Medicine has been developing at an accelerated pace for many centuries. Many years ago, the question of surgical intervention was equated with the death of the patient. Now surgery is not only a development in medicine, but also a chance for millions of people to receive the necessary help that conventional drugs can no longer provide. Endotracheal anesthesia (ETN)
The most
important element in surgical intervention is undoubtedly anesthesia, which should ensure comfort and safety for both the patient and the doctors operating him.
Over the years of studying various methods of anesthesia, doctors around the world have achieved incredible heights in their field. One of the advances is endotracheal anesthesia (ETN) . This is a type of anesthesia that provides anesthesia by injecting a narcotic substance through a special tube into the trachea. ETN is indispensable for operations on the heart, lungs, alimentary tract, and nervous system. It can be used for severe patients of all ages.
What is endotracheal anesthesia
Endotracheal anesthesia is the most common type of anesthesia, which is achieved by introducing volatile liquids or gases of a narcotic nature into the human body through an endotracheal tube.
Inhalational anesthetics pass from the respiratory tract into the circulatory system. Next, they are uniformly distributed in human organs and removed through diffusion laws.
The effectiveness of painkillers, the duration of anesthesia and the speed of return to wakefulness depend on many indicators:
- partial pressure;
- lung ventilation volume;
- diffusion capacity of the lungs;
- alveolivenous pressure difference of a single component of the gas mixture;
- penetration of blood cells into tissues and organs;
- volume of blood flow in the lungs;
- human blood circulation.
There are certain requirements for drugs acting as anesthetics for endotracheal anesthesia.
These include the presence of:
- reserve, which is a source of oxygen;
- alarm warning of a decrease in oxygen pressure;
- a blocker that helps stop the flow of nitric oxide when oxygen pressure decreases;
- antiseptics;
- the ability to disassemble the breathing circuit;
- safety of use of medical equipment for patients and doctors.
Modern technology for performing endotracheal anesthesia consists of the following components:
- a high-pressure system (it supplies compressed medical gases to the main components of the device);
- dosimeters that provide gradual dosing of oxygen and nitric oxide;
- evaporators of volatile narcotic substances (necessary for the formation of a combination of gas anesthetics and oxygen);
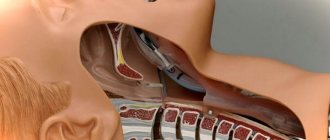
- a breathing circuit that guarantees the supply of narcotic drugs to the patient and the removal from him (consists of recirculation valves, an adsorber, connection elements and special hoses for breathing);
- devices for artificial lung ventilation;
- control and measuring devices;
- laryngoscope;
- endotracheal tube.
What is a structure note and how does it work?
Exchange traded notes (or ETN - Exchange Traded Notes) are a type of structured product. Like any other structural product, notes consist of two parts:
- the protective part is usually a deposit or government bond;
- speculative part - it is based on a certain underlying asset, for example, a share, a set of shares, a stock index, a volatility index, etc.
Technically, the speculative part is an option that is exercised when certain conditions are met, or expires.
In simple terms, structured notes are investments in a deposit with the possibility of receiving additional income if the investment idea is implemented.
For example, an investor expects growth from Apple shares, but wants to hedge against a fall in price. In this case, he buys a structured note, the profitability of which directly depends on the dynamics of Apple’s value. So, if the company’s shares rise, the investor will receive, for example, 20% per annum. But if the company's shares fall, the investor will receive a guaranteed return - for example, 5%. The specific terms of the note are specified in the specification.
Thus, structured notes in investments are used to reduce risk and obtain a certain minimum return on the “buy and forget” principle.
Structured notes are available for purchase only to qualified investors.
The issuer of a structured note is a bank or broker, so there is an additional risk of bankruptcy of the issuer. Moreover, the note is technically a subordinated bond, therefore, it can be “written off” without undergoing a bank default procedure in order to recapitalize the institution.
For Russian investment notes, the issuer pays a coupon. As a rule, there are no coupons for foreign ETNs. The investor receives a reward at the maturity of the note, when the issuer repays the face value of the bond.
Advantages and disadvantages
Endotracheal anesthesia is a serious and responsible undertaking. Before surgery, it is important to familiarize yourself with all its pros and cons.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Increased controllability (you can easily vary the depth of anesthesia, increase the duration of anesthesia, and also facilitate immediate awakening of the patient) | The dosage of painkillers is carried out inaccurately (most often using old equipment) |
| It is possible to combine painkillers with the process of artificial ventilation of the lungs | Frequent contamination of the operating room air with vapors of anesthetic drugs during different operating modes of anesthesia equipment (except for a closed circuit) |
| Excellent combination of drugs required for general anesthesia | To obtain the expected result, complex medical equipment is required, which is expensive. |
| Total muscle relaxation (facilitates the process of long-term surgery on the abdominal and chest organs) | The procedure requires strict sanitization (if carried out incorrectly, it contributes to the spread of pathogenic microorganisms inside the hospital) |
| The separation of the respiratory and digestive systems is carried out using an endotracheal tube (this ensures the prevention of aspiration of stomach contents) | When clearing the trachea of accumulated fluid, damage to the mucous membrane of the oropharynx, tongue, hard and soft palate, damage to teeth and vocal cords may occur. |
| It is always possible to clear the trachea of accumulated fluid through an endotracheal tube | Incorrect placement of the endotracheal tube often leads to intubation of the right bronchus and esophagus |
| Small amounts of drugs are used | After surgery, airway patency and recurarization are impaired |
Main events
The endotracheal tube is connected to the ventilator, the patient is breathing stably, all indicators are normal. Under such conditions, anesthesia maintenance is organized using:
- intravenous administration of muscle relaxants;
- inhalation of nitrous oxide with oxygen;
- intravenous administration of Droperidol, Promedol, Fentinyl;
- inhalation of Ftorofan, Etran, Foran or other halogenated anesthetics.
In each case, measures to maintain anesthesia are selected individually. Anesthesia is organized at a level corresponding to the surgical intervention. Drugs can be administered urgently if necessary, and the dose can be adjusted according to the patient's response.
The ability to quickly adapt to the patient’s needs makes endotracheal anesthesia the safest for health.
How to do it step by step
The sequence of endotracheal anesthesia:
- Immersion in anesthesia is carried out by administering painkillers necessary to obtain deep anesthesia sleep without an exciting stage; modern barbiturates, fentonyl and promedol are used in combination with sombrevin. After administration of the medication, muscle relaxants are used, tracheal intubation is performed, then the patient is transferred to artificial ventilation to prevent normal gas exchange during surgery.
- Maintenance of anesthesia - a period that lasts throughout the entire operation. The main goal is to achieve the necessary components of anesthesia care and the environment for an experienced specialist to work. The human body is protected from operational risks. Anesthesia is maintained at 1 level of surgery. Its main stage is achieved with a mixture of nitrogen oxide and oxygen in a 2:1 ratio, halothane, and cyclopropane. Muscle relaxants are often used to reduce muscle tone. The main condition for endotracheal anesthesia is artificial ventilation of the lungs. Neuroleptics are administered in small portions - fentanyl and droperidol, 1-2 ml each, over 10-25 minutes. The anesthesiologist must intelligently manage the components of anesthesia and the body's abilities.
The figure shows how the procedure for administering endotracheal anesthesia is performed. - Awakening - the restoration of the previous functions of the human body begins at the moment when the anesthesiologist stops administering narcotic drugs. General anesthesia ends long before the invasion stops. First, specialists remove components of anesthesia that are no longer needed. Next, the final stitches are applied. The patient is sent to the recovery room and his health continues to be monitored.
Final events
When the operation is completed, the patient needs to be prepared to emerge from narcotic sleep. The drugs are discontinued gradually, the dosage is reduced smoothly.
At this stage, complications are possible, so to restore spontaneous breathing, Atropine is administered, and after 4-6 minutes Proserin. These drugs compensate for each other's side effects, start the lungs and stabilize the heart.
Administration of drugs at the final stage of anesthesia
The use of Proserin has contraindications; it should not be used:
- for bronchial asthma;
- for epilepsy;
- with angina pectoris.
If the patient suffers from allergic reactions or any chronic diseases, it is necessary to notify the attending physician about this so that this information appears on the card.
While the anesthetics and analgesics wear off, the patient may experience chills and discomfort from the endotracheal tube.
Extubation is performed after spontaneous breathing has been restored. For warming use:
- electric mattresses;
- heating pads with warm water;
- transfusion of warm solutions.
Preparation for extubation involves suctioning out accumulated mucus from the tracheobronchial tree. To collect fluid, an electric aspirator is used, a device that draws in mucus, blood, pus and other secretions.
After removing the tube, the oral cavity and esophagus are cleaned in the same way. If required, a tube is inserted into the stomach for lavage.
Read: What parents need to know about anesthesia
During the postoperative period, all vital signs of the patient are monitored. If any consequences or complications arise, measures are immediately taken to normalize the condition. Painkillers are discontinued as you feel better.
Specifics of implementation in children
Endotracheal anesthesia in children is a more complex process. The most important difference between adults and children is the amount of oxygen consumed, which is almost 2 times more in minors. In children, mucus secretion in the respiratory tract is increased. Experts also note the presence of narrow nasal passages and a large tongue.
Due to the fact that the larynx is located too high and the epiglottis has large volumes, when intubating the trachea, it is advisable to use a straight blade that will help raise the epiglottis.
The size of the endotracheal tube is of great importance, since the mucous membranes in children are very delicate, and a large-diameter device can affect the development of postintubation edema with tracheal obstruction after extubation.
To perform an operation on children 10-11 years old, it is necessary to use a tube without a lapel with a slight leak of gas flow around it; during ventilation, it is mandatory. It is important to know that the water-salt balance in minors is variable. This is due to daily changes in body weight, cell and tissue structure.
The kidneys are underdeveloped, so children do not tolerate water loads well and quickly remove electrolytes. It is important to maintain fluid infusions during operations with low blood loss. The process is calculated depending on the child’s body weight: 4 ml/kg per 10 kg + 2 ml/kg per 10 kg. Further 1 ml/kg for each kg above 20 kg. Maintenance therapy helps replace the fluid the baby needs.
After surgery, it is recommended to drink a lot of clean water to replenish fluid deficiency on your own. In a hot operating room, babies can overheat if their body temperature was elevated before the infection. Hyperthermia often develops as a result of the administration of atropine. The dosage of drugs in children also differs.
More often, anesthesiologists are guided by the following principle:
- for newborns – 1/10 of the adult dose;
- from 1 to 6 months. – 1/5 dose;
- 7 – 12 months – 1/4 dose;
- from 1 year to 3 years – 1/3 of the adult dose;
- from 4 to 7 years – 1/2 dose;
- from 8 to 12 years – 2/3 of the adult dose.
Complications subsequently of endotracheal anesthesia
Endotracheal anesthesia is not without complications .
Most often they occur during tracheal intubation, large blood loss, if the patient has diseases of the cardiovascular system or incorrect dosage of narcotic substances and relaxants. Consequences after surgery can be different, and the doctor is not always to blame. People have different sensitivities to medications. Therefore, each person tolerates endotraechal anesthesia differently. However, common complications include:
- Nausea.
- Sore throat, subsequently intubation.
- Injuries to the tongue, throat, teeth (also associated with intubation).
- Trembling in the body.
- Muscle pain.
- Blurred consciousness.
- Thoughts begin to get confused.
- Frequent itching.
- Half-fainting state.
- Possible lung infection.
- Allergic reaction, possible anaphylactic shock.
- Brain damage.
- Damage to the nervous system.
- It is possible that the tube may become dislodged during surgery.
- Laryngospasm after tube removal.
- Vocal cord injuries.
To avoid some complications , the laryngeal mask was invented in London in 1981.
Unlike the previous one, the laryngeal mask is inserted into the pharynx and is located at the entrance to the larynx. Tightness is ensured by inflating the cuff. This mask does not require work with a laryngoscope and other instruments. Due to the fact that the tube does not enter the larynx and trachea, the mask becomes safe for insertion and does not cause laryngospasm upon completion of the operation and recovery from anesthesia. But this mask also has its drawbacks. Firstly, it does not provide a tight seal at the entrance to the larynx from the esophagus, so there is a high probability of asphyxia.
Secondly, its use is impossible in emergency cases , due to the problem of a “full stomach”. Thirdly, the cost of the laryngeal mask is quite high, so its adoption is very slow.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for endotracheal (intubation) anesthesia are:
- performing surgical interventions on the chest organs, accompanied by surgical accumulation of air or gases in the pleural cavity;
- poor conductivity of the respiratory system channels;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- risk of aspiration of gastric contents into the respiratory tract;
- risk of rapid movement of liquids or gases in a direction opposite to normal;
- operations on the abdominal organs;
- difficulty breathing due to a certain position on the table;
- the likelihood of using muscle relaxants and artificial ventilation with intermittent positive pressure during the surgical process;
- surgical interventions performed on the facial skeleton and head (often used in cosmetology centers for plastic surgery);
- intranasal and ophthalmic invasions;
- treatment of the thyroid gland, upper ear, sinusitis (in this case, endotracheal anesthesia ensures the obstruction of blood and other biological fluids into the respiratory tract);
- operations aimed at treating intracranial diseases;
- dental treatment;
- long processes requiring the presence of microsurgical medical equipment;
- tendency to laryngospasms;
- frequent disruptions in the central nervous system.
But there are situations when this method of anesthesia is contraindicated.
These include:
- chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- inflammation of the bronchi;
- acute respiratory viral infections;
- hemorrhagic hemostasiopathies;
- pneumonia;
- malignant tumors of the oral cavity (there is a risk of cancer cells spreading throughout the body, so such people can only undergo endotracheal anesthesia through a tracheostomy);
- problems with the cardiovascular system;
- cachexia;
- anemia;
- old age;
- pregnancy;
- severe damage to the liver and kidneys (anesthesia will cause additional intoxication and distort the patient’s body’s response to anesthetics and their breakdown products).
Risks of structural notes
Owning investment notes involves taking on a number of risks:
- Firstly, the risk of a decrease in the value of the shares included in the note . If the note contains a basket of shares, then a decline in at least one of them is sufficient for the option not to be exercised and the investor to lose the right to receive additional profit. If an investor bets that an asset will fall, the risk is an increase in value.
- Secondly, the risk of non-payment of the coupon . For Russian structured notes, the issuer may not pay the coupon if the conditions do not match (and sometimes the coupon is “remembered” and paid later).
- Thirdly, the risk of early withdrawal . If the note is non-exchange, then it can only be sold to the bank or broker that issued the paper, and at a cost significantly lower than its face value.
- Finally, the last risk is the risk of bankruptcy of the issuer . In addition, the bank can write off its structural notes as part of additional capitalization (as “junior” debt).
Consequences and complications
Endotracheal anesthesia is an event during which adverse reactions, negative consequences and other complications rarely occur. More often they are associated with serious conditions of patients or medical errors. Every step of this anesthesia is potentially dangerous in terms of complications.
During water anesthesia and intubation, the following may occur:
- the impossibility of inserting an endotracheal tube into the trachea to ensure conduction of the respiratory tract due to technical reasons;
- asphyxia due to regurgitation of stomach contents into the respiratory system;
- severe pneumonia;
- damage to the laryngopharynx and a kind of continuation of the larynx - the trachea;
- improper bending of the endotracheal tube;
- sudden limitation of the available space in the respiratory tract, which leads to the impossibility of artificial ventilation of the lungs;
- lung rupture;
- inadequate oxygenation of the patient's body.
When anesthesiologists maintain anesthesia, the following may occur:
- disruption of the heart (up to cardiac arrest and further death);
- left ventricular failure;
- oxygen starvation;
- violation of the conductivity of the gas mixture;
- hemodynamic disturbances (drop in blood pressure);
- large blood loss;
- overdose of narcotic medications;
- pain shock (occurs when doctors violate instructions on the use of narcotic drugs);
- premature removal of the endotracheal tube in combination with insufficient monitoring of the patient (often leading to suffocation).
It is important to remember that during surgery the patient must be closely monitored and vital signs measured. Only timely measures can protect a person from complications. Fortunately, they happen very rarely!
Exchange-traded and over-the-counter notes
All structural notes are divided into two large categories:
- stock exchange;
- over-the-counter.
As the name implies, exchange-traded notes are traded on the stock exchange, as a rule, among bonds, i.e. in the stock section of the market. They can be bought and sold at any time, and their price is determined by supply and demand.
So, when the note is “in the money”, i.e. the conditions of the optional part are met, it costs more. If the note is “out of the money”, i.e. the conditions of the option part are not met, and the investor will receive only a guaranteed reward, then its price is lower.
Over-the-counter notes are sold exclusively by the bank or broker and are not traded on an exchange. To purchase such a note, you must enter into an agreement directly with the issuer.
I also recommend reading:
Investing in gas - TOP 7 ways to make money on blue fuel
In the past, natural gas was viewed as an almost useless additive to oil. Over time, the attitude towards him changed, [...]
The purchase price of an OTC note is usually equivalent to the face value. So, if an exchange-traded note costs, say, $10,000, then the investor buys one note at full price, even if the note is “out of the money.”
Over-the-counter notes are less liquid because they cannot be easily sold on an exchange or transferred to another person. An over-the-counter investment note can only be sold back to the issuer, and, as a rule, at a price significantly lower than the purchase price.
Despite these shortcomings, about 90% of all investment notes are OTC notes, since they are much more profitable for the issuer and allow the investor to earn more money.
The best drugs
Endotracheal anesthesia is a well-known type of anesthesia.
Modern inhalational anesthetics include:
- Sevoflurane is a new generation pain reliever. Has a pleasant smell. Causes rapid loss of consciousness due to the fact that it dissolves poorly in the blood. Often causes muscle relaxation. In some conditions it exhibits nephrotoxicity. Cost about 10,500 rubles. for 250 ml of liquid;
- Desflurane is a medicine similar to Isoflurane. Requires the use of special evaporators. It is poorly soluble in blood, so anesthesia occurs quickly. Used in bariatric surgery. Price about 12,400 rubles. for 240 ml;
- Isoflurane – the product is similar to Ftorotan. Has a pungent ether smell. It is not recommended to use it for operating on patients with coronary artery disease. Affects a decrease in the metabolic needs of the brain. Can be used for cerebroprotection in neurosurgery. The price of the medicine ranges from 5600 to 6700 rubles. for 250 ml;
- Ftorotan (halothane) is a well-known drug that contains halogen. Has a narrow therapeutic effect. Excellent for children with obstruction and reduced minute ventilation. It has a pleasant smell and does not irritate the respiratory tract. This is a very toxic product. After surgery, liver dysfunction and other pathologies may occur. Approximate cost – about 400 rubles. for 50 ml of liquid;
- Enflurane (ethrane) is a medicine that quickly induces general anesthesia. It is capable of inhibiting the functioning of the central nervous system, increasing the sensitivity of the myocardium to sympathomimetics and relaxing the skeletal muscles. Excreted by the lungs. Often used in obstetrics - during caesarean section. Enflurane can only be used using an anesthesia machine with a special evaporator.
Capital protection and participation rate
Structural notes are offered:
- with full capital protection;
- with partial capital protection.
Thus, with 100% capital protection, the investor will receive 100% of the invested funds in the event of an unfavorable outcome. With partial capital protection, for example, 70%, only part – in this case, 70%.
In some cases, capital protection above 100% is offered - for example, 115%. This means that the investor is guaranteed to receive a certain amount of compensation even if the option is not exercised.
The amount of remuneration depends on the participation rate . So, if the participation rate is 60%, then the investor will receive 60% of the increase in the underlying asset.
Typically, the higher the capital protection, the lower the participation rate. Conversely, the lower the capital protection, the higher the participation rate is assumed. That is, the investor can regulate his own level of potential profitability and accepted risk.
Example of a stock exchange note
To make it clear, let's look at a specific example. There is a certain investment note with 90% capital protection and a participation rate of 80% for the growth of the S&P 500 index. The terms of participation stipulate that the investor will receive a reward if the S&P 500 grows by at least 10% over the next 3 years.
- Option 1 : The S&P 500 fell, not rose. In this case, the investor receives 90% of the deposited funds and receives no additional remuneration.
- Option 2 : The S&P 500 is up only 5%. The conditions of the "bet" are not met, and the investor receives 90% of the capital.
- Option 3 : The S&P 500 is up 15%. The conditions are met, and the investor receives 80% of 15%, i.e. 12% (average annual return for 3 years is 3.85%).
- Option 4 : The S&P 500 is up 40%. The conditions are met, the investor receives 80% of 40%, i.e. 32% (average annual return - 9.696%).
Conditions for obtaining increased profitability may include:
- individual shares - in this case, the buyer of the note can bet not only on the growth, but also on the fall in the value of the shares;
- a group of shares - for example, the creator of the note selects 5 shares and sets the condition that each of these shares will not fall in price over the next 3 years;
- index – you can “play” to lower or increase the index;
- the price of a certain product - gold, oil, currency, etc.
An investor wishing to invest in structured notes should carefully study the terms of the award to adequately weigh the chances of a favorable outcome.
I also recommend reading:
Investments in equipment - profitability, risks, investment methods
Investments in equipment are part of the capital costs that are incurred by an enterprise to conduct its activities. Outside investors typically evaluate […]
Reviews from doctors and specialists
- Dmitry Agapov is an anesthesiologist. He believes that endotracheal anesthesia has little effect on the condition and functioning of internal organs and provides a controlled effect. This type of anesthesia is well suited for operating on young children. They inhale the anesthetic inhalation mixture through a mask and fall asleep without problems.
- Ekaterina Smirnova is an anesthesiologist who recommends endotracheal anesthesia to turn off the patient’s consciousness. He will not feel pain, the muscles will completely relax. After surgery, there is no memory of it at all.
- Experienced specialist Irina Lapshina believes that endotracheal anesthesia is the most powerful type of anesthesia, making the sick person completely immune to external stimuli. A combination of medications used in general anesthesia prevents the sensation of pain. They immobilize the patient during the procedure.
Endotracheal (intubation) anesthesia is the forced immersion of a sick person into a medicated sleep. It is only important before the operation to carefully study the information about this type of anesthesia, consult with your doctor and take the necessary tests to prevent the development of complications.
Author: Timokhina Angelina
Consequences of a tube in the throat
After tracheostomy, early complications may occur:
- bleeding;
- subcutaneous emphysema;
- erosive tracheitis with the formation of crusts that clog the lumen of the tracheostomy tube during coughing;
- tracheoesophageal fistula;
- tracheostomy infection;
- immersion of the trachea into the wound.
Late complications of tracheostomy include narrowing of the larynx, changes in voice, narrowing and bedsores of the larynx, and gross cicatricial changes in the skin in the stoma area. With prolonged pressure on the walls of the larynx, ischemic necrosis can develop. Tracheitis may form at the site of cuff pressure.