Home|Developmental anomalies of the upper and lower extremities|Syndactyly
Anomalies of the upper extremities manifest themselves in different ways. This may be hypoplasia of the hand (underdevelopment), aplasia of the fingers (absence of fingers), fusion of the fingers, amniotic bands, syndactyly of the fingers (there is also syndactyly of the foot, not just the hands). There is a phenomenon opposite to syndactyly - polydactyly , that is, a double finger.
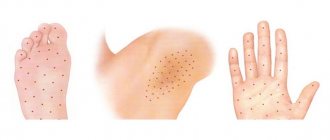
Syndactyly is a congenital anomaly of the lower or upper extremities, which is characterized by complete or incomplete fusion of the fingers. Today, fused toes occur in more than 10 percent of children, with cases of symmetrical fusion of the toes on both feet or hands being more common.
Is it possible to recognize syndactyly on your own?
Yes it is possible. Syndactyly is clearly visible to the naked eye. The neonatologist makes a preliminary diagnosis after the initial examination of the child. Further diagnostics will be carried out to clarify the type of syndactyly.
X-ray examination is the simplest and most informative procedure. X-rays will show whether the fingers are connected only by skin and soft tissue, or whether bones are also involved. In more severe cases, an MRI or CT scan may be required. Tomography provides more detailed information about the structure of the bones.
In some cases, signs of syndactyly are detected in utero, during mandatory ultrasound screening examinations during pregnancy. The skin bridges between the toes usually disappear before the 56th day of pregnancy. Their detection at a later date indicates syndactyly.
Postoperative period
Two weeks after surgery, the sutures are removed and rehabilitation measures begin. At this stage, the patient is prescribed a set of additional procedures, the purpose of which is to restore the normal functioning of the limb.
The recovery period after surgery includes the following procedures:
- massage (improves blood circulation, blood supply to tissues);
- physical therapy (prevents congestive processes in the limbs and muscle atrophy, restores motor activity);
- electrical stimulation of the fingers (prevents muscle atrophy, restores blood circulation, accelerates healing);
- mud therapy (has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect);
- ultraphonophoresis (stimulates the process of absorption of medications under the influence of ultrasound, accelerates the supply of useful substances to the cells of the body);
- paraffin and ozokerite applications (have a warming effect and promote better tissue nutrition).
Complete restoration of all functional capabilities of the limb takes from two months to six months.
What types of syndactyly are there?
Not all cases of syndactyly are the same. It can be complete (fingers fuse along the entire length) or incomplete (only individual phalanges of the fingers fuse). Depending on which fingers are involved in the process, there are 5 types of the disease:
- Zygodactyly, type 1 is the most common form of pathology. It is characterized by fused ring and middle fingers.
- Synpolydactyly, type 2, also affects the ring and middle fingers - they grow together, and an additional ring finger appears.
- Ring and little finger syndactyly, type 3, usually affects both hands at the same time. In more severe cases, the distal phalanges may fuse.
- Haas syndactyly, type 4, is a rare form of pathology in which all fingers are fused. The hand becomes deformed and takes on the shape of a bowl.
- Type 5 is a combination of a fused ring and middle finger with a fused second and third toe.
Syndactyly is an exclusively congenital pathology. It may also be a component of complex genetic syndromes, such as Saethre-Chotzen syndrome and Apert syndrome. In this case, correction of the fingers can be carried out at a later date, giving way to the treatment of pathologies with a higher health risk (for example, heart disease).
Diagnostics
Fused toes in a newborn are detected immediately after birth. But to determine the form of pathology and choose treatment tactics, the child needs to be examined by an orthopedist or surgeon. It is also recommended to seek genetic advice, as syndactyly may be accompanied by other congenital genetic abnormalities.
An x-ray examination is usually performed to help assess the condition of the bone tissues of the extremities. If the bones and joints are not deformed, and fusion occurs only at the level of soft tissue, the operation is postponed. In the first year of a child’s life, it is necessary only if the terminal phalanges are fused. After all, this form of pathology can lead to deformation of the limbs and other complications.
Before the operation, the child is prescribed additional examination. Ultrasound, angiography, Doppler, and electrothermometry are performed. All these methods help determine the location of blood vessels and nerves, the condition of soft tissues, which is necessary for effective surgery and prevention of complications.
How is the treatment carried out?
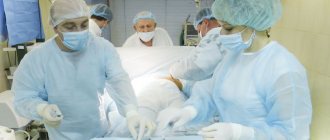
Treatment for syndactyly involves surgery; there is no other effective way to separate the fingers. A timely operation performed in a good medical institution allows you to achieve the following results:
- Improving the appearance of the hand, correcting a cosmetic defect.
- Prevention of progression of pathology during arm growth.
- Preservation of normal function of the upper limb.
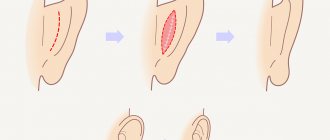
The operation is not limited to a simple incision because the available skin is often not enough to cover the surface of two separate fingers. Thus, the skin defect is carefully restored using several skin flaps. Sometimes skin grafting is required to cover the entire surface and provide a good cosmetic and functional result. Skin grafts can be taken from the thigh or the front of the elbow. Another option is to use skin from the top of the hand, which is more resistant to injury and prevents scarring.
In cases where syndactyly affects the bones of the fingers, more complex intervention is required. Bone joints usually form next to the nails and can often be separated in the same way as simple folds of skin. The problem is that after such intervention the fingers usually remain deformed (for example, spread out or bent). In this case, additional surgical interventions are performed.
The appropriate age for treatment depends on the type of syndactyly. If the ring finger and little finger or thumb and index finger are fused, surgery is performed as early as possible (at about 6 months of age). Other types are less functionally significant and can be treated at a later age (up to 2 years).
Symptoms of the defect
With syndactyly on the feet, a child most often experiences fusion of the 2nd and 3rd toes. In this case, undivided phalanges can be either underdeveloped or normally developed. In some cases, there is a decrease in the number of fingers due to their amniotic amputation.
Unlike children with syndactyly on the hands, children with syndactyly on the feet develop quite normally. They have no problem performing a wide range of activities. At the same time, functional inferiority of the foot does not in any way complicate studies, and almost never limits the choice of a future profession.
Is it necessary to visit a doctor regularly after treatment?
Yes, you will need to visit the clinic regularly for the first few months. Immediately after surgery, the arm will be protected with a voluminous soft bandage covering the arm and forearm. An additional rubber pad may be placed between the affected toes to prevent recurrence of syndactyly while the wound is healing.
One of the main tasks of the postoperative period is the prevention of scar formation. During the healing process, the skin may be replaced by connective tissue. Connective tissue effectively and quickly covers the surface of the wound, but cannot stretch. Thus, the fingers lose their normal shape and function. In such cases, a repeat operation is performed.
In specialized clinics abroad, physiotherapy is mandatory during rehabilitation. It helps to avoid stiffness and swelling and restore normal range of motion. All procedures are performed under the strict supervision of a qualified medical professional.
Send a request for treatment
Which clinics are leading in the treatment of syndactyly?
Clinics in European countries with developed medicine are leaders in the field of plastic surgery. Equipment for precise (down to the cellular level) interventions, 3D planning of optimal aesthetic results and high competence of surgeons contribute to the best treatment results. Plastic surgery in Germany combines low risks and optimal functional results, which is extremely important when treating children.
The list of the best clinics in Germany that demonstrate outstanding results in the treatment of syndactyly includes:
- HELIOS Clinic Krefeld, Department of Plastic, Aesthetic and Reconstructive Surgery.
- University Hospital of the University of Munich. Ludwig Maximilian, Department of Hand Surgery, Plastic and Aesthetic Surgery.
- Oberberg Waldbröll Clinic, Department of Otolaryngology, Plastic Surgery, Facial Surgery.
German clinics provide assistance to children and adults with this pathology. Doctors also perform revision interventions and correct complications after previous operations (this is a common situation in children who are treated in non-core medical institutions). Specialists in Germany always develop an individual, comprehensive treatment program - from initial diagnosis to full functional recovery after surgery.
Prognosis and complications
Provided that treatment of the disease is started in a timely manner, syndactyly can be successfully eliminated surgically and by undergoing a full range of rehabilitation procedures.
The effectiveness of the manipulations is evidenced by the absence or presence of scars and scars, the complete restoration of all motor capabilities of the fingers of the limb, the restoration of their sensitivity, and the reproduction of an anatomically correct shape.
If the patient did not receive qualified assistance or the operation was performed untimely, a number of complications may occur. Defective functioning can provoke deviations in the mental development of the child, complicates professional self-determination, and causes serious psychological trauma to the small patient.
Organization of treatment in leading foreign clinics
If you want plastic correction of your child’s fused fingers to be performed in Germany, you need to resolve a number of issues. The first is to choose the most suitable clinic and obtain permission for treatment there. Treating children is a big responsibility, and not all clinics and doctors are ready to accept it. You should also take care of all medical and administrative documents related to traveling abroad for treatment. Please pay attention to the translation of documentation - medical reports must be in German. After this, you can begin to find an interpreter who will accompany you in the clinic.
You can undergo surgery to restore the appearance and function of the hand at the Helios Clinic Berlin-Buch. The Department of Pediatric Surgery, under the direction of Prof. Dr. med. Klaus Schaarschmidt, successfully performs operations on young children with all types of congenital hand defects. The pediatric surgeons of the department remove additional phalanges and fingers for polydactyly types I-VII, and separate fused fingers for syndactyly. If necessary, skin grafting from the thigh or forearm is also performed - this allows you to completely restore the function of the hand and prevent the development of postoperative contracture as the child grows.
Considering that hand pathologies are often found in complex genetic disorders, the department’s specialists pay special attention to a comprehensive examination, involving specialists in related fields in this process. As a rule, hand surgeries are performed in a hospital setting. For the convenience of parents and children, the clinic offers a Rooming-in placement system, when a small patient and one of his parents are located in the same room.
An easier and more convenient way to organize treatment is to use the professional help of Booking Health. Booking Health is a certified medical tourism operator that organizes treatment abroad for children and adults from 75 countries. Booking Health doctors and coordinators will assist you in the following matters:
- Choosing the right clinic for your child
- Communication with a doctor, agreement on a preliminary treatment plan
- Providing favorable cost of treatment, without surcharges and coefficients for foreign patients (savings up to 50%)
- Sign up for surgery on the desired date
- Additional independent control of the treatment program
- Communication with the clinic after completion of treatment, organization of follow-up examinations and remote consultations
- Strict control of accounts and return of unspent funds
- Booking accommodation and air tickets, organizing transfers
- Translation services
In addition, your personal medical coordinator will stay in touch with you 24 hours a day. You will feel confident and protected while treating your child.
Causes of the disease
Genetic predisposition is the reason that is considered a priority. This implies the likelihood of pathology in the parents. Syndactyly (if it is hereditary) is transmitted according to an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance. Among all forms of development of the disease, one fifth is genetic in nature.
If there are no cases of anomaly in the family, the factor of adverse effects on the intrauterine development of the fetus during the formation of the limbs is considered. The first signs of development of the hands are observed in an embryo aged 4-5 weeks. During this period, the fingers have layers of tissue between them, which are caused by the physiological underdevelopment of parts of the body. If the process of fetal formation proceeds normally, then by 7-8 weeks the digital rays acquire a normal outline: by this moment the process of membrane development slows down significantly in favor of the dynamic formation of the digital rays. If this stage does not proceed normally, then the interdigital septa do not smooth out: the abnormal structure remains until the birth of the child.
Another important factor influencing the intrauterine development of the fetus is intoxication of the mother’s body. Toxins can be any external processes, products, substances or drugs that have a general or individual toxic effect on the body:
- air pollution;
- occupational hazard;
- alcohol;
- medications and other factors.
Serious infectious diseases such as syphilis, influenza, tuberculosis, as well as radiation (including x-rays) can lead to intoxication of the body.
If all of the above influence factors are excluded, syndactyly is diagnosed as a disease of unknown origin.
Syndactyly of the fingers or toes can occur due to chemical burns or thermal exposure.