Table of contents
- Etiology and pathogenesis
- Clinical manifestations
- Principles of treatment
Melasma (chloasma, pregnancy mask, melasma, melasma , chloasma ) is a chronic recurrent acquired dyschromia caused by increased activity of epidermal-melanin units. The epidermal-melanin unit is a union that consists of one melanocyte and several keratinocytes, facilitating the transfer of pigment granules from the melanocyte to the surrounding keratinocytes.
In our company you can purchase the following equipment for the treatment of melasma:
- M22 (Lumenis)
- Fraxel (Solta Medical)
Melasma occurs in areas of the skin that are exposed to severe and/or regular sun exposure, more often in women of reproductive age. It negatively affects quality of life due to its high prevalence, involvement of visible areas of the face and body in young patients, and relative resistance to therapy. Melasma affects mainly women (90% of cases) of any race, but more often with dark skin phototypes (IV-VI). The average prevalence of the disease in the population ranges from 8.8% to 40%. According to some reports, the likelihood of melasma developing during pregnancy is 15–50%.
Chloasma is the name given to melasma that occurs during pregnancy (“mask of pregnancy”). The word chloasma comes from the Greek chloazein (green), while melasma comes from the Greek melas (black). Since chloasma is never green, it is more correct to call it melasma.
Diagnosis of chloasma
The first step in diagnosing chloasma is visualization of the pigment spot. It is important to determine the characteristics of the manifestation of chloasma (acquired or congenital). It is important to differentiate its inflammatory nature. To determine the depth and extent of chloasma, dermatoscopy and siascopy are indicated.
Considering the many predisposing factors to the occurrence of chloasma, it is necessary to conduct many additional examinations of the organs and systems of the human body. It is important to examine the gastrointestinal tract, liver, central nervous system, and conduct a series of laboratory tests (coprogram, biochemical liver tests, analysis for dysbacteriosis). Sometimes ultrasound of the liver and abdominal organs and gastroscopy are indicated. Women need to consult a gynecologist to exclude pathologies of the reproductive system and resolve the issue of contraception.
Differential diagnosis of chloasma is carried out with secondary hyperpigmentation, professional melasma, and Mongolian spot.
Etiology and pathogenesis
An important etiological factor for melasma is heredity . In one study of 324 women with the condition, 48% reported having it in their immediate family. Melasma almost always occurs in identical twins, while it may not occur in fraternal siblings.
Another factor in the appearance of melasma is ultraviolet radiation of spectrum B (UVB, 290–320 nm) and spectrum A (UVA, 320–700 nm). It causes lipid peroxidation, promoting an increase in the number of reactive oxygen species, which stimulate melanocytes to actively synthesize pigment.
Melasma is caused by hormonal changes in the body. Moreover, this can be not only pregnancy, but also taking oral contraceptives. In nulliparous women, there is usually no significant increase in estrogen or melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) levels, but they do have an increase in the number of cellular estrogen receptors in the area of melasma lesions. In postmenopause, melasma can occur while taking drugs with progesterone (whereas it usually does not occur when estrogen is prescribed), which indicates a significant role of this hormone in the pathogenesis of the disease.
In general, the pathogenesis of melasma has not been well studied. It is noted that in this case, melanogenesis differs from tanning and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. In this case, epidermal-melanin units, mast cells and cytokines produced by fibroblasts and endothelium are involved in the process. Abnormalities that differ from other acquired pigmentation disorders occur in the upper layers of the dermis.
Review
The first time I developed chloasma was about 5 years ago after a strong passion for tanning. Then it intensified during pregnancy, and after childbirth it remained the same. I tried a huge number of ointments and creams, folk remedies. There was a noticeable improvement, but after a while the spots darkened again.
So I suffered until a friend recommended a good dermatocosmetologist. He selected me a medicinal cream with kojic acid, lemon and cucumber extracts “MICROCELLULAIRE” and prescribed vitamins B and C. I also had a medium peeling with glycolic acid, 3 procedures.
There are several barely noticeable spots left on the face that are easily hidden under foundation. Now I always use sunscreen and plan to undergo peeling procedures once a year.
Albina Voevodina, 38 years old.
Clinical manifestations
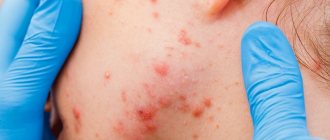
The disease manifests itself either as a single lesion or as multiple foci of dark brown or black hyperpigmentation, symmetrically located on the face and/or neck ( Fig. 1 ). Clinically, there are 3 variants of melasma localization:
- Centrofacial (forehead, cheeks, nose, upper lip and chin)
- Painting (nose and cheeks)
- Mandibular (in the lower jaw area)
It is still unclear why some areas of the face may remain intact with melasma. This is thought to be related to the density of the sebaceous glands on the skin and their activity. In rare cases, melasma appears clinically on the forearm and is associated with progesterone use.
The depth of pigment in melasma can be determined using a Wood's lamp - this method is good for determining epidermal melanin, but poorly assesses the dermis. One can only indirectly judge the presence of melanin in the dermis with a bluish tint of hyperpigmentation in the glow of a Wood's lamp. Unfortunately, this approach does not work for people with dark skin phototypes.
Clinicians typically use the Melasma Area and Severity Index (MASI) and the Melasma Quality of Life scale (MELASQoL) to assess disease severity.
Rice . 1. Centrofacial melasma (Danish national service on dermato-venereology)
https://www.danderm-pdv.is.kkh.dk/atlas/4-161.html
How to prevent the occurrence of the disease?
Chloasma is not dangerous to human health and has no complications. If a large area of facial skin is affected, it can lead to serious discomfort and psycho-emotional disorders. Therefore, it is important to learn how to prevent exacerbations of the disease.
Facial skin care
Skin care begins with cleansing. To do this, use milk, kefir or whey specially designed for pigmented skin. After cleansing, a toner is applied to the skin to prepare the skin for the application of medicated creams.
The use of medicinal cream depends on the activity of the components. This can be local application or treatment of the entire surface of the face, daily use or 2-3 times a week.
People with dry skin may experience irritation, so in these cases it is necessary to additionally use moisturizers with an oily base. It is advisable to select products with a high antioxidant effect.
For home peeling, products with fine abrasive particles are used. The procedure is carried out 1-2 times a week, trying not to injure the skin.
You need to carefully select medicinal, care and decorative cosmetics. They should not contain aggressive esters, salicylates, mercury, unidentified additives and harmful preservatives.
Pigmented skin reacts sharply to esters contained in perfume. During an exacerbation, it is better to avoid them or select perfumes and deodorants with a low content of fragrances and without alcohol.
Prevention
First of all, it is year-round sun protection. To do this, use photoprotective creams containing several filters. The higher the Sun Protective Factor (SPF) indicated on the label, the longer and more reliable the skin protection.
The full activity of the cream begins 15-20 minutes after application, this should be remembered before going outside. On days of high solar activity, the skin is additionally protected with wide-brimmed hats and clothing made of light fabrics.
Additional rules:
- regular consumption of foods containing vitamins C and B;
- annual examination of the body;
- treatment of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, urinary tract;
- control over gynecological diseases, hormonal levels;
- restriction or exclusion of solariums;
- exclusion of drugs and products with photosensitizing properties.
Since the only consequence of chloasma is psychological discomfort, it is important for patients with a chronic form of the disease to perceive the problem as accomplished. Long-term stress can lead to serious neurological damage.
Today there are many decorative products and cosmetic methods that successfully mask age spots. It is always important to remember that often facial defects are visible only to their owner. People around you rarely evaluate appearance based on details; moreover, the inner content of a person is always much more valuable.
Principles of treatment
Hyperpigmentation with melasma appears slowly and disappears just as slowly with treatment, so doctors and patients should be patient.
An important therapeutic factor is complete avoidance of sunlight . Moreover, sunscreen cosmetics cannot fully protect the skin, since they usually block only the UVB range, while UVA gets on the skin and continues to worsen the condition of the disease. Therefore, if you have melasma, it is recommended to wear closed clothes, hats with wide brims and visors, and stay mostly in the shade. This does not replace the need for UV filters, although patients should note that they should not be relied upon solely.
Hydroquinone is used as a skin lightening ingredient in a number of countries where it is permitted . To increase effectiveness, it is combined with tretinoin and/or glycolic acid (due to their exfoliating effect, they improve the penetration of hydroquinone) and corticosteroids (to reduce inflammation). In one study, a formulation containing 4% hydroquinone, 0.15% retinol and antioxidants significantly reduced melasma pigmentation after 12 weeks of use. It is important to remember that because hydroquinone penetrates the skin well and can be absorbed into the blood, it should not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding. In addition, it has a number of serious side effects, which is why it has been banned in the European Union and Switzerland since February 2001.
Tranexamic acid acts in several directions at once: it directly blocks the formation of melanin in cells, does not allow it to accumulate locally, and disperses the melanin that is already present in the skin. In cases where it is necessary to act on deeper-lying pigment granules, tranexamic acid is transported into the dermis using liposomal delivery systems.
Azelaic acid can be used to treat melasma in the form of a 15% gel or 20% cream.
It is impossible not to note the possibilities of chemical peels - glycolic acid (50–70%, pH 2.0–3.0), trichloroacetic acid 10–30%, Jessner’s solution (14% lactic acid + 14% salicylic acid + 14% resorcinol) are recommended. , resorcinol (20–50%).
Long-term improvement in refractory melasma has been reported following microneedling , a minimally invasive procedure in which the skin is pierced with short, thin needles, resulting in stimulation of fibroblast proliferation, release of growth factors, and increased collagen production. However, the exact mechanism for the positive effect of this procedure on melasma has not been established.
To treat melasma, such types of hardware cosmetology as non-ablative fractional photothermolysis, IPL therapy and short-pulse Q-switched Nd:YAG laser are used. The principle of operation of fractional lasers is the destruction of micro-areas of the epidermis and dermis, followed by their healing and the formation of healthy, defect-free skin. Thus, the non-ablative fractional laser Fraxel has shown high efficiency in the treatment of melasma when performing 2-3 procedures with an interval of 1 month. Non-ablative fractional photothermolysis is the method of choice for patients with skin phototype IV and above who cannot undergo other laser procedures.
IPL therapy is also actively used to treat melasma . In this case, the target for exposure to high-intensity pulsed light is melanin. This method gives good results in patients with light phototypes. Finally, in cases of difficult-to-treat melasma, the development of which is stimulated by thermal procedures, Nd:YAG Q-switched laser , which also selectively affects melanin, but does not heat the skin, due to its ultra-short pulse duration.
Questions from our users:
- melasma laser treatment
- melasma cream
- melasma effective treatment
- melasma treatment on face
Folk remedies used at home
Sulfides, phenols, glycosides, phenolcarboxylic acids and ascorbic acid, found in many plants, have brightening properties and suppress melanin production.
Many of them are actively used by cosmeceuticals to create depigmenting agents. Therefore, the use of plant-based folk remedies is effective and approved by dermatologists. This review contains the best recipes from readily available ingredients.
Brightening masks
Before applying the mask, you need to cleanse your face with lotion and steam the pores over hot water steam for 5-7 minutes.
Compositions:
- honey and onion juice are mixed in equal proportions;
- starch (1 tbsp) is diluted with lemon juice until medium thick;
- finely chopped parsley (30 g) is mixed with kefir (100 ml), left for 1 hour;
- mix grated cucumber (1 tbsp), cottage cheese (1 tbsp), milk (1 tsp), olive oil (1 tsp);
- make a mixture of lemon juice (1 tbsp), white clay (1 tbsp), parsley juice (1 tbsp), kefir (1 tbsp);
- Finely grated horseradish and green apple are mixed 1:1.
Masks are applied to the entire face or only to pigmented areas. The average exposure time is 15-20 minutes, after which the mixture is washed off with warm water. 2-3 procedures per week are recommended, formulations can be combined.
Lotions and tonics
The products are used for daily wiping of the skin instead of the usual lotions, before applying a medicinal cream and mask.
Compositions:
- parsley leaves and stems (50 g) are poured with boiling water (250 ml), left for 3 hours, the raw materials are squeezed out;
- crushed bearberry leaves (20 g) are poured with 40% ethyl alcohol, left for 2 weeks in a dark place;
- dry thyme (2 tsp) is poured with water (200 ml), boiled for 10 minutes;
- dandelion leaves and flowers (30 g) are poured with boiling water (250 ml), boiled for 15 minutes and left for 2 hours;
- fresh mint (50 g) is boiled in 250 ml of water, the cooled broth is mixed with the juice of 2 lemons.
The prepared products are filtered and poured into a glass container. With the exception of alcohol tincture, store in the refrigerator for no more than 3 days.
Compresses
Compresses and lotions can be used on mask-free days. They are also done on previously cleansed and steamed skin.
Juices used for the procedure:
- lemon;
- cucumber;
- parsley;
- blackberries;
- grapefruit;
- viburnum;
- Luke.
A gauze cloth folded several times is moistened in the selected juice and applied to the surface of the pigmented area. Leave for 20 minutes and rinse with warm water.
How to remove chloasma on the face
Successful treatment of chloasma is possible after an accurate diagnosis of the diseases that caused it. Once metabolism and hormonal balance are restored, pigmentation of areas of the skin becomes a cosmetic problem that can be easily corrected. For successful recovery you need to follow several rules:
- avoid being in bright sun;
- use sunscreen;
- take vitamins prescribed by the doctor: aevit, folic acid, methionine, riboflavin, injections of B vitamins.
- stop visiting the solarium;
- Avoid using essential oils in cosmetics; they increase sensitivity to the sun and cause pigmentation.
Methods of cosmetic facial correction
A visit to a cosmetologist gives lasting results in the treatment of hyperpigmentation on the face. The work of a cosmetologist on chloasma comes down to the following actions:
- Protection from direct sun exposure. For this purpose, suitable protective equipment is selected for the patient.
- Removing the layer of dead cells. Thus, some of the dark cells are mechanically removed and the spots become lighter. The skin begins to renew itself more actively, and the stain gradually disappears.
- Suppression of melanin production in certain areas. For this, whitening cosmetics with traditional and modern components are used: acids, plant extracts, omega-3 and others.
In addition to cosmetics, hardware procedures are used for correction: dermabrasion, laser corrections, massages, injections.
Medicines
Drugs prescribed for the treatment of chloasma require careful adherence to instructions, dosages and specialist supervision. Overdosing or increasing the time of procedures can lead to the opposite effect: the skin in the affected area will be excessively whitened, and this area will also stand out on the face. In addition, in some cases, actively targeting melasma can cause increased melanin production, causing the spot to darken even more.
To control the production of melanin, doctors prescribe vitamins that affect its production and excretion:
- The essential amino acid methionine effectively lightens chloasma. It is prescribed three times a day, 0.5 g.
- Ascorbic acid, when applied to the skin, easily penetrates the external barrier, stops the formation of melanin, promotes active collagen production and whitens the skin. To enhance the effect, ascorbic acid is prescribed for oral administration.
- Folic acid (vitamin B9) has a beneficial effect on the skin. Among its many beneficial properties is the ability to create invisible protection against UV radiation. Take 0.1 g per day.
- Skinoren cream not only solves the problem of excess pigmentation, it cleanses the skin of inflammation and helps remove traces of acne. The active ingredient of the cream is azelaic acid. It suppresses the development of excess melanocytes, making them non-viable. To get rid of pigmentation, a course of about three months is required. A 2.5 cm strip of cream is enough to apply to the entire face.
Which doctors should I contact for this problem?
Skin problems are dealt with by specialists - dermatologists. You can also start treatment by making an appointment with a therapist, who will write a referral to a dermatologist and specialists in major chronic diseases. Based on the test results and taking into account your medical history, you can receive a referral to a gastroenterologist, gynecologist, oncologist, neurologist and other specialized specialists.
Causes
The reasons for its appearance do not lie on the surface of the skin; it is caused by malfunctions in the body. Indicating serious internal problems, chloasma cannot be treated until the underlying fault in the system is corrected.
Excessive and uneven concentration of melanin can be caused by hormonal disorders, metabolic problems, and excessive exposure to the scorching sun or in a solarium. The appearance of chloasma is a signal of a disruption in the functioning of some organ or system associated with metabolism or the production of hormones.
This fact is confirmed by the fact that chloasma often “decorates” pregnant women, patients with a diseased liver, taking hormonal medications, and patients with inflammation in the reproductive system.
Another common cause of age spots is parasites in the body. If the spots are localized on the lips and near the mouth, an urgent visit to the doctor is necessary.