Lung cancer is a malignant tumor of the main organ of the respiratory system, capable of growing into the surrounding tissues, destroying them and creating metastases - additional foci of the disease in other organs. Fighting it is an extremely difficult task, since its cells develop rapidly, multiply uncontrollably and move throughout the body through the blood and lymphatic vessels. The lymphatic system complements the cardiovascular system. The lymph circulating in it - the intercellular fluid - washes all the cells of the body and delivers the necessary substances to them, taking away waste. In the lymph nodes, which act as “filters,” hazardous substances are neutralized and removed from the body. systems
Today, there are many methods to destroy, inhibit the growth or reduce dangerous tumors, but the only way to completely remove them from the body is surgery.
Who should undergo surgery for lung cancer?
Surgery is rarely used as the primary treatment for small cell tumors
, accounting for 15% to 20% of all lung cancer cases. This approach is explained by their very rapid development - in most cases, by the time they are detected, they manage to affect a large number of body tissues, which makes it extremely difficult to combat them. In less than 1 out of 20 patients, they are detected as a single focus that has not spread its cells to the lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are tiny organs of the lymphatic system that detect and neutralize substances dangerous to the body. or other organs. Patients with a similar diagnosis in the initial stages may be prescribed surgery followed by chemotherapy - taking medications that destroy the changed cells. In addition, they are carried out not only with the aim of completely removing the cancer, but also as part of palliative therapy, the goal of which is to relieve symptoms and improve a person’s quality of life.
For non-small cell tumors
the prospects are more optimistic - usually in the early stages such tumors can be completely cured with surgery.
What is lung and why is it needed?
In a healthy human body there are two such soft, elastic, spongy organs. The right lung consists of 3 main parts - lobes, and the smaller left lung, located next to the heart, consists of two.
How do we breathe?
The air enters the mouth or nose, and then into the trachea, which bifurcates into bronchi, which divide and form small branches - bronchioles. At the end of them are alveoli - tiny sacs that absorb - transfer oxygen into the blood and remove carbon dioxide from it during exhalation. Both organs are surrounded by a thin protective film called the pleura, which helps them slide back and forth along the chest wall during expansion and contraction. Below them is the diaphragm, a thin, dome-like muscle that separates the chest from the abdomen, which contains major vital organs such as the intestines, liver, kidneys, spleen and others. As you breathe, it moves up and down, allowing the lungs to expand and contract in volume, taking in and releasing air.
Is it possible to remove a lung?
Most people can get by with just one lung, as long as the other is healthy, intact, providing enough oxygen and clearing out carbon dioxide.
The respiratory system plays a very important role, and its improper functioning can affect a person's quality of life. That is why doctors try to preserve a maximum of tissue and remove a minimum - only a small area, or segment. Unfortunately, such intervention is not always sufficient. In case of serious injuries, tuberculosis, severe fungal infections, certain diseases, as well as cancer and its metastases, complete removal of the lung may be necessary.
Preparing for surgery
Before undergoing surgery, it is necessary to undergo preparation:
- A complete examination, during which doctors assess the patient’s health status, the size and contours of the tumor, the number of tissues affected by the disease, and identify metastases - additional cancerous tumors in various organs. It includes taking tests and performing a whole range of diagnostic procedures:
- blood and urine tests to detect infections and malfunctions of internal organs;
- esophagoscopy – assessment of the condition of the esophagus;
- bronchoscopy - examination of the bronchiBronchi are branches of the trachea through which air passes into the lungs.;
- thoracoscopy - examination of the respiratory organs through small incisions on the chest and back;
- or MRI, during which the doctor receives a clear image of the internal organs, determines the size of the tumor, its exact location and contours;
- sputum cytology - detection of cancer cells in the mucus produced by the respiratory tract;
- mediastinoscopy – study of the condition of the lymph nodes;
- assessment of the condition of the cardiovascular system and other vital organs;
- functional pulmonary tests, which allow us to determine the quality of the respiratory system and the ability to provide the body with oxygen to the tissues remaining after the operation;
- if necessary, the doctor prescribes other procedures.
biopsy - sampling of tumor tissue to study the properties of its cells;
No smoking.
- About bleeding disorders.
Before the operation begins, the doctor talks about the planned intervention, its progress, goals, possible risks, consequences and complications. After which the patient or his legal representative signs a document - informed voluntary consent to medical intervention.
Risks and complications of thoracic spine surgery
Possible risks after thoracic spine surgery include risks that are typical for any type of procedure and risks for specific spinal problems. Common risks include:
- Complications associated with anesthesia;
- Infections;
- Bleeding;
- Blood clot formation.
Complications after spinal surgery:
- Spinal injuries;
- Nerve damage;
- Strong pain;
- Transit syndrome.
Thanks to the surgeon's skills, it is possible to get rid of some complications, especially those associated with spinal trauma and nerve damage.
Surgeries to treat lung cancer
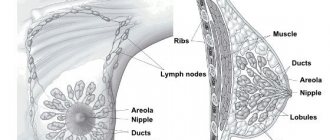
Doctors use several methods of surgical treatment of cancer, each of which requires hospitalization in the clinic. The choice of type of intervention depends on the location of the tumor, its size, damage to nearby tissues and lymph nodes - the “filters” of our body that retain and neutralize dangerous substances. Often, specialists prefer to do more extensive surgery to remove as many of the altered cells as possible, since this approach increases the chances of a full recovery.
All such procedures are performed under general anesthesia - using a drug that puts the patient into a deep sleep with loss of consciousness - and are usually performed through a large incision between the ribs on the chest or back. In their course, not only the affected lung tissue is removed, but also the nearest lymph nodes. Such intervention is necessary to identify damage to their altered cells and the spread of oncology beyond the tissues of the respiratory system.
Depending on the type and size of the tumor, the following are used to treat cancer: Lobectomy
– removal of one lobe containing a dangerous neoplasm.
Bilobectomy
– removal of two lobes of the right lung.
Segmental resection
- during this, the surgeon cuts out only the affected segment - a small part of the lobe.
This procedure is suitable for patients whose respiratory system cannot cope with its function if the entire lobe is removed. Pulmonectomy
– complete removal of the lung.
Surgery may be required if the tumor is located near the center of the chest. Sleeve lobectomy
is the removal of a large lesion of cancer located in the main or lobar bronchus. During this procedure, the doctor removes the damaged part of the airway and sews together the remaining tissues located above and below the affected area. This type of intervention can be prescribed as an alternative to pneumonectomy, allowing maximum lung function to be preserved.
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery -
VATS
VATS is a minimally invasive procedure for the treatment of early stage cancer, during which a minimal amount of tissue is damaged. Traditional surgeries are performed through a large incision, while video-assisted surgeries are performed through several small punctures in the chest. They introduce special instruments and a thoracoscope - a device with a light source and a camera that displays a clear image on the monitor. The surgeon controls and controls his movements based on real-time video data.
Robotic Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery –
RATS
RATS is a minimally invasive treatment of small tumors using a robotic system. When performing it, a specialist sits at a console in the operating room and controls the actions of manipulators that remove tumors through small punctures in the patient’s chest. The procedure provides even greater maneuverability and precision when moving instruments than VATS.
VATS and RATS are complex operations, the result of which depends entirely on the skill of the surgeon. They have several important advantages over traditional interventions: they allow minimal tissue trauma, shorten recovery time, shorten hospital stay, reduce blood loss and pain. In addition, they do not leave large scars or scars on the skin.
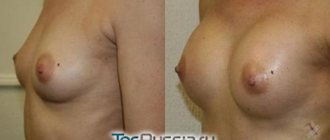
Narrowing waist
This operation is most often accompanied by other plastic surgeries - breast augmentation, abdominoplasty or liposuction in the abdomen or waist. The degree of waist narrowing is determined personally with the patient and the doctor at a preliminary consultation. During a consultation with a plastic surgeon, the scope of the operation is precisely agreed upon according to the patient’s wishes.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The duration of the operation itself to create a narrow waist is about 40-50 minutes. In case of combination with other plastic surgeries, it lengthens. A prerequisite for this operation is a preoperative computed tomography of the chest and abdomen with reconstruction of the bone skeleton. This study will allow you to accurately mark and determine the levels of the XI and XII ribs on both sides.
In the operating room, after tracheal intubation and fixation of the endotracheal tube, the patient turns over from his back to his stomach. Next, at the previously designated points of location of the XI and XII ribs, an incision is made into the skin and soft tissues in the projection of the bends of the ribs. The ribs are mobilized one by one from the thickness of the muscles, carefully, without damage, the intercostal neurovascular bundle is isolated and retracted down. Next, with a special tool - an oscillating saw - an incision is made into the dorsal outer plate of each of the XI and XII ribs. At the next moment, the surgeon applies pressure through the thickness of the tissue to the free ends of the previously osteotomized ribs, thereby breaking the inner cortical plate of the rib, which remains connected by the periosteum and connective tissues on the inside of the ribs. Confirmation of the adequacy of the technique performed is a significant increase in the mobility of this area and intraoperative radiography.
Next, the surgeon performs hemostasis, layer-by-layer suturing of the wound with the application of an intradermal suture. The operation is repeated on the opposite side.
Immediately after applying aseptic dressings to the postoperative sutures, a lumbar corset is put on the patient’s body. A wide (at least 7 cm) leather belt is placed on top of the corset along the patient’s waistline and tightened. The duration of wearing this design is at least 1 calendar month (preferably 2 months) and is determined by the timing of the formation of callus in the area of broken ribs.
Comparison of preoperative and postoperative photographs, as well as objective measurements before and after surgery, allow us to objectify (prove) the result of the operation - waist reduction.
An important feature of this aesthetic operation is that it is less traumatic compared to operations to narrow the waist, when the 11th and 12th ribs are removed: the operation is performed through small incisions up to 3 cm without removing the ribs. The ribs are preserved, the waist narrows, and the ribs moved in this way continue to perform frame and protective functions, and are also the attachment points for a large number of muscles of the human body.
How is traditional surgery to remove a lung tumor performed?
The prepared patient is brought to the operating room, where he is given anesthesia - a drug that allows him not to feel pain and puts him into a state similar to deep sleep. A tube is then inserted into his throat and connected to a ventilator, and sensors are attached to his body to measure his heart rate, blood pressure and other data. A catheter is inserted into the bladder - a soft flexible tube that drains urine. The skin in the operated area is treated with a disinfectant, after which an incision is made on the front of the chest, running along the rib and ending on the back. A special instrument spreads the ribs, after which a lobe, a small fragment of it - a segment, or the entire lung is removed. One or more tubes are placed in the chest to remove any air or fluid that may form during healing. The wound is sutured or closed with staples, a bandage is applied to it, and the patient continues to be closely monitored until he comes to his senses and all indicators of his body return to normal.
Decompression surgery on the thoracic spine
One of the most common back problems is compression of the spine and spinal nerves caused by various degenerative diseases, including herniated discs, spinal stenosis, spondyloarthritis, etc. There are several types of treatment to relieve symptoms associated with pinched nerves:
- Thoracic surgery for herniated discs. The procedure to remove a herniated thoracic spine is performed in cases of advanced myelopathy (compression of the spine) with neurological symptoms, such as increasing weakness in the legs and radicular pain, that cannot be relieved by other means. To gain access to a herniated disc, the surgeon cuts out the diseased portion of the disc to make room for nearby spinal nerves. In recent years, surgery for herniated discs has become increasingly performed using minimally invasive techniques, in which a much smaller incision can be made. This type of surgery is called microdiscectomy.
- Laminectomy or laminotomy. These two surgeries have the same purpose but differ in the techniques used. Laminotomy is a minimally invasive back surgery. During this procedure, the surgeon removes the lamina (the back of the vertebra), which relieves pressure on the spine. Thoracic laminectomy/laminotomy can be performed in conjunction with treatment of herniated discs or separately.
- Transthoracic decompression is a technique designed to minimize pressure on the spine. The surgeon gains access through the chest by inserting the instrument between the ribs.
Surgeries to improve quality of life in lung cancer
Surgery is used not only to completely remove cancer from the body, but also as part of palliative treatment in advanced stages of the disease, the goal of which is to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
For example, when a pleural effusion occurs, an accumulation of fluid in the chest outside the lungs, the patient has difficulty breathing. In such cases, the following may be prescribed:
- Thoracentesis
, or
thoracentesis
, is the insertion of a hollow needle into the space between the ribs to drain fluid. - Pleurodesis
is a procedure that prevents its re-formation. During this procedure, a small incision is made in the skin, through which the fluid is removed, after which a substance is injected, causing the mucous membrane of the lung and the chest wall to stick together. This intervention seals the space and limits further accumulation of effusion. - In some situations, it is possible to get by by inserting a catheter
- a thin flexible tube that is inserted through a small puncture and drains the liquid into a special container.
In some patients, pericardial effusion is formed - an accumulation of fluid in the space between the heart and the surrounding membrane, which leads to disruption of the main “pump” that pumps blood throughout the body. In such cases, the following can be done:
- Pericardiocentesis
- Creating a pericardial window
is an operation to remove part of the pericardium - the cardiac membrane. During its course, a hole is created that allows fluid not to accumulate, but to drain into the chest or abdomen.
– removal of effusion using a needle inserted under ultrasound guidance.
Possible complications
After such a serious intervention as removal of the first rib, there may be various complications, but detailed surgical technique and compliance with precautions allow them to be avoided. According to the literature, the following complications are possible:
Pneumothorax is the entry of air into the chest cavity due to damage to the dome of the pleura. To monitor the condition of the lungs, the patient must immediately after surgery undergo a plain X-ray of the lungs and, if necessary, install a drainage into the pleural cavity.
Damage to the brachial plexus - may be due to increased abduction of the arm. For timely diagnosis, a neurological examination is necessary as soon as the patient has sufficiently recovered from anesthesia.
Bleeding from a postoperative wound is a rare complication, since this operation does not require the use of antithrombotic drugs in the postoperative period.
The addition of infection when the pleural cavity is damaged can lead to pleural empyema; this complication is extremely rare.
Removal of metastases from lung cancer
Unlike ordinary, normal cells, cancer cells are able to move throughout the body. They enter the blood and lymphatic vessels. The lymphatic system complements the cardiovascular system. The lymph circulating in it - the intercellular fluid - washes all the cells of the body and delivers the necessary substances to them, taking away waste. In the lymph nodes, which act as “filters,” hazardous substances are neutralized and removed from the body. systems, with their help they spread to various areas, become established in them and create metastases - additional tumors. As a rule, there are several of them, they damage a large number of tissues, and even the most experienced doctor cannot remove all the affected areas. Usually, surgery makes sense only if there is only one such lesion, it is located in the brain, it can be removed without damaging the vital parts of the organ, and the main tumor in the lung can be completely cured surgically or with the help of radiation and chemotherapy.
Shaping a narrow waist
Is it possible to make your waist thinner without removing ribs?
There are many different ways - physical exercise and a strict diet, liposuction of fat deposits, but it is not possible to achieve a fundamental result: the width of the waist depends on the shape of the chest and, in particular, the position of the lower pairs of ribs. Therefore, those who want to get a narrow waist at all costs are looking through the Internet for surgeons who remove ribs. However, this method is very traumatic and dangerous and therefore has not become widespread.
How to get a thin waist without removing ribs?
A new forming method was developed and patented in Russia. Dr. Kudzaev's method (patent No. 2652964) allows you to change the position of the ribs in a gentle way and make your waist thinner. The ribs are preserved.
Indications for reducing waist size
Who is this method suitable for? Ideal candidates are those who do not have excess fat deposits (BMI around 20) and the anterior abdominal wall is not deformed. These are patients over the age of 18 years, whose anatomical feature is the insufficient expression of the difference between the circumference of the waist and hips with a normal and even thin body type.
What is a contraindication to such a waist reduction?
The main contraindications to surgery are:
Pulmonary, heart failure; Chronic diseases of internal organs in the stage of decompensation/exacerbation; Acute diseases; Presence of blood-borne infections; Obesity; Oncological diseases; Pregnancy, lactation period; Mental illnesses; Planning a pregnancy in the next 12 months.
How to make a narrow waist? The essence of the technique
By surgically changing the position of the lower ribs, performed through mini-incisions or punctures, and further shaping a new waist by wearing a special corset, the waist narrows. At the same time, the main function of the ribs - protecting internal organs from injury - is preserved.
The method of waist reduction according to Dr. Kudzaev’s method is low-traumatic, unlike the removal of ribs, since the intervention is carried out through small accesses, preserving the ribs and their protective function.
Result after surgery
The operation makes it possible to make the waist smaller by 6-10 cm. The result is directly related to the initial anatomical data and the carefulness of the patient in performing the necessary actions with a special corset.
Anesthesia
The reduction surgery takes about 30-40 minutes and is performed under both local and general anesthesia.
Recovery
Pain during the rehabilitation period is minimal. For 2 months after the operation, you must wear a corset, gradually tightening it. The feeling of tightness and swelling in the first time after surgery is caused, first of all, by constantly wearing a corset.
Restrictions during the recovery period
: You can’t lift weights or play sports for several months. Once the recovery is complete, all restrictions are removed.
Reception
The appointment is conducted by appointment by orthopedic traumatologist Dmitry Vladimirovich Polyakov
. The cost of consultation is 1050 rubles.
For residents of other cities - Chelyabinsk, Perm, Tyumen, Omsk, Khanty-Mansiysk, Surgut, Nizhnevartovsk, Salekhard, etc. - we provide a free initial consultation remotely. Please read the terms and conditions for obtaining a consultation in the section How to obtain a consultation.
Cost of waist reduction surgery
The total cost, including the cost of surgery, anesthesia, a special corset, 2 days of hospital stay - 130,500 rubles. Preoperative examination is not included in the stated price.
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS, SPECIALIST CONSULTATION IS REQUIRED
Where are surgeries to remove lung tumors performed?
Removing a lung cancer tumor or metastases is a complex intervention that can only be performed by experienced surgeons in specialized clinics, public or private.
Large budget medical organizations have all the capabilities to carry out such operations, but the timing of their implementation and the conditions of stay in the hospital often leave much to be desired. For those who do not want to waste precious time and days of their lives waiting, we offer treatment at an oncological center. We have all the necessary doctors - true professionals with extensive experience in the field of diagnosing and fighting cancer, the most modern equipment and our own laboratory, which reduces the time required to obtain research results to a minimum. We do not create queues, quickly perform all procedures and provide not only surgical but also other oncology treatment, including chemotherapy, immunotherapy and targeted therapy using original drugs that give predictable results. Our specialists are fluent in the most advanced innovative techniques and perform any interventions, and the staff does everything to make the stay in the Center as comfortable as possible for every visitor.
Discharge after surgery for lung cancer
Once the patient’s well-being has stabilized and allows for discharge, doctors confirm the timing of the next appointment and send him home. As a rule, this occurs 5-10 days after the intervention. The rehabilitation period depends on the type of surgery undergone and the amount of tissue removed. For example, it may take several weeks to a month to return to your normal lifestyle and complete recovery after a pneumonectomy.
What should you do after returning from the clinic?
- Get up and walk at least several times a day - movement is extremely important for restoring and establishing proper functioning of the respiratory system.
- Avoid lifting anything heavy for several weeks.
- Follow all of your doctor's instructions about medications, diet, wound care, and drainage—a soft tube that drains fluid that forms during healing.
- Perform prescribed breathing exercises.
- Call your doctor immediately if you have difficulty breathing, fever, swelling - fluid accumulation in some areas of the body, shortness of breath - a feeling of shortness of breath, nausea or vomiting, or cough with or without phlegm.
- Contact your doctor if you have any questions about your symptoms, how you are feeling, or taking any medications, including vitamins and supplements.
You should seek emergency medical help if:
- Coughing up blood or brown sputum.
- Dizziness, fainting or lightheadedness.
- Violation of heart rate.
- Severe pain in the chest area.
- Swelling, redness, pain, or tenderness in the leg.
- When a wound opens, becomes red, swollen, or discharges pus.
Thoracoabdominal department of the Lapino-2 cancer center.
Advantages
Any surgical intervention performed using a minimally invasive technique is much preferable to traditional surgery. This is due to the presence of a number of significant advantages - minimal trauma during the operation, minimal blood loss, short period of postoperative treatment, short rehabilitation period and many others.
The advantages of minimally invasive thoracoplasty include:
- excellent cosmetic result due to the absence of large scars on the anterior surface of the chest;
- minimal trauma to soft tissues during surgery compared to radical methods;
- Suitable for children of any age with funnel-shaped deformities;
- The duration of the operation is 1.5-2 times less compared to radical methods.
To perform minimally invasive thoracoplasty, we use titanium plates; this material is bioinert to the patient’s surrounding tissues (allergies to this metal are practically excluded) and has a certain elasticity, which is an important detail in achieving and maintaining correction of the sternocostal complex.
Risks and side effects of lung cancer surgery
Surgery to remove a lung cancer tumor is a serious procedure that can lead to serious side effects. The number and severity of such consequences depend, among other things, on the volume of tissue removed and the general health of the person. During the first few days after the procedure, the patient may feel not only discomfort, but also pain - in the chest, arm, in the area of the incision or in the drainage tube that removes the fluid formed during wound healing.
Risks and possible side effects of surgical procedures for respiratory cancer include:
- undesirable reactions to an anesthetic - a drug that puts the patient into a state of deep sleep and allows you not to feel pain;
- development of bleeding;
- empyema - accumulation of pus in the cavity surrounding the lungs;
- infections;
- damage to organs and structures near the area where surgery was performed, including the heart, nerves, and blood vessels;
- prolonged pain;
- accumulation of air or gas in the chest;
- formation of a bronchopleural fistula - an opening connecting the bronchi with an internal organ or the surface of the chest wall;
- leakage of air from the lung, which leads to compression of the organ and deterioration of gas exchange - disruption of the supply of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide.
Treatment of chest deformity - surgical and conservative methods
Ryzhikov Dmitry Vladimirovich
Ryzhikov Dmitry Vladimirovich (Head of the Department of General Bone Pathology of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "National Medical Research Center for Pediatric Traumatology and Orthopedics named after G.I. Turner, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest qualification category, traumatologist-orthopedist)Unique methods of surgical treatment at the National Medical Research Center named after. G. I. Turner
Thanks to new technologies and our own developments, we at the National Medical Research Center for Pediatric Traumatology and Orthopedics named after. G.I. Turner began to use minimally invasive procedures, which involve less trauma to soft tissues and an immeasurably better cosmetic effect than open operations used for the same purpose. Thanks to this method, it is possible to reduce the time of treatment and hospital stay for patients. Treatment takes an average of a week. Household restrictions are in effect for no more than two months; professional sports with extreme loads require a longer rehabilitation period.
Two more not fully resolved areas in thoracoplasty are the issue of adaptation of the lungs in pleural cavities of changed size and pain relief in the early postoperative period. The National Medical Research Center is working to improve these two tasks as well.
Of particular importance is the introduction in our center of new transpleural thoracoplasties, which reduce the number of complications in comparison with traditional operations (For example, in comparison with G. Abramson’s operation for carinatum deformity, which is widespread).
The vast majority of our operations for severe degrees of funnel-shaped, keeled, and combined deformities are performed using surgical approaches up to 35-40 mm in length, have a high degree of stability of the installed structures, and a high corrective moment when correcting severe degrees of deformities.
How is the operation performed?
Using a minimal incision technique, we implant patients with a titanium plate that holds the shape of the chest.
Minimally invasive technologies have a high corrective (corrective) moment, leave minimal postoperative scars, reliably fix the sternocostal complex in the correct position, relieve psychological discomfort and functional difficulties of such deformities. This method has already been appreciated by a large number of mothers and children, and dozens of patients are waiting in line.
We will be happy to help you and are ready to work with children from all over Russia.
Recovery after surgery, postoperative period
Minimally invasive operations used in our national medical research center named after. G.I. Turner, allow you to reduce bed rest - the patient sits already on the first day, and rises to his feet on the second day. The fastest possible restoration of physiological recovery, sleep, appetite and everyday stress. It is these factors that bring our technologies to leading positions in Russia and in world practice.
Are there any contraindications to such operations?
In some cases, surgery is postponed when acute diseases are detected or chronic concomitant diseases worsen. In this case, the patient first restores his health, and then orthopedic treatment is carried out. We are talking about planned surgery, that is, we have time for the operation in conditions of complete health.