What is an abscess and what causes it?
An abscess is a painful pustule surrounded by inflamed tissue. Often it can be easily felt. Such a formation can appear on any part of the body, but most often it affects:
- armpits;
- area around the anus and vagina (Bartholin gland abscess);
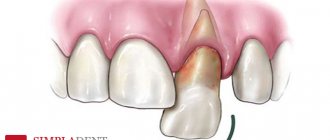
- tissue around the tooth;
- skin in the groin area;
- hair follicles.
During their development, abscesses are filled with necrotic masses and can open on their own. However, it is best to consult a doctor in case of such a disease, who will open the purulent focus and clean (drain) it.
Causes of abscesses:
- as an independent disease, abscesses of the skin and soft tissues most often occur, caused by blockage of the openings of the sebaceous and sweat glands, the formation of cysts and the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms there;
- purulent soft tissue abscess can be a complication of skin damage;
- a post-injection abscess develops when the drug is administered with a non-sterile syringe; in severe cases, a purulent process – phlegmon – may spread;
- such a process often complicates the course of any infectious diseases of a bacterial nature, for example, a peritonsillar abscess develops as a complication of tonsillitis;
- Abdominal abscesses can develop when microbes are transferred through blood vessels;
- in some cases, the cause of the disease is not bacteria, but protozoan microorganisms, for example, amoebic liver abscess;
- pathology may arise primarily due to the penetration of a large number of pathogens with high virulence (damaging ability) into the tissues, and a lung abscess may form.
Signs of an abscess occur more often in people with weakened immune systems. Risk factors for developing pathology:
- long-term treatment with glucocorticoids and chemotherapy drugs;
- diabetes mellitus, malignant tumors;
- diseases of the blood and hematopoiesis – sickle cell anemia, leukemia, HIV infection;
- Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis;
- severe injuries or burns;
- alcoholism, drug addiction.
Other risk factors are exposure to a polluted environment, contact with dust, hydrocarbons, poor skin hygiene, atherosclerosis of peripheral arteries or severe varicose veins.
Abscess symptoms
Symptoms characteristic of an abscess are as follows:
- a sharp increase in temperature (up to 40 degrees);
- general weakness;
- dizziness;
- decreased appetite;
- the formation of subcutaneous capsules with pus, accompanied by redness, swelling and pain (with a superficial abscess), ending with its rupture and release of pus.
If you experience similar symptoms, consult your doctor
. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Symptoms and diagnosis of abscess
Symptoms of an abscess vary depending on its location. When skin and soft tissues are affected, the following is noted:
- skin redness;
- swelling and soreness;
- palpation of a soft space-occupying formation under the skin.
Abscesses of internal organs are accompanied by corresponding symptoms: cough, sore throat, sore throat, right hypochondrium, lower back, back, headache, dysfunction of the affected organs.
The infection causes signs of intoxication - high fever, headache, weakness, nausea. Sometimes the course of abscesses is not accompanied by pronounced symptoms; they become chronic, and in these cases, diagnosing the disease is difficult. Complications of an abscess are associated with the entry of microorganisms from its cavity into the blood vessels. At the same time, they spread throughout the body, causing sepsis (“blood poisoning”). This condition is life-threatening. Therefore, it is very important to identify and eliminate the purulent focus in time.
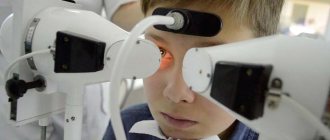
Diagnosis of an abscess is carried out by external examination. To detect ulcers in internal organs, ultrasound, CT, MRI, and radiography are used. Blood tests reveal signs of inflammation, but they do not provide information about the location of the pathology.
How is the treatment carried out?
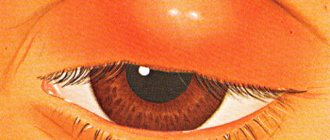
Treatment of eyelid abscess occurs only by surgical intervention.
In this case, the abscess is opened , and such a procedure is performed only in a hospital setting, although, as an exception, such a procedure can also be performed in a clinic.
After opening the abscess, its contents are removed , and then the cavity is washed using antibacterial and antiseptic solutions .
The operation usually does not take more than 15 minutes and is considered a relatively easy procedure in ophthalmic practice.
After opening, no cosmetic defects remain in the area of the abscess.
But experts recommend not only going to the hospital in time if abscesses occur, but also taking a number of measures that will help prevent the onset of the disease . In particular, it is advisable to carry out procedures such as systemic antibiotic therapy, ultraviolet irradiation of the blood, and autohemotherapy .
In the latter case, a course of treatment is performed, which involves 12 procedures of administering drugs to the gluteal region to help strengthen the patient’s immunity.
Note! Ultraviolet irradiation of blood is a process of ultraviolet irradiation, which occurs through a special needle equipped with an emitter.
Such a needle is inserted into the patient’s vein, and all harmful and opportunistic microorganisms present in the body die. Ten procedures are enough - and the risk of formation of an abscess of the eyelid and other purulent inflammatory diseases is reduced.
Abscess treatment
If you experience pain, swelling of the skin, the formation of a tubercle or a lump with a softened center, you should contact a surgeon.
- Treatment of an abscess is carried out under local anesthesia.
- The skin is disinfected, an anesthetic is injected, and the abscess is opened.
- After emptying the cavity, it is washed with an antiseptic solution and dried.
- A drain is inserted into the wound for 1–2 days and covered with a sterile bandage.
Immediately after such an operation, the patient’s well-being improves significantly. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. After a few days, the drainage is removed.
For abscesses of internal organs, the principle of treatment is the same - opening, cleansing, draining. Access to the desired organ may require extensive surgery or the use of endoscopic techniques.
Surgeons do not recommend treating an abscess at home, as this can lead to a delay in the process and the development of sepsis. However, people often use lotions with aloe juice, onion gruel, and compresses with rye bread. We advise you to immediately contact the clinic by making an appointment by phone.
Do not puncture or squeeze out the contents of the abscess. This can cause the infection to spread through the blood vessels.
Prevention
To prevent abscess, patients are recommended to:
- promptly disinfect and treat abrasions, wounds, injuries;
- observe the technique of performing therapeutic and diagnostic procedures;
- observe the rules of sanitation and hygiene;
- promptly treat inflammatory diseases, primary purulent processes, local foci of infection (caries, periodontitis).
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Treatment at the Mama Papa Ya clinic
The network of family clinics “Mama Papa Ya” offers medical services for the treatment of abscesses by a qualified surgeon. The clinic's branches are located in Moscow and Moscow Region.
Our advantages:
- quick appointment of a patient without a long wait in line;
- immediate surgical care - opening and draining the abscess in a sterile office;
- comprehensive recommendations for caring for the postoperative wound to prevent complications;
- if necessary, consultation with other specialists (gynecologist, ENT doctor, neurologist and others);
- diagnosis of internal abscesses using multislice computed tomography.
To obtain a doctor’s consultation, you must contact our manager by phone or through the feedback form.
Reviews
Good clinic, good doctor!
Raisa Vasilievna can clearly and clearly explain what the problem is. If something is wrong, she speaks about everything directly, not in a veiled way, as other doctors sometimes do. I don’t regret that I ended up with her. Anna
I would like to express my gratitude to the staff of the clinic: Mom, Dad, and me. The clinic has a very friendly atmosphere, a very friendly and cheerful team and highly qualified specialists. Thank you very much! I wish your clinic prosperity.
Anonymous user
Today I had a mole removed on my face from dermatologist I.A. Kodareva. The doctor is very neat! Correct! Thanks a lot! Administrator Yulia Borshchevskaya is friendly and accurately fulfills her duties.
Belova E.M.
Today I was treated at the clinic, I was satisfied with the staff, as well as the gynecologist. Everyone treats patients with respect and attention. Many thanks to them and continued prosperity.
Anonymous user
The Mama Papa Ya clinic in Lyubertsy is very good. The team is friendly and responsive. I recommend this clinic to all my friends. Thanks to all doctors and administrators. I wish the clinic prosperity and many adequate clients.
Iratyev V.V.
We visited the “Mama Papa Ya” Clinic with our child. A consultation with a pediatric cardiologist was needed. I liked the clinic. Good service, doctors. There was no queue, everything was the same price.
Evgeniya
I liked the first visit. They examined me carefully, prescribed additional examinations, and gave me good recommendations. I will continue treatment further; I liked the conditions at the clinic.
Christina
The doctor carefully examined my husband, prescribed an ECG and made a preliminary diagnosis. She gave recommendations on our situation and ordered additional examination. No comments so far. Financial agreements have been met.
Marina Petrovna
I really liked the clinic. Helpful staff. I had an appointment with gynecologist E.A. Mikhailova. I was satisfied, there are more such doctors. Thank you!!!
Olga
Clinical picture of the disease
In the initial stages, abscesses and phlegmons adjacent to the lower jaw are manifested by compaction and progressive swelling of the soft tissues of the face. The skin over the purulent focus is often hyperemic. The key symptom of suppuration is fluctuation - the feeling of fluid in a confined space.
The course of phlegmon is accompanied by general intoxication, in which the patient presents the following complaints:
malaise and feeling of chronic fatigue; increase in body temperature; fatigue and joint pain.
Abscesses, as a rule, do not cause such symptoms due to the limited nature of the pathological process.
Abscess, phlegmon of the maxillofacial area in children is characterized by an acute and severe course of the disease. Diffuse purulent lesions of soft tissues are formed as a result of the imperfection of the children's immune system.
Forecast and prevention of the disease
The prognosis of odontogenic abscesses and phlegmons is usually favorable. A positive treatment result is observed with timely indication of full surgical care. In such cases, the patient must be hospitalized in a specialized medical hospital.
Lethal outcomes from purulent lesions of the soft tissues of the maxillofacial area are associated with late presentation of the patient and systemic suppression of his immunity.
Prevention of the disease is achieved in the following ways:
sanitation of the oral cavity, during which the dentist treats all carious, pulpitic and periodontitis teeth; strict adherence by patients to the rules of personal hygiene and regular brushing of teeth; undergoing regular preventive examinations at the dentist, at least twice a year; timely consultation with a doctor if symptoms of dental diseases are detected. Every person should remember that the cost of prevention is much lower than the cost of treatment. And in some cases, sanitation of the oral cavity can prevent the development of severe complications, which are accompanied by high mortality in patients.
General principles of treatment of the disease
The doctor who treats phlegmon of the maxillofacial area is an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Each doctor, when starting to treat an odontogenic process in the maxillofacial area, is guided in his actions by the following principles:
The tooth that caused the development of phlegmon is removed. Timely diagnosis is very important due to the characteristics of this area, from where the infection can spread, causing severe consequences (in particular, mediastinitis). It is necessary to eliminate the spread of the infection, that is, promptly open the lesion and eliminate the inflammatory exudate, relieve tissue tension. The rate of subsidence of inflammation depends on the quality of evacuation of all decay products from the wound, that is, careful postoperative treatment of the wound is necessary. Comprehensive treatment of pathology using all means and methods available in this medical institution. Friendly management of the patient with colleagues from other areas, timely appointment of consultations with all specialists for combined lesions. Visible external changes often occur, which are not always pleasant for the patient, which is especially painful in the face area. Therefore, there is an urgent need to organize work with patients by a medical psychologist in the early stages after surgery, especially if there is a significant visible defect. Correct stage-by-stage treatment, organization of medical rehabilitation, referral to the appropriate department with complete information about the patient. Fully informing relatives and the patient about the violation of significant functions of the maxillofacial area, if any. Upon leaving the hospital, the patient should have clear further recommendations, especially if it is necessary to continue treatment on an outpatient basis.
Complications of abscesses and phlegmon
Purulent lesions of the maxillofacial area can be complicated by the following pathologies:
Sepsis is a serious condition of the body that is caused by the penetration of a bacterial infection into the circulatory system. Treatment of such a complication is difficult due to the development of body resistance to antibiotic therapy. Sepsis is often the cause of death. Mediastenitis in the form of purulent inflammation of the tissue of the mediastinum, where the heart, lungs and bronchi are located. Meningitis . Inflammatory damage to the meninges develops as a result of the spread of purulent infection through the lymphatic and blood vessels of the head.
Diagnosis of the disease
Establishing a diagnosis for acute odontogenic infections includes the following measures:
Collection of medical history. The doctor finds out the patient’s complaints and the general condition of the patient. External examination of the maxillofacial area and palpation of regional lymph nodes. Most inflammatory and purulent processes cause enlargement and pain of the lymph nodes. Instrumental examination of the oral cavity, during which the doctor detects chronic foci of odontogenic infection. X-ray in frontal and lateral projection. Laboratory blood test, in which there is an increase in SOE, leukocytes and a decrease in the concentration of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
Reasons for formation
Due to their development, there are two types of perimaxillary abscesses:
- Odontogenic. The cause of development is damaged dental elements.
- Non-odontogenic. Not caused by the condition of the dentofacial apparatus.
The most common causes of anomalies are dental diseases:
- Advanced carious lesions of units, pulpitis.
- Deep periodontal pockets.
- Periodontitis.
- Pericoronitis.
- Infected and impacted molars and premolars.
- Root cyst.
The development of a lesion can be triggered by penetration of infection under the periosteum from a diseased unit.
Reasons for the development of non-odontogenic foci of pus:
- Traumatic lesions of the jaws, elements or soft membranes of the oral cavity with infection.
- Nasopharyngeal and ear infections.
- Complications of unqualified dental treatment.
- Spread of infection to the jaw from other organs and systems.
The development of an abscess depends critically on the general health and immunity of the patient.