Breast augmentation, or breast augmentation or augmentation mammoplasty, is a surgical procedure aimed at increasing the size, shape or fullness of the breast.
To enlarge the breast, the plastic surgeon places breast implants filled with special silicone, saline or biocomposite material under the pectoralis major muscle or under the breast tissue. Modern implants can last the patient's entire life, and most manufacturers offer a lifetime warranty on their implants.
Why does a woman need breast augmentation?
Breast augmentation is done for:
- Naturally enlarge small breasts
- Restore breast size and shape after pregnancy, weight loss or breastfeeding
- Restore symmetry when the mammary glands are asymmetrical
- Restoring breasts after breast removal surgery
Plastic surgery includes reconstructive and aesthetic surgery .
Breast reconstructive surgery is performed as part of treatment for breast cancer. Aesthetic breast surgery is performed to improve appearance. Breast augmentation is usually an aesthetic surgery.
In 2007, a study conducted by researchers at the University of Florida found that breast augmentation through cosmetic surgery improves women's self-esteem and their feelings and sexuality. Allows you to get a higher paying job and achieve greater recognition.
Reduction mammoplasty and mastopexy
In case of hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the mammary glands, breast reduction is necessary. A woman with an enlarged bust suffers from constant stress on her back. As a result, problems with joints and spine occur. Diaper rash and a feeling of discomfort are also possible.
During surgical intervention, the excess amount of fatty and glandular tissue is resected, and then the nipple-areolar complex is moved using the method of free transplantation or using nourishing dermal and parenchymal pedicles. These operations are usually complemented by plastic surgery and nipple lifting, which are also recommended in cases of severe ptosis of the mammary glands. General anesthesia and local anesthesia are used.
What are breast implants?
A breast implant is a medical device that is placed under the breast or pectoralis major muscle to enlarge, reconstruct, or create an aesthetically pleasing breast shape.
Breast implants may contain silicone, saline, or another compound.
There are three main types of breast implants:
Saline implants are filled with sterile saline, which is simply sterile salt water. The solution is contained inside a silicone shell. These implants can be filled with varying amounts of saline. This affects the sensation experienced when pressing on the mammary gland; it can be either softer or harder, at the request of the patient, in addition, different densities will determine the different shape of the mammary gland.
If the saline implant is damaged and leaking, the solution will not cause any harm to the patient, since the saline solution is natural for the body and will simply be absorbed by the body without residue, the only negative is that the implant will have to be changed since the volume of the mammary gland will decrease.
Silicone gel implants consist of a silicone outer shell filled with silicone gel. If a silicone implant leaks, the gel will either remain in the shell or end up in the breast implant pocket. And it will not spread throughout the body. Modern implants do not spread even if the shell is damaged. Currently, these implants are the most commonly used.
Alternative composite implants are rarely used and may be filled with either biodegradable material, soybean oil or some other material.
What needs to be decided before surgery?
Breast augmentation is a surgical procedure, so patients need to carefully consider whether they really need this procedure.
- It is necessary to choose where the implant will be installed - under the pectoralis major muscle or under the gland tissue. Your operating doctor will help you decide this. Most often, implants are placed under the muscle.
- Before the operation, the surgeon, together with the patient, selects the required implant size. This is done either with the help of special sizers that are placed in the bra, and the patient can evaluate the size and comfort of wearing it. In addition, the patient, together with the doctor, chooses the density of the implant and its shape (round or anatomical). Manufacturer of the implant.
- The surgeon and patient should discuss incision options.
The following options are possible:
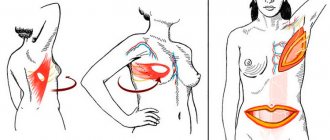
- A submammary incision made in the crease under the breast
- Transaxillary incision in the armpit
- An incision around the edge of the areola (periareolar) or through the areola (transareolar)
The choice of incision depends on several factors, including the degree of augmentation, patient anatomy, implant type, and surgeon-patient preference.
In addition, the patient must choose the type of anesthesia; this operation is often performed under general anesthesia. But if the patient wishes, in principle this is also possible under local anesthesia.
How is the operation performed?
After the patient is put into medical sleep, or after local anesthesia, the surgeon makes a skin incision in the place, according to the type of access agreed upon with the patient, about 4.5 centimeters long, and then, using special tools, forms a pocket into which the endoprosthesis will then be placed.
The pocket can be formed either directly under the breast tissue or under the large muscle mass (this is discussed with the patient before surgery):
1. With an axillary pouch, it is placed under the pectoralis major muscle.
2. The submammary or subglandular location of the pocket is simpler, with the pocket formed in the space between the mammary gland and the pectoralis major muscle.
Suturing the wound
In their practice, plastic surgeons more often use so-called cosmetic, or more correctly, intradermal sutures; usually several rows of threads are applied, which most often do not need to be removed; over time they dissolve on their own. In addition, the plastic surgeon can use special surgical glue and special sterile strips to tighten the edges of the wound so that the scar is less noticeable in the postoperative period.
The cut lines will be visible at first, but over time they will almost disappear.
Evaluation of results
Surgery may lead to swelling and hematomas (bruises), but this should go away within two to four weeks. Usually the final result is formed no earlier than 3-6 months after the operation. Therefore, the patient will only be able to decide whether the procedure meets her expectations after some time.
Recovery period
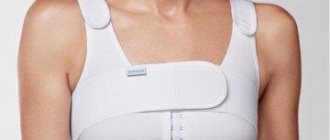
The recovery period takes 1 month. During this period, there are certain restrictions that will be explained to the patient by the doctor and a special reminder will be issued for their exact implementation. Pain bothers the patient only on the first day after surgery; non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ketonal, are used for pain relief. In rare cases, narcotic analgesics. Then the pain practically goes away. There remains a slight inconvenience. After the operation, you should not swim in open or closed waters, take a bath, sleep on your back, raise your arms high, engage in active sports or heavy physical work. All these restrictions are temporary, for 1 month. Then the patient can live peacefully as she lived before the operation; she can fly on an airplane and scuba dive. The most important thing in the postoperative period is to wear special compression garments. Underwear must be worn strictly for 1 month after surgery, and then for another 3 months when playing sports or heavy physical activity.
The next day after the operation, the patient can leave the clinic if she wishes. The patient is monitored once a week, in the first two weeks, then every other month. Then after three months. And then an annual follow-up examination.
Absorbable (absorbable) sutures usually dissolve within 6 weeks. The patient will take care of the suture independently at home. This is a no-brainer.
If the patient has non-absorbable sutures, an additional visit will be required to remove them.
After the operation, the surgeon will not only tell you how to behave in the postoperative period, but will also provide you with an extract with recommendations, where it will be written:
- How to care for your breasts after the procedure
- How to use prescribed medications
- When to come for your next visit
- When to call the doctor
You should seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- any signs of infection such as a temperature above 38 degrees, fever or redness of the skin in the chest area
- severe chest pain, or a sharp increase in the size of the mammary gland
BREAST ENLARGEMENT / BREAST ENDOPROSTHETICS
The cost of the procedure is from RUB 194,950 including implants.
This is an operation aimed at increasing the size and improving the shape of the mammary glands.
The operation is performed for aesthetic reasons, it allows you to increase the volume of the breasts and can also eliminate mild “sagging” of the breasts and make the breasts more elastic. With this method of breast surgery, it is impossible to do without various mammary gland endoprostheses, the shape and volume of which are selected directly during a visit to the doctor. The incision during endoprosthesis surgery can be localized in the armpit area, in the area of the edge of the areola, in the area of the natural fold under the breast. The insertion of the endoprosthesis can be performed in two ways: subglandularly, that is, under the mammary gland, or subpectorally, that is, under the muscle. Indications
- small breast sizes from birth – a cosmetic defect without functional deficiency
- reduced breast volume after breastfeeding, “sagging” breasts
- deformation of both or one breast due to surgical treatment
- reduction in size due to rapid weight loss - after a strict diet or as a result of metabolic disorders
At least 8 months must pass after the end of feeding. During this time, important changes will occur: lactation will stop completely, and weight will stabilize, and, accordingly, the size and shape of the breast.
Contraindications
- Lactation. Less than a year has passed since the end of lactation. Or the woman plans to become pregnant and breastfeed soon
- Blood diseases, blood clotting disorders
- Diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory system are acute, exacerbation of chronic ones or in a state of decompensation
- Severe diabetes mellitus
- Infectious diseases
- Active tuberculosis of any location
- Oncology of any location
- Having a large number of cysts or lumps in the breasts, or having large cysts or lumps that require treatment
Operation time
2-3 hours
Anesthesia
General
Primary rehabilitation (sutures, swelling, hospital).
Wearing compression garments: 1 month
Hospital: 2 days
Stitch removal: 7-9 days
Swelling: up to 14 days
Compression garment: bra
Complete rehabilitation
The final assessment of the results of the operation is made after six months
Limitations of the rehabilitation period
- For a month after surgery, any strength training is prohibited.
- Visits to saunas, baths, swimming pools are limited for 2-3 weeks
- DO NOT sleep on your stomach for a month after surgery. You can lie on your side 2 weeks after the intervention
- Avoid lifting heavy objects for a month after surgery
- It is not advisable to drive for the first week after surgery.
- You will have to wait a week with sex after surgery.
Work 7 days after surgery, if without physical labor, if with physical activity, then after 1.5 months
What risks might this operation have?
Any surgical procedure increases the risk of sudden death from myocardial infarction, stroke, or thromboembolism during or immediately after surgery. But, fortunately, such complications are extremely rare. And in our clinic there is all the modern resuscitation and anesthesiology equipment that minimizes these risks to almost zero.
Some of the risks and complications associated with breast augmentation are:
- Painful mammary glands
- Inflammation of the mammary gland
- The sensation in the chest and nipples may temporarily change or become more or less pronounced
- Implant rupture
- Bleeding
- Fluid accumulation (seroma)
A specific complication of this operation is capsular contracture - in which a thick capsule is formed around the implant. Which can deform the mammary gland, or make it extremely painful and dense. During your consultation, the surgeon will tell you in detail about this complication and how to avoid it.
In addition, even cosmetic stitches can become red, thick and painful, or, conversely, flat and wide. This may lead to repeat surgery to remove such scars.