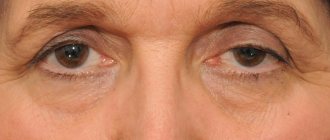
Facial swelling is not only a cosmetic defect; if it appears frequently or is accompanied by redness and pain, it is a sign of quite serious health problems that need to be identified and treated.
ALENA PARETSKAYA
Pathophysiologist, immunologist, member of the St. Petersburg Society of Pathophysiologists ANDREY GRACHEV Leading cardiologist of the SM-Clinic holding, MD, academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences
Facial edema is not a separate disease, but only a reflection of an imbalance between retention and excretion of fluid in the body. But what problems in the body can cause the face to swell and how serious is it?
Symptoms of puffy eyes
Experts consider two options for swelling: when the eyelids, conjunctiva, orbits or subcutaneous tissue under the eyes swell. Both or one eye may swell, most often without additional symptoms. Unilateral swelling in the absence of other symptoms is usually not a cause for concern. But if there is severe swelling of the upper and lower eyelids (on one or both sides), it is worth checking your health. Along with swelling, the following symptoms may appear:
- limited vision (especially due to severe swelling);
- profuse lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- feeling of dryness;
- peeling of the skin.
Sometimes, with severe swelling, mucous discharge appears. They may have a sticky consistency, be wet or dried out. Swelling of the eyelids can also be accompanied by pain, redness, and irritation of the mucous membrane.
Swelling in the morning due to ophthalmic diseases
Swelling of the upper eyelid is a common symptom characteristic of many eye diseases, especially inflammatory ones. Swelling can occur at any time of the day. But in the morning they are especially strong. Almost all symptoms intensify. During the night, more fluid accumulates in the intercellular space of the eyelids, including pathological fluid, so after sleep the swelling is more pronounced.
A symptom such as swelling of the eyelids is observed with conjunctivitis, blepharitis, barley, chalazion, dacryocystitis. Also, the eyes and eyelids swell with severe keratitis, uveitis and various inflammatory diseases that affect the internal structures of the eyeball.
The symptoms of ophthalmic diseases with inflammation are similar. There is no need to treat them yourself. Most of these pathologies can become chronic if treated incorrectly. This will subsequently affect your vision.
Causes leading to swelling of the eyes
Short-term swelling, which goes away quickly and independently, is usually not associated with external factors, diseases, or physiology. More often it is caused by the following factors:
- poor nutrition (drinking large amounts of liquid before bed, drinking alcohol, addiction to smoked meats, spicy, salty foods);
- stress;
- cry;
- violation of wearing contact lenses;
- visual stress;
- individual characteristics of the body;
- violation of the work and rest schedule;
- bad habits;
- constant lack of sleep.
Other subjective symptoms of eyelid swelling include a burning sensation, blurred vision, and redness of the sclera. Usually they are persistent and pronounced, which once again confirms the presence of ocular or systemic diseases.
Diagnostic methods
Facial swelling and headaches are not an independent disease, but a symptom of dysfunction of a number of systems. In order to prescribe effective treatment, it is important to understand the cause of their occurrence. Based on appearance, one can first guess the nature of the edema in order to prescribe a more detailed diagnostic scheme. It may include the following steps:
- ultrasound examination of the condition of the heart and blood vessels, kidneys, liver and other internal organs;
- clinical and biochemical blood and urine tests are an important stage in the diagnosis of kidney disease;
- specific tests, including allergy tests.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, you can undergo a full examination if swelling in the face and headaches occur. Based on the results of the examination, the doctor will prescribe tests that will allow you to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the stage of the disease.
Could swelling be a symptom of an allergy?
An allergic reaction is one of the common causes of swelling. This happens because mast cells release biologically active proteins to neutralize allergens. But when combined with irritants, they cause a reaction that is similar to inflammation. Hence the swelling and redness of the eyelids. Among the ophthalmological causes of eyelid swelling, the most common are:
- glaucoma;
- conjunctivitis;
- periorbital cellulitis;
- eyelid tumors;
- injuries;
- insect bites;
- thermal, chemical burns.
Often the appearance of swelling is the body’s reaction to smoke, dust and other irritants from the external environment.
Swelling of the eyelids due to conjunctivitis
With conjunctivitis, the conjunctiva and upper eyelid swell. They also turn noticeably red. The patient is bothered by itching, burning, and in some cases, painful sensations. The causes of this inflammatory disease determine the nature of its course and the method of treatment. Thus, with film conjunctivitis, grayish films form on the connective membrane of the eye. Because of them, vision deteriorates. They can lead to scar formation. When a bacterial infection occurs, a large amount of pus is released. During an allergic reaction, the eyelids become very itchy. Itching can only be relieved with the help of medications.
Infectious conjunctivitis usually affects the upper eyelids. Swelling of the lower ones occurs, for example, due to an allergic reaction. The extent of inflammation depends on the form of its course and treatment. If it is prescribed on time, that is, after the first signs of the disease appear, conjunctivitis does not cause complications.
Why does swelling occur in dry eye syndrome?
Dry eye syndrome (DES) is a pathological condition that is based on a violation of the stability of the tear film.
It provides nutrition, hydration and protection to the cornea. But when few tears are produced or their composition changes, the tear film quickly begins to evaporate. Because of this, the mucous membrane dries out, a burning sensation, itching, redness, and swelling appears.
Various reasons contribute to the development of dry eye syndrome. This could be taking antidepressants, antihistamines, working at a computer for a long time, or staying in a room with dry air. Dry eye syndrome may progress during sun exposure (summer) because too much air temperature causes tears to evaporate.
You can compensate for moisture deficiency with the help of tear substitutes. These are special drops that contain moisturizing components. But, despite the fact that they have a composition close to tears, they do not contain mucins and lipids, which help the tear film to adhere to the surface of the eyeball and maintain stability.
One of the effective ways to restore the tear film is the use of Delfanto® in capsules. They contain a record amount of antioxidants (at least 35%), which help stimulate the production of your own tears.
When do they occur most often?
Due to a number of circumstances, adds cardiologist Andrei Grachev, such as the flow of fluid to the upper half of the body in a lying position, changes in the biorhythms of hormone production (more often their active synthesis occurs at night or in the early morning hours), edema syndrome most often manifests itself in the early morning hours .
Morning
If we talk about physiological reasons, morning swelling is usually associated with constant lack of sleep, fasting or strict diets (limiting protein and fats). Sometimes swelling in the morning is caused by the wrong selection of skincare products (face cream, toner or cleanser). Also, morning swelling of the face can be caused by crying or stress in the evening or at night.
Possible swelling of the face in the morning due to an incorrectly selected pillow (it is too high, it provokes a narrowing of the blood vessels in the neck). Another physiological factor is an excess of fried, salty foods or liquids taken in the evening, before bed. In women, facial swelling in the morning can be caused by hormonal fluctuations, PMS or pregnancy. Some women report morning swelling during menopause.
Pathological causes of morning edema are mainly kidney damage. Such swelling is usually soft, mobile, appears on the face after sleep, and the skin acquires a waxy or yellowish tint. The most common causes of facial swelling are:
- glomerulonephritis - the acute form of the disease leads to edema, which lasts up to 2-3 weeks, if the process enters the chronic phase, edema is typical for periods of exacerbation of inflammation;
- Kidney amyloidosis - edema is typical of the second stage (proteinuria), when protein loss occurs and kidney function gradually deteriorates;
- membranous nephropathies - occur after taking certain medications, tumor therapy, acute infectious pathologies. Edema occurs in waves, with sharp or barely noticeable symptoms;
- chronic kidney disease (previously called renal failure) - swelling occurs gradually as renal damage progresses;
- kidney damage in severe systemic pathologies - edema is typical for nephropathy due to diabetes or systemic lupus erythematosus.
Evening
Sometimes facial swelling becomes noticeable in the evening, especially after an active day. Often this is one of the manifestations of pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Often, swelling of the face is accompanied by severe swelling in the area of the extremities - hands and feet, legs. These swellings are denser, the skin has a lower temperature than on other parts of the body, and such swelling goes away slowly. Often occur against the background of the following pathologies:
- amyloidosis of the heart and blood vessels;
- cardiomyopathy;
- sclerotic heart disease (cardiosclerosis);
- certain types of arrhythmia;
- constrictive pericarditis;
- some heart defects;
- arterial hypertension;
- cardiac lesions due to rheumatism.
Day
Sometimes facial swelling is most pronounced during the day or its appearance is not clearly related to the time of day. Among the main pathologies that lead to such edema are endocrine disorders - especially a lack of thyroid hormones (hypothyroidism). Facial swelling is especially pronounced with congenital hypothyroidism, in pregnant women or with autoimmune thyroiditis, cytokine-induced thyroiditis.
Rapidly increasing swelling of the face during the day can be a sign of allergies - to food, insect bites, cosmetics, medications and even cold. Sometimes facial swelling occurs during an attack of bronchial asthma due to difficulty breathing and fluid retention in the veins.
Facial swelling is possible in people who smoke and drink alcohol. This is due to the increased work of the lymphatic system to remove toxins from tissues.
Severe swelling of the face during the day is possible with respiratory infections and their complications - sinusitis, tonsillitis, frontal sinusitis. Swelling of the face is possible with a deficiency or excess of vitamins (especially fat-soluble ones).
What diseases can cause swollen eyes?
This symptom accompanies not only ophthalmological pathologies. It may be associated with systemic diseases. For example:
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- pathologies of the pituitary gland, thyroid gland;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- infectious, viral diseases;
- liver and kidney diseases.
The list goes on, because there are more than 70 diseases that are accompanied by swelling of the eyelids. This could indicate problems with almost any organ.
Blepharitis and swelling of the upper eyelids
This disease is worth mentioning separately. It is characterized not only by swelling of the eyelids, but also by gluing of eyelashes in the morning. This happens due to the secretion of mucus and pus. Blepharitis develops as a result of microbes entering the excretory ducts of the eyelids. Bacteria are often the culprits of inflammation. The pathology occurs acutely, but often becomes chronic and periodically recurs. At the very beginning of the disease the patient complains of:
- severe itching;
- lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- diplopia.
Later other signs appear. Eyelid gluing can result in graying and loss of eyelashes.
How to remove puffiness under the eyes?
It is difficult to immediately determine the cause of swelling. But you can try to eliminate provoking factors, for example, normalize your daily routine, diet, and get rid of bad habits.
If swelling is persistent, you need to seek medical help. Only a specialist can determine the reason why the eyelids are swollen and prescribe therapy.
If there is reason to believe that swelling of the eyelids is associated with everyday factors (crying, working at the computer, sleep disturbances, etc.), you can try to cope with this problem yourself. For example, using cold compresses. Cold causes blood vessels to contract, which reduces swelling.
Sometimes chilled tea bags can help relieve swelling quickly. Tea contains caffeine, which helps remove excess fluid from tissues. Tea bags must be applied for 15-20 minutes.
You can also try to remove swelling with massage (10-15 minutes a day). You also need to get good rest. Sleep should last at least 7 hours a day, and it is advisable to go to bed at the same time.
If swelling still periodically reminds itself, then you need to seek help from a specialist. Early detection of pathologies that cause swelling of the eyelids helps prevent serious complications.
If swelling is accompanied by a burning sensation, dry eyes, itching, irritation, you should take Delfanto® capsules regularly. They help increase the production of tear fluid by 89%, due to which the cornea and conjunctiva receive natural hydration.
Common drugs
Among diuretic tablets, drugs that do not have a strong diuretic effect are recommended.
This is a non-specific treatment, and similar drugs are used for problems of the urinary system, therefore, for edema, drugs of average effectiveness are preferred:
- Cyclomethiazide . The product begins to act within an hour after administration and promotes the rapid removal of excess fluid from the body. But it is characterized by a large number of side effects, including intestinal disorders, removal of sodium and chlorine from body tissues, and lowering blood pressure. The recommended dose is one piece per day in the morning.
- Hypothiazide. It stimulates urinary processes, but potassium is excreted in large quantities along with urine. Therefore, therapy using such tablets is combined with taking drugs containing potassium. The maximum effect is observed three hours after administration. You can take no more than two tablets per day.
- Veroshpiron . One of the least toxic drugs in the diuretic group. Side effects of this drug include loss of sensation in the fingers and drowsiness. It is better to take the drug once every two to three days, one piece per day.
- Triamterene . When taking this drug, potassium is not removed from the body. The peak effect of the drug occurs in the first hour after use. The permissible dose for eliminating bags and bruises is no more than one tablet per day and no longer than three weeks.
- Spironolactone . A slow-acting drug whose effectiveness increases over several days of treatment. It has a small number of side effects. You can take the medicine up to four times a day.
For swelling caused by allergies , you can take antihistamines.
One of them is zodak , which can be used to eliminate edema in adults and children.
Note! This is a long-acting drug that additionally relieves itching associated with allergies and eliminates signs of irritation.
At the age of six to twelve years, it is allowed to take one tablet per day, but it must be divided into two parts and given one of them in the morning, and the second in the evening.
The adult dosage, which is also allowed for the treatment of children over 12 years of age, includes taking one whole tablet once a day.
Another antiallergic drug that eliminates swelling is the medicine Cetrin .
Treatment
Pre-hospital assistance
In case of burns, rinse the eye with running water. The use of alkalis and acids to neutralize the effects of chemicals is prohibited. For trauma patients, a bandage should be applied to provide rest and eliminate eye movements and visual strain. You cannot remove foreign bodies yourself, so as not to aggravate the damage. For all eye diseases, it is important to observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Conservative therapy
Conservative treatment tactics are determined by the cause of swelling under the eyes. The following drugs can be used:
- Painkillers
. Analgesics in drops are administered to reduce pain during the examination. Subsequently, tablet forms are prescribed. - Antibiotics
. In the first days, broad-spectrum antibacterial agents are used. After receiving the result of the microbiological study, the treatment regimen is adjusted taking into account antibiotic sensitivity. - Antiseptics
. Indicated for conjunctivitis, after removal of superficial foreign bodies. - Reparation stimulants
. Necessary for corneal damage due to wounds, erosions, post-traumatic defects. - Antihistamines
. Recommended for allergic diseases.
According to indications, parabulbar, retrobulbar, subconjunctival injections are performed. Physiotherapeutic techniques are used and eyelid massage is performed.
Surgery
Taking into account the nature of the pathology, the following surgical interventions can be performed:
- Traumatic injuries
: suturing the eyelid, conjunctiva or cornea, removal of foreign bodies of the conjunctiva and cornea, necrectomy and keratoplasty for burns. - Purulent processes
: opening of barley, dacryocystorhinostomy, vitrectomy, evisceration, enucleation of the eyeball. - Other eye diseases
: penetrating keratoplasty, corneal transplantation.
In the long-term period after injuries and purulent diseases, some patients require elimination of ptosis, correction of eversion or entropion of the eyelid, antiglaucomatous operations for secondary glaucoma, and other interventions.