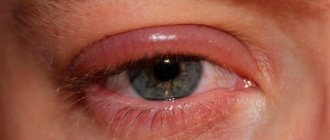
What determines how young we look? Oddly enough, the condition of the skin on the eyelids plays a primary role. If it is healthy and elastic, we perceive the gaze as open, and the face and person as young. Alas, bruises, swelling and bags under the eyes age the faces of even very young people.
Swelling under the eyes is a very common problem, regardless of age and gender, especially relevant in our time - a time of time pressure, lack of movement and fresh air. If your eyelids are swollen, neither an Armani suit nor respectable Mont Blanc accessories will save your look.
Pathologies
Inflammatory diseases of skin folds are acute and chronic. It can affect the upper, lower eyelid, or both eyes at the same time.
Acute
Among the most common acute ones:
- Barley. External (purulent inflammation of the hair follicle) or internal (meibomian gland). Caused by Staphylococcus aureus disease.
- Furuncle. Purulent necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle, sebaceous glands and surrounding connective tissue. Localized on the upper eyelid, in the eyebrow area. Rarely on the edge of the eyelid in the area of the outer canthus. The causative agent is staphylococcus.
- Dacryoadenitis is inflammation of the upper eyelid. Complications after common infections (flu, sore throat, etc.)
- Dermatitis. Occurs as a result of allergies, gastrointestinal disorders, autoimmune diseases. To the symptoms listed above are added itching, peeling, and rashes in the form of blisters.
Less common are eyelid abscess and phlegmon.
Chronic
Chronic diseases include:
- Blepharitis is inflammation of the edges of the eyelids. Caused by skin bacteria. Demodectic blepharitis - caused by mites of the genus demodex. There is redness and swelling of the edges of the eyelids. Itching. Eyelash loss. With ulcerative blepharitis, there are ulcers and purulent crusts.
- Chalazion is a proliferative inflammation of the meibomian gland and the cartilage around it. It can occur both after barley and independently.
Blepharitis and chalazion are often combined with conjunctivitis.
How to relieve puffiness under the eyes
At Platinental Laser Cosmetology and Plastic Surgery Clinic
A whole exclusive range of treatments for puffiness under the eyes has been developed for you:
- a course of professional masks that will not only help get rid of puffy eyes, but also eliminate bruises and wrinkles under the eyes .
- microcurrent therapy,
- drainage massage for puffy eyes, etc.
And the Medical Boutique will offer you special masks against puffiness under the eyes for home care and creams against puffiness around the eyes.
With proper and regular use, cosmetic products and procedures can completely relieve you of swollen eyes after sleep, and when you wake up in the morning, swollen eyelids will no longer spoil your mood.
However, one type of swelling and bruising under the eyes should be mentioned separately. The fact is that eye swelling is often a symptom of so-called eye hernias - fatty protrusions. Even the best anti-puffy eye cream is powerless against hernias. Alas, practice shows that after 30, the main cause of swelling of the upper and lower eyelids is the presence of hernias. In this case, the question of how to get rid of puffiness under the eyes has no alternative answer: only with the help of blepharoplasty. Eyelid surgery, performed by plastic surgeons at the highest level, in this case is the only possible effective cure for swelling under the eyes and swelling above the eyes, allowing not only to remove swelling of the eyes, perform an eyelid lift , and smooth out crow's feet . If desired, you can even correct the shape of your eyes . And all this – in one procedure!
How to treat eyelid inflammation
Treatment of inflammatory diseases of the eyelids is carried out in accordance with their cause. Depending on the pathology, therapy includes:
- the use of ointments (with sulfonamides, antibiotics, corticosteroids), an alcohol solution of brilliant green, drops;
- general therapy (antibiotics, sulfonamides, oral antihistamines);
- massage of the eyelids with removal of the contents of the glands;
- hardware physiotherapeutic treatment with UHF, laser heating, electrophoresis;
- surgical removal of chalazion;
- vitamin therapy autohemotherapy.
Sign up for an initial consultation with an ophthalmologist at the Optic-Center clinic by phone 8-800-775-78-58
.
Sign up for a comprehensive examination
Reasons for the development of eyelid edema
Often, swelling of the eyelids becomes one of the first signs of disease, which indicates the need for an early examination. Allergic swelling of the eyelids may be a manifestation of angioedema, with a characteristic sudden appearance and rapid disappearance. Such swelling is usually unilateral, very significant, developing in the upper eyelid, but not accompanied by any subjective sensations. Its cause is an allergic reaction that developed under the influence of an allergen, for example food products: eggs, milk, chocolate, citrus fruits, strawberries, various types of fish products, some flowers and other specific or nonspecific irritants, as well as some medications and cosmetics.
In addition, swelling of the eyelids is caused by diseases of the kidneys, heart, liver and connective tissues. Diseases of the eyelids and orbits may also be accompanied by swelling. With diseased kidneys, swelling appears on the face and especially on the upper eyelids. Often, renal edema is very watery.
In some cases, swelling in the upper eyelids is caused by eyelid tumors, including squamous cell carcinoma, or disorders in which swelling is not a symptom - trauma, burn, basal skull fracture, condition after surgery. Today, quite a significant number of causes of swollen eyelids are known. But it is absolutely certain that swelling has nothing to do with prolonged work at the computer and eye strain.
Swelling of the upper eyelids is sometimes confused with blepharochalasis - the formation of a somewhat sagging skin fold on the outside of the upper eyelid. Blepharochalasis typically occurs in older people and is associated with age-related weakening of the connective tissues of the upper eyelid. It is more of a cosmetic problem and can be eliminated by cosmetic surgery.
Prevention measures
Preventing swelling is not so difficult if you follow these simple rules:
- giving up alcohol and smoking;
- healthy eating, adherence to sleep and rest patterns;
- sports, hardening;
- limiting salt intake;
- use of high-quality cosmetics, compliance with hygiene rules;
- the use of eye protection in hazardous industries, at sea, in the sunny season;
- caution when playing and playing sports to avoid eye injuries;
- timely treatment of any infectious diseases.
Conclusion. Puffiness of the eyelids is not such an innocent phenomenon as many people believe, and not just an unsightly cosmetic defect. Often this is a symptom of a serious internal disease that must be treated. Ignoring eye swelling can cause swelling of the eyeball, elephantiasis, glaucoma and even blindness. Therefore, you should first of all remember a healthy lifestyle and preventive measures. And if an unpleasant symptom does appear, then promptly seek help from a doctor.
Tests and diagnostics
Examination of a patient by an ophthalmologist. This is usually enough to identify the disease and make a diagnosis. If necessary, additional examinations are prescribed:
- Culture of eye discharge.
- demodicosis is suspected .
- Ultrasound.
- Biochemical tests to assess kidney and liver function.
- Determination of the level of specific IgE in allergic diseases.
- Tests with allergens (nasal/conjunctival) in case the results of determining allergen-specific IgE are questionable.
Causes of eye swelling
As they say, forewarned is forearmed. Therefore, you must not only be able to get rid of the problem, you also need to know why it arises. The reasons may be varied. Swelling of the eyelids develops as a result of the following factors:
- local inflammatory process of the upper eyelid – blepharitis;
- dacryocystitis – inflammation of the lacrimal gland and its ducts;
- mechanical damage to the mucous membrane;
- furunculosis;
- conjunctivitis;
- insomnia;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- use of low-quality cosmetics;
- insect bites;
- lymphatic drainage disorders;
- allergic reactions;
- age-related changes in the skin and tissue of the eyelid;
- formation of fatty hernias;
- use of medicines;
- excess salt intake;
- pregnancy.
In the presence of chronic diseases, water-salt metabolism is disrupted, so swollen eyelids are often a symptom of serious systemic pathologies:
- lesions of the cardiovascular system - arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease;
- hormonal disorders;
- chronic diseases of the genitourinary system - pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, renal failure, urolithiasis;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - gastritis, ulcers;
- metabolic disorders due to diabetes mellitus.
It is important to remember: the cause of a cosmetic defect is hidden inside the body.
Consequences and complications
With timely diagnosis and treatment, chalazion has no consequences. If you ignore a hailstone for a long time and allow it to grow to 5 millimeters or more, there is a risk of complications:
- transfer of infection to the conjunctiva, cornea;
- chronic compression of the eyeball and irreversible decrease in visual acuity;
- formation of ulcers on the cornea;
- development of phlegmon of the century;
- fistula formation.
Treating these pathologies is tens of times more difficult and expensive than eliminating a small chalazion. But even with a successful outcome, scars will remain and the shape of the palpebral fissure will change. Therefore, you should not hope that the tumor will resolve on its own. It is better to enlist the help of an ophthalmologist and undergo a course of treatment.
Swelling on the eyelid. What is it and how to treat it
The term "chalazion" comes from a Greek word meaning "small nodule, hailstone." A chalazion (chalazion) is a slowly developing tumor-like formation that occurs due to blockage and swelling of the sebaceous gland (meibomian gland) in the eyelid.
The Meibomian glands are located inside the eyelid, just behind the eyelashes. Their number is about 50-70 in each century. These glands help keep the eyes moist by preventing the evaporation of the aqueous layer (tears) from the surface of the eyes. This is achieved due to their production of the outer layer of the tear film - lipid (consisting of fatty acids - lipids).
Chalazion is often confused with styes, which also appear as swelling on the eyelid. A stye is an infection of the oil gland in the eyelid. It causes redness, swelling, and painful swelling at the edge or inner surface of the eyelid. Styes usually occur closer to the surface of the eyelid than the chalazion. Sometimes an untreated stye turns into a chalazion.
Chalazion is a common eye problem. This disease affects people of all age groups, but more adults than children, and occurs most often between the ages of 30 and 50 years.
Chalazion symptoms
At first, a chalazion looks and feels the same as a stye: a swollen eyelid, mild pain and irritation.
However, these symptoms disappear after 1-2 days, but a round, painless swelling in the eyelid remains, growing slowly during the first week. Rarely, the swelling continues to grow and may press on the eyeball, causing slight blurring of vision. A red or gray spot may form on the back of the eyelid. If the chalazion grows very large, it can become painful.
Causes
The causes of most chalazions are unclear, but the glands can become blocked due to infection, as with a stye, or when they grow abnormally, as with a tumor (although this is rare). Skin conditions that cause infection or inflammation, such as seborrheic dermatitis or rosacea, can also cause clogged glands. In most cases, such blockages resolve on their own, and the contents come out naturally. But if this does not happen, then a chalazion is formed.
Chalazion treatment
About 25 percent of chalazion cases have no symptoms and resolve without any treatment. For other cases, there are several treatment methods.
Self-help. Hot compresses followed by eye massage can help clear the blockage and release the contents of the inflammation. For a compress, use napkins soaked in heated, but not scalding hot, water. The compress should be comfortable for the skin. Place it on your eyelid for about 15 minutes. Repeat this procedure 4-6 times a day. Massage the eyelid with your finger, using circular movements directed upward if the chalazion is on the lower eyelid, or downward if on the upper eyelid. You should do this for a minute. Massage will help remove blockages and release accumulated contents.
Steroid injections. Steroid injections may be used to treat chalazion. This reduces inflammation within 1-2 weeks after the injection. The doctor injects steroids directly into the center of the chalazion through the tissue on the inside of the eyelid.
Surgery. If the chalazion is very large, causes discomfort, or constantly recurs, then surgical removal may be necessary. It is performed by cutting and curettage (curettage). This procedure is usually performed on an outpatient basis or as a day hospital. A local anesthetic is used to completely block pain sensitivity in the eye area. The operation lasts about 20 minutes. After the procedure, you will be prescribed an antibacterial eye ointment. The eyelid may become swollen and bruised during the first week after surgery. If a chalazion reoccurs despite treatment, you should be examined by a physician. Sometimes a chalazion may be caused by another underlying condition, such as a skin disorder, or (very rarely) the lump may be malignant.
What to do if you have an eyelid tumor
- Consulting a doctor is a must for any swelling. Self-medication can lead to disastrous consequences, including angioedema and hospitalization;
- Some folk remedies are quite effective, but their use must be under the supervision of a doctor;
- One of the main preventive measures is following the rules of facial skin care;
- Refuse all types of cosmetics, be it creams or decorative cosmetics, as well as the use of contact lenses;
- Don't rub your eyes;
- Avoid using any medications on your own - they can cause an increase in eye pressure;
- If you are sure that the cause of swollen eyelids is an allergy, then you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist - the doctor will prescribe you antihistamines.
If your eyelids are swollen, visit an ophthalmologist's office - a specialist will examine you and refer you for further examinations. To diagnose pathologies of the excretory, digestive, and circulatory systems, general tests are usually performed.
If you have not found the cause of eyelid swelling on your own, then this is an undeniable reason to visit an ophthalmologist's office. Many people begin treating eyelid swelling on their own, without resorting to medical help - this is a mistake. After all, without identifying the actual cause of the disease, self-medication can only complicate the situation and aggravate the condition of the body. Many begin to apply a warm cloth to their eyes for relief, while others take antihistamines - all these measures can lead to serious negative complications.
Diet
Diet 15 table
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 2 weeks
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of food: 1600-1800 rubles per week
For swelling of the face and eyelids, it is recommended to limit the consumption of salt and spicy fatty foods. At the same time, an increase in vegetables and fruits in the diet has a diuretic effect. Plums, apricots, peaches, watermelons, cranberries, and rosehip decoction have this effect. You can supplement your diet with herbal teas. Drinking a lot of water is beneficial, provided that the person leads an active lifestyle and moves a lot. At the same time, the kidneys cope well with their function and fluid is not retained.
If you have a tendency to edema and abuse salty foods, drinking large amounts of liquid has the opposite effect - the liquid is retained in the body. It has been noticed that in hot weather, fluid is retained more, causing swelling not only of the face, but also of the feet and fingers.
List of sources
- Kucherova A.A., Osidach N.V., Pobedennaya G.P. On the issue of differential diagnosis of conjunctivitis / Clinical immunology. Allergology. Infectology. 2015.— No. 1 (80), p. 49-51.
- Zaikov S.V. Allergic conjunctivitis: clinical picture, diagnosis, treatment/ Clinical immunology. Allergology. Infectology. – 2011. – No. 1. – P. 38–43.
- Avetisov S. E. Ophthalmology. National leadership. Brief edition 2022, 736 pp.
- Sidorenko E. I., Dubovskaya L. A. Eye diseases 2010.
Pathogenesis
In the pathogenesis of any edema, the following are important:
- increased permeability of the vascular wall;
- high intravascular pressure;
- a decrease in the level of proteins in the blood that hold the liquid part of the blood inside the vessel;
- increased concentration of salts in tissues;
- disruption of the outflow of venous blood and lymph.
The development of swelling of the eyelids is facilitated by the increased extensibility of the skin in this area, good blood supply, loose fatty tissue that can accumulate fluid and poor development of the muscles that provide elasticity to the eyelids. If we consider allergic edema, then all allergy symptoms, including swelling, are associated with the release of mediators from mast cells and basophils. The main mediator of the immediate response is histamine . Through H1 and H2 receptors, this mediator causes vasodilation, increased vascular permeability and the formation of prostaglandins (inflammatory mediators). These mechanisms explain the development of allergic tissue edema .