A newborn has different ears: why are the ears different shapes?
One of the common topics among concerned parents is the different ears of a newborn. This issue is often discussed in various forums, pediatricians are addressed with this complaint, they leaf through a mountain of specialized literature and an endless number of Internet sites. And as a result - even greater anxiety.
But is this phenomenon worth such parental nerves and worries? That is why we will next talk about the features of ear development and hearing function in infants, and also find out the causes of ear asymmetry.
Hearing in a newborn: stages of development
Newborn babies do not have very well developed vision, but their hearing is excellent. While still in the womb, babies hear many different sounds: the beating of mother’s heart, her voice, the noise of the outside world. He even begins to react to most sounds: he may flinch from a sharp sound and turn his head in the direction of the noise.
The formation of hearing in a newborn occurs in stages
Reference. By the time of birth, the child's basic hearing apparatus is already fully formed.
At birth, the outside world with all its sound wealth falls on the newly born little man. This activates his hearing function.
From this moment on, hearing will largely determine the development of the brain activity of a new person, initially stimulating certain skills (rolling over, sitting, crawling), and later speech and intellectual abilities.
Hearing development in babies goes through the following stages of formation:
- 1 month of life – the final formation of auditory function. The child begins to listen to the conversation and freezes if he hears a familiar voice. From an extraneous loud sound - he will flinch;
- 3 months – hearing and speech are already developed so much that the child can not only respond to his mother’s voice, but also “answer” her by babbling. But don’t rush to read fairy tales and poems to your baby - the baby is not yet able to concentrate on this;
- 5-6 months - children at this age respond to their name, turn their heads towards the sound, and listen. Loud, sudden noises can frighten little ones so much that they may burst into tears. And if you play with them, they will laugh;
- 6 months - 1 year - children begin to respond to sounds of varying intensities, easily recognizing where they come from. They hear and understand the voices of their parents. At the same time, the feedback is the children pronouncing an increasing number of words and accompanying them with various gestures.
Scheme of hearing development and the child’s interaction with the outside world.
Going through these stages of formation, hearing in children contributes to the development of speech ability. These two functions are closely interrelated. And if parents notice any deviations from the norm in the development of auditory function in their baby, rehabilitation must begin immediately.
In this regard, the age of 3 is critical, since later it will be very difficult to teach a child with hearing loss to distinguish sounds and understand speech.
Having examined the features of hearing development in newborns, let's move on to the question of why a child has different ears.
Why does a child have different ear shapes?
In many children, ear asymmetry disappears with age.
First, perhaps, it is worth reassuring the parents. Many experts do not advise worrying about this at all, since this phenomenon occurs quite often in children.
That's all: ears of different shapes, different sizes, one ear is protruding, and the other is normal - a phenomenon that simply disappears with age.
The ears become the same, but if by the age of 5 the ears have not “evened out”, then you can undergo a cosmetic procedure if this difference is so embarrassing.
To prove the above, here are the comments of several mothers on forums who have experienced these problems:
Marina: “Mommies, don’t worry and don’t sound the alarm ahead of time. When we noticed a difference in the size of our baby’s ears (she was 4 months old at the time), we immediately rushed to the doctor. He examined and felt our ears and said that everything would be fine. And yes, we are now 2 years old and our ears are the same!”
Anna: “I experienced this problem myself. As a child, I had different ears: one was normal, and the other was slightly curved and protruding. I was little and didn’t really understand this, but when I started to grow up, the problem disappeared by itself. Now she is the mother of two children: her daughter has the same ears, but her son got one ear from his mother, and the other from his father.”
It’s a completely different matter if the baby has different ears and this causes him discomfort. The ear can fold during sleep, after which it hurts. The baby can constantly tug and rub and comb it.
The causes of such defects can be either congenital or acquired. The following pathologies can be classified as congenital defects of the concha:
- Macrotia is an excessive growth of cartilage tissue, which affects the proportional formation of the ear, making it large.
- Microtia is a partial formation of the ear shell (small, flat or ingrown ears).
- Prominent ears - the position of the ear in relation to the head is not parallel, but at an angle. The greater the angle, the more the ear protrudes.
- Changes in the shape of the ear curl - the curl and tubercle on the auricle may be absent, rudimentary formations may form on it.
- The top of the cartilage may be folded inward and downward.
- Violations of the anatomical shape of the earlobe - double lobe, fused or its complete absence.
While almost every deviation is predominantly cosmetic, microtia can be associated with occlusion of the auditory canal, which leads to impaired auditory function.
Types of congenital deformation of the auricle
Reference. Each defect can be either unilateral or bilateral.
The acquired type of ear concha defects is caused by the following phenomena:
Keloid scar is an acquired form of ear deformation that occurs most often. The nature of its appearance and formation is varied. It looks like a growth on the skin in the area of the earlobe or the entire ear.
Conclusion
To a greater extent, this phenomenon causes aesthetic problems. They do not pose any harm to health, with the exception of some previously mentioned species.
In addition, for very young children this condition (if it does not bother or cause discomfort) does not represent anything terrible and in most cases simply disappears with age, leaving a mark only on the nervous system of the parents.
gorlonos.com
Bathing
- You can bathe a newborn girl as soon as the umbilical wound dries. Up to six months, baths should be daily, then you can bathe the baby every other day, and when she reaches a year, even less often, replacing bath procedures with showers.
- You should carefully wash all the folds and spaces between your fingers and toes.
- It is recommended to use soap (not toilet soap, but a special one for children, with a minimum amount of additives!) or baby foam no more than 1-2 times a week, and do not add it to water, but apply it to the skin and wash it off with a shower. Soapy water dries out the vaginal mucosa. There is an opinion that until the moment the child begins to crawl on the floor (i.e., until the moment when he can really get dirty) or until the moment when the baby begins to eat complementary foods (i.e., smearing porridge on his face with his hands or puree) - there is no point in washing it with soap, because the child does not get dirty with anything and is constantly either in the arms of his parents or in a clean crib. And once again disturbing his skin with soap products is not only pointless, but also harmful - the protective layer of the skin is washed off. But, firstly, daily bathing in clean water is still necessary, and secondly, this does not exclude washing the child with soap after he pooped.
- Adding various herbal infusions to the bath is at your discretion. However, it must be borne in mind that almost all of them dry out the already dry skin of babies. At the end of winter and spring in cities, an increased amount of chlorine is added to the central water supply, which greatly dries out the skin of children during daily bathing. In this case, it is recommended to add special softeners to the bathing water, for example, calendula bathing agent (Weleda has this). And after bathing, lubricate the baby’s skin with baby oil.
- A newborn girl should use her own, purely individual, bathing set: towel, washcloth and mitten. By the way, you can wash the baby with a piece of gauze instead of a washcloth, since it can be washed and boiled.
- After bathing, the newborn girl is blotted dry with a clean towel or warm sheet, and the skin folds, if necessary, are treated with baby hygienic oil.
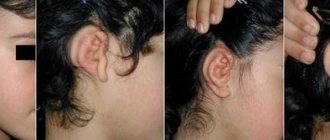
Different ears on a newborn baby
Doctors state the fact that at birth many children have ears of different sizes and positions. How bad is this deformation of the ears? Should we be afraid of the consequences? Will the size of the ears somehow negatively affect hearing and what can be done about it? We will try to answer all questions in our material.
Why does a child have different ears?
At birth, infants often have different ears:
- by size, when one ear is larger than the other;
- protrusion;
- drawing of the ears;
- location.
Causes
Doctors classify the causes of different ears by type:
- congenital;
- acquired.
Congenital causes include the anatomical features of the formation of cartilage and bones of the ear system. Deformation of cartilage tissue can lead not only to macrotia - a disproportionate increase in the external auricle, but also to protruding ears. Also considered congenital is a defect when the upper cartilages of the auricle fold down, which creates the effect of drooping upper tips of the ears. These changes may be hereditary or related to the position of the fetus during the formation of the external ear.
Thickenings, tumors, scars, wrinkles on the ears are acquired defects.
This is important: Ears that are different in size at birth can spontaneously straighten out up to 6 years of age, while the child’s auricles are forming. This defect is not a pathology and does not require treatment.
In what cases is surgical treatment used?
If after 6 years the ears remain different in shape, but this factor does not bother the child in any way:
- ears don't hurt;
- hear well;
- no noise, itching or discharge.
This defect can be considered cosmetic. It requires surgery only if it causes psychological discomfort to its owner. When a child is laughed at, his ears are pulled, his peers call him names, then such a child is in constant stress, and this negatively affects his overall health. Then, after consultation with an otolaryngologist, you can resort to surgery to straighten the outer auricles. If this defect can somehow be covered with hair, a hat, etc., then the doctor will advise the parents to avoid surgery. But if they and the child are adamant and continue to demand surgical intervention, then in the absence of contraindications such an operation can be performed.
Contraindications may include:
- poor blood clotting;
- any diseases of different organs;
- diabetes;
- tumor or cyst formations and so on.
The doctor is obliged to warn you about possible complications or unpleasant consequences after surgery:
- bleeding;
- suppuration of sutures;
- inflammation of the cartilage, as a result of which wrinkles may remain on the auricle;
- the presence of scars and so on.
Is this feature dangerous?
Different ears are absolutely safe for hearing health. As a rule, this visual defect disappears by 5-6 years. It does not in any way affect the ear system itself, or the health of the organs, tissues, or cartilages of the complex auditory mechanism. Therefore, you can live peacefully with different ears. If this fact still confuses you, then you can:
- make an asymmetrical hairstyle that hides one ear;
- wear bandanas or headscarves;
- cover your ears with long hair.
We must remember that any operation is a direct surgical intervention in the body. It’s all the more offensive that in this case, it’s in a healthy body. Make this a plus for yourself - your zest. Or just be humorous about your ears. After all, the main thing is that they are healthy.
Rate:
StopOtit.ru » Additional information - tips and tricks
stopotit.ru
Nasal care
It is necessary to carefully ensure that snot and crusts do not accumulate in the girl’s nose and that she has the opportunity to breathe fully. Therefore, you need to clean your baby’s nose, if it is filled with crusts, every day. The crusts are pre-softened using sterile vegetable oil. To clean the nose, it is preferable not to use store-bought cotton swabs: those with a limiter will not be able to penetrate to the required depth, and without limiters you risk damaging the baby’s nasal mucosa. Prepare small flagella (“turundas”) from cotton pads and, carefully inserting them into the nostrils, clean out the contents of the nose with gentle rotational movements. It is better not to use children's nasal aspirators, because... with frequent use, you can damage the nasal mucosa and disrupt its microflora. In addition, there is an opinion among experts that the recently noted earlier appearance of adenoids in children, the proliferation of the nasal mucosa, is also a consequence of too zealous care of the nasal mucosa by parents (frequent use of aspirators, nasal sprays, etc.) .
Different ears in a newborn
Currently, many young parents are often faced with the problem of different ears in a newborn child. Naturally, it causes concern and many questions for pediatric doctors, so the etiology of such features should be studied in more detail.
Causes and types
Differences in the ears of infants can be manifested by the following morphological characteristics:
- Size.
- Position in relation to the head.
- Anatomical pattern on the ears.
- Symmetry.
- Form.
The causes of such changes in the ears of infants can be congenital, acquired developmental anomalies, as well as minor functional characteristics of each baby, which disappear over time.
Congenital developmental defects are disorders that arose during the prenatal period. At this time, the child’s body is just forming, and the formation of one or another organ system is often disrupted. The auricles normally consist of cartilage tissue, the formation of which, unfortunately, is also sometimes affected.
Among the birth defects, the following are distinguished:
- Macrotia. Excessive amount of cartilage in the ears, which makes them visually appear larger.
- Microtia. Insufficient development of ears (one or two). These ears are quite small, slightly flat or ingrown. This pathology often causes hearing loss.
- Prominent ears. Normally, the ears are located almost parallel to the head; with protruding ears, they are located at an angle. The larger the angle, the greater the so-called protrusion of the ear.
- Changes in the ear helix (tragus). In some cases, it is completely absent, as is the tubercle. Instead, rudimentary elements (those that are not needed for humans) can develop; they do not cause much discomfort.
- Change in the shape of the upper part of the cartilage. It may be bent downwards and slightly inwards.
- Anatomical changes in the earlobe. Double, fused, completely absent.
Of the listed deviations, only microtia is a consequence of occlusion of the auditory canal and leads to impaired auditory function. All other defects are cosmetic.
Acquired defects are considered: tumors, thickenings, scars, wrinkles that form on the ears.
Should I worry?
Of course, if differences are detected in the structure of a newborn’s ears, it is better to seek advice from a pediatrician so as not to miss the above-mentioned congenital developmental anomalies. If they are nevertheless detected, then it is worth finding out whether this in any way affects the child’s hearing and whether it causes discomfort. If not, then this should not be a cause for concern, since it will not affect the general condition of the baby in any way.
True developmental defects are quite rare, and in most cases there is nothing to worry about.
Treatment
Different ears are considered a cosmetic defect. Usually it is not treated in any way and they try to cover it up with long hair, wearing bandanas, scarves or panama hats. In this case, girls find it a little easier to cope with such a problem.
However, due to such characteristics, children may suffer from serious conflicts in kindergarten and at school; they begin to be ashamed of their appearance, which brings psychological discomfort.
In such situations, parents ask a doctor to somehow correct the situation. Most often, defects can be corrected through surgery; it can only be performed after consultation with an otolaryngologist. In most cases, doctors advise avoiding surgical procedures, but the final word remains with the parents.
Before performing the operation, all contraindications should be taken into account:
- Poor blood clotting.
- Diabetes.
- Cyst or tumor formations.
The doctor must also warn about the presence of possible complications and consequences that may arise after the operation:
- Bleeding.
- Festering of the sutures.
- Inflammation of the cartilage, which provokes the formation of wrinkles on the auricle.
- Scarring.
Different shapes and sizes of ears are absolutely safe for the normal functioning of the auditory mechanism and do not have any effect on the ear system or the health of tissues and cartilage. This visual defect most often disappears by 6 years.
elaxsir.ru
Meeting your baby after birth
The first days and weeks of a newborn's life are a time of great wonder and delight for most new parents. Feeling responsible for such a fragile creature, you may be intimidated by the fact that you are not familiar with what a normal newborn looks and acts like. If you feel anxious or unsure about any aspect of caring for your baby, do not hesitate to reach out to your doctor, other healthcare providers, family members, or friends who have experience caring for a newborn. Their advice and friendly participation will help you overcome your first fears and become more confident in your own abilities.
Why does a child have different ears: an expert answers
People say a lot about the shape of their ears, other than judging success in life, financial wealth or self-confidence. Lop-eared, different-eared, crooked-eared, ears with a fused lobe, ears with a fleshy lobe or a protruding ridge. Physiognomists like to draw conclusions about a person’s abilities based on the shape of their ears: they say, he has musical talent or he is a classical leader. In fact, this is only a matter of physiology.
Natalya Beglyarova, geneticist, expert at the Center for Molecular Diagnostics (CMD) of the Central Research Institute of Epidemiology of Rospotrebnadzor, told Letidor why the shape of the ears is not the same as that of the parents, and in what cases the shape of the auricle can indicate the health of the child.
The shape of the ears and their size are formed during the fertilization of the egg by the sperm. In most cases, babies are born with ears similar to their parents. But sometimes, contrary to the parents’ expectations, the newborn exhibits structural features of the auricle.
As a rule, the cause of congenital deformity can be a violation of the intrauterine development of the fetus, as a result of which the outer rim of the auricle and the underlying cartilage are formed incorrectly.
Some infectious diseases in women during pregnancy also have a serious impact on the development of the auricle:
cytomegalovirus infection, toxoplasmosis, rubella and herpes infection, herpes zoster.
If a woman encounters the causative agents of these diseases for the first time, there is a serious risk of developing other more serious malformations. Therefore, screening for these infections (the so-called TORCH complex) is recommended for every woman not only during pregnancy, but also when planning it.
Provoking factors are also diabetes mellitus, difficult pregnancy, taking toxic drugs during this period and bad habits of the expectant mother.
Genetic factors (mutations) also play a role, but the likelihood of developing ear pathology in this case is low.
The ear is a complex multicomponent system.
are responsible for the characteristics of the earlobe.
And how many of them are involved in the formation of Darwin’s tubercle or cochlea of the auricle!
So it is impossible to predict what the ears of an unborn child will be like.
Deformation of the auricle usually becomes obvious at birth or in the first months after birth.
The most common pathologies are:
- protruding ears, we can talk about it if the angle between the ear and the surface of the head is at least 30 degrees. In some cases, the ears may be located at a right angle, that is, actually perpendicular to the head;
- the upper part of the auricle bends inward, usually due to incorrect position of the fetus during pregnancy;
- deformed curl of the auricle;
- structural features of the lobe, which bifurcates or fuses with the head.
All these defects of the auricle do not affect hearing and have only aesthetic significance.
But sometimes there are serious pathologies that are accompanied by hearing problems.
We are talking about excessive growth of cartilage tissue and underdevelopment of the ears. As a rule, in this case the ear canal may be partially or completely closed, and then surgery is prescribed for medical reasons.
There are also various types of deformation of connective (cartilaginous) tissue as one of the manifestations of a whole group of hereditary diseases, although relatively rare.
In most cases, we are talking about the aesthetic preferences of parents (most likely mothers), who may not like the fact that the child’s ears are too large, protruding, or, in their opinion, ugly in shape. Accordingly, the issue of surgery is decided based on how the parents and the child himself perceive imperfect ears.
Aesthetic surgeries to correct the auricle are usually performed on children from the age of 4-5, when the auricle is already formed, or later.
When deciding whether to undergo surgery at school age, it is worth considering that this may cause additional psychological distress. In addition, the postoperative period takes some time, which will have to be chosen taking into account the school schedule.
In most cases, aesthetic surgeries are performed using a laser, which is the most accurate and effective method of surgical intervention, carries minimal risks and requires less time.
However, in some cases surgery is also required. The method of surgical intervention can only be chosen by a doctor, taking into account the age of the small patient and the type of pathology.
Photo: Shutterstock.com
letidor.ru
In the first days
During the first time after birth, a light gray or creamy coating - remnants of smegma, the original lubricant. If there is not a lot of plaque, it will gradually be absorbed into the skin. However, if the plaque is abundant, it is recommended to remove it, since after a day or two the fats it contains oxidize, causing the proliferation of microorganisms and, ultimately, inflammation. This plaque is quite dense, so it needs to be removed delicately, in several steps. It is best to use cotton swabs and warm boiled water for this. The plaque will be removed in pellets and will completely disappear in 2-3 days.
Acute otitis media
Diagnostic feature
Clinical diagnosis. The sequence of development of acute otitis media is the same as in children of other age groups: catarrhal stage of inflammation, formation of exudate, perforation of the eardrum and suppuration from the ear, development of complications or favorable resolution of the process. The most important symptom of the disease—ear pain—in newborns and infants is detected by changes in the child’s behavior. Acute pain occurs suddenly and is usually so severe that the child holds his breath. Children in the second half of life stop playing and grab their ear with their hand. When sneezing, swallowing, coughing, accompanied by an increase in air pressure in the tympanic cavity, the pain intensifies; sometimes the pain subsides. The child is inhibited, pliable, drowsy. At certain intervals, the painful attack is repeated with the same or greater intensity. Sometimes the child’s restless behavior is replaced by seeming calm, the child sleeps a lot, falls asleep during feeding, and is lethargic, which indicates depression of the nervous system. Body temperature rises; children sleep poorly, often wake up screaming and do not calm down for a long time, shudder, moan. The facial expression is pained, a fixed gaze, painful grimaces. Changing the child's position does not have a calming effect.
A child under 4-5 months cannot localize the pain, only helplessly turns his head. Erratic and obsessive movements are observed: a pendulum-like movement of the head and a “symptom of chewing the tongue.” The reason for these movements is the child’s desire to find an optimal position in which the ear would hurt less. At the height of pain, hand cramps (kapellmeister's position) or false opisthotonus are possible. As intoxication increases, convulsive contractions of the eye muscles may occur. Children in the second half of life reach out with their hands to the sore ear, rub it with the back of their hand, and try to stick their finger into the ear canal. Infants refuse to eat; They are more willing to suckle on the breast opposite the side of the sore ear. Pain when pressing on the tragus is characteristic (Vash's symptom), since pressure is directly transmitted through the non-ossified part of the ear canal to the inflamed eardrum (after a year of life, pain when pressing on the tragus indicates only damage to the external auditory canal).
Diagnosis of ENT diseases in infants
Examination and treatment of children differs markedly from working with adult patients. A young patient cannot always clearly explain what is bothering him; he does not know how to properly dissolve pills or gargle. The ability and skills of a good pediatric ENT doctor to find an approach to a sick child and establish psychological contact with him are no less valuable than the professional skills of an otolaryngologist. The physiological and anatomical characteristics of a small child’s body determine the specificity of treatment procedures, examination of ENT organs, and anesthesia (if necessary).
Modern methods for diagnosing ENT pathology include: clarification of parental complaints, questions of the diagnostic and treatment complex, etc., objective examination, laboratory tests, endoscopic and computer studies of the nose, throat, and ear, ultrasound.