the finished injection material. They are equivalent to hemorrhage into the joint cavity, causing inflammation and increased pain. It is also required to comply with the parameters of two-stage centrifugation, and maintain time and speed conditions. If you reduce the time and speed during centrifugation, then in the supernatant layer, which is collected for the second stage, there will be a lot of leukocytes and erythrocytes, which will worsen the result.
The most common complication is the occurrence of pain when the patient is injected with activated plasma, which contains a large amount of released platelet-derived growth factors. Pain in the affected vertebra can last up to several days. The therapeutic and protective regime, wearing a corset, helps relieve pain. Compresses, distracting and cooling ointments, and short-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
Also, unfortunately, it is impossible to exclude local soft tissue abscess and infiltration associated with a violation of the procedure for introducing the material. There may also be a hematoma, which, however, quickly resolves and does not bother the patient for long.