December 3, 2020
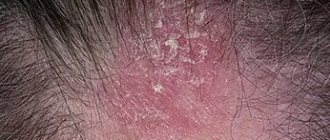
Contact dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin in an area that has come into contact with an irritating substance or environmental factor. Children under 12 years of age are most susceptible to the disease. The point is the structural features of children's skin and the weakness of its protective mechanisms. The disease manifests itself in any area that has been in contact with the irritant, but more often on the face, arms, neck, and groin area.
If the provoking agent is recognized in time and the child is protected from it, the inflammation is well treated and the symptoms quickly pass. When the cause is difficult to identify or parents do not consult a doctor on time, the course of the disease becomes more severe.
Contact dermatitis occurs:
- simple - local irritation by some factor;
- allergic.
The second option will appear when the child has an increased sensitivity to this substance. The first interaction with it is outwardly unnoticeable, but chemicals are formed in the skin that bind to immune cells - T-lymphocytes. Immune cells remember the stimulus. Upon repeated contact, which can occur after a long time, T-lymphocytes trigger an allergic reaction and cause skin symptoms.
How to recognize allergic contact dermatitis in a child
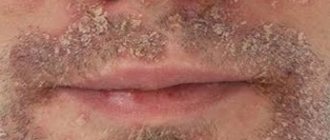
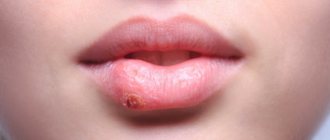
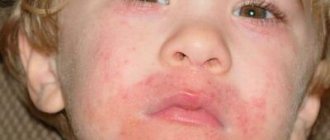
The contours of the inflammation often coincide with the outlines of the object that caused the irritation. The rash spreads little beyond the area of skin that came into contact with the causative factor. The skin here becomes red and swollen, very itchy, blisters, wounds and crusts appear.
Fungal and bacterial infections easily attach to wounds and suppuration occurs. Babies may experience an increase in general temperature.
Frequent exacerbation in the same places leads to unpleasant outcomes: areas of increased or decreased pigmentation, scars, thickening and roughening of the skin.
If you notice a rash or red spots on your child’s skin, be sure to see a doctor to get tests done to determine the exact cause and begin treatment.
The disease may worsen. To prevent this from happening, you need to find and eliminate the provoking causes.
Methods of treating diathesis
When dealing with diathesis in a young child, the main thing is to choose the right diet, excluding foods that may cause an allergic reaction.
For a child in his first year of life, it is very important to receive breast milk.
The proteins of human milk are easily broken down by the baby's enzymes and are completely devoid of allergic properties. However, a nursing mother must also follow a diet excluding fish, poultry, tomatoes, chocolate, smoked meats, spices and other allergenic foods.
When mixed feeding, the child should not be given some juices: orange, carrot, tomato. Introduce any new product carefully - from a small amount. It is important to prevent an allergic exacerbation, and at the same time, to give the baby’s body everything it needs for its development.
Specialist consultation
The Family Doctor pediatric allergist-immunologist will help you deal with your child’s skin problems, determine the cause of allergies, and also build a rational diet that is suitable specifically for your child.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
External causes of the development of allergic dermatitis in children
The disease can be caused by one of the factors or a combination of several.
- Physical - friction or pressure on the skin of fabrics, leather products, high or low temperatures, humidity, electric current, ultraviolet or x-rays.
- Chemical - various acids and alkalis, substances included in creams and hygiene products, medicines, tobacco smoke.
- Biological - sap and pollen of plants, bites and secretions of insects and animals.
Of the plant agents, the most dangerous are the juice of celandine, hogweed, nettle, pollen of meadow and weeds.
In industrial cities in winter, there are widespread cases of contact dermatitis under the eyes and on the hands of children. Three factors are combined here: cold, chemical impurities in the air and touching the skin with wet mittens.
In infants, allergic inflammation can be caused by a combination of high humidity in diapers, fabric friction and the action of inappropriate cream.
A special type of contact dermatitis is phototoxic, when sunscreens degrade in sunlight and cause allergic damage to the epidermis.
Caring for a child with dry, sensitive skin - tips for parents
At the moment of birth, the child finds himself in new conditions; he moves from the dark, warm and constantly moist uterine cavity into the air space.
The largest organ of the body, the skin, which protects the baby from all external negative influences, is gradually being rebuilt to a new level of work. In the first months of life, the skin is not ideal: it turns red, peels, becomes dry, or becomes covered with small pimples.
These are completely acceptable reactions after a long stay in a humid environment, surrounded by amniotic fluid. The functioning of the skin in the air, where temperature, humidity and the speed of air flow constantly fluctuates, requires a certain “tuning”. This takes on average about a month.
Therefore, it is important to properly care for your baby from the first days, maintaining the health of his skin, and to know what products are needed, how to avoid problems, what is needed for hygiene, how to help with minor injuries, rashes, and itching?
Sensitive skin is a major problem
A baby's skin is thin, delicate and more sensitive than that of an adult. This is due to the structural features of the children's epidermis: the cells do not adhere so tightly to each other, lose moisture faster and peel off at the slightest negative impact.
The sweat and sebaceous glands are just adjusting their work, so they either work too sluggishly, then the skin dries and cracks, or they produce an excess of secretions - then pimples, clogged pores and sweating occur.
Considering that approximately 20% of children have an initial hereditary predisposition to allergies, including skin allergies, proper care of the baby from the first days after birth becomes one of the main tasks.
Risk areas are the skin in the diaper area, in contact with urine and stool, the face, and natural folds of the skin.
The most common problems for children are diaper rash, prickly heat and dry, flaking skin, even cracking in particularly affected areas. This is not a very pleasant sight, especially if it is just a baby who himself will not complain of irritation and pain, itching and discomfort.
Dry skin of a child can be easily eliminated with the help of simple home measures; only in rare cases does the baby need the help of a doctor and the use of any medications.
Features of a newborn
To understand why dry and hypersensitive skin occurs in children, parents must understand the specific physiological changes in the epidermis of the newborn.
Babies are born covered with a whitish coating of vernix caseosa (vernix caseosa). The cream-like substance coats and protects the baby's skin from amniotic fluid until the baby is born. After childbirth, the lubricant is wiped off the skin, and the epidermis is exposed to air and bacteria, which gradually colonize its skin.
Deprived of lubrication, the top layer of skin dries out and peels off a few days after birth. Consequently, some dry skin is common in newborns.
Experts say newborns don't need extra moisturizer or lotions in their first month of life. They need to properly adjust the functioning of the glands and the activity of the upper layers of the epidermis to work in new conditions.
Excessive use of creams, cosmetics and various moisturizers during this period can only do harm!
As a child gets older, dry skin develops in response to certain external and internal irritants. In this situation, parental attention and immediate elimination of irritants are important.
Dry skin in children: what factors are to blame?
Dry skin (medical term: xeroderma) is mainly caused by increased loss of moisture, which leads to cracking and peeling of the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin.
Factors that affect the functioning of the epidermis and its condition:
Weather . Extreme cold and extreme heat significantly affect humidity, causing the skin to lose moisture and dry out at a high rate.
Temperature and humidity in the nursery. If the temperature at home is very high or too low, the air in the rooms will gradually lose moisture and dry out the child’s skin.
By the way, heaters and air conditioners dry out the air a lot, so humidifiers for an apartment are a very useful thing, especially if you have kids.
Long baths. Bathing a child for too long washes away the natural protective hydrolipidic film on the skin secreted by the sebaceous glands. Taking a bath in potassium permanganate-treated or chlorinated water or herbal decoction damages and dries out the skin.
Hard soap. Regular, non-baby soap is too “harsh” for a child’s skin, which causes it to become dry. “Adult” cosmetics and bathing products have a similar effect.
These were common conditions that a child might encounter in everyday life. But dryness and irritation can also be a sign of a serious problem with your baby's skin.
There are many reasons that explain dry skin in children. But it is important for parents to know what symptoms should cause alarm when the baby needs help.
Actually, parents quickly notice dry skin, and quite simple methods eliminate irritation. But there are a number of symptoms that require you to visit a pediatrician or dermatologist.
These include:
• bleeding from cracked skin; • severe itching, which makes the child whiny and irritable; • pus or yellow crusts on dry skin; • swelling of the epidermis, increased temperature; • dry skin, causing colic attacks.
How to care for your baby's skin?
Preventing and treating dry skin is quite simple and all you need to do is follow a few simple steps and procedures.
Limit your baby's bath time. Prolonged stay in the bath, especially in hot water, washes away the natural protective film from the skin, leaving the epidermis vulnerable to the external environment. Experts recommend limiting bath time to ten minutes in warm (not hot) water.
Use mild, delicate soap. Always use soap specifically made for children as it does not contain harsh or harmful chemicals. Choose bathing gels and liquid soaps with added moisturizers as they protect the skin. Avoid soaps containing dyes and fragrances, as they quickly dry out the skin and cause allergies.
Follow the washing regime. Even if it is a gentle soap, it does not have to be used daily. It is enough to wash the child’s body and head with shampoo and soap 2-3 times a week or when the baby is very dirty. The rest of the time, washing with warm water is enough.
Use moisturizing lotions after bathing your baby . From about one month of age, moisturize your baby's entire body immediately after a bath using a hypoallergenic body lotion. The fats in moisturizing lotion form a thin layer on the skin that replenishes and prevents further moisture loss. Using moisturizers is the safest home remedy for baby's sensitive skin.
Choose clothes made from natural fabrics and without tight seams. Natural fabrics such as cotton are soft, non-allergenic and allow the skin to breathe easily. If your child has dry skin, it is important to switch to cotton clothes.
Use baby detergent. Children's clothes and bedding should be washed only with special baby powder without caustic chemicals or allergens. Look for a detergent designed for children with sensitive skin.
Use a humidifier. Dry air is the worst enemy of a child's skin. Use a portable cool mist humidifier that maintains a constant level of air humidity and prevents moisture loss from the skin.
Dress your child according to the weather. It is important that during walks the child does not freeze, but does not overheat. Very hot or very cold air lacks moisture, which can increase skin dryness and irritation.
Don't forget to give your child water more often . In hot weather or when the air is very dry, the body loses more moisture. Therefore, it is important to monitor the baby’s drinking regime. Infants need to be put to the breast more often; artificial babies and children receiving complementary foods should be offered a bottle of water more often.
Simple prevention and treatment steps can help relieve dry skin quickly. Parents should constantly ensure that their child has silky smooth skin.
Alena Paretskaya
Photo depositphotos.com
The opinion of the author may not coincide with the opinion of the editors
Dermatitis in a child and psychosomatics
Skin health directly depends on a person’s mental well-being. Stress changes hormonal levels and metabolism, causing disruptions in the functioning of the immune system. Therefore, a calm emotional state will prevent exacerbation of the disease and delay the first appearance of symptoms.
When faced with contact dermatitis, analyze the causes and identify the allergen that caused it.
It's not always easy. To be sure of the correct diagnosis, conduct the necessary tests and receive treatment, come for a consultation at our center. In addition to treatment, you will learn how to properly prevent this disease. December 3, 2020
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich
Symptoms
With atopic dermatitis in children, skin tightness, redness appears, the skin flakes, feels rougher to the touch, and thickening may appear. Microscopic bubbles form, around which moisture is released. The child is worried and scratches the affected areas. When an infection occurs, local inflammation develops and the wounds heal poorly. With significant spread in young children, general intoxication of the body manifests itself: the temperature rises, the peripheral lymph nodes enlarge. Due to severe itching, sleep and appetite are disrupted, and the child often cries. Dermatitis most often affects the face, neck, armpits, scalp, groin, areas under the earlobes, popliteal fossae, and elbows.
What to feed a child with atopic dermatitis
In order not to provoke an exacerbation of dermatitis, to relieve itching and redness of the skin, you need to follow a diet. Foods that burden the immune system are excluded from the children's diet: citrus fruits, chocolate, eggs, honey, seafood. Red (strawberries, cherries, currants, apples) and exotic (mangoes, coconuts, pineapples) fruits are dangerous.
Split meals are recommended: small portions every 3-4 hours. It is better to boil, stew, bake, but not fry. Do not use spices, black pepper. The diet should be balanced and contain enough protein, vitamins, and microelements.
Avoid giving your child sugary carbonated drinks, chips, crackers and other snacks for as long as possible. If the infant is receiving breast milk, introduce new foods carefully. Add the product once a week to make sure it doesn't cause breakouts. After meals and between meals, offer your baby clean boiled water.
Hormonal ointments for diathesis
A special group of local drugs used for diathesis are hormonal ointments. They are used if non-hormonal drugs do not help. Hormonal drugs have a more serious composition, including hormonal components - glucocorticoids. These are steroid hormones synthesized by the adrenal cortex. The most common among them are:
- Natural glucocorticoids: cortisol, hydrocortisone. Their effect lasts for 8-12 hours.
- Synthetic analogues: prednisolone, prednisone, methylprednisolone, mometasone, clobetasol. The substances act within 12-36 hours.
- Synthetic analogues containing fluoride: dexamethasone, betamethasone, paramethasone, fluprednisolone. The effect of the substances lasts up to 3 days.
Such substances have the following effects:
- Antiallergic. Hormones reduce the level of basophils - substances activated during allergies.
- Anti-inflammatory. Substances reduce the level of inflammatory mediators in the blood.
Hormonal drugs have a faster effect, but also have a more impressive list of side effects. For this reason, few hormonal ointments are approved for children, and they try to resort to them in extreme cases, when the child’s condition is advanced and he suffers from itching, large lesions and other unpleasant symptoms.
The list of hormonal drugs used for diathesis includes:
- Advantan (methylprednisolone) – from 4 months;
- Lokoid (hydrocortisone) – from 6 months;
- Afloderm (alclomethasone) – from 6 months;
- Beloderm (betamethasone) – from 6 months
- Dermovate (clobetasol) – from 1 year;
- Elokol (mometasone furoate) – from 2 years.
What are the dangers of using hormonal ointments for diathesis?
Because children have a larger surface area to weight ratio than adults, they are at greater risk for side effects from hormonal medications. With long-term use there is a risk of growth and development disorders. For this reason, children are prescribed minimal doses of ointments, as well as short courses. For example, Advantan cannot be used for longer than 4 weeks.
There are other features of the use of hormonal ointments associated with the small surface area of the child’s body. For example, Beloderm ointment is used very carefully and should never be applied under a diaper, since due to the increased absorption of the active components, the risk of developing serious side effects increases.
It is equally important to apply hormonal ointment with caution in the area of body folds. In these places, the ointment is absorbed more actively and can have a systemic effect on the body, that is, enter the bloodstream and influence from the inside.
In the case of hormonal ointments, it is also important:
- do not exceed the prescribed dosage;
- use the amount of ointment prescribed by the specialist;
- do not extend the period of use (in most cases no longer than 5 days);
- Apply only to the affected areas.
Bathing
After a light shower to thoroughly cleanse your entire body, apply Atopic Bathing Gel to damp skin from head to toe, massage lightly and rinse thoroughly. Dry your baby with a soft towel using blotting, but not rubbing, movements. After water treatments, apply Atopic skin softening cream for daily care. Apply it several times throughout the day: after washing your hands and washing your face.
When taking a bath, the water temperature should not exceed 36 degrees. Place your child in the water and offer him toys or other entertainment. After 5-7 minutes, apply Atopic Bathing Gel from head to toe and rinse well. After bathing, use Atopic cream for daily care, and if itching bothers you, let the cream absorb, and then treat the affected skin with an anti-itching drug.
Prevention
Atopy is translated from Latin as strangeness. The causes of the disease cannot always be determined. But long-term observation of patients and members of their families has revealed that it develops more often:
- with a genetic predisposition - if the parents are healthy, the probability of developing dermatitis in the child is 20%, if one of them is sick - 50%, if both are sick - 80%;
- in case of unfavorable pregnancy, active or passive smoking of the expectant mother, consumption of food that provokes allergy attacks, use of certain medications;
- when a newborn is in a dusty room, insufficient care for his personal hygiene;
- with prolonged exposure to allergens that enter the child’s body with food through the respiratory tract.
Breastfeeding for up to 6 months and avoiding allergy-provoking foods reduces the likelihood of developing atopic dermatitis.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with an allergist-immunologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT) - maintenance course (excluding the cost of the drug) | 8100 rub. |
Hives
- Symptoms
Your baby may develop a rash in the form of blisters ranging in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters. Against the background of an acute allergic reaction, swelling may develop. Sometimes individual blisters merge with each other and affect large areas of the skin.
- Treatment
The doctor chooses a course of treatment depending on the cause of the condition. Thus, urticaria often appears as a reaction to insect bites, medications, pollen, foods, etc. This condition can be closely associated with systemic diseases, and sometimes occurs spontaneously. The basis of therapy is the exclusion of the factor that provokes this specific reaction. Your doctor may recommend a hypoallergenic diet even if your hives are not caused by food. If a reaction to cold, heat, or ultraviolet radiation occurs, the baby’s skin must be reliably protected from this factor. The doctor may prescribe antihistamines to treat allergies on the child's cheeks.
Rating of the best remedies for atopic dermatitis
To treat atopic dermatitis, use special children's products recommended by a dermatologist. During exacerbations, medications are prescribed for oral administration, application to atopic areas and general body care:
- preparations for removing allergens from the body - Enterosgel, Lactrofiltrum, Enterodes;
- skin softening products – Atopic cream for daily care;
- drugs that relieve itching - Panthenol spray;
- bathing products - soft shower gels for atopic dermatitis should be purchased at the pharmacy: dermatologists recommend using Atopic bathing gel from head to toe.