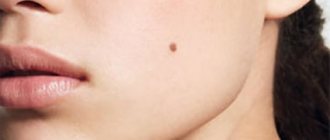
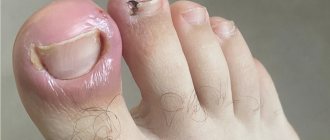
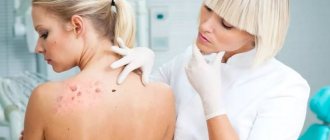
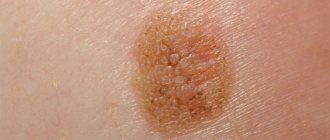
Papilloma is a benign neoplasm of a viral nature. It is a small growth that can appear on any part of the body or mucous membranes. The formation looks like a papilla on a narrow stalk. The cause of papillomas is the human papillomavirus (HPV). Papilloma does not go away on its own, it can spread, and in most cases the tumor is removed. Papillomas located on the genitals have a high risk of malignancy. Occurs in men, women and children.
Features of papillomas
Papillomas can be of the following types: ordinary or vulgar warts, filiform (the most common type), flat, genital warts, plantar warts, juvenile warts. A dermatologist diagnoses and treats papillomas.
Most often, papillomas are localized in the armpits and inguinal folds, hands, on the surface of the foot, neck, under the mammary glands in women, as well as on the genitals. Papillomas located on the mucous membranes of internal organs are very dangerous; they can cause ulceration or bleeding. As a rule, papillomas that have a pronounced cosmetic defect are removed with a laser, i.e. which are located in open areas of the body, as well as those with a high risk of cancer.
Wart treatment
Treatment of any growth on the lips begins with a medical examination and determining whether the growth is malignant.
Next, the doctor selects a method of therapy.
In case of a malignant form, the patient is referred to an oncologist, who will decide how to treat the patient.
Treatment of the disease is complex.
Treatment consists of the main stages: removal of the growth and drug therapy.
Removal of the tumor can be done in one of the following ways:
- ✓ Using pharmaceutical products
- ✓ In a medical institution where modern excision techniques will be used
- ✓ Folk remedies. The use of alternative medicine methods must be agreed with a doctor
When is it necessary to remove papilloma?
Benign skin tumors cannot always be removed; sometimes observation and regular examinations are sufficient. The most common indications for removal are the following:
- papillomas located on visible parts of the body and causing psychological discomfort;
- papillomas that are constantly injured by clothing, jewelry, and a comb;
- neoplasms that increase in size, tend to spread, change size, shape and color;
- papillomas located in the intimate area or soles;
- if the tumor begins to hurt, itch or bleed.
And is it possible to remove benign epidermal tumors on your own?
Having noticed specific neoplasms on the skin, which in medicine are called papillomas, many patients strive to cut or rip off the epidermal growth on their own, believing that such actions will lead to the disappearance of this defect. In addition, the Internet is actively discussing questions about what will happen if a papilloma is torn off and whether it is worth contacting a specialist if the papilloma comes off accidentally. Due to the relevance of such information, we will try to sort it out.
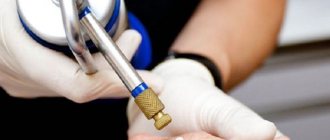
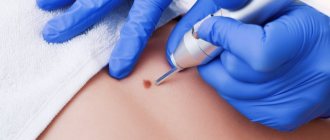
Preparation and carrying out laser removal
Laser removal is preceded by a thorough examination and examination of the tumor. The doctor must be sure of its benign quality; in case of any doubts and the borderline state of the cells, laser technology is not used, but a surgical operation is performed.
During the procedure, under the influence of a laser, heating and layer-by-layer destruction of neoplasm cells occur, so it is impossible to take biological material for subsequent research. Additionally, the doctor surveys the patient about possible contraindications to the procedure, and also conducts a number of studies (blood tests).
No special preparation is required for the procedure. At the appointed time, the patient comes to the specialist, the operation includes the following stages:
- Disinfection of the surgical field.
- Conducting anesthesia (if necessary). For this, an injection, gel or spray is used.
- Installation of the device to the required laser length.
- Layer-by-layer evaporation of the neoplasm.
- Treat with an antiseptic and apply a bandage if necessary.
To avoid relapse of the disease, it is necessary to carry out antiviral therapy, as well as take immunomodulating and immunostimulating drugs to strengthen the immune system.
Diagnosis of warts
The main diagnostic method is to examine the patient's face for the presence of warts on the lips and oral mucosa.
To confirm or refute the presence of HPV, it is enough to take tests:
- ✓ Blood tests for antibodies
- ✓ To conduct a histological examination (biopsy), a small part of the tumor is taken for analysis
- ✓ The PCR technique allows you to detect the genetic material of a pathogen with one hundred percent probability
Before getting rid of the growth, you should visit an oncologist.
A specialist will use dermatoscopy to determine the condition of the wart to rule out signs of malignancy.
Post-procedure care
For a quick and complete recovery and to avoid possible complications, the following measures are recommended:
- avoid contact with water in the first 2-3 days;
- Do not remove the crust that has formed (it will fall off on its own);
- Treat the wound with an antiseptic 2 times a day;
- protect the manipulation site from injury;
- wounds and new skin formed must be protected from ultraviolet radiation;
- refrain from shaving and epilation if the papilloma was in this area until complete healing.
Pharmacy products for removing warts
You can buy medications at the pharmacy that will help you deal with warts at home.
Among them:
- Super clean . The product is an alkaline solution that has a chemical effect on the growth, causing cauterization.
- Cryopharma, Wartner . These agents cause cryodestruction of the wart; as a result of cold exposure, the neoplasm is frozen.
- Solcoderm . A drug containing acids that have a cauterizing and mummifying effect on pathological tissues.
- Immunomodulators – Viferon, Oxolinic ointment will help increase immunity and the body’s fight against the virus.
- Antiviral agents – Isoprinosine, Interferon.
The use of cauterizing agents on the lips and face is extremely undesirable; application of these agents to the oral mucosa is especially dangerous.
Benefits of laser papillomas removal
Laser removal of papillomas has long been used to remove skin tumors, because this method has many advantages:
- Excellent result. Laser destruction removes the tumor completely, there is no risk of relapse.
- Minimum of unpleasant or painful sensations. The procedure is carried out using local anesthesia and there is no discomfort or pain.
- Speed of the procedure. Laser destruction of papillomas takes no more than 5 minutes to remove one tumor
- Minimal trauma. The laser beam has a directed effect and acts only on the cells of the formation, without affecting nearby tissues.
- No postoperative scars or scars. After laser removal, a small crust remains at the site of the papilloma, which disappears on its own within 1.5-2 weeks. New, intact skin appears at the site of formation.
- Versatility. Due to the precision of the laser, this method can be used on any part of the body, including areas with thin and sensitive skin, mucous membranes, intimate area, eyelid skin, etc.
- No rehabilitation period. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis, after which you can lead your normal lifestyle.
- Minimal risk of postoperative bleeding. The action of the laser coagulates blood vessels, which eliminates the risk of bleeding.
Clinical manifestations of warts on the lip
A wart on the lip does not appear the next day after the papilloma virus enters the body.
The incubation period can last from six months to several years.
This often occurs when the immune system malfunctions.
Having penetrated the skin or mucous membrane, the virus integrates its genetic material into human cells and thus begins to multiply.
As a result, characteristic neoplasms appear at the site of virus introduction.
The pathogen provokes warty growths, disrupting the processes of keratinization of the skin.
Oncogenic strains of papillomavirus change the genetic apparatus of cells in such a way that a malignant formation is formed.
Contraindications for laser removal of papillomas
Laser procedures are not performed under the following conditions:
- oncological diseases of any localization;
- HIV, MSID, viral hepatitis, diabetes mellitus;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- infectious or inflammatory diseases;
- mental disorders;
- severe damage to the heart and lungs;
- organ failure;
- bleeding disorders;
- skin photosensitivity;
- autoimmune systemic diseases;
- inflammatory skin diseases, exacerbation of herpes infection.
Laser removal of papillomas and other skin formations can be performed in medical settings. The operations are carried out at a high professional level using modern laser technology of the latest generation, which eliminates the risk of complications or relapse. Removal of papillomas with a laser is carried out at any convenient time on an outpatient basis. After the intervention, you can go about your daily routine; it will not affect your usual lifestyle in any way. You can make an appointment by calling the center or leaving a request on the website.
Causes of warts
The appearance of warts is caused by infection with papillomavirus or HPV.
Since the skin on the lips is quite thin, it is therefore easily permeable to viruses.
It should be noted that signs of infection with the human papillomavirus do not always occur.
The better the immune system, the less likely it is that symptoms of the disease will appear.
And yet, most of the world's population is infected with HPV.
The incubation period for the development of the disease can be several months or years.
As soon as the immune system fails, the first signs of infection appear.
Activation of the virus is accompanied by the formation of warts.
As a rule, growths appear on the area of the skin or mucous membrane where the pathogen entered the body.
Infection can occur both through sexual contact and through household contact.
Can the virus be transmitted by kissing on the lips?
The most common cases of infection are:
- intrauterine infection of the fetus if a pregnant woman is infected with papillomavirus
- shaking hands or kissing an infected person (if there are wounds or abrasions, the risk of infection increases)
- the use of personal items of an infected person (toothbrush, dishes, lipstick) is unlikely, since the pathogen is not stable in the environment
- sex accompanied by oral sex
- visiting common areas (swimming pool, sauna, shower)
People at risk are those who:
- patients with diabetes mellitus or other pathology of the endocrine system
- suffer from obesity and metabolic disorders
- taking antibiotics for a long time
- have chronic diseases
- suffer from increased sweating, especially on the feet, as this is where plantar warts often form
A malfunction of the immune system can occur for the following reasons:
- If there is a deficiency of essential substances in the body
- After suffering stress or physical exhaustion
- In case of hormone imbalance: during puberty, during pregnancy, with the onset of menopause, during treatment with hormonal drugs
- In case of chronic lack of sleep and overwork
- Due to a recent infectious disease
- If a person abuses smoking and alcoholic beverages
HPV. Symptoms
The papilloma virus is constantly present in a person’s blood, but is activated only when immunity decreases. With weakened immunity, HPV begins to accumulate on the skin or mucous membrane and leads to the appearance of tumors.
At a young age, HPV manifests itself as warts that are located on the fingers, elbows, and knees. Then a papilloma grows on a person’s skin (a soft-to-the-touch round formation on a stalk, with the help of which the papilloma is attached to the skin). Most often, papillomas are located on the skin of the face, neck, armpits, and papillomas are also found on the labia.
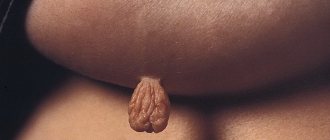
One of the most common manifestations of HPV is condyloma (uneven to the touch, soft, attached to the body with a stalk or a wide base, grows quite quickly, sometimes in a few hours).
Thus, warts, papillomas and condylomas are different signs of the same papillomavirus infection. Papilloma is a benign formation that can “show off” on a person’s face and body, not too pleasing to him aesthetically, but without causing much harm. Unlike papilloma formations, human condyloma tends to inflame and damage the skin and mucous membranes.
Condylomas
Condylomas are formations on the skin of the genitals, on the pubis, inner thighs, in the urethra, around the anus (anal condylomas) and inside the anus, having a lobed structure, flesh-pink in color, pedunculated or with a wide base, from a few millimeters to ten centimeters (eg, giant Buschke-Levenshtein condylomas).
Condylomas usually come in 2 types:
- condyloma lata, wide neoplasms with a wide base with which they attach to the skin, these neoplasms are considered a sign of secondary syphilis;
- genital warts, similar to soft pinkish bubbles with a thin stalk.
Condylomas acuminata
Genital warts are small flesh-colored formations that choose the genitals and anus as their location. In appearance, condylomas are sometimes confused with pearlescent papules, which are not a disease. Unlike pearlescent papules, genital warts are soft to the touch, attached to a thin stalk, and can be of different sizes.
Pointed papillomas are transmitted only sexually (through all types of sexual contact), therefore they belong to the group of sexually transmitted infections.
Causes of condyloma
There are various reasons for the appearance of condyloma, among which there are several main ones:
- having multiple sexual partners;
- long incubation period (time from infection to clinical manifestations);
- complex diagnostics;
- the presence of many types of PVI viruses;
- combination with other sexually transmitted infections;
- lack of protection effect using condoms from infection, etc.
1 Urethroscopy for diagnosing HPV
2 Urethroscopy for diagnosing HPV
3 Urethroscopy for diagnosing HPV
Wart removal in the clinic
The clinic uses modern hardware techniques to excise growths:
- Laser therapy . The method allows you to quickly and without blood remove the growth. There is no discomfort during the procedure, as pain relief is performed. During one session, you can get rid of several tumors in a very short time. The method is suitable not only for adults, but also for children. The likelihood of relapse is minimized. Skin defects in the form of scars after laser use are very rare.
- Radio wave therapy . The technique is considered the safest. When excising a wart using a radio wave, there is no contact with the skin. It is not always possible to completely remove the growth. The procedure leaves no traces of impact.
- Electrocoagulation . The procedure requires anesthesia. Using an electrode to which a high-frequency electric current is applied, the wart is burned out, followed by cutting off the growth with a special metal loop. Scarring may appear after removal.
- Cryodestruction . Liquid nitrogen is used and the wart is treated until it turns white. As a result of exposure to low temperatures, the growth tissues die. There is no need for anesthesia for the manipulation. The disadvantage of the technique is the lack of control over the depth of nitrogen exposure. For this reason, frequent relapses occur.
- Surgical. Removal is done using a scalpel. The disadvantage of the procedure is the formation of a scar, so this technique is used only for certain indications (in case of malignancy of the process and large size of the wart).
The rehabilitation period after removing papilloma with a scalpel
Among all existing methods of combating papilloma, surgical excision is characterized by the longest rehabilitation period. Depending on the number, location and size of the tumor, the recovery period can last 3-4 weeks.
Throughout the entire rehabilitation period, the patient should follow the following recommendations:
- Do not scratch or damage the crust that has formed at the site of the postoperative wound;
- Do not visit the solarium or sunbathe on the beach;
- Do not wet the wound for 7-10 days after surgery;
- Do not expose the skin in the area of the procedure to excessive stress or mechanical stress;
Carry out regular wound care (you can change the postoperative dressing yourself only with the doctor’s permission).
Compliance with these rules will not only speed up the healing of the skin, but also prevent the occurrence of adverse complications. After surgery for papilloma, in order to eliminate visible scars and achieve a higher aesthetic effect, plastic correction is possible.
10-14 days after surgical removal of the wart, the patient comes for a second consultation with a specialist, where he receives the results of a histological examination of the removed wart. Also, if necessary, the doctor removes stitches and conducts a preventive examination of the postoperative wound to assess the results of the intervention and the healing of the skin.
Clinical picture
Condylomata acuminata are formations of flesh-pink color, lobulated, ranging in size from 2 millimeters to ten centimeters, with exophytic growth, in which the apex of the genital condyloma is often wider than the base. Externally, the growths may resemble cauliflower or cockscomb.
The incubation period can range from 2-3 months to 2-3 years or more. The growth rate of formations varies, which is often associated with the state of local immunity, the presence of concomitant STIs, and sexual activity.
Asymptomatic carriage of human papillomavirus (HPV)
In reality, many more people are infected with HPV than statistics show. Most of them simply do not know about it, since there are no symptoms of condyloma.
The virus may not manifest itself in any way for a long time, since the human immune system does not allow it to develop to the required extent. However, at any time, with a decrease in both general and local immunity, this can happen, and then papillomas and/or condylomas appear.
1 Laboratory diagnostics
2 Dermatoscopy
3 Extended colposcopy