An allergy is a specific reaction of the body to any irritant (allergen). The response of the immune system can manifest itself not only in the flowering of plants and pets, but also in hypothermia. Cold allergies occur when exposed skin is exposed to low temperatures and is otherwise called cold urticaria. The hands and face are most susceptible to this pathology1.
Symptoms of an allergy to cold
The reaction can occur upon contact with cold objects or prolonged exposure to frost. Most often, manifestations occur in winter. The likelihood of such a reaction increases in damp, windy weather. Sometimes the peak of development of an allergy to cold occurs at the moment when the patient gets into the heat. Main symptoms:
- pink or red rashes;
- itching;
- swelling in exposed areas of the body.
Sometimes patients experience a systemic allergic reaction - redness of the skin throughout the body. Its characteristic symptoms are:
- chills;
- tachycardia;
- swelling of the fingers and toes;
- a feeling of heaviness in the chest and throat (tightness);
- and even loss of consciousness2.
What is cold allergy and why does it occur?
This pathology, in its essence, is an inadequate response of the immune system to the effects of low ambient temperature or water. For what reason such changes occur is currently not known for certain. Some scientists suggest that cryoglobulins, special proteins that are produced in the cold and activate histamine, thus triggering a cascade of allergic reactions, play an important role in the mechanism of the allergic reaction.
The foundation for this pathological process is various somatic pathologies: chronic diseases of the respiratory, urinary and reproductive systems, infectious and parasitic diseases. An extremely important role is played by disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract due to intestinal dysbiosis, gastritis, cholecystitis, enterocolitis, etc. In principle, almost any long-term health disorder can provoke an allergic reaction.
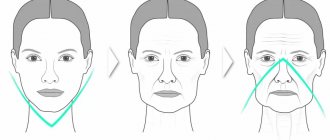
Allergy to cold on the face
It is very important to learn to recognize this type of allergy, as it can masquerade as colds or dermatitis. The main symptoms appear as follows:
- Finding yourself outside in the cold, a person begins to experience a headache.
- Spasms (tone) of the muscles of the face and neck appear.
- Nausea sets in.
- In particularly severe cases, extensive facial swelling may develop, which is accompanied by redness.
- Spots and blisters appear, like a burn, and severe itching occurs.
- People suffering from cold urticaria experience a runny nose with watery nasal discharge and frequent sneezing.
Also, the cold may cause pain in the eye area and watery eyes. This phenomenon is called pseudoallergic conjunctivitis.
Protection with special equipment
Now many manufacturers produce special series for children, including creams and balms with protection from frost and wind. Preference should be given to formulations that have been tested, are hypoallergenic and have a greasy texture.
Such funds contain:
- paraffin;
- fish fat;
- beeswax;
- oils;
- antibacterial additives;
- herbal extracts.
Creams and gels are used according to the instructions, but on average they are applied 30 minutes before going outside.
Allergy to cold on hands
It is quite rare. The reasons for its occurrence have not been fully studied, so it is impossible to say with certainty why exactly cold allergies occur in the hands. It is known that a reaction occurs in patients with increased sensitivity of the body to cryoglobulin. This is a protein in the blood that can appear in various diseases, myeloma, nephrosis, cirrhosis, rheumatism. When exposed to cold, it triggers a pathological reaction3.
It all starts with a feeling of slight discomfort and scratching. A little later, the skin of the hands becomes dry and rough. Small cracks appear, followed by pink-red rashes and swelling. All these manifestations become most pronounced after warming up the hands, but within an hour, as a rule, no trace remains of them. In some cases, symptoms may persist for a week.
Why is cold dangerous?
Frozen skin is easier to injure, it becomes dry and prone to irritation.
- Low temperatures cause spasm of small blood vessels that nourish the epidermis. This leads to a slowdown in metabolic processes in cells.
- The sebaceous glands, which are supposed to protect the integumentary tissues from hypothermia, work worse.
- Cold air dries out the dermis, makes it less elastic, and increases the tendency of the epidermis to desquamate.
People with dry skin types, children under 10 years of age, older adults, people with diseases of the digestive system, and reduced thyroid function are more affected.
Allergy to cold in a child
The body's reaction to hypothermia can occur at any age. In children it manifests itself differently and is of a purely individual nature. For example, with the first case of a reaction to cold, children tolerate allergies much easier than with repeated attacks of the pathology (relapses). Clinical manifestations depend on the form of the disease and severity. Cold allergies in children are not much different in appearance from skin lesions such as seborrheic eczema (a skin disease characterized by inflammation, rash and severe itching) or atopic dermatitis (a disease caused by a genetic factor, accompanied by a rash and severe itching)4,5.
Children with weak immune systems are most susceptible to reactions. In the vast majority of cases, a child develops cold urticaria:
- due to genetic inheritance;
- after viral infections;
- with a tendency to skin diseases6.
2. Causes of the disease
There is no clear opinion among doctors about the causes of cold allergies. The background for this violation can be various internal and external factors. This is confirmed by multiple cases of self-healing under changed conditions. It has also been noted that allergies to cold are often isolated, i.e. not accompanied by other types of allergies. From this we can conclude that the mechanism of its development is somewhat different than that of other allergic diseases, which, on the contrary, quite often manifest themselves in a complex (urticaria, asthma, allergic rhinitis).
Conditions for an allergy to cold may include:
- long-term antibiotics;
- the presence of parasites in the body;
- chronic foci of infection (caries, tonsillitis, staphylococcus);
- gastrointestinal and liver diseases;
- stress, excessive physical activity, intoxication;
- immune and hormonal disorders.
Visit our Allergology page
Treatment of allergies to cold
As with any other type of allergy, the first step is to get rid of the irritant. No allergen – no reaction. But it is not always possible for a person to determine what exactly a cold allergy is caused by.
First of all, you should take an antihistamine to stop the attack and prevent its development. If the allergen is known, it must be excluded or, at least, contact with it must be reduced as much as possible. In the case of allergies to cold, doctors recommend:
- Minimize exposure to cold.
- Approximately 30 minutes before leaving the house, lubricate your face and hands with protective cream.
- Instead of soap for washing, use gentle gels and foams. Regular toilet soap causes dry skin, making it more sensitive to cold.
- To avoid general hypothermia of the body, it is necessary to dress according to the weather, do not neglect hats and protect your hands from the cold. Preference should be given to clothing made from natural materials. Eliminate synthetic underwear and nylon tights from your winter wardrobe.
If preventive measures are not enough to eliminate an inadequate reaction to cold, and it is impossible to completely eliminate the presence of the allergen, symptomatic treatment is necessary.
Depending on the type of reaction, either corticosteroids for topical use (ointments, gels and sprays) or antihistamines (suspensions, tablets) are prescribed. If necessary, treatment lasts throughout the entire cold period of the year.
One of the modern antihistamines for the treatment of allergies is Cetrin®. The action of the drug is based on blocking the receptors to which histamine, which is responsible for the development of an allergic reaction in the body, binds. Moreover, the effect of Cetrin® does not depend on the cause of the allergic reaction, so it can also be used for cold allergies.
As for the dosage, in accordance with the recommendations, the drug Cetrin® must be consumed, adhering to the following rules:
- children over 6 years of age – ½ tablet 2 times a day or 10 mg 1 time a day;
- adults – 1 tablet 1 time per day1.
The medicine must be taken with water (at least 200 ml). Chewing is not recommended. It is recommended to follow a certain diet and preventive measures:
- Eliminate from your diet spicy, fried foods and foods that can irritate the gastric mucosa.
- Include foods rich in polyunsaturated acids. The highest content is in flaxseed, cod liver, olive and rapeseed oil. It is also useful to include fatty sea fish (mackerel, tuna, herring) in your diet.
- Hardening the body can be a good preventative measure for cold allergies.
By following the recommendations, you can significantly reduce the intensity of pathological manifestations or completely get rid of allergies to cold.
Bibliography
- Goryachkina L.A. Urticaria / L. A. Goryachkina, N. M. Nenasheva, E. Yu. Borzova // Moscow, Newspaper “News of Medicine and Pharmacy”. – 2010. – No. 8. – 321 p.
- Nusinov E.V. Hives. Atopic dermatitis: methodological recommendations for students of medical, pediatric and dental faculties / E.V. Nusinov; edited by V. M. Chervenets. – M.: Alquist editorial office, Tver, 2012 – 22 p.
- Muzychenko A.P. Urticaria: educational and methodological. Manual / A. P. Muzychenko. – M.: BDMU, Minsk, 2014. – 16 p.
- Federal clinical guidelines for the management of patients with eczema / Ed. V. A. Okhlopkova. – M.: Moscow, Russian Society of Dermatovenerologists and Cosmetologists, 2013. – 18 p.
- Atopic dermatitis: hand. for doctors / Ed. Yu. V. Sergeeva. – M.: Moscow, 2002.
- Nusinov E.V. Hives. Atopic dermatitis: methodological recommendations for students of medical, pediatric and dental faculties / E.V. Nusinov; edited by V. M. Chervenets. – M.: Alquist editorial office, Tver, 2012 – 22 p.
- Instructions for use of the medicinal product for medical use Cetrin®. – Registration number: P N013283/01.
“Martyrs of the cold. Cold allergies - the scourge of the winter period"
This misfortune comes with the first cold weather. As soon as the mercury dropped below zero, dark times began for a very impressive part of our fellow citizens. Increased sensitivity to low temperatures prevents the unfortunate from enjoying the first snow and other delights of late winter. in other words, cold allergy.
At first glance, its manifestations resemble an ordinary allergic reaction. In a person suffering from a cold allergy, the skin begins to itch, turn red, become covered with spots or a small rash. True, in this case, only those parts of the body that are exposed to cooling are affected: the face, hands, inner thighs, calves, skin around the knees. In addition to purely allergic manifestations, cold allergies can also masquerade as illnesses that are quite common for the cold season: colds, migraines, conjunctivitis. When going out onto a windswept street, for no reason at all the unfortunate people may start to have water from their eyes and nose, their forehead and temples to ache, and they may lose their breath (just like during an attack of bronchial asthma). But as soon as they enter the room, the unpleasant sensations disappear. Until the next foray into the piercing cold.
The reaction to cold is considered pseudo-allergic
Doctors call this reaction pseudoallergic. It differs from ordinary allergies in that the culprit of the problem - the allergen - is absent from the body. According to its principle, a physical factor operates - frost, causing local cooling of tissues and damaging the cell membrane, from which the main allergy provocateur - histamine (and other similar substances) comes out. Under the influence of low temperature, short-lived, unstable immune complexes are formed from antibodies and proteins in the body, which quickly disintegrate in heat. With a true allergy, you can’t easily bring the body back to normal. This circumstance is of little comfort to “false” allergy sufferers. What difference does it make what causes the hated itchy spots on the skin and the nasty slush in the nose, when because of them it is simply impossible to go outside?
Sure salvation - warm equipment
The poor fellows are much more interested in the answer to another question: how to avoid such an obsession? What can you do to prevent a walk through the winter forest or to a nearby store from turning into torture? Warm yourself! Short skirts and bare heads are not for you. The equipment of a person suffering from cold allergies should be impervious to wind and moisture - with a hat for the season, a deep hood, leather gloves, and long boots. Underwear only made of cotton, flannel or flannel: synthetics and wool increase the manifestation of allergies. Before going outside, do not lubricate your face with hydrating (water-containing) cosmetics. Protect your facial skin with special seasonal cosmetics. At the same time, it is absolutely not necessary to splurge on expensive creams. Thrifty American women have for some time now preferred modest Vaseline and vegetable oil (from sunflower to peanut). However, these products have one drawback: they make the skin shine. But this can be easily fixed by lightly powdering your face. By eating ice cream, you can get a cold migraine. For those who suffer from allergic rhinitis, 10-15 minutes before going outside, it’s a good idea to prevent a snotty episode by instilling special anti-allergy drops. But vasoconstrictors are contraindicated for pseudoallergy. They only dry out the nasal mucosa and increase the manifestations of cold allergies. With the help of special antiallergic drops, you can also get rid of sudden tearfulness. Eyes sensitive to cold generally require super-gentle treatment. In cold weather, it is better not to irritate them by wearing contact lenses and excessive makeup (if mascara gets into your eyes, it will only intensify the manifestation of cold conjunctivitis). And drinking cold drinks or ice cream can easily trigger a cold migraine attack. Experts call this type of headache an ice-cream headache, which translated means “headache from ice cream.” If you want to treat yourself to a portion of your favorite popsicle on a cold day, let it melt. Dry heat will prevent your suffering. Are you already sick? Do you have a headache, your hands and face itch, your nose is running, and your eyes are clouded with tears? Get warm! If you get wet, immediately change into dry clothes, drink hot tea and take a tablet of any antihistamine. Wipe itchy areas on the skin with a soda solution (1/3 teaspoon per glass of warm water), lubricate with agave juice or an oil solution of vitamin E. You will see: relief will come in a few minutes. For those who do not yet have a cold allergy, we can recommend herbal medicine - one of the main methods of naturopathic treatment, which has been successfully used for many millennia in all countries of the world. To do this, it is enough to purchase at the pharmacy the herbal collection of the FITODOL series for the prevention of allergies, made by specialists from the Institute of Naturotherapy from herbs collected in the regions of the Altai Mountains, according to the recipes of Altai healers, although before such prevention it is better to consult a doctor.
Before treatment, do an allergy test
And under no circumstances “wear out” your sensitive skin with constant hygiene procedures: soap, especially cheap alkaline-based varieties, only dries out the skin, depriving it of its natural protective lubricant. The same applies to visiting the pool. In the autumn-winter period, citizens suffering from cold allergies will have to give up this pleasure (“water” urticaria is much more severe than “air urticaria”), and also reduce the consumption of chocolate, oranges, fish, eggs, honey - the most common allergy provocateurs. Although, of course, before limiting yourself in anything, make an appointment with a doctor. This is what Marina Gennadievna Ukolova, a doctor at the Independent Laboratory Invitro, told us. “In Vitro there are many blood tests to determine specific immunoglobulins for various types of allergens, and not only. There is also common immunoglobulin E, which allows you to determine in general whether there is an allergy or not (it is a screening indicator). All other specific immunoglobulins already specify the source of the allergy. For example, if you take a blood test to determine immunoglobulins for cat epithelium, you will get the result for this particular allergen! And so you can test for immunoglobulins in many products (we have more than 90 of them), for pollen of various plants (weeds, trees), mold, nuts, animals, cockroaches, ticks. Using diagnostics, it is also possible to recognize pseudo-allergic diseases, such as cold allergies. Since with allergy tests, experts recommend studies of the liver and gallbladder, intestinal flora, tests for viruses, helminths. These pathologies can simulate the clinical picture of true allergies. You can test for cold allergies yourself. To do this, just put a piece of ice on your wrist. After holding it for 20 minutes, observe your reaction. If rashes appear on the skin, itching begins, there can be no two opinions: you have a cold allergy. True, such a test is only suitable for confirming the simplest form of cold allergy. More complex types of allergic reactions to low temperatures can only be tested in laboratory conditions.
How to treat?
Since cold allergy is a reaction to an external factor, then, firstly, it is necessary to reduce or completely eliminate skin contact with the pathogen: cold air or an object. Secondly, you should contact a specialist. After all, any allergic manifestations require careful observation by an allergist and, depending on concomitant diseases, the participation of other doctors: therapist, infectious disease specialist, hematologist, etc. If we are talking about an independent allergy that was caused by a genetic factor or characteristics of the body, then this The disease cannot yet be easily and quickly cured. Medicine focuses on relief (elimination of the disorder through therapy) and reduction of symptoms. However, if cold allergy is a secondary disease, for example, manifests itself after an infection, then as the main problem is treated, the urticaria will disappear.
Will linen and cotton protect against cold allergies? More details
General rules of prevention
Eye allergies require not only eliminating the allergen, but also taking appropriate preventive measures . In order to avoid the occurrence of the disease, it is important to follow these rules:
- compliance with the rules of personal and general hygiene (especially in new places);
- no contact with allergen spreaders;
- periodic use of sorbent drugs;
- cleaning the nasal passages after returning from the street (often allergens enter the body with inhaled air);
- regular use of “Artificial Tear” drops for problems with the secretion of tear fluid, which washes away foreign microorganisms and particles from the eye and prevents the occurrence of allergic processes;
- We will take antihistamines not only during treatment, but also after it for 2-3 days;
- runny nose of allergic origin requires mandatory surgical treatment.
This is enough to prevent a repeat reaction, but given that the mechanisms of such a disease have not yet been fully studied, doctors do not give a complete guarantee that the allergy will not return.
Contact dermatitis in winter in children
The child came back from a walk and had red spots and abrasions on his hands and under his eyes, resembling abrasions. This is contact dermatitis, a common problem in industrial cities. Three factors are combined here: cold, chemical impurities in the air, friction with wet mittens and a scarf.
It is good when the wounds heal in a warm place, after moisturizing with creams containing panthenol. But these rashes may be the beginning of an atopic process, a manifestation of food allergies, diseases of the nasopharynx or digestive organs.
It is necessary to show the baby to a dermatologist. The diagnostics carried out - dermatoscopy, measuring skin pH, blood tests, examination of internal organs - will help determine the diagnosis.