Memo for patients when visiting the clinic for surgical treatment under anesthesia
To your health:
- The state of health plays an important role in how anesthesia will proceed, as well as how comfortable it will be to awaken from anesthesia. Before anesthesia, it is important to undergo a comprehensive examination of the body, including a consultation with a general practitioner, a series of tests and instrumental research methods. If there are any chronic diseases, then with the help of the attending physician it is necessary to achieve a stable remission of these diseases.
- Routine anesthesia is possible against the background of a stable state of health; on the day of surgery there should be no signs of acute respiratory viral infection.
- The most important role during anesthesia is assigned to the heart and lungs, therefore, before anesthesia, the performance of these organs should be as close to satisfactory as possible - this means that colds, obstructive bronchitis, asthma, hypertension, angina pectoris, heart failure should be treated and be in the stage of compensation .
- Avoid smoking cigarettes 6 weeks before the proposed surgery. This will significantly reduce the risk of respiratory complications after surgery. If you were unable to quit smoking, then at least try not to smoke on the day of surgery.
- If you have loose teeth or crowns, get treatment from a dentist, as these teeth may be lost when the anesthesiologist manages the airway (using devices specially designed for this in the oral cavity).
- Don't forget to take all your medications to the hospital.
Before the operation, it is necessary to undergo tests, then, based on the results of a laboratory examination, undergo a consultation with a therapist and an anesthesiologist. Tests are taken on an empty stomach (you cannot eat or drink, the day before you must refrain from fatty and salty foods).
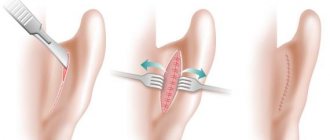
Preparation for ENT surgeries
1) BLOOD TESTS:
- Complete blood count
with leukocyte formula - Biochemical blood test
, indicators: glucose, total protein, bilirubin, creatinine, urea, ALT, AST - Blood electrolytes
(potassium, sodium, chlorine) - Coagulogram
(blood clotting test) - Blood test for infections:
syphilis (RW or RPR), hepatitis B and C (HBsAg and AntiHCV), HIV - Blood type
and Rh factor
2) GENERAL URINE ANALYSIS 3) CARDIOGRAM (ECG) with a description 4) THE THERAPIST’S CONCLUSION about the absence of contraindications to surgery on the ENT organs under anesthesia 5) FLUOROGRAPHY or chest radiography, with a radiologist’s conclusion.
You can download this list of studies to prepare for surgery in PDF format below.
Note! The results of laboratory tests of blood, urine and ECG must be received no more than 2 weeks before the operation and their originals must be presented on official forms with stamps and details of the medical institution or laboratory.
Fluorography results are valid for 1 year.
You can undergo all tests to prepare for ENT surgery where it is convenient for you: both at the ENT Center, and in advance at the clinic at your place of residence or in a private laboratory.
ON THE MORNING OF THE DAY OF OPERATION:
- Don't have breakfast! (anesthesia is carried out strictly on an empty stomach, the last meal and liquid is allowed no later than 12 hours before surgery);
- Do not apply makeup to your face and remove your manicure in advance;
- Arrive at the clinic at the appointed time, be sure to take your passport and all examination results with you;
- Bed linen, towels, clothes, food, etc. You don’t have to take it with you - all this will be provided to you at the hospital.
ADDITIONAL (MAY BE REQUIRED IN SOME CASES)
- CT scan of the paranasal sinuses (if surgery is planned in the nasal cavity);
- The results of a study of external respiratory function (RF) and a pulmonologist’s report with recommendations for adjusting basic therapy for the period of surgery (only for patients with bronchial asthma);
- Conclusions of specialized specialists: cardiologist/endocrinologist and others (only if the patient has concomitant chronic diseases);
- Consult with your doctor and stop taking medications that affect blood clotting (thrombo-ASA, cardiomagnyl, warfarin) in advance;
- An infectious disease specialist's conclusion on the degree of disease activity and the treatment provided (if the test results are positive for hepatitis B, C or HIV) or a dermatovenerologist (if the test is positive for syphilis);
IMPORTANT!
- Planned operations on the ENT organs are not performed in the first week of the menstrual cycle (during menstruation) due to changes in blood clotting. For any sudden changes in your cycle, be sure to notify your surgeon.
- You cannot be in an ENT surgical hospital in a state of acute infectious disease. If the day before or on the morning of the operation you feel signs of an incipient cold, be sure to inform the doctor about this and reschedule the operation date;
Conclusion
To summarize what has been said, let's draw a conclusion about whether it is possible to do general anesthesia for fever, cough, and runny nose. If these symptoms are associated with a cold, then clearly, if the situation is not an emergency, surgery and anesthesia are postponed until complete recovery and after waiting for at least three to four weeks.
Why can't you do anesthesia for a cold? Complications to the lungs, heart, kidneys are possible, and infection of the surgical wound is possible. All this complicates the postoperative period and delays recovery. There is often a delayed recovery from anesthesia.
All this applies equally to all patients, and especially to young children.
But! If surgery under anesthesia is needed urgently (for health reasons), then a runny nose, cough and fever will not cause cancellation of the surgical intervention. Because in this case we are talking about the patient’s life.
Indications and contraindications for sedation
Dental treatment under anesthesia is a modern method of providing dental care and the best way to quickly, painlessly and efficiently treat teeth!
Sedation is a method of pain relief that leads to a state of artificial sleep: the patient completely loses consciousness and does not feel pain, which is achieved through the use of modern drugs that allow control of the patient’s breathing, do not cause complications and are quickly eliminated from the body.
One of the indicators for dental treatment under sedation is the need to perform a large amount of work (a large number of teeth) in a limited period of time. ⠀ Treatment of such a plan (including tooth extraction) allows you to deal with existing dental problems in a shorter time
- We most often treat children in one visit (there are often cases when 8-10 teeth are treated at a time). ⠀ Situations, of course, are different, and once is not enough to deal with all the problems in the mouth. But there is nothing wrong with the fact that sedation sometimes has to be repeated. The drug is non-toxic and does not accumulate in the body, its effect stops 4 minutes after the syringe dispenser is turned off, and after 6 hours the drug is completely eliminated from the body.
- With adult patients it is a little more difficult. It should be borne in mind that a course of dental care for adults can last for years. Especially if it concerns the treatment of advanced forms of caries, root canal filling (and there can be 4 or even 5 of them in 1 tooth), preparation for prosthetics, implantation, bone tissue augmentation, orthodontic treatment, etc. But even in such situations, treatment under sedation can reduce the overall treatment time by two or even three times.⠀ ⠀
| Indications for the use of sedation: | Contraindications for use sedation: |
|
|
The main requirements (conditions) for medical sedation are:
- Extract from a pediatrician/generalist and OAC and OAM, after 40 years - ECG
- Additional diagnostics when establishing a diagnosis (according to indications) prescribed by an anesthesiologist
- “empty stomach”: eating is prohibited for at least 3 hours before anesthesia for children and at least 6 hours for adults
- Healthy state of the body at the time of treatment (absence of viral, infectious and respiratory diseases)
If you need dental treatment under anesthesia and there are no contraindications, you can contact our medical center
In order to treat teeth without pain under anesthesia, you must:
1. Call one of the numbers:
+375 29 376 02 80 A1
+375 33 376 02 80 MTS
2. Agree on the date and time of treatment.
The staff of the Family Dentistry Center will be happy to help you!
Causes of symptoms
Increased body temperature, cough, runny nose, both in children and adults, require a diagnosis, i.e. identifying the cause of these symptoms. Let's consider the possible options:
- ARVI = acute respiratory viral infection, symptoms: fever, cough, runny nose, sore throat, muscle and headache, general weakness.
- ARI is a cold, an acute respiratory disease, the symptoms are almost the same: fever, cough, runny nose, sore throat, muscle and headache, general weakness.
- Cough – possible causes: chronic and acute diseases (tracheitis, bronchitis, including smoker’s bronchitis), diseases of the cardiovascular system, asthma, pulmonary tuberculosis.
- A runny nose and sneezing are likely causes: allergies, viral infections, sinusitis, sinusitis.
Increased body temperature not associated with a cold (some causes):
- Caused by the surgical disease itself.
- In women of childbearing age during ovulation. The release of a mature egg in the middle of the cycle may be accompanied by an increase in temperature to subfebrile, this is up to 37.5.
- Against the backdrop of emotional tension.
- Endocrine diseases.
- PE – pulmonary embolism. (this, in some cases, is an indication for emergency surgery).
- Overheating of the baby, imperfect thermoregulation.
- This is a complete list.
Is it possible to do general anesthesia for a runny nose?
As we found out, this unpleasant symptom can be a sign of a cold (infection or flu), acute sinusitis, or exacerbation of chronic sinusitis. In addition, a runny nose can occur due to adenoids and allergies. But in any of the above cases, it disrupts nasal breathing, often affecting the nasopharynx, larynx and trachea.
Therefore, to the question: is it possible to give anesthesia for a child or an adult with a runny nose, the answer will be as follows.
If the operation is planned, it is possible to postpone it - the date is postponed until the runny nose is completely cured. This is done to avoid complications from the respiratory system after general anesthesia.
You can do general anesthesia for a chronic runny nose! You just need to inform the anesthesiologist about this nuance.
Under no circumstances should you hide this symptom from your doctor or mask it with vasoconstrictor drops.