Etiology and pathogenesis of rhinophyma
Since rhinophyma mainly represents “advanced” cases of rosacea, this disease is the etiological factor. An important role in the pathogenetic mechanisms contributing to the transition of rosacea to rhinophyma is played by the increased activity of 5-alpha reductase of the pilosebaceous complex and the influence of androgens .
There is evidence of inheritance of rhinophyma , but how it is realized is not completely clear. In one study involving 55 patients with rhinophyma, 12 people reported having it in their immediate family.
An important role in the pathogenesis of rhinophyma is played by abundant vascularization of the nasal area and chronic inflammation . Finally, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages (alcoholism) , as noted in the many English names for rhinophyma, contributes to its occurrence.
4.Treatment
Attempts at drug or physical therapy treatment of rhinophyma to slow or stop tumor growth are reported from time to time; however, effective conservative therapy, by and large, does not exist today. The method of choice is surgical removal of overgrown tissue with the obligatory capture of intact areas (to avoid a possible relapse). High-tech devices are increasingly being used, for example, laser or radio frequency scalpels, but they do not yet have any real advantages over a traditional scalpel. Depending on the clinical characteristics of a particular case, the normal anatomical shape of the nose is restored using plastic surgery methods. Treatment of concomitant and background diseases is mandatory.
It is clear that the scope and outcome of intervention critically depends on the timeliness of care; in advanced cases, eliminating the defect is much more difficult, and sometimes complete reconstruction is completely impossible. Therefore, when the first signs of any growth on the skin appear (and this applies not only to the skin of the nose), you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Clinical manifestations
The phymatous form of rosacea ( Fig. 2 ) is presented in 4 clinical and histological variants, each of which can be present in rhinophyma - glandular, fibrous, fibroangiomatous and actinic.
Rice . 2. Rhinophyma in a man (Danish national service on dermato-venereology)
https://www.danderm-pdv.is.kkh.dk/atlas/4-143.html
With glandular rhinophyma , which occurs most often, the patient’s nose is knobbly enlarged due to lobular and tuberous growths. On its surface there are multiple telangiectasias with dilated openings of the sebaceous glands. The affected glands secrete an excessive amount of sebaceous secretion, which consists of a mixture of sebum with horny scales, bacteria and mites of the genus Demodex. Due to uneven growths, the symmetry of the nose can be disrupted.
In patients with fibrous rhinophyma, the nose takes on a blue-violet hue. Multiple telangiectasias and dense tumor-like growths are visible on its surface. In this case, the collagen fibers of the connective tissue are hyperplastic to a much greater extent than the sebaceous glands.
Fibroangiomatous rhinophyma manifests itself as pustular formations and telangiectasias. The nose takes on a copper tint, and the skin becomes dense to the touch.
Actinic rhinophyma is not prone to massive growths, although the size of the nose in such patients is slightly increased. Its color can vary from pale red to bright red, telangiectasias are present on the wings, and the openings of the sebaceous glands are dilated. Actinic keratosis and hyperplasia of the sebaceous glands are noted.
In rare cases, rhinophyma can spread beyond the nose and affect the ears.
2. Reasons
The above-mentioned association between alcoholism and rhinophyma has long not been considered as a direct etiopathogenetic connection. “The red nose of a drunkard” is played out satirically in countless jokes, fables, and anecdotes on this topic, but in relation to rhinophyma, ethanol abuse is only one of the risk factors, since drunkenness actually provokes and aggravates almost all diseases known to medicine, including rhinophyma .
In fact, the mechanisms for triggering hypertrophic, hyperplastic and fibrosing processes in rhinophyma remain not entirely clear to this day. It has been established that in most cases, rhinophyma develops during a long course of pink acne - rosacea - and some sources on this basis interpret tumor-like growth as a natural late stage of rosacea.
However, this does not explain those cases where rhinophyma develops without a history of clinically significant acne. In addition, rosacea affects women much more often, and then the multiple predominance of men among those affected remains unclear (attempts to explain this, again, by the greater prevalence of male alcoholism are legitimate and logical, but statistically still insufficient).
The main etiopathogenetic factor today is considered to be abnormally intense vascularization of nasal tissue (hypertrophied capillary network) in combination with chronic inflammation - rosacea is a special case, but not the only variant of this process. Hair follicles pathologically expand, sebaceous glands and cells of other tissues increase in number and/or size, which leads to characteristic growth. Sometimes rhinophyma is combined with similar phymatous processes on the eyelids, chin, ears, etc.
The role of such factors as burdened heredity, environmental and occupational hazards, gastroenterological diseases, dietary imbalances and excesses, viral activity, autoimmune disorders and metabolic disorders, hormonal imbalances, angioneurosis, capillary circulation disorders, demodicosis (tick-borne dermatosis), seborrhea is studied and discussed. , long-term use of vasodilating drops, hypovitaminosis, etc. Each of these hypotheses is confirmed to a certain extent, but only as a more or less significant risk factor. A 100% trigger (launching mechanism) has not yet been found and, perhaps, will never be found: many authors reasonably consider rhinophyma as a polyetiological disease, i.e. as a disease that can develop under the influence of various combinations of causes and favorable conditions.
Visit our Dermatology page
Treatment methods for nasal rhinophyma
Drug treatments for rhinophyma have not become widespread. There is data on off - label oral isotretinoin - studies have shown slowing or stopping the progression of the disease with treatment. But this method is not suitable for involution of existing changes. In addition, isotretinoin is used off-label, that is, the FDA has not approved this protocol, and the doctor acts at his own peril and risk.
Cosmetic improvement in patients with rhinophyma can be achieved through the use of dermabrasion , layer-by-layer ablation with a CO2 laser, or surgical excision of hypertrophied parts of the nose.
One study compared the effects of a CO2 laser and electrosurgery and found almost identical results. Another study compared the excision of phymatous growths with a scalpel and a laser; these methods did not reveal significant differences in operating time, blood loss, complications and aesthetic results.
In the initial stage of development, rhinophyma can be successfully treated using IPL therapy. This method is based on the selective destruction of blood vessels when they absorb light energy. IPL is also used before using a CO2 laser to increase hemostasis during laser rhinophyma resurfacing.
Rhinophyma can mask malignant neoplasms, so some experts recommend sending excised tissue samples from patients for histological examination during the treatment process.
1.General information
Rhinophyma (ancient Greek lit. “growth on the nose”, “abscess on the nose”) is a benign growth of soft tissues in combination with fibrosis (replacement of normal, parenchymal tissues with scar connective tissue), which leads to a progressive increase in the size of the nose, its deformation, thickening and redness. As a result, a disfiguring cosmetic defect is formed that is practically inaccessible to conservative treatment.
Rhinophyma is mentioned in the oldest archaeological sources; Apparently, this disease accompanies humanity throughout its existence in its modern evolutionary form. As a historical illustration, the fragment of “Portrait of an Old Man with His Grandson” by D. Ghirlandaio (late 15th century) is most often used, where the famous Florentine master captured rhinophyma, as they say today, with photorealistic accuracy. There are a lot of synonyms and figurative definitions; most of them associate rhinophyma with alcohol: “drunkard nose”, “bottle nose”, “wine”, “rum”, “skin”, etc., however, non-alcoholic metaphors for rhinophyma are found in various languages, for example, “potato nose” ", "bumpy" or "turkey nose".
In men, phymatous proliferation of nasal tissue occurs, according to various sources, from 5 to 30 times more often than in women. Among Caucasians - more often than among representatives of the other two races. The age of most common primary diagnosis of rhinophyma begins at about 40-45 years, although the true onset of the hyperplastic process probably occurs at earlier stages of life.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
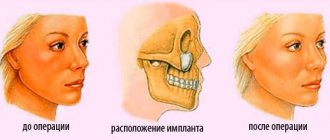
Benefits after septoplasty, does the shape of the nose change?
Many patients faced with the problem of deformation of the nasal septum are often concerned with the question of whether after septoplasty the shape of the nose changes and how long the achieved effect lasts. The operation itself is a type of less traumatic procedure, the advantage of which is the preservation of the bone and cartilage structures of the nose. There is no damage or negative changes. Surgical procedures are performed in the inside of the nose using small incisions through which the shape of the septum is corrected. Experts note that after septoplasty, the quality of breathing in the nose has changed in a short time, and patients also receive a number of advantages:
- rapid improvement in quality of life;
- nasal breathing resumes;
- getting rid of numerous problems that periodically arise due to chronic diseases of the ENT organs and associated with septal deformation.
It is important to take into account that the shape of the nose after septoplasty does not change dramatically, and the operation does not fall into the category of aesthetic procedures. But at the same time, it is perfectly combined with rhinoplasty.
Some patients note that after septoplasty the tip of the nose becomes slightly numb. But complete restoration of physical condition and full breathing is observed after two months, which should be taken into account and not worried. It is worth noting that patients rarely change the shape of their nose after septoplasty, but unnoticed against the background of their face. Operations today are performed using laser and radio wave methods. This does not lead to the fact that after septoplasty the shape or any parts of the nose have changed.
Symptoms, causes of the disorder: nose shape, septoplasty
Deformation of the nasal septum can be determined by the following main signs that are repeated or present in patients:
- breathing through the nose is difficult;
- swelling of the mucous membrane, the appearance of allergic rhinitis;
- frequent colds;
- nosebleeds with a certain frequency;
- itching, pain in the face and head.
Every person needs to breathe fully through the nose for health and prevention of bronchi. Before entering the lungs, the inhaled air is cleaned and moistened in the nasal passage, after which the filtered air enters the body, supplying all vital organs. If the nasal septum is deformed, then frequent, protracted respiratory diseases that become chronic are possible. In particular, rhinitis, sinusitis, as well as tonsillitis, otitis and other chronic diseases develop.
In most cases, many people self-treat, using drops and antiviral drugs, unaware of the cause associated with a defect and structural changes in the septum. This requires correction of the nasal septum - septoplasty.
In the absence of proper treatment for a long time, snoring, changes in shape, formation of crusts in the nasal cavity, recurrent bleeding due to thinned walls of the septal mucosa and, subsequently, loss of natural functions are possible. More rare symptoms of a deviated nasal septum are:
- hearing impairment;
- dryness of the nasal cavity.
If your hearing is impaired, you must contact an otolaryngologist, as well as use the services of the specialized clinic “First Surgery” and undergo surgery.
Causes of acromegaly
When listing the main causes of a rare disease, doctors call the genetic predisposition of family forms that are inherited:
- Rosenthal-Klopfer syndrome (large folds on the occipital part, provoked by a combination of folded pachyderma, gigantism and acromegaly);
- acromegaloid face syndrome (thickening of the lips, eyelids, eyebrows, “potato” nose);
- Sotos syndrome (increased growth with obvious signs of illness);
- somatotrophin;
- gigantism caused by excess somatoliberin.
There is a list of ailments that can primarily cause death in patients with acromegaly:
- cardiac ischemia;
- hypertension;
- obstructive sleep apnea syndrome;
- hyperparathyroidism;
- polyps in the intestines;
- infectious diseases.
If acromegaly is not treated promptly, the patient's condition will rapidly deteriorate. A person will die in 3-4 years.
Anthropological parameters of the nose
With different combinations of length, width, height, and base-to-tip ratio, each person has a unique nose. In plastic surgery, a nose is considered ideal if it has the following characteristics:
- the length of the nose should be equal to 1/3 of the length of the face;
- the width should not exceed 1/3 of the length of the nose;
- the height of the nose should be equal to 1.5 parts of the width of the nose;
- The ideal nose angle is 30 degrees.
The ratio of the width of the nose to its length as a percentage can vary from 60% to 110%. The nasal indicator is often found in anthropology with the following meanings:
- up to 69.9% - leptoria, high narrow nose;
- 70-84.9% - mesorinia, a characteristic indicator of medium size;
- 85-99.9% - chamerinia, characterized by a wide and low nose;
- an indicator of 100% is hyperchamarinia, a sign of a very large nose.
Lepthorinia is most common among Eskimos and Europeans, while chamerinia is common among residents of Africa and Australia. Anthropologists argue that the appearance of the nose is associated with the body’s adaptation to climate and living conditions.
Treatment of acromegaly
If a patient is diagnosed with acromegaly, there is no need to panic. Medicine does not stand still. Much is available to science, but the patient must remember: one must work proactively. Medicine uses 3 methods of treating pathology:
- Medications. The classical method of treatment is used if there are no serious changes or tumor formations in the body. An important point is the contraindication to surgery. Special medications will suppress growth hormones.
- Radiation therapy. When drug therapy is not effective and surgery is contraindicated, the doctor will suggest a course of radiation therapy. It is prescribed for a malignant tumor on the pituitary gland. The results of treatment are expected in 1-2 years.
- If the pathology progresses and other forms of treatment are not effective, a surgical method is used. Surgery is recommended when the tumor presses on the optic nerve. Postoperative rehabilitation lasts from 3-4 months to several years.
An obligatory part is symptomatic treatment: the fight against diabetes, hypertension, obesity. If you are faced with this disease, medical specialists will help you overcome it. Doctors will help you overcome psychological problems, prescribe an examination, and select the right treatment.
Causes
There is still no consensus among experts as to what is the direct cause of the development of the disease. The only thing that is known is that it begins to progress under the influence of the following factors:
- The presence of chronic inflammatory skin diseases, especially rosacea.
- Presence of scabies mite.
- Having problems with the endocrine system.
In addition, doctors identify a set of provoking factors:
- Unfavorable environmental conditions.
- Alcoholism.
- Diseases of the stomach and intestines.
- Chemotherapy for oncology.
- Ultra-violet rays.
- Age-related changes.
- Stress.