Since ancient times, humanity has been interested in the question of what the ideal body proportions should be and what facial features should be considered the generally accepted standard of beauty. Despite many disagreements, most participants in this thousand-year-old dispute agree that beauty is strongly associated with youth. Smooth, flawless skin that seems to glow from within, the absence of wrinkles, the smoothness and roundness of facial features, high cheekbones, a soft jawline - all these features are inherent in youth and, of course, from an aesthetic point of view are the most attractive. However, the process of age-related changes that occurs in the body under the influence of internal and external factors invariably leaves its mark on our appearance.
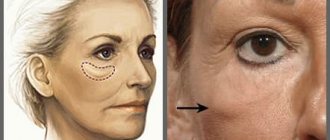
One of the most noticeable signs of this process is a reduction in the volume of subcutaneous fat, changing the shape and features of the face. In combination with ptosis - the drooping of tissue under the influence of natural gravity - such changes visually add several decades, make the oval of the face less clear, and make a person look tired and haggard.
Fat packets. Features of facial aging.
Understanding the deep anatomical changes that occur with age allows you to choose the right tactics to correct the signs of aging.
Deep fat packets are:
Medial suborbicularis oculi fat, Medial SOOF. It is adjacent to the periosteum of the medial part of the lower edge of the orbit, located under the orbicularis oculi muscle. Passes from the medial canthus to the outer canthus. The zygomaticocutaneous ligament separates the medial SOOF inferiorly from the deep medial buccal fat pad.
Lateral suborbicularis oculi fat, Lateral SOOF. Located in the lateral part of the lower edge of the orbit in the sagittal plane, it does not rise above the lateral canthus. The upper border is formed by the lateral thickening of the orbit. The medial half is covered by the orbicularis oculi muscle. The lateral SOOF lies above the protruding part of the cheekbone, not reaching the upper edge of the zygomatic arch. The lateral SOOF is located above another, deeper fat pad, so it does not have direct contact with the periosteum. Its medial border is the medial SOOF.
Deep medial cheek fat (DMCF). Located below the level of SMAS, the upper part lies under the orbicularis oculi muscle. Its superior border is the zygomaticocutaneous ligament, separating it from the medial SOOF; laterally it is bordered by the deep buccal fat (Bichat's lump) and the zygomaticus major muscle. The medial border is the piriformis ligament surrounding the base of the nose, and the inferior border is the fat under the orbicularis oris fat. This fat packet is located on the periosteum of the upper jaw.
Deep buccal fat pad or Bish's lump (Buccal fat) . Located below the cheekbone on the anterior side of the mandibular branch, it surrounds the medial pterygoid muscle of the maxilla and the masseter muscle. This fat pad has a buccal extension adjacent to the medial buccal fat pad, the deep medial buccal fat pad, the midbuccal fat pad, the orbicularis oculi fat pad, the mandibular fat pad, and the premassector fat pad.
Age-related changes occurring in subcutaneous fat tissue:
The aging process of deep fat bags.
Medial and lateral SOOF. Both packages are located on the periosteum - aging is characterized by malnutrition with a low tendency to ptosis. Hypotrophic involution of the medial SOOF causes the formation of a recessed zone in the infraorbital region. It has been observed that a decrease in medial SOOF increases the appearance of the tear trough and V-shaped deformation of the lower eyelid. The medial SOOF holds the tissues of the lower eyelid, which means that with loss of its volume, there is an increase in relaxation of the lower eyelid tissue and intraocular fat packet. Hypotrophy of the lateral SOOF reduces the projection of the malar region and cheekbone, which facilitates ptosis of the superficial fat pads of the cheeks.
The deep medial buccal fat pad (DMCF) is characterized by a gradual and pronounced decrease in volume and caudal migration. Its hypertrophy is found mostly in the upper two-thirds and slightly in the lower third, where caudal migration of fat compensates for the hypotrophy.
Deep buccal fat. Part of this package is the well-known Bisha lump; it affects the aesthetic formation of the cheek area, and therefore the harmonization of the face as a whole. More changes are characteristic of the hypotrophic type of aging. Some sources indicate that a decrease in the volume of Bichat's lump in elderly patients led to a lack of support for the superficial medial buccal and middle buccal fat pads, exacerbating their prolapse. And from other authors, you can read about the anteroinferior protrusion of the deep buccal fat pad, due to which the bulge and sagging of the cheeks increase.
Correction of these undesirable changes occurs taking into account the type of aging and, of course, the wishes of the patient. First of all, as you can see in the image, the deep fat bags need volume restoration . Therefore, the treatment strategy should include the introduction of a volumizer .
The volumetric contouring procedure using fillers can have a lifting effect if specific anatomical zones within certain deep fat packets are selected for injection, and when the lost volume is restored, a lifting effect will be achieved on the superficial fat packets.
For patients with aging types 1 (hypotrophic) and 2 (hypotrophic/ptotic), correction should be carried out with the elimination of the main defects - reducing the volume of the deep medial buccal fat pad and lateral SOOF. Therefore, first you need to increase the volume of the deep medial buccal fat pad and ensure the initial lifting effect of the soft tissues of the cheeks. And then, restoring the volume of the lateral SOOF, increase the projection of the cheekbone, this will further enhance the lifting effect of the soft tissues of the cheeks.
For patients with type 2 aging, following anatomical logic, it would be reasonable to increase the amount of filler injected into the lateral SOOF, because such patients require a lifting effect to a greater extent than patients with type 1 aging. Finally, injections should be made into the medial SOOF to correct retraction in the periorbital region.
Patients with type 3 aging (ptotic/hypertrophic) are characterized by defects - ptosis and downward migration of adipose tissue of superficial fat packets. In this situation, it is necessary to achieve lifting of ptotic fat packets by increasing the volume of the lateral SOOF. Restoring the volume of this package will increase the projection of the cheekbone and have a lifting effect on the superficial fat package.
It should be noted that it is not worth introducing very large very large volumes into the area of the deep medial buccal fat pad, since in this type of patient the lower part of the upper jaw is already characterized by hypertrophy and excess volume. In type 3 aging, it is necessary to correct the medial SOOF to correct retraction in the periorbital region.
A similar approach can be applied to patients with aging type 4 (hypertrophic/ptotic), in this case it is necessary to increase the volume of the lateral SOOF to lift the soft tissues of the cheek to balance the excessive volume of the lower part of the maxillary region. Correction of the deep medial buccal fat pad, as a rule, is not carried out, except in its upper part, at the border with the lateral SOOF.
A fairly common problem with which patients turn to a cosmetologist is “bags” under the eyes or on the cheekbones.
This problem arises due to age-related loss of muscle tone and decreased elasticity, thinning of the skin, so there is a “protrusion” of intraorbital fat in the lower eyelid area. Under the influence of gravity, the malar fat pad should gradually descend to the cheeks and be located in the entire middle zone, but the nasolacrimal groove becomes an obstacle, and then an overhang of the zygomatic “bag” occurs.
There are many ways to combat this problem, both radical surgical and non-surgical. Non-surgical treatments include: gymnastics, massage, electrical stimulation, mesotherapy with lipolytic drugs, contouring, lipofilling, RF lifting. Surgical correction includes blepharoplasty and check-lifting. Radical methods have to be used if others have not had the desired effect.
Due to the reduction in the volume of the nasolabial fat packet, the skin above it becomes thinner, and as a result, deep static wrinkles appear. In this situation, mesotherapy, biorevitalization or botulinum therapy procedures will have virtually no positive effect. To correct these wrinkles, methods that fill the wrinkle are better suited - injection of fillers or lipofilling.
Specialists have to work with the deep fat layer also when patients complain of the appearance of jowls . And again we return to the Bisha lump, because in addition to the superficial fat packets, it is he who plays a certain role in the formation of this problem. The fat layer of the lower third of the face is poorly held by the muscular-fascial structure, and the tissues from the middle third, under the influence of gravity, end up at the bottom, creating sagging of the lower third, i.e. jowl formation.
The fight against this phenomenon can initially be carried out using non-surgical methods that are aimed at reducing sagging fat packets (lipolytics), and strengthening and tightening the skin - massage, mesotherapy, biorevitalization, contouring, RF lifting, lipofilling, thread implantation, etc. The drastic method would be surgical intervention, for example, liposuction of the jowls, endoscopic lifting, removal of Bisha's lumps.
Age-related changes in the temporal region are another common problem that patients come with. The temporal fat pad often atrophies due to individual anatomy, and can descend into the middle third of the face due to gravitational ptosis. To replenish the lost volume in this area, contour plastic surgery and lipofilling are used.
To summarize, we can say that the correction of age-related changes associated with changes in subcutaneous fat is reduced to replenishing the lost volume of subcutaneous fat in thinning areas - temporal, cheek, as well as reducing and destroying fat in the area of its sagging - jowls, painters.
When talking about subcutaneous fat on the face, one cannot miss another common problem: “fat traps” - areas where the most persistent fat deposits accumulate. Their localization on the face is the cheek area and double chin, which have clear boundaries, spoil the aesthetic appearance and accelerate the aging of the skin - these problem areas are difficult to miss.
The problem with “fat traps” is that it is almost impossible to remove them through exercise, diets, etc., persistent fat deposits will be the last to go away or will not disappear at all. Therefore, specialists use hardware techniques, lipolytics and multi-component mesotherapy cocktails to correct them.
It is worth understanding that the fight against aging cannot occur in one area or with the help of one procedure. Specialists build a whole strategy using various methods for correcting problem areas, recommendations for home care and lifestyle changes, depending on the wishes, age, anatomical features and concomitant diseases of the patient, as well as taking into account contraindications to certain procedures for a particular person.
For training issues: Lyudmila; +79219015105; email Consultation on medications: Oksana, +79119952960; e-mail We will be glad to see you at the address: Ordinarnaya street, 21, St. Petersburg.
Sources: https://www.med-era.ru/, https://e-cosmetology.livejournal.com/, estet-portal.com.
Method 3. Plastic surgery
Valery Yakimanets: The fat layer that supports the skin and tissues of the face decreases with weight loss, and accordingly, ptosis becomes more pronounced. And if it is pronounced, it can only be eliminated surgically. But first you need to complete the weight loss process, consolidate the result, and only after that deal with the aesthetic side. Moreover, I always recommend that patients who come to us for a facelift lose 3-5 kg before surgery. This way we will have an additional opportunity to eliminate newly acquired excess skin. One plastic surgery can solve several problems at once. Most often we do this. We perform total face lifting, including endoscopic forehead lifting, endoscopic midface lifting, eyelid blepharoplasty, SMAS face lifting, platysmoplasty (neck surgery), chin liposuction. All this allows you to achieve maximum aesthetic results, and the patients themselves believe that after it they “lose” about 20 years. As with any surgical intervention, plastic surgery leaves scars. But comparing them with scars after abdominal surgery is incorrect. It is not for nothing that plastic surgeons spend years studying the art of creating invisible seams, so within one year the scars after plastic surgery become almost invisible.
Periorbital hyperpigmentation
The formation of hyperpigmentation can be due to various reasons:
- pathology of the endocrine system (hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, Addison's disease, pathology of ovarian function);
- chronic sinusitis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver (hepatitis, cirrhosis, cholelithiasis, chronic colitis);
- taking medications that stimulate melanin synthesis (tetracycline antibiotics, antidepressants, hormonal contraceptives, etc.);
- chronic dermatoses (allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, atopic dermatitis, eczema).
The intensity of pigment spots is determined by the amount of melanin, and the color is determined by the depth of deposition. Shades of brown indicate a superficial epidermal accumulation of pigment, but shades of black, blue and gray indicate a deep intradermal location of the pigment.
Medications that block melanogenesis are used as therapy. Externally used: arbutin, mulberry extract, kojic and azelaic acids, hydroquinone.
Injectable mesotherapy drugs that regulate melanogenesis have proven themselves well: vitamin C, taurine, glutathione, sodium pyruvate.
Hardware methods for correcting hyperpigmentation have become very popular: BBL and IPL phototherapy, laser systems for melanin destruction.
Relapse Prevention
Facial plastic surgery helps to cope with the problem of a “double chin” at any age. But after the operation you should not relax - relapses are likely. Therefore, you need to adjust your lifestyle - change your diet, give your body physical activity, regularly undergo facial massage sessions and perform special gymnastics for the face.
How to get rid of fat traps on the face is decided by the doctor - the choice of method is made taking into account the patient’s age, assessment of the condition of the facial skin, body weight, and the presence of contraindications to surgical intervention.
By seeking help from our plastic surgery medical center, each patient will receive full assistance - from the initial consultation to recovery after surgery. The call will give you the opportunity to get preliminary estimates of the cost of the service and make an appointment with a doctor. The professionalism of surgeons and full technical equipment are a guarantee of positive results.
Circles under the eyes of vascular origin and swelling
An abundant, superficially located vascular network in the eyelid area contributes to the formation of bluish circles under the eyes. Since the skin here is very thin, even minor hemodynamic disturbances are immediately reflected in the appearance.
A simple test helps determine the presence of a vascular component in the formation of dark circles. Pressing the soft tissue with the fingers against the bony edge of the orbit causes blanching, which suggests a predominance of the vascular component in the formation of dark circles.
Swelling of the eyelid area is associated with a pathological increase in the amount of interstitial (intercellular) fluid as a result of transudation (exit) of the liquid part from the vascular bed. A large number of vascular anastomoses contribute to fluid retention in the tissues. Fatty tissue is loose and highly hydrophilic compared to other zones. An age-related decrease in the tone of the orbicularis oculi muscle also contributes to increased swelling. Interstitial pressure decreases and lymph drainage is disrupted.
Endogenous (internal) causes of edema formation:
- diseases of the excretory system;
- cardiovascular pathology;
- venous and lymphatic insufficiency;
- hormonal disorders (thyroid gland, adrenal glands).
- Exogenous (external) causes:
- violation of the drinking regime (lots of fluids at night);
- alcohol;
- salty food;
- taking hormonal drugs.
Methods of treating swelling (it is necessary to strengthen the drainage activity of the lymphatic and vascular network):
- microcurrent therapy;
- manual lymphatic drainage massage;
- phonophoresis;
- mesotherapy with drugs that have a drainage effect (caffeine, L-carnitine, artichoke extracts, ginkgo biloba, Asian centella and green tea, rutin).
Skin tightening procedures also have a good effect: fractional photothermolysis, RF needle lifting, photorejuvenation, etc.
Obesity as a medical problem
Excessive accumulation of fat - obesity - poses a big problem for the modern world and medical community. Statistics say that over the past 10 years, the number of patients with obesity has increased by 75%; in 2003, the number of patients was 1.7 billion adults worldwide, then in 2014 - almost 1.9 billion.
Primary causes of obesity
- Unbalanced diet, excess fats and carbohydrates (sugars) in the diet.
- Eating disorders, chaotic and irregular meals, alcohol.
- Insufficient physical activity in relation to the amount of calories consumed (inactivity).
- Psychogenic overeating, stress.
- Endocrine diseases (hypothyroidism, Itsenko-Cushing's disease).
- Genetic predisposition.
- Development of insulin resistance, vitamin D deficiency.
- Taking certain medications.
Obesity is not only an aesthetic defect, but also, first of all, poses a great danger to health, and also significantly reduces the quality of life of patients, creates psycho-emotional personality disorders, reduces social activity, contributes to the development of anxiety-depressive disorders and decreased self-esteem.
Since obesity significantly changes metabolism and creates persistent pathophysiological changes in the body, patients are at risk for developing diseases such as:
- diabetes mellitus type II;
- hypertonic disease;
- atherosclerosis, ischemic heart disease, heart attack, stroke;
- arthrosis and pathologies of the musculoskeletal system;
- pancreatitis, gastrointestinal pathologies;
- infertility;
- respiratory diseases;
- oncological diseases.